1 简介
针对变压器故障的特征,结合变压器油中气体分析法以及三比值法.提出了基于原子搜索算法改进极限学习机的故障诊断方法.由于输入层与隐含层的权值和阈值是随机产生.传统的极限学习机可能会使隐含层节点过多,训练过程中容易产生过拟合现象.该方法运用原子搜索算法对极限学习机的输入层与隐含层的权值与阈值进行优化,从而提高模型的稳定性和预测精度.将诊断结果与传统的基于极限学习机故障诊断进行对比,结果表明,基于原子搜索算法改进极限学习机变压器故障诊断的精度更高.
基于ASO 优化 ELM 的变压器故障诊断的具体步骤为:
1)确定 ELM 的拓扑结构。即输入层神经元个数,隐含层神经元个数以及输出层神经元个数;
2)对 ELM 中输入层到隐含层的权值以及阈值进行编码,得到初始种群;
3)解码得到权值和阈值,将权值和阈值带入到ELM 的训练网络中,使用训练样本进行训练;
4)训练完成后,使用测试样本进行测试,将测试样本的期望值和预测值的误差平方和作为适应度函数;
5)对种群进行选择,交叉,变异,得到新的种群,如果满足条件,则得出了误差平方和最小的网络权值和阈值,如果不满足条件,则返回步骤 2);
6)将优化后的权值和阈值带入到训练网络中,计算隐含层输出矩阵 H, 并求解矩阵 H 的 MoorePenrose 广义逆 H+;
7)计算输出层权值β赞=H+T;
8)将测试样本带入到模型中进行预测。
2 部分代码
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Atom Search Optimization.
function [X_Best,Fit_XBest,Functon_Best]=ASO(alpha,beta,Fun_Index,Atom_Num,Max_Iteration)
% Dim: Dimension of search space.
% Atom_Pop: Population (position) of atoms.
% Atom_V: Velocity of atoms.
% Acc: Acceleration of atoms.
% M: Mass of atoms.
% Atom_Num: Number of atom population.
% Fitness: Fitness of atoms.
% Max_Iteration: Maximum of iterations.
% X_Best: Best solution (position) found so far.
% Fit_XBest: Best result corresponding to X_Best.
% Functon_Best: The fitness over iterations.
% Low: The low bound of search space.
% Up: The up bound of search space.
% alpha: Depth weight.
% beta: Multiplier weight
alpha=50;
beta=0.2;
Iteration=1;
[Low,Up,Dim]=Test_Functions_Range(Fun_Index);
% Randomly initialize positions and velocities of atoms.
if size(Up,2)==1
Atom_Pop=rand(Atom_Num,Dim).*(Up-Low)+Low;
Atom_V=rand(Atom_Num,Dim).*(Up-Low)+Low;
end
if size(Up,2)>1
for i=1:Dim
Atom_Pop(:,i)=rand(Atom_Num,1).*(Up(i)-Low(i))+Low(i);
Atom_V(:,i)=rand(Atom_Num,1).*(Up(i)-Low(i))+Low(i);
end
end
% Compute function fitness of atoms.
for i=1:Atom_Num
Fitness(i)=Test_Functions(Atom_Pop(i,:),Fun_Index,Dim);
end
Functon_Best=zeros(Max_Iteration,1);
[Max_Fitness,Index]=min(Fitness);
Functon_Best(1)=Fitness(Index);
X_Best=Atom_Pop(Index,:);
% Calculate acceleration.
Atom_Acc=Acceleration(Atom_Pop,Fitness,Iteration,Max_Iteration,Dim,Atom_Num,X_Best,alpha,beta);
% Iteration
for Iteration=2:Max_Iteration
Functon_Best(Iteration)=Functon_Best(Iteration-1);
Atom_V=rand(Atom_Num,Dim).*Atom_V+Atom_Acc;
Atom_Pop=Atom_Pop+Atom_V;
for i=1:Atom_Num
% Relocate atom out of range.
TU= Atom_Pop(i,:)>Up;
TL= Atom_Pop(i,:)<Low;
Atom_Pop(i,:)=(Atom_Pop(i,:).*(~(TU+TL)))+((rand(1,Dim).*(Up-Low)+Low).*(TU+TL));
%evaluate atom.
Fitness(i)=Test_Functions(Atom_Pop(i,:),Fun_Index,Dim);
end
[Max_Fitness,Index]=min(Fitness);
if Max_Fitness<Functon_Best(Iteration)
Functon_Best(Iteration)=Max_Fitness;
X_Best=Atom_Pop(Index,:);
else
r=fix(rand*Atom_Num)+1;
Atom_Pop(r,:)=X_Best;
end
% Calculate acceleration.
Atom_Acc=Acceleration(Atom_Pop,Fitness,Iteration,Max_Iteration,Dim,Atom_Num,X_Best,alpha,beta);
end
Fit_XBest=Functon_Best(Iteration);
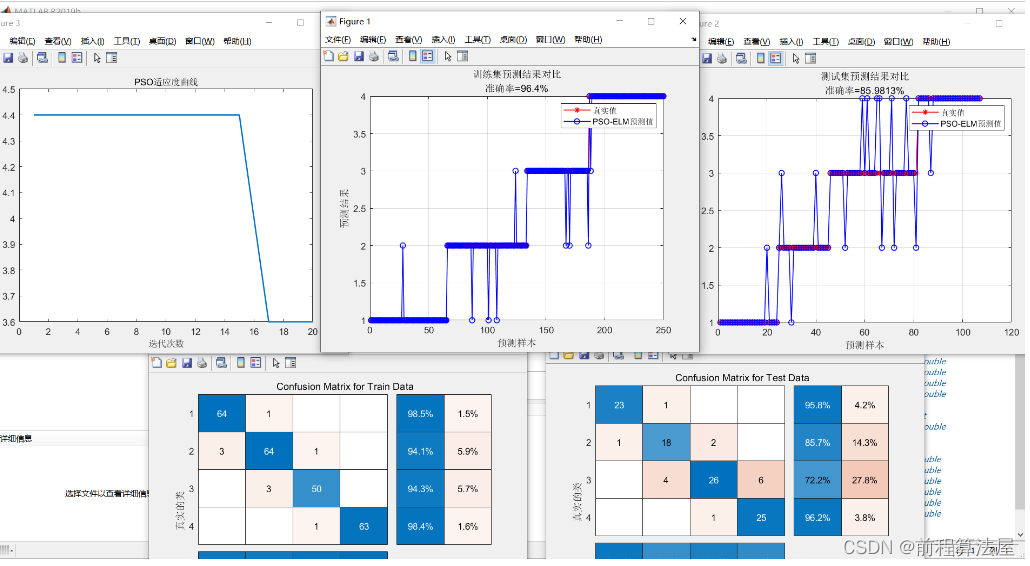
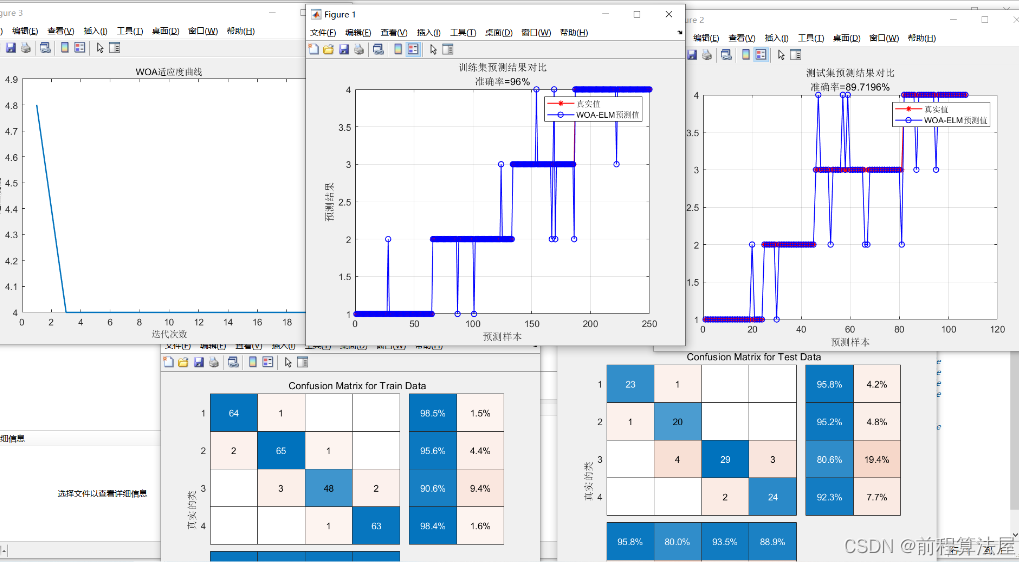
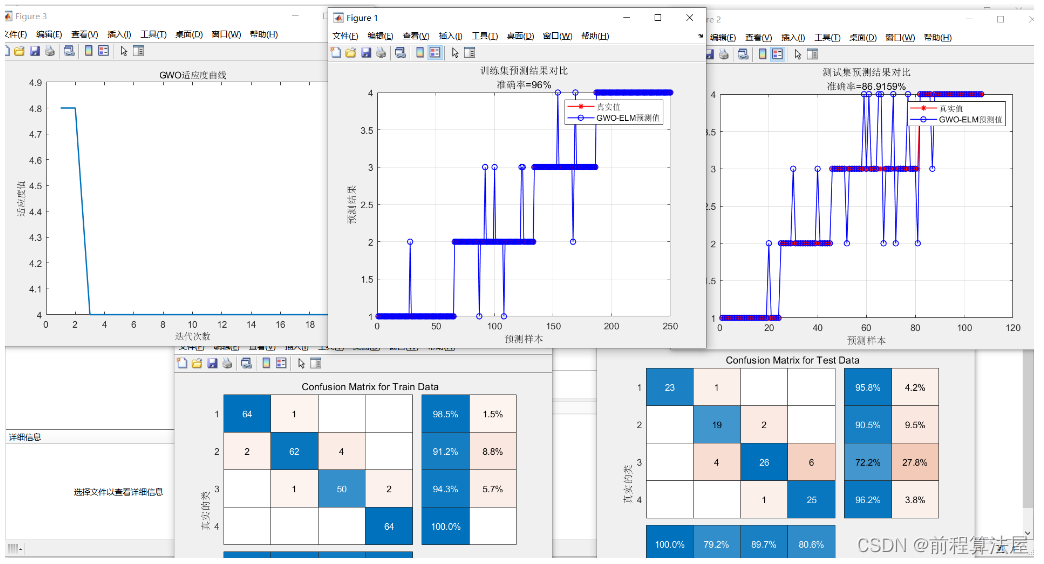
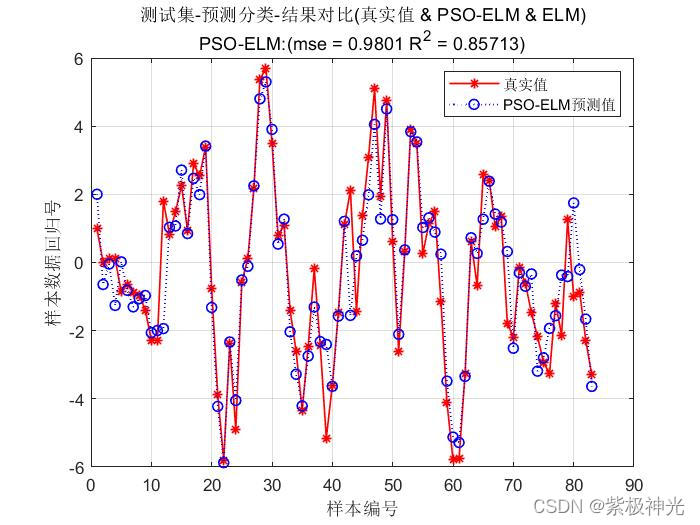
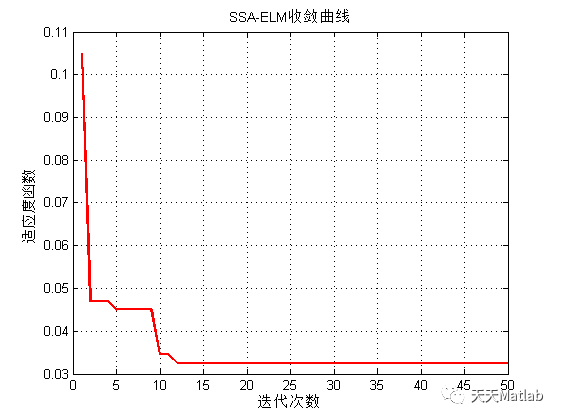
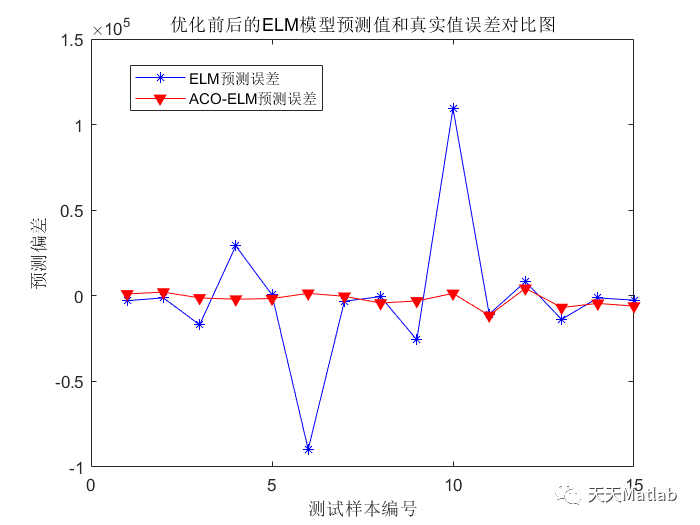
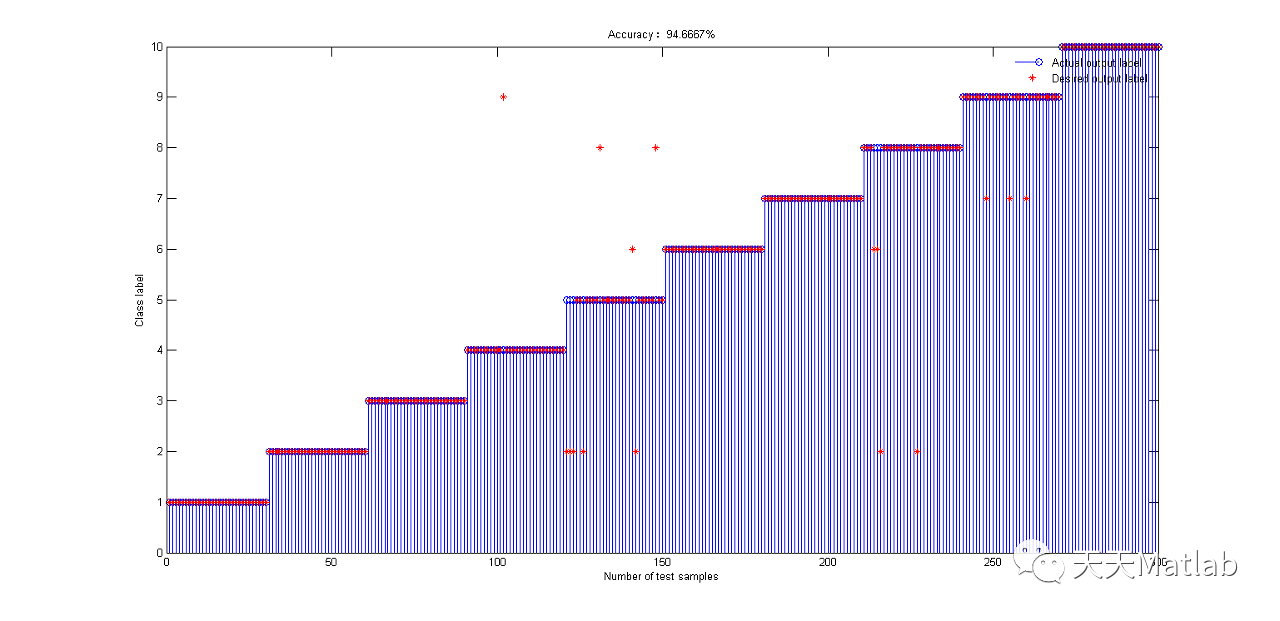
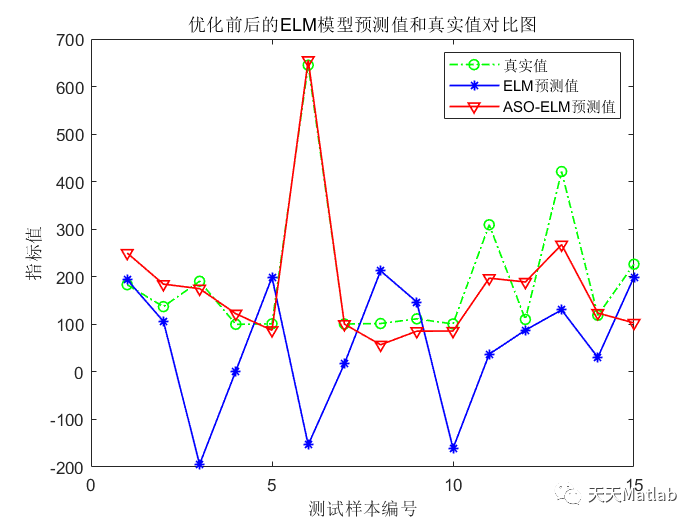
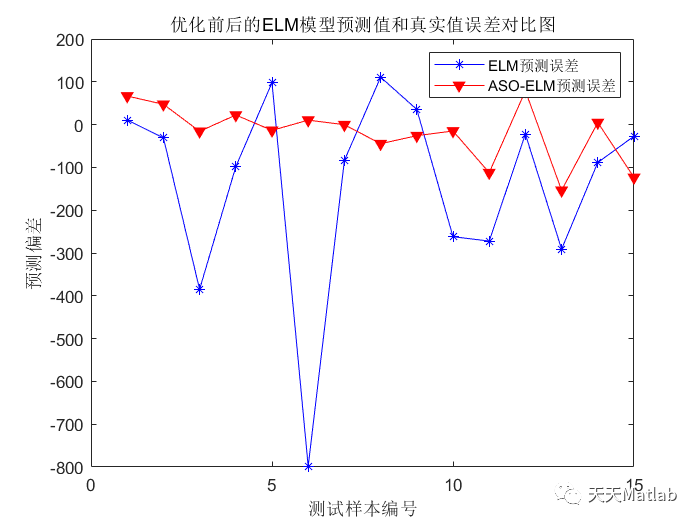
3 仿真结果
4 参考文献
[1]郑嘉利, & 王哲. (2019). 一种基于蝗虫算法和极限学习机的RFID室内定位方法. CN109598320A.
5 MATLAB代码与数据下载地址
见博客主页