背景:
本文承接事务-1 事务隔离级别和Spring事务传播机制,是事务专题的第二篇;主题内容是Mybatis和Spring事务原理,结合源码和案例进行介绍。
本文主题内容为事务原理, 尤重Spring事务原理; 会结合源码讲解整体流程, 但不会拘限于源码细节
1.JDBC事务
在介绍Mybatis和Spring的事务前, 有必要从基础的JDBC事务入手, 因为无论Spring还是Mybatis框架关于事务实现机制的根源在于数据库的事务机制. JDBC是Java对数据库接口的一层封装, 而开源ORM框架是对JDBC进行了一层封装.
/*** @author : Ewen Seong* @since : 2022/8/27 20:41*/
public class JdbcApplication {private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JdbcApplication.class);public static void main(String[] args) {run(false);}@SneakyThrowsprivate static void run(boolean isRollback) {Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(CommonConstant.JDBC_URL, CommonConstant.USER, CommonConstant.PASSWORD);connection.setAutoCommit(false);Statement statement = connection.createStatement();String sql = "update t_account set money = 100 where name = 'a'";statement.execute(sql);if (!isRollback) {LOGGER.info("Execute commit");connection.commit();} else {LOGGER.warn("Execute rollback, sql is {}.", sql);connection.rollback();}
// connection.setAutoCommit(true);statement.close();connection.close();}
}
如上所示, JDBC提供了获取数据库连接以及设置非自动提交、执行sql、回滚与提交等功能. 其中connection.setAutoCommit(false);,connection.commit();,connection.rollback();会在后面介绍Spring和Mybatis的事务对象的源码中看到.
2.Mybatis事务
2.1 案例介绍
测试类:
public class MybatisTest {private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MybatisTest.class);@Testpublic void test() {exec(false);}@SneakyThrowsprivate static void exec(boolean isRollback) {SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);AccountMapper accountMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(AccountMapper.class);accountMapper.updateMoney(100);if (!isRollback) {LOGGER.info("Execute commit.");sqlSession.commit();} else {LOGGER.warn("Execute rollback.");sqlSession.rollback();}}
}
Mapper接口:
public interface AccountMapper {void updateMoney(@Param("money") int money);
}
mapper配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.seong.transaction.mybatis.mapper.AccountMapper"><update id="updateMoney" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">update t_accountset money = #{money}where name = 'a'</update>
</mapper>
如上述案例, Mybatis中的数据库资源为sqlsession(可以粗略地理解为对connection的封装), 并基于sqlsession提供了事务机制.
对应JDBC中的3个API, Mybatis的事务API为:SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);、
sqlSession.commit(); 和sqlSession.rollback();. 其中openSession方法的参数true表示取消自动提交.
2.2 Mybatis工作机制
在介绍Mybatis的事务原理之前,先简要复习一下Mybatis的工作机制。
本文以事务为核心, 会省略与事务主线无关的内容, 介绍时默认读者已熟悉Mybatis内部原理
工作机制—Configuration对象:
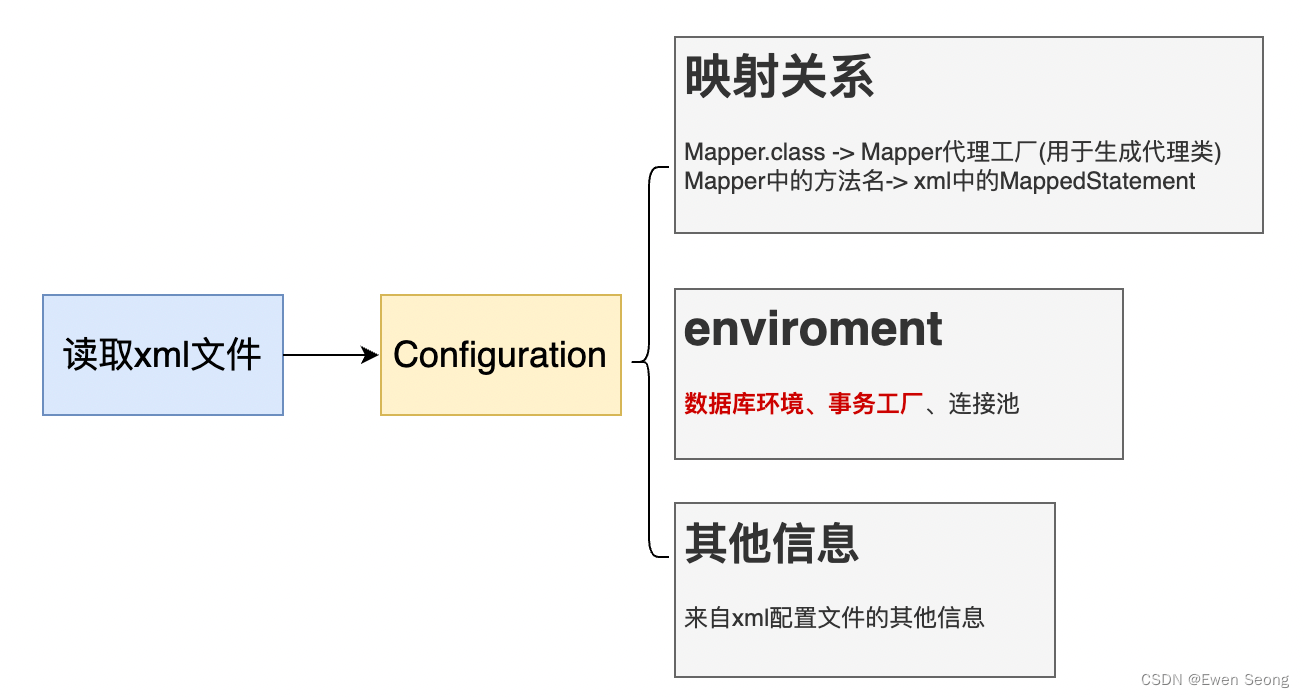
如上图所示,Mybatis启动时读取mybatis.xml配置文件,生成Configuration对象,该对象中包含所有mybatis.xml以及mapper.xml文件携带的信息。
这里我们关注的重点是enviroment对象,内部包含了DataSource对象,事务工厂对象等。
Datasource可用于生成connection对象,SpringJdbc和Mybatis等类型的ORM框架以此对象作为连接资源。
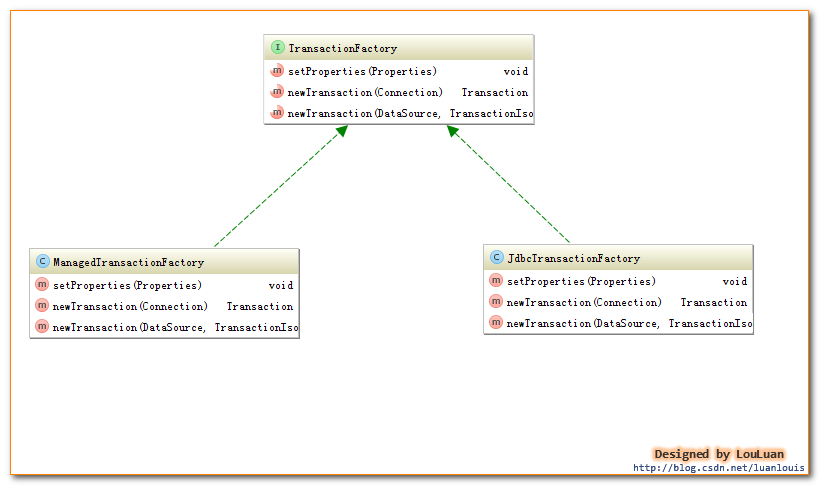
事务工厂对象用于创建事务对象,Mybatis中存在两种类型的事务: JdbcTransaction和ManagedTransaction,分别对应 JdbcTransactionFactory和ManagedTransactionFactory事务工厂。
其中,Mybatis使用何种类型的事务工厂,取决于enviroment对象,即来源于mybatis.xml中的配置;
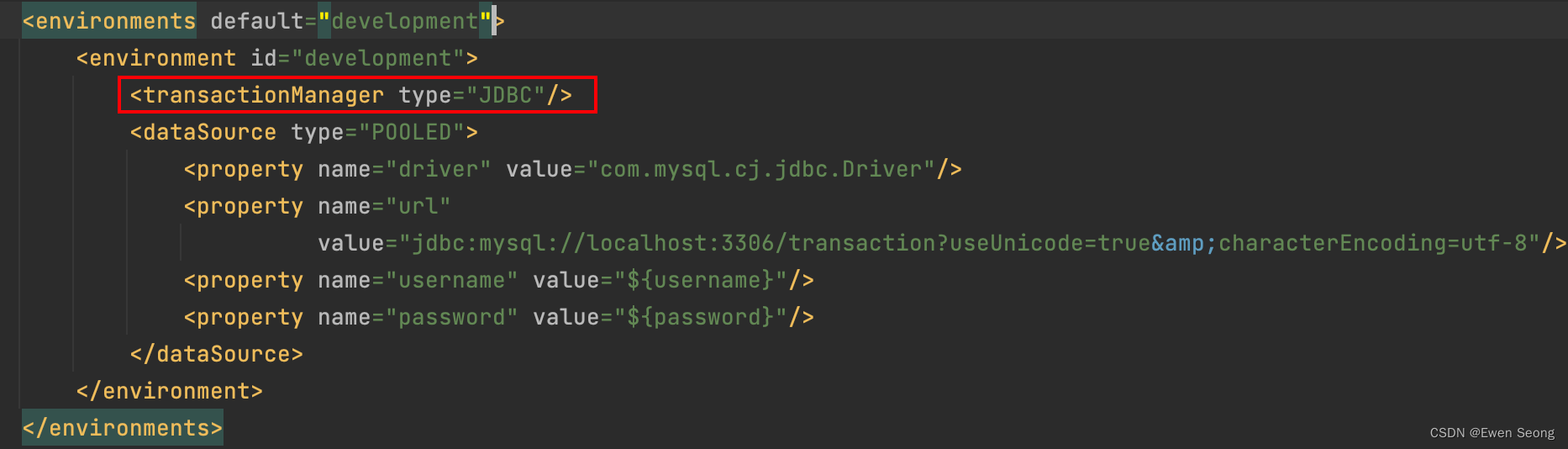
当<transactionManager>标签配置为MANAGED时,使用ManagedTransactionFactory-ManagedTransaction,当标签设置为JDBC时,使用JdbcTransactionFactory-JdbcTransaction.
工作机制—sqlsession对象:
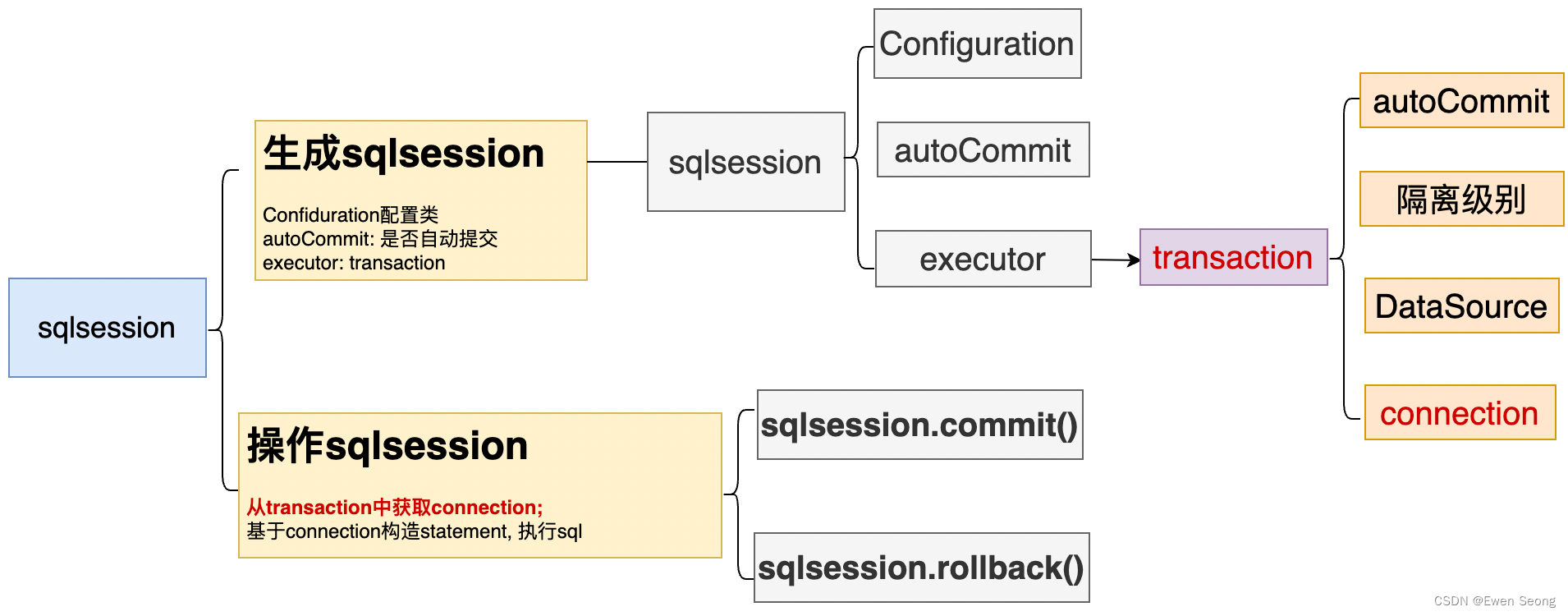
如上图所示: sqlsession对象中包含Configuration对象、autoCommit标识、Executor执行器对象;其中Executor执行器包含一个事务对象,事务对象内部封装了隔离级别属性、DataSource属性、connection属性、autoCommit标识等,用于为sqlsession提供执行sql以及事务的能力.
基于内持的事务对象, sqlsession通过commit和rollback方法对外提供事务能力.
另外, 需要注意的是事务对象的connection属性初始为null, 直到第一次执行sql时才获取;且获取方式由事务对象确定。
sqlsession作为Mybatis的资源对象, 承载了执行sql、事务提交与回滚等任务, sqlsession对象会将这些任务交给内部的执行器去执行. 执行器的本质是对事务对象的一层包装, 即sqlsession执行任务的能力来源于事务对象.
2.3 Mybatis事务原理
Mybatis事务原理的重点在于事务对象: 框架提供了两种事务类型, 分别为JdbcTransaction和ManagedTransaction; 同时提供了对应的事务工厂, 分别为JdbcTransactionFactory和ManagedTransactionFactory。用户通过xml文件可以配置事务工厂, 从而确定使用的事务类型, 配置方式参考2.2 Mybatis工作机制.
如下所示是Transaction类的继承关系图:
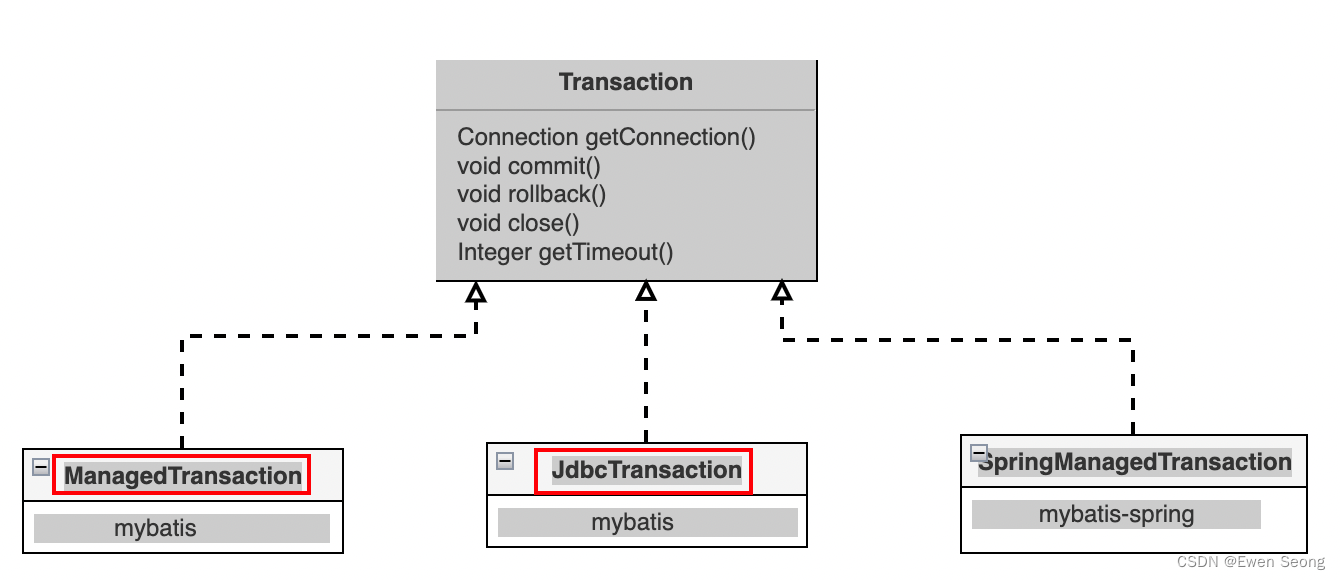
其中SpringManagedTransaction是Spring整合Mybatis实现的类, 后续介绍Spring-Mybatis事务时进行介绍.
事务原理—Transaction接口:
Transaction定义了Mybatis中的事务规范, 接口比较简单:
public interface Transaction {Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;void commit() throws SQLException;void rollback() throws SQLException;void close() throws SQLException;Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException;
}
我们需要关注的方法有getConnection(),commit(),rollback(), 分别表示获取链接、提交和回滚事务;
事务原理—JdbcTransaction对象:
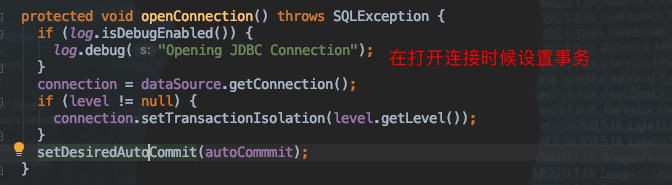
[1] getConnection()方法:
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {if (connection == null) {openConnection();}return connection;
}protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");}connection = dataSource.getConnection();if (level != null) {connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());}setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommmit);
}
可以看出JdbcTransaction使用Datasource对象获取connection连接资源, 并根据是否自动提交和隔离级别对connection对象进行属性设置.
[2] commit()方法:
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");}connection.commit();}
}
JdbcTransaction事务提交方法比较简单, 直接调用connection提供的commit方法.
[3] rollback()方法:
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");}connection.rollback();}
}
JdbcTransaction事务回滚中直接调用connection提供的rollback方法.
因此, JdbcTransaction就是基于JDBC事务的封装.
事务原理—ManagedTransaction对象:
[1] getConnection()方法:
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {if (this.connection == null) {openConnection();}return this.connection;
}protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");}this.connection = this.dataSource.getConnection();if (this.level != null) {this.connection.setTransactionIsolation(this.level.getLevel());}
}
ManagedTransaction也是根据DataSource获取connection对象, 并对其设置数据库的隔离级别, 但没有设置autoCommit属性, 即默认为自动提交. 由此可以看出ManagedTransaction不支持事务.
[2] commit()方法:
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {// Does nothing
}
因为每次提交的sql操作都立刻被提交, 因此提交事务的内容设置为空, 毋需反复提交.
[3] rollback()方法:
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {// Does nothing
}
每次sql操作都立刻被提交, 因此无法回滚, rollback方法体也被设置为空.
顺便提一下, 这里有代码规范问题, 应该给空的commit()和rollback() 加上debug日志.
3.Spring事务
3.1 案例介绍
@Service
public class SpringService {private AccountDao accountDao;private OperationbLogDao operationbLogDao;public JdbcService(AccountDao accountDao, OperationbLogDao operationbLogDao) {this.accountDao = accountDao;this.operationbLogDao = operationbLogDao;}@SneakyThrows@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)public void updateMoneyAndLog() {accountDao.updateMoney("a");operationbLogDao.insertLog("a", "update");throw new Exception("test exception");}
}
// AccountDao.java
@Repository
public class AccountDao {@Autowiredprivate JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;public void updateMoney(String uname) {jdbcTemplate.update("update t_account set money=100 where name = ?", uname);}
}// OperationbLogDao.java
@Repository
public class OperationbLogDao {@Autowiredprivate JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;public void insertLog(String uname, String operationType) {jdbcTemplate.update("insert into t_operation_log(uname,oper_type,oper_time) values(?,?,?)", uname, operationType, System.currentTimeMillis());}
}
上述案例源自事务-1 事务隔离级别和Spring事务传播机制, 读者可基于该案例debug查看@Transactional注解的源码实现.
3.2 原理分析
Spring为事务管理提供了一致的编程模版, 高层次的事务抽象使得无论用户选择Spring JDBC、Hibernate还是Mybatis, 都可以使用统一的编程模型进行事务管理. Spring提供了声明式和编程式两套编程模型, 二者使用方法不同而原理相同: 声明式必须以方法为单位, 而编程式可以自定义范围; 另外, 编程式相对于声明式, 对代码的侵入性较高.
本文以声明式编程模型为例介绍Spring原理:
可以用一句话概括Spring事务实现原理: AOP + 动态代理
Spring初始化时会对@Transaction注解进行扫描, 为匹配项(用目标对象表示)生成一个代理对象并存放在IOC容器中:
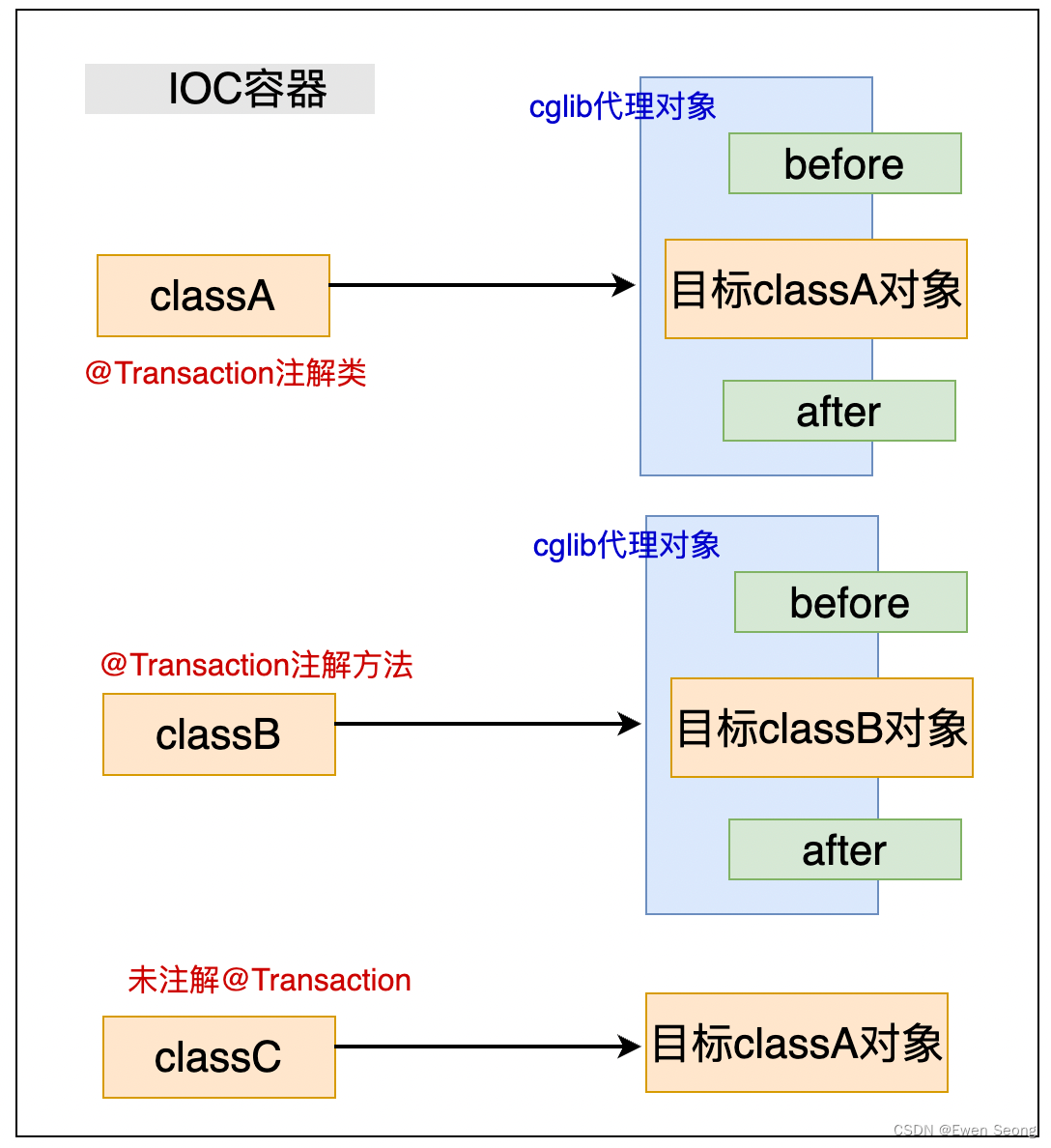
因此, 当用户以目标对象类型从IOC获取Bean对象时, 得到的是代理对象.
Spring原理—AOP过程:
下图为SpringBoot整合Mybatis的启动过程:
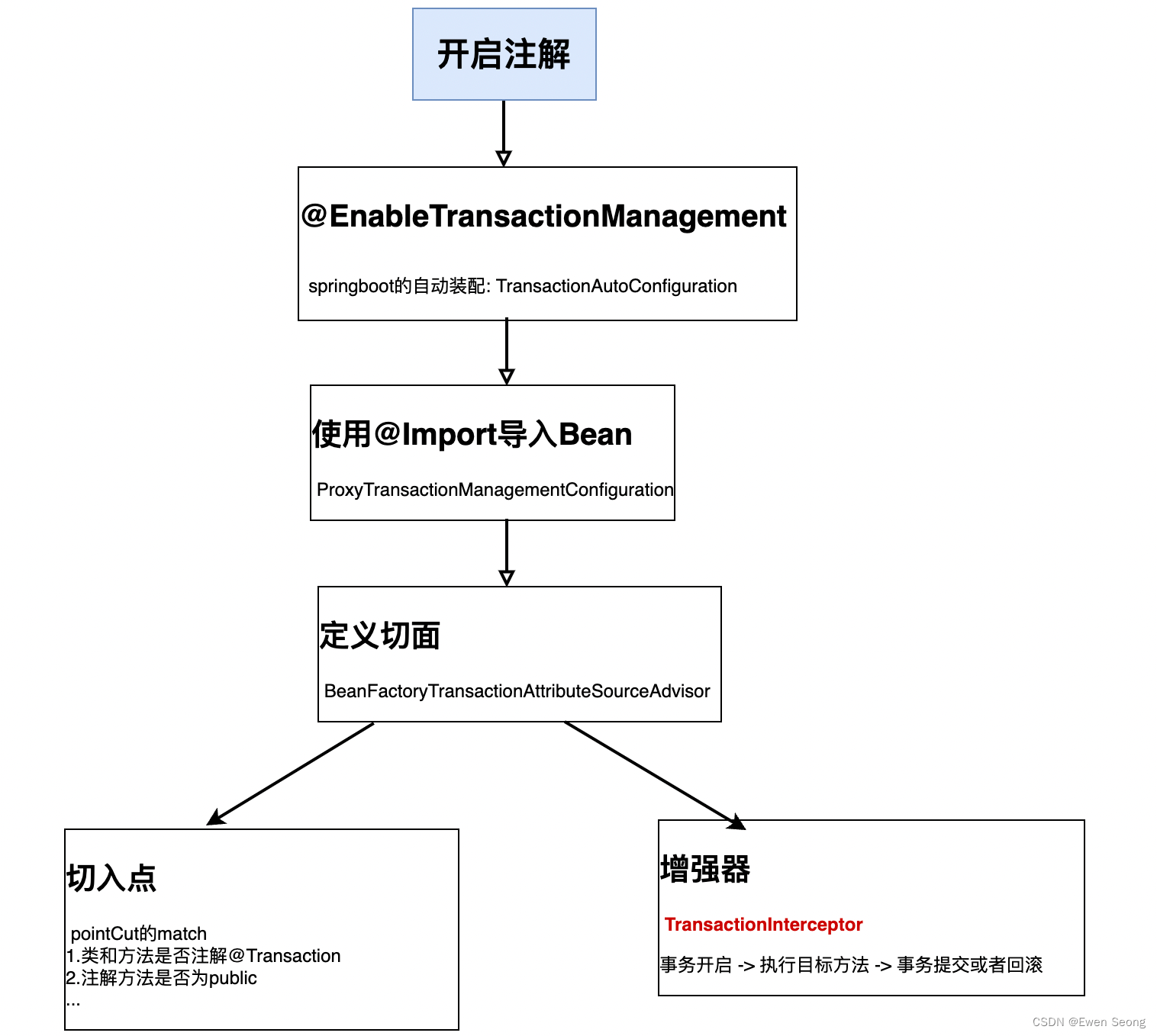
其中: 切入点匹配条件中有一条要求方法为public, 这解释了非public方法事务失效的原因.
Spring原理—动态代理:
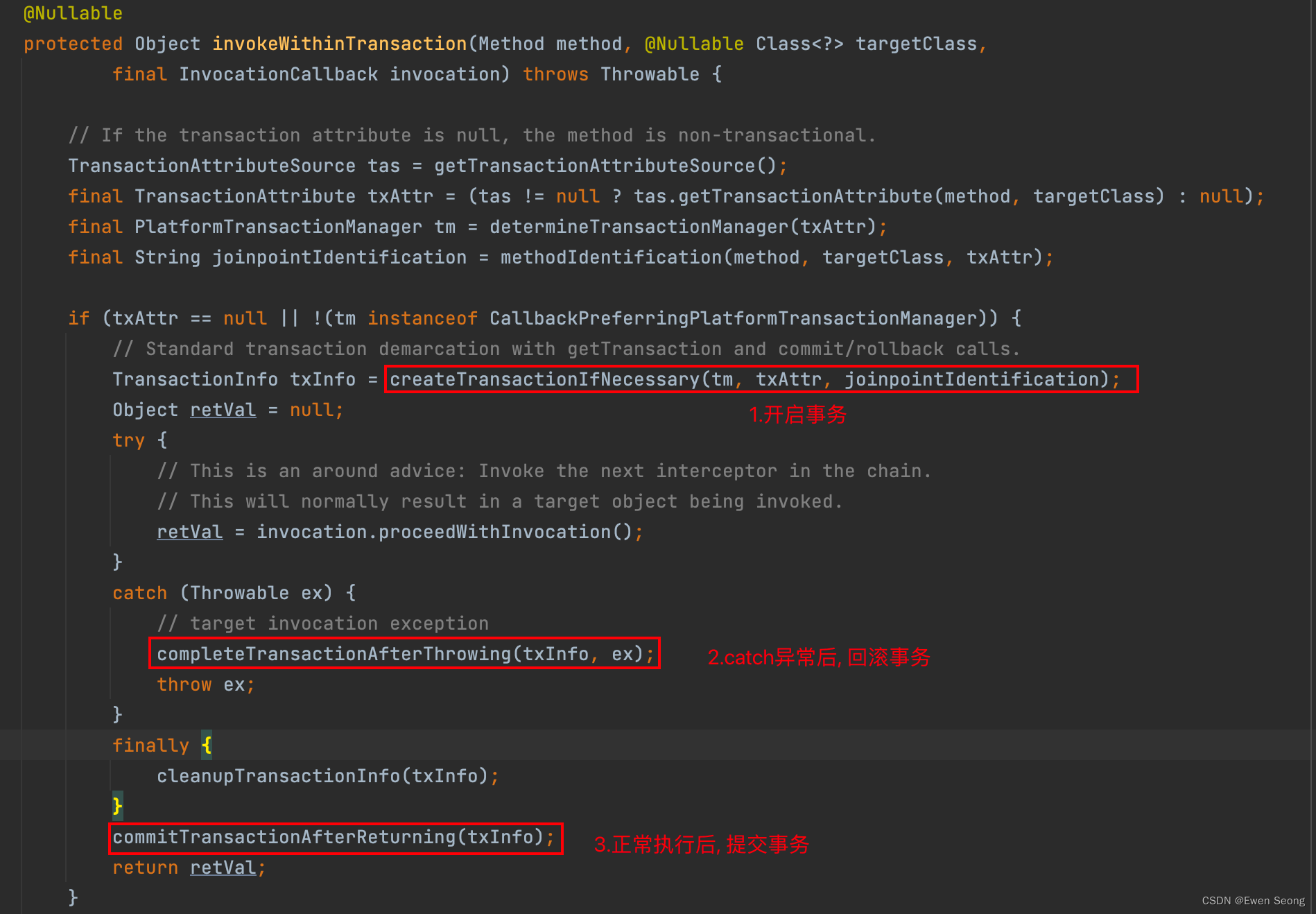
由此, 当用户以目标对象类型从IOC获取Bean对象时, 得到的是代理对象; 当调用目标对象的方法时, 被增强器TransactionInterceptor所拦截, 并进入invoke方法中:
@Override@Nullablepublic Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);}
invoke方法继续调用invokeWithinTransaction方法, 并传入三个参数: invocation.getMethod()表示用户调用的方法, targetClass表示目标对象类型, invocation::proceed提供了调用目标方法的能力.
查看TransactionInterceptor源码前, 不妨先看一下TransactionInterceptor的主线功能:
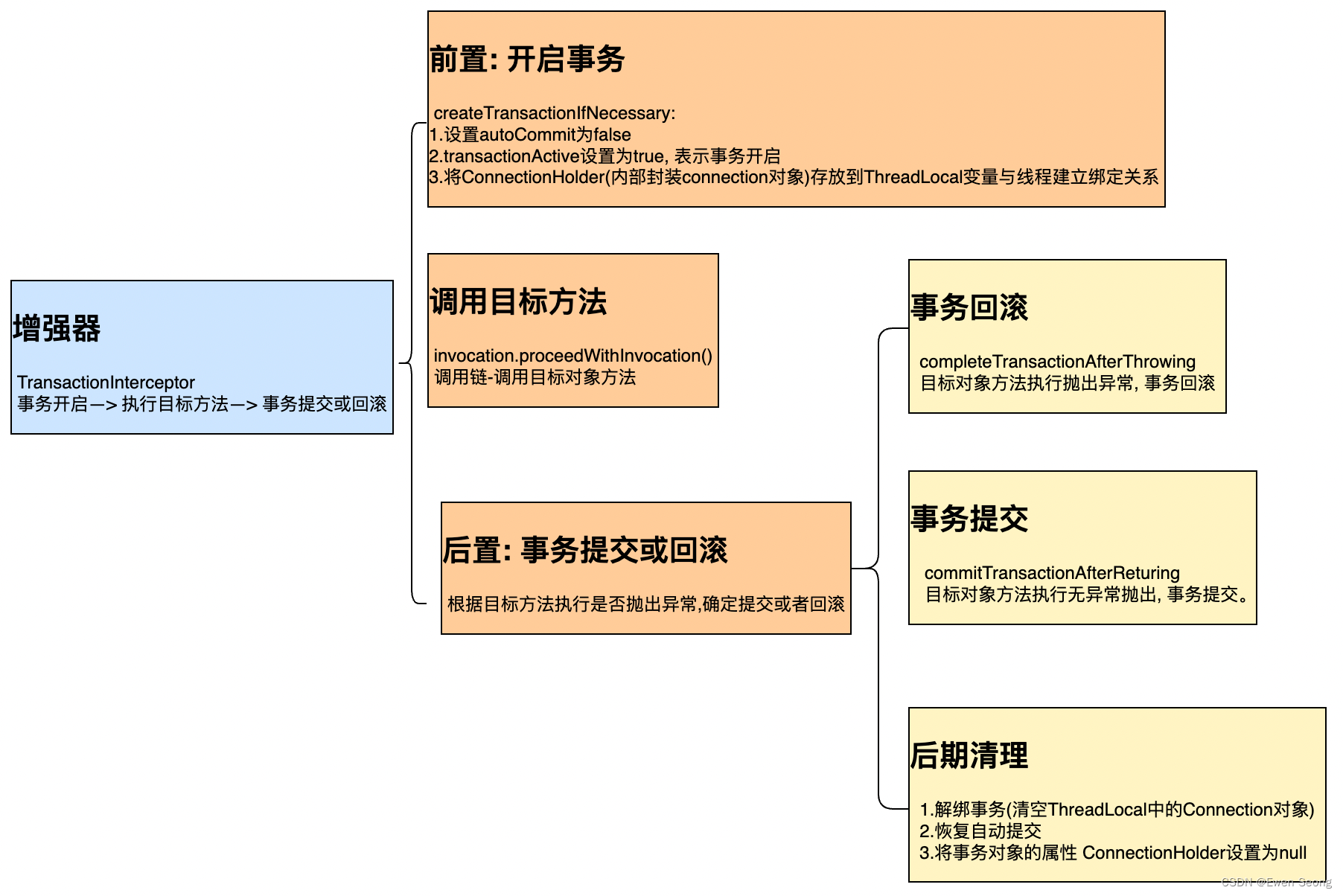
对应源码如下:
4.Spring整合Mybatis
Spring整合Mybatis:
—> 将Mybatis中的对象作为Bean存入IOC容器中, 在需要的地方进行依赖的注入;
—> 需要在Mybatis中找到一个值得存入IOC容器中的对象, 要求该对象要求数据库执行与回滚能力;
—> 即: 在Mapper和Sqlsession中选择一个.
另外被注入的对象作为全局资源会被多个线程共用, 因此需要考虑线程安全问题.
4.1 选择Mapper对象
Mybatis的一大亮点在于Mapper接口类中的方法与Mapper.xml中sql的映射关系, 使得用户可以通过Mapper接口类对象操作数据库, 如下所示:
AccountMapper accountMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(AccountMapper.class);
accountMapper.updateMoney(100);
否则, 同JdbcTemplate一样, 需要在Java代码里写sql语句.
Mapper作为接口类, 由Mybatis框架为其实现代理类. Mybatis为Mapper接口生成的动态代理类的InvocationHandler中维持了对sqlsession的引用:
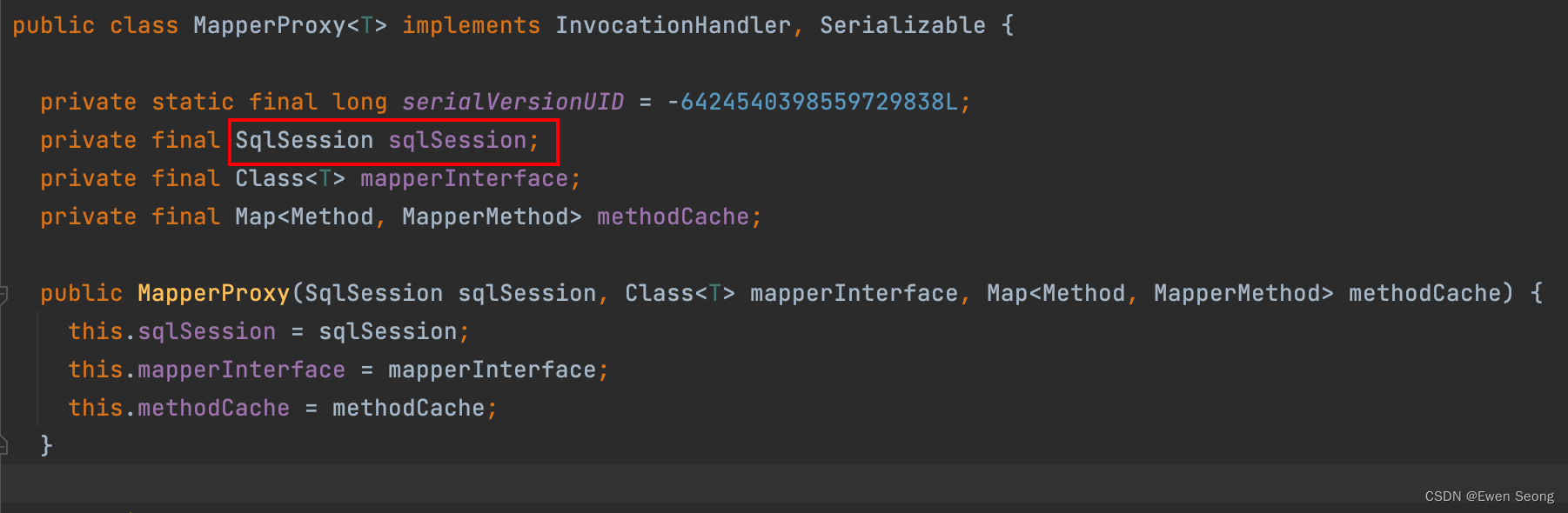
以下是Mapperproxy类中的invoke方法实现逻辑:
@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {//...细节return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);}
跟进mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args):
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Object result;switch (command.getType()) {case INSERT: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));break;}case UPDATE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));break;}case DELETE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));break;}case SELECT://... 细节return result;}
可以看出用户提交给Mapper的任务, 最后还是委托给sqlsession对象去执行。即,本质上Mybatis框架依赖的对象是sqlsession,而Mapper对象仅仅是对其进行的一层封装,使得用户可以通过操作接口而不是操作sql语句的方式实现数据库操作。
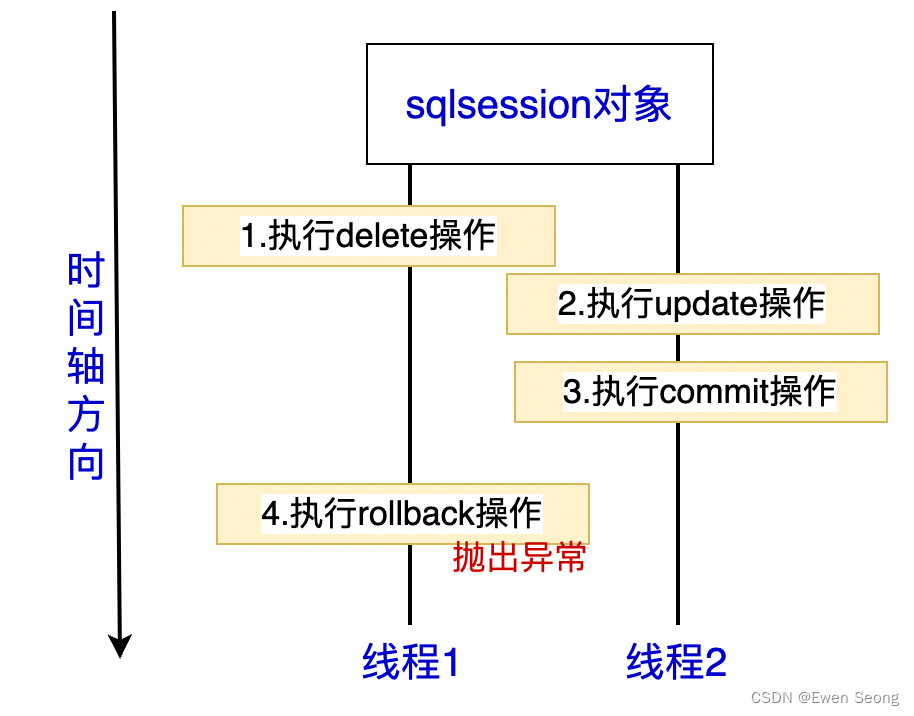
需要注意,上述流程还说明了一个问题: 一个Mapper对象关联了一个Sqlsession对象. 由于Connection对象是线程不安全的, 基于Connection的SqlSession显然也是线程不安全的, 如下图所示:
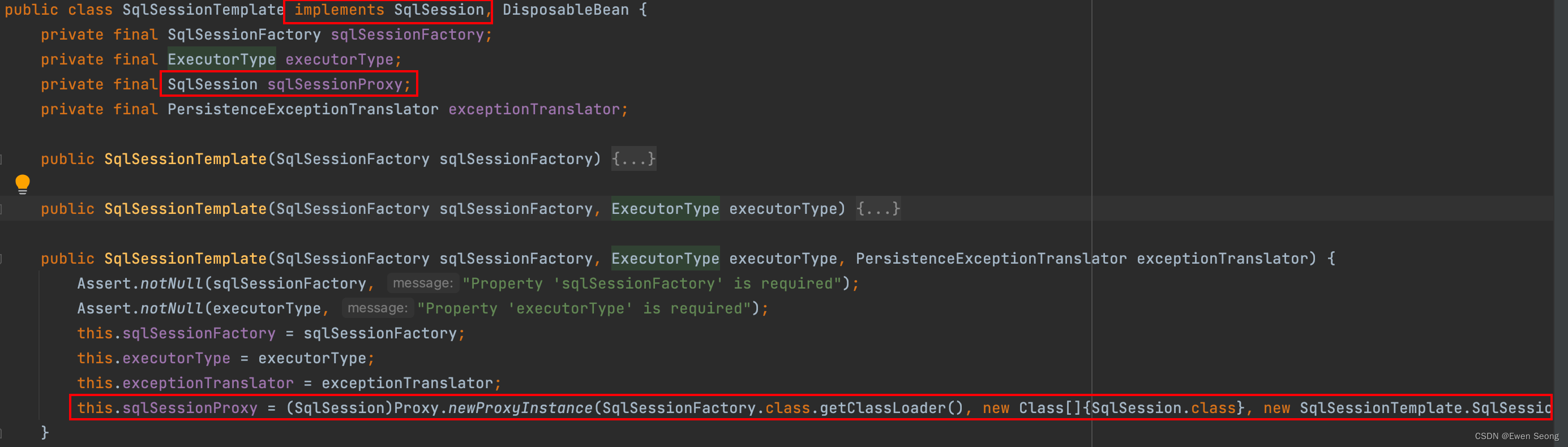
4.2 SqlsessionTemplate
Spring通过引入SqlSessionTemplate类解决了线程安全问题, 即SqlSessionTempalte本身是线程安全的, 本章节会结合源码分析一下SqlSessionTemplate线程安全的原因.
SqlSessiontemplate作为SqlSession接口的实现类, 同时内部持有一个SqlSession对象属性, 且所有的方法都委托给内部的sqlsession对象去执行, 这是个很明显的静态代理:
与常规静态代理不同的是, 被代理的对象本身是个动态代理对象; 即所有SqlsessionTemplate的方法调用, 都会被动态代理所拦截(此处的InvocationHandler类为SqlSessionInterceptor), 并调用对应的invoke方法:
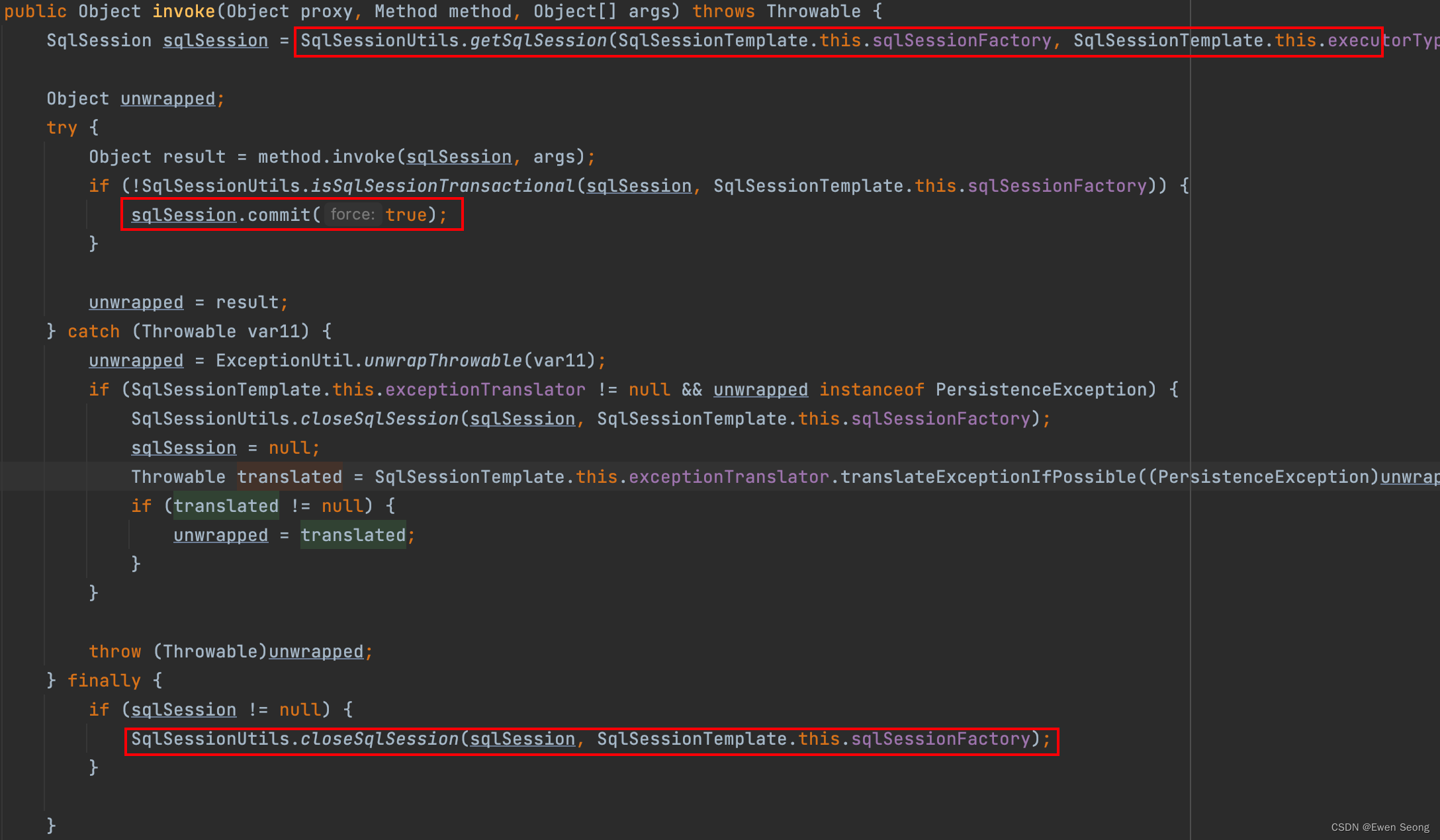
可以看到真正用于处理起作用的Sqlsession对象通过SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession方法得到.
跟进SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession:
// 省略断言和日志
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType, PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder)TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);if (session != null) {return session;} else {// 获取新的SqlSession对象session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);// 绑定SqlSession对象与当前线程registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);return session;}
}
TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory)方法从ThreadLocal中获取与当前线程绑定的SqlSessionHolder对象:

当前线程第一次调用Mapper接口方法时, 从TheadLocal中获取的SqlSessionHolder对象为空; 此时根据sessionFactory.openSession(executorType)获取SqlSession对象, 递归跟进该方法:
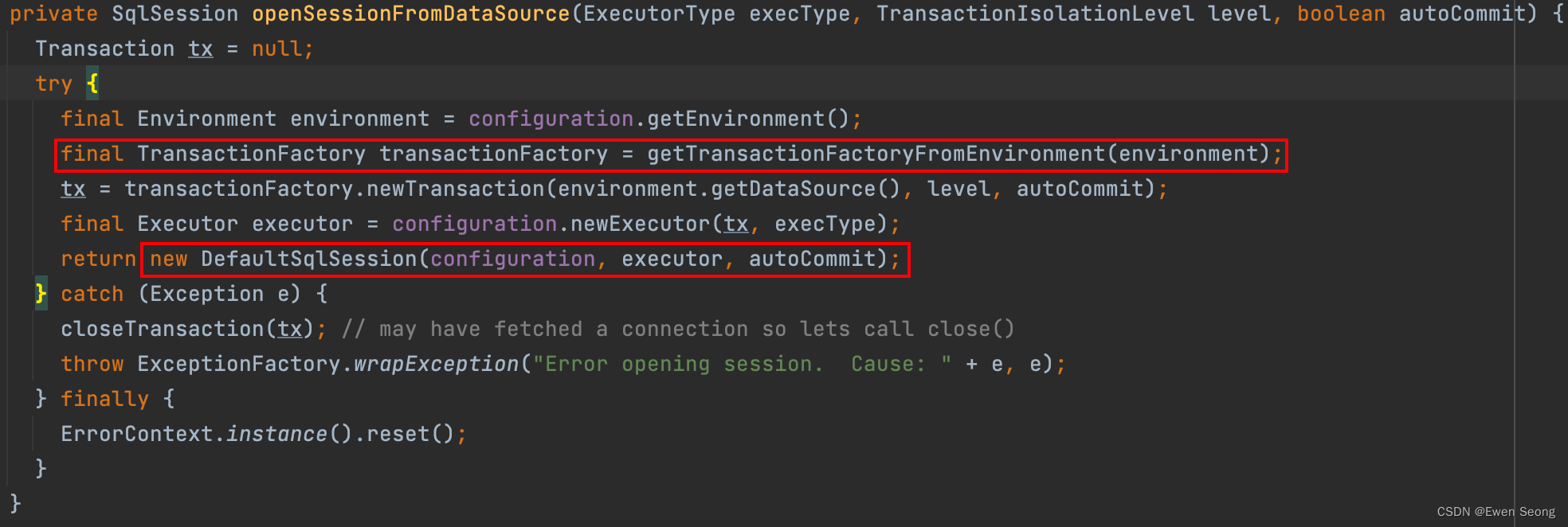
可以看到最终新创建了一个DefaultSqlSession对象返回.
这里同时需要注意的是, 该DefaultSqlSession对象中的事务为SpringManagedTransaction(从enviroment对象中得到的事物工厂为SpringManagedTransactionFactory类型).
当前线程再次调用Mapper接口方法时, 从TheadLocal中获取的SqlSessionHolder对象不为空, 并从中得到与该线程绑定的SqlSession对象, 从而实现不同线程使用不同的SqlSession对象 达到线程安全的目的.
核心问题理清后, 再介绍一下SpringManagedTransaction对象.
4.3 SpringManagedTransaction
当引入mybatis-spring依赖后:
<dependency><groupId>org.mybatis</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId><version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
Spring启动过程中会加载SqlSessionFactoryBean, 将enviroment的事务工厂属性设置为SpringManagedTransactionFactory类型对象.
if (this.transactionFactory == null) {this.transactionFactory = new SpringManagedTransactionFactory();
}
configuration.setEnviroment(new Enviroment(this.enviroment, this.transactionFactory, this.dataSource));
进入SpringManagedTransaction源码中看一下对Transaction接口的实现:
// 省略日志public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {if (this.connection == null) {this.openConnection();}return this.connection;
}private void openConnection() throws SQLException {this.connection = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(this.dataSource);this.autoCommit = this.connection.getAutoCommit();this.isConnectionTransactional = DataSourceUtils.isConnectionTransactional(this.connection, this.dataSource);
}public void commit() throws SQLException {if (this.connection != null && !this.isConnectionTransactional && !this.autoCommit) {this.connection.commit();}}public void rollback() throws SQLException {if (this.connection != null && !this.isConnectionTransactional && !this.autoCommit) {this.connection.rollback();}
}
其中有两处重点:
[1] 通过this.connection = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(this.dataSource);获取链接对象:
DataSourceUtils是Spring提供的资源获取类, getConnection方法用于获取与当前线程绑定的Connection对象; 由此线程使用的Connection对象相互隔离.
[2] 通过DataSourceUtils.isConnectionTransactional(this.connection, this.dataSource)获取isConnectionTransactional标识:
用于表示此connection是否有事务性:
public static boolean isConnectionTransactional(Connection con, @Nullable DataSource dataSource) {if (dataSource == null) {return false;} else {ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder)TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);return conHolder != null && connectionEquals(conHolder, con);}
}