接上文—————>
目录:
- 一.安装
- 二.have基本命令操作
- 三.hive数据仓库
- 四.hive表的类型:
- 五.hive中重要的元数据表
- 六.hive的连接方式
- 七.使用jdbc编写外部程序操作hive
- 八.hive的基本数据类型
- 九.hive的复杂的数据类型
- 十.hive的建表语句
- 十一.hive 删除表
- 十二.hive 修改表
- 十三.查看表信息
- 十四.DML
- 十五.hive单词统计 (count)
- 十六.hive分布表
- 十七.分桶表
- 十八.hive排序
- 十九.hive变量:
- 二十.hive命令行中执行hadoop命令
- 二十一.hive表的数据类型与文件格式:
- 二十二.数据操作
- 二十三.在hive中何时不会hql转换为mr执行
- 二十四.hive常用函数:
- 二十五.hive中事务的使用
- 二十六.操作:
- 二十七.操作:
- 二十八.hive的优化
- 二十九.UDF:User define function 用户自定义函数
一.安装
1.解压下面压缩包
tar -xzvf apache-hive-2.1.1-bin.tar.gz
2.重命名
mv apache-hive-2.1.1-bin hive
3.配置环境变量
进入文件:
vi /etc/profile
填入环境变量(注意修改hive路径):
#HIVE
export HIVE_HOME=/root/soft/hive
export PATH=$PATH:$HIVE_HOME/bin
更新文档:
source /etc/profile
检验hive版本(出现版本号说明成功):
hive --version
4.修改hive-site.xml
cd /soft/hive/conf
重命名:
cp hive-default.xml.template hive-site.xml
进入文件修改:
vi hive-site.xml
修改以下环境变量(推荐Notepad++软件编辑):
javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName = 改为mysql 用户名
javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword = 改为mysql 密码
javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL = jdbc:mysql://你的IP:3306/hive
javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver (直接复制这是MySQL驱动)
5.将mysql-connector-java-5.1.18-bin.jar连接驱动包上传到hive/lib下
 6.需要在MySQL下建立hive数据库:
6.需要在MySQL下建立hive数据库: 
7.在Hadoop下创建hive临时目录:
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /soft/hive/tmp
8.修改hive-site.xml文件,设定为false
将${system:java.io.tmpdir} 替换为 /soft/hive/tmp
将${system:user.name} 替换为 root
9.Linux输入schematool -dbType mysql -initSchema进行初始化:
schematool -dbType mysql -initSchema
出现如下completed则成功:

10.执行hive命令测试是否能进入 hive>
hive
hive环境搭建到此结束.
二.have基本命令操作
1. 查看数据库$hive> show databases;
2. 创建数据库$hive> create database db1;
3. 选择某个数据库$hive> use db1;
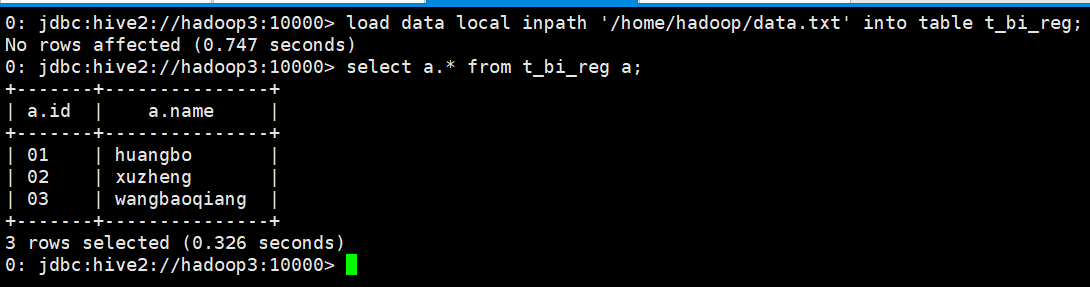
4. 删除数据库$hive> drop db1;[结论] 1. 通过查看hdfs中的目录结构,确定了hive中的数据库就是hdfs中的一个文件夹(dbname.db)$> hdfs dfs -lsr /2. 在元数据库中(mysql), 存储了数据库的数据结构(dbs)。$mysql> use hive ;$mysql> select * from dbs;5. 清空hive命令行$hive> !clear;查看表$hive> show tables;6. 查询表$hive> select * from employee;
7. 创建表(*****)内部表外部表分区表桶表($hive> create table db1.employee(id int,name string,age int);(没有数据加入))$hive> create table db1.employee(id int,name string,age int) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' stored as textfile ;(创建的是内部表)注意: 一定要使用数据库名.表名创建$mysql> select * from tbls;查看属于那个数据库8. 修改表(不建议)$hive> alter table db1.employee add column (sid string);9. 删除表$hive> drop table db1.employee;10. 添加数据(新增数据)做此操作,必须启动yarn!$hive> insert into db1.employee(id,name,age) values(1,'xxx',18); (不推荐, 会将语句转换为mr执行,效率低)$mysql> select * from columns_v2;CD_ID查看表信息$mysql> select * from tbls;SD_ID列
11. 加载数据(常用的三种方式)[准备工作]cd ~mkdir datatouch d.txtvi d.txtmv d.txt data创建一个文件d.txt(用tab建隔开)-------------------------1 xiaoming 172 xiaohong 183 xiaoqiang 19create table test_part (id int,name string,no int) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' stored as textfile ;1. 拷贝$> hdfs dfs -put ~/data/d.txt /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/employee$hive> select * from employee;2. 加载linux本地文件 什么类型的数据都可以拷贝分片$hive> load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/d.txt' into table employee;$hive> select * from employee;3. 加载hdfs文件$> hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /root/hive/data$> hdfs dfs -put ~/data/d.txt /root/hive/data$> hdfs dfs -lsr /root/hive/data$hive> load data inpath '/root/hive/data/d.txt' into table employee;$hive> select * from employee;12. insert与load区别:load data:将某些数据文件上传至hdfs,数据量大insert:将insert操作转换为mr作业,每一次进行insert的话,在表目录下生成一个新的数据文件cd datavi a.txt输入:(tab键隔开)4 xiaogang 205 xiaowang 21$> hdfs dfs -put a.txt /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/employee$> hdfs dfs -lsr /$hive> use db1;$hive> select * from employee;$hive> inser into employee(id,name,age) values(6,'yyy',19);访问http://192.168.110.3:8088 查看yarn进程$> hdfs dfs -lsr / 多出来一个/root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/employee/000000_0$> hdfs dfs -cat /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/employee/000000_0显示 6 yyy 1913. hive不支持update,delete操作14. 排序操作order by 字段 asc\descorder by 操作转换成mapreduce$hive> select * from employee order by id desc;//降序15. 分页操作oracle: rownum(数据伪列)select * from xxx where rownum >=10 and rownum <20;mysql: limit 数据开始条数,数据条数;select * from xxx limit 10,10;limit操作不会转换成mapreduce$hive> select * from employee order by id asc limit 0,5;//查询排序后的前5条记录(1,2,3,4,5)$hive> select * from employee limit 0,5;//查询当前的前5条记录16. 子查询建表:1. user$hive> create table db1.usr(uid int,uname string,rid int) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' stored as textfile;--------------------cd datavi usr.txt输入:1,admin,12,user1,23,user2,24,user3,3$hive> load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/usr.txt' into table db1.usr;2. role$hive> create table db1.role(rid int,rname string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' stored as textfile;-------------------cd datavi role.txt输入:1,管理员2,工程师$hive> load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/role.txt' into table db1.role;* 查询user表中rid在role中存在的数据。转换成mapreduce$hive> select * from usr where rid in (select rid from role); 结果: 1 admin 12 user1 23 user2 217. 连接查询------------------[需求]查询用户的账号以及角色名。inner :多表匹配,匹配不到的数据不显示[语句]-------sql 1993:(不好使用外连接)$hive> select u.uname,r.rname from usr u,role r where u.rid =r.rid;结果:admin 管理员user1 工程师user2 工程师sql 1998:$hive> select u.uname,r.rname from usr u inner join role r on u.rid=r.rid;outer :按特定的表匹配,匹配不到的数据使用null填充- left 以左边的表为基准$hive> select u.uname,r.rname from usr u left outer join role r on u.rid=r.rid;结果:admin 管理员user1 工程师user2 工程师user3 NULL- right$hive> select u.uname,r.rname from usr u right outer join role r on u.rid=r.rid;- full$hive> select u.uname,r.rname from usr u full outer join role r on u.rid=r.rid;连接查询会将操作转换成mapreduce执行。
三.hive数据仓库
数据仓库:OLAP(在线分析处理):延迟高,处理数据量大,不支持在线事务
数据库:OLTP(在线事务处理):延迟低,处理数据量没有那么大,支持事务
四.hive表的类型:
内部表(托管表)create table : 当删除表(drop table)时,元数据(MySQL)和数据文件(hdfs)都会被删除。
外部表create external table : 元数据和数据文件分离,当删除表时,元数据会删除,数据文件会保留。(表没有了,但数据还保留着)
分区表由于在hive下每一个表就是一个文件夹,数据就是文件。在一个文件夹下有可能存储特别多的数据文件。这时,当执行数据分析操作时,会遍历整个表文件夹下的所有文件,执行效率是比较低下的。分区表就是在表文件夹下继续分子文件夹,加载数据(load)时,数据会根据命令进入到不同的分区文价夹,这样我们在进行数据分析时,就可以根据分区逻辑进行查询了。
桶表有可能在分区子文件中数据文件依然很大,hive可以自定义分桶规则,对这些文件进行分桶(根据数据hash值,把数据分入到不同的桶文件),继续提高查询效率。
五.hive中重要的元数据表
DBS -> hive数据库的信息
TBLS -> hive表的信息
SDS -> hive文件信息
COLUMNS_V2 -> hive表的列信息
PARTITIONS -> hive表的分区信息
六.hive的连接方式
hive 命令 cli 和 beeline 2选一
1. hive cli
------------在hive2.0之前,最常用的一种命令,只能在本机运行。$> hive --service cli 等同于 $>hive常用参数-d 以键值对的形式定义一个变量,可以在命令行中使用[centos@master bin]$>hive -d tab=employee ->在Linux中 直接声明变量tab$hive> use db1;$hive> select * from ${tab} ; ->在hive命令行中直接引用-e 在Linux中直接使用hive命令执行某条Hql语句[centos@master bin]$>hive -e "select * from db1.employee"执行完后直接退出hive,回到Linux命令行窗口-f 在Linux中直接执行某个hql文件$>cd ~$>mkdir hql$>touch hive1.hql$>vi hive1.hql$>cat hive1.hql--------------use db1;select * from db1.employee;[centos@master hql]$ hive -f hive1.hql$>hive -f ~/hql/hive1.hql执行完后直接退出hive,回到Linux命令行窗口2. hive beeline在hive2.0之后的,准备替换cli一个命令行,支持本机运行和远程运行------------------------------------修改Hadoop的core-site.xml------------------------------<property><name>hadoop.proxyuser.centos.hosts</name><value>*</value></property><property><name>hadoop.proxyuser.centos.groups</name><value>*</value></property>修改hdfs-site.xml<property><name>dfs.webhdfs.enabled</name><value>true</value></property>打开服务,打开另一个窗口专门运行hive服务,因为它不在后台运行。$>hive --service hiveserver2 //开启了一个RunJar节点$>beeline -u jdbc:hive2://master:10000-n 用户名-p 密码3. hive server2
-------------------hive server2 本身是一个服务 RunJarhive 对外提供的连接端口10000:外部连接端口10002:webUI端口http://192.168.110.3:10002/hiveserver2.jsp 连接hive server2 的webUI
七.使用jdbc编写外部程序操作hive
1.导入hive相关依赖
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.apache.hive</groupId><artifactId>hive-jdbc</artifactId><version>2.1.1</version></dependency>
</dependencies>
2.编写hive的jdbc程序
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{Class.forName("org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiverDriver");Connection conn=DriverManger.getConnection("jdbc:hive2://192.168.58.100:10000/db1","centos","123456");Statement stmt=conn.createStatement();ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from employee");while(rs.next()){System.out.println(rs.getInt("id"),rs.getString("name"),rs.getInt("age"));}rs.close();stmt.close();conn.close();}
八.hive的基本数据类型
在hive中声明列的时候不需要指明列的长度。MySQL:create table user(id int(32),name varchar(32));hive:create table user(id int,name string);整数:tinyint -> byte(Java) -> 1字节smallint -> short(Java) -> 2字节int -> 4字节bigint -> long(Java) -> 8字节
小数:float:单精度浮点double: 双精度浮点
字符串:string -> varchar(mysql)
布尔:boolean -> true / false
九.hive的复杂的数据类型
1. Map : 一组有序的字段,字段类型必须相同(Java中的List)
2. Array : 无序键值对,键值对内部字段类型(Java中的value)必须相同(Java中的Map)
3. Struct : 一组字段,字段类型可以不同(Object集合)
十.hive的建表语句
create [external](外部表) table [if not exists(判断是否存在)] table_name
(col1_name(列名) type(类型) [comment col_comment(对列的说明)],col2_name type [comment col_comment]....)
[comment table_comment]
partitioned by(分区表)(col1_name type [comment col_comment],col2_name type [comment col_comment]...)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
clustered by(分桶表)(col_name)(需要分桶的字段) into n(桶的数目)buckets
stored by file_type(数据文件存储类型)
location hdfs_path(文件存储位置);1. external:在建表语句中添加external选项,代表这个表为外部表。外部表在删表时,只删元数据(mysql),不删数据文件(hdfs),故删除后数据一般不会丢
[创建student(sid sname age)]1创建内部表:$hive> create table student_1(sid int , sname string,age int) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';[centos@master ~]$cd data/[centos@master data]$ touch student.txt[centos@master data]$ vi student.txt$hive>load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/student.txt' into table student_1;2创建外部表:$hive> create external table if not exists student_2(sid int , sname string,age int) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';mysql元数据中的区别(tbls表中 TBL_TYPE字段有区别):内部表:MANAGED_TABLE外部表:EXTERNAL_TABLE数据文件区别: $> hdfs dfs -lsr /drwxrwxrwx - centos supergroup 0 2020-04-01 20:07 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/student_1-rwxrwxrwx 1 centos supergroup 28 2020-04-01 20:07 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/student_1/student.txtdrwxrwxrwx - centos supergroup 0 2020-04-01 20:17 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/student_2-rwxrwxrwx 1 centos supergroup 28 2020-04-01 20:17 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/student_2/student.txt执行删表操作时,mysql元数据删除,内部表会删除hdfs上的数据文件,外部表不删除$hive> drop table student_1;$hive> drop table student_2;$> hdfs dfs -lsr /drwxrwxrwx - centos supergroup 0 2020-04-01 20:17 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/student_2-rwxrwxrwx 1 centos supergroup 28 2020-04-01 20:17 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/student_2/student.txt
2. comment :注释table comment : 表声明语句后(表名后面)column comment : 字段声明语句后(列后面)
3. 指定字段分割符row format delimited fields terminated by ',' : 在某张表中的字段是以","作为分隔符的,在load数据时数据文件以,分割
4. partitioned by 分区表分区表就是表文件夹下多个子文件夹。-------------------------------分区表:1. 创建分区表:$hive> create external table stu (sid int,sname string) partitioned by(bir_year int,bir_month int) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';[centos@master data]$ touch stu.txt[centos@master data]$ vi stu.txt[centos@master data]$ cp stu.txt stu1.txt2. 上传文件$hive> load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/stu.txt' into table stu partition (bir_year = 2000,bir_month = 10);$hive> load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/stu1.txt' into table stu partition (bir_year = 2000,bir_month = 11);影响数据存储,但不影响数据分析$> hdfs dfs -lsr /drwxrwxrwx - centos supergroup 0 2020-04-02 16:54 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/studrwxrwxrwx - centos supergroup 0 2020-04-02 16:55 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/stu/bir_year=2000drwxrwxrwx - centos supergroup 0 2020-04-02 16:54 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/stu/bir_year=2000/bir_month=10-rwxrwxrwx 1 centos supergroup 23 2020-04-02 16:54 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/stu/bir_year=2000/bir_month=10/stu.txtdrwxrwxrwx - centos supergroup 0 2020-04-02 16:55 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/stu/bir_year=2000/bir_month=11-rwxrwxrwx 1 centos supergroup 23 2020-04-02 16:55 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/stu/bir_year=2000/bir_month=11/stu1.txt$hive> select * from stu;1 tom 2000 102 jerry 2000 103 jorden 2000 101 tom 2000 112 jerry 2000 113 jorden 2000 115. clustered by (col_name) into n buckets桶表:根据某个字段,将数据分入不同的文件中
6. stored by file_type指定hdfs中数据文件的类型:textfile : 文本文件sequencefile : 序列文件rcfile :orcfile : 二进制文件(常用)
十一.hive 删除表
$hive> drop table table_name;
十二.hive 修改表
修改表名alter table employee(旧) rename to emp(新);
添加列alter table emp add columns (cls(列名) string);
修改列类型alter table emp replace columns (cls int(类型));
十三.查看表信息
desc formatted table_name;
十四.DML
加载文件load data [local] inpath 'file path' [overwrite] into table tablename [partition (partcol1 = value1,partcol2 = value2)];'file path' ——> '文件路径' 有local是Linux上的文件,不加是hdfs[overwrite] ——> 重写[partition (partcol1 = val1,partcol2 = val2)] ——> 分区(分区列=......)1. 加载文件 只是单纯的复制/移动操作,将数据文件移动到hive表所在的位置(在Hdfs上)2. 'file path'相对路径load data local inpath 'data/stu1.txt' into table stu partition (bir_year = 2000,bir_month = 11);绝对路径load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/stu1.txt' into table stu partition (bir_year = 2000,bir_month = 11);完整URIload data local inpath 'hdfs://master:9000/user/live/data/data.txt' into table stu partition (bir_year = 2000,bir_month = 11);3. local : linux(加) / hdfs(不加)4. overwrite : 使用overwrite,目标表(或者分区)中的内容如果存在就会被删除,然后再将file path指向的文件/目录中的内容添加到表/分区的目录中。如果目标表(分区)已经有文件,并与filepath中的文件名冲突,新的文件会替换旧数据文件。
插入操作
十五.hive单词统计 (count)
(words.txt中每一行的数据存储到textlines表中每一行,line代表数据文件中的每一行数据,再利用explode()展开函数将textlines表中的每一行展开,展开后的数据存储在words表中)
准备数据words.txt -> textlines -> words---------- --------------- --------------hadoop,java,hive line (列,有三条数据) word(字段,展开的记录)hive,c,hadoop hadoop,java,hive hadoophive,java,c hive,c,hadoop javahive,java,c hive方法一:1. 分布查询(mr思路)
-------------1.1 建表(line代表数据文件中的每一行数据)textlines(line string);hive>create table textlines(line string);1.2 建表(word代表每一个单词)words(word string);hive>create table words(word string);1.3 加载数据(words.txt -> textlines,即从文件中插入到表中)load data 'xxx' into table textlines;hive>load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/words.txt' into table textlines;*1.4 拆分单词并插入words表(textlines -> words,即将表中每一行数据进行拆分,将数据插入到另一表中,语句中的line是表中的列名)hive>insert overwrite table words select explode(split(line,',')) as word from textlines;步骤解析:1查询语句:先将行按照,作为标志进行分割,但此时仍为行并不为列select (split(line,','))2查询语句:将分割好的每一行进行转列,并为数据表起别名为wordselect explode(split(line,',')) as word from textlines3插入语句:将查询出的数据插入到另一张表中insert overwrite table words select explode(split(line,',')) as word from textlines;1.5 进行单词统计select word, count(*) from words group by word;hive>select word, count(word) as cont from words group by word;方法二:2. hql子查询(此法可省略words表)
----------------准备工作:即1.1和1.3将数据插入到textlines;实质是1.4和1.5的结合给(select explode(split(line,',')) as word from textlines)表添加别名为w hive>select w.word, count(*) from (select explode(split(line,',')) as word from textlines) as w group by w.word;3. 函数介绍
-----------------explode() :展开函数 -> 行转列split() :分割函数
十六.hive分布表
create [external] table [if not exists] table_name
(col1_name type [comment col_comment],col2_name type [comment col_comment]....)
[comment table_comment]
partitioned by (col1_name type [comment col_comment],col2_name type [comment col_comment]...) ->存在此行是分区表
clustered by (col_name) into n buckets
stored by file_type
location hdfs_path
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';分区:
---------------------------严格模式 : hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode = strict;由于hive是分布式的数据仓库,而这个数据仓库中每一张表中都存在大量的数据,这些数据是以文件的形式存储的。所以我们在执行某些HQL的时候,效率的非常低。严格模式下,只允许静态分区。非严格模式 : hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode = nonstrict;为了提高某些hql语句的执行效率,启动非严格模式,用户就可以在加载数据时形成新的分区。静态分区:在严格模式下,用户只能通过建表来确定分区,加载数据时确定分区,加载数据时不能创建新的分区动态分区:非严格模式下,用户可以通过load data 或 insert ... select 创建的新的分区(若出错检查是否配置)动态分区出现的目的(严格模式的一些限制):-------------------------------防止用户查询时出现意外1. 带有分区表的查询:在严格模式下,用户不允许扫描所有的分区进行这个限制的原因:通常分区表都有非常大量的数据集,而且数据增长非常迅速。2. 进行order by查询:在严格模式下,用户在进行order by 操作时,必须添加limit操作。(?)3. 进行join操作(笛卡尔积):MySQL :select a.a,a.b,b.a,b.b from a join b where a.xx = b.xx;MySQL中可以将join where 语句转换为 join on 语句的。Hive :在严格模式下 join where 是不允许的。4. 严格模式下限制bigint类型数据与string和double进行比较。hive中修改配置的两种常用方法:1. 临时 :只在当前会话中起作用$hive> set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true ->允许hive使用动态分区$hive> set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode = nonstrict; ->打开非严格模式,表示所有分区为动态性能设置:最大动态分区数:hive.exec.max.dynamic.partition.pernode = 100(默认值,可修改,在hive.site中修改)一个动态分区创建语句可以创建的最大动态分区数:hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions = 1000 (默认值,可修改,在hive.site中修改)全局最大文件数:hive.exec.max.created.files = 100000 (默认值,可修改,在hive.site中修改) 2. 永久 :修改hive-site.xml常用操作:1.测试分区表的使用(严格模式下测试 partition.mode = strict)1.1 创建一张带有分区的表:studentid name age分区(静态分区是在创建时已经指定分区了)year month day 建表语句,很多内容都使用默认 $hive> create table if not exists student (id int,name string,age int) partitioned by (year int,month int,day int) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';1.2 加载数据时,有分区时需要指定加载数据到哪个分区,进行分区指定。此时是加载进两个分区load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/student.txt' into table student partition(year=1998,month=7,day=31);load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/student.txt' into table student partition(year=1999,month=7,day=31);1.3 使用动态分区语句报错:insert into table student partition (year,month,day) select id,name,age,year,month,day from test_student;2.测试动态分区(非严格模式下测试 partition.mode = nonstrict) 打开非严格模式:set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode = nonstrict;建立表:create table test_student(id int,name string,age int,year int,month int,day int) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';加载数据:load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/p_stu' into table test_student;执行动态分区语句(通过字段形式在执行过程中改变分区):insert into table student partition (year,month,day) select id,name,age,year,month,day from test_student;根据其他表中的字段,来确定分区。3.半自动化分区:insert into table student partition (year=2002,month,day) select id,name,age,month,day from test_student;4.分区后的检索将分区看做字段进行条件查询select * from student where year = 1998; ->会将1998的列出来select * from student order by year; ->会根据年进行整体排列
=======================================================================4.15
十七.分桶表
Map Reduce:1. partition 3 ->分区2. split ->切片 3. map ->映射 4. shuffle ->分发 5. reducereduce 个数 = partition 分区的个数 :将文件按照分区数物理切割桶表:hive中的桶表就相当于Hadoop中mapreduce的分区,分区(hive中分桶)数量等于文件数。1.建立一张桶表:create table stu2 (sid int,sname string,sex string,age int,dept string) clustered by(sid) into 3 buckets row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
2.数据插入的三种方式:数据准备stu2.txt-------------------1,xiaoming,男,18,12,xiaowang,男,18,13,xiaoli,男,18,14,xiaohong,女,19,25,xiaolan,女,19,26,xiaolv,女,19,22.1 load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/stu2.txt' into table stu2;load data 这种方式不分桶,只是物理复制。2.2 insert into .. values : 不推荐由于每次insert操作,都会创建一个桶文件的copy文件(不会影响原数据文件),所以insert操作(只添加一条记录)会创建多个桶文件,不推荐使用。2.3 insert into table .. select ..hive属性设置:$hive>set hive.enforce.bucketing = true; -> 强制分桶$hive>set mapreduce.job.reduces = 3; -> 设置reduce个数建表:create table stu3 (sid int ,sname string,age int) clustered by(sid) into 3 buckets row format delimited fields terminated by ',';sorted by(sid asc) 测试:$hive> insert into table stu3 select sid,sname,age from stu2;所有的数据不会分入不同桶文件$hive> insert into table stu3 select sid,sname,age from stu2 distribute by sid sort by sid asc;distribute by sid 保证数据分桶sort by sid asc 保证桶内有序分桶逻辑:bucket: 3sid % 3 = 0 -> bucket 1= 1 -> bucket 2= 2 -> bucket 3[centos@master data]$ hdfs dfs -cat /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/stu3/000000_06,xiaolv,193,xiaoli,18[centos@master data]$ hdfs dfs -cat /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/stu3/000001_04,xiaohong,191,xiaoming,18[centos@master data]$ hdfs dfs -cat /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/stu3/000002_05,xiaolan,192,xiaowang,18【桶表总结】:1. clustered by 指定分桶所用列into n buckets 指定分桶的个数分桶的逻辑:hive对分桶的字段(key)的hash值与bucket个数进行取余操作(hash%bucketNum),从而可以保证数据均匀的随机的分布在所有的bucket文件中。2. sorted by 指定桶文件的排序规则3. 桶 = mapreduce 分区,完全相同。【桶文件的个数 = reduce的个数】4. hive中的分区和分桶有什么区别?分区:指的数据仓库中表目录下的子目录。每个目录下面都放数据文件,通过文件夹名称作为条件查询,可以查询到某个文件夹下的内容,但是这个文件夹本身与数据没有任何的联系。分桶:按照分桶指定的字段(hash值)进行分桶,将原本应该出现的特别大的数据文件分割为多个小数据文件。
十八.hive排序
1. order by : 全局排序:所有的数据传入一个reduce,在数据量大的情况下,将会花费大量的时间$hive> set hive.mapred.mode = nonstrict;$hive> select * from t1 order by id;
2. sort by : 非全局排序:数据进入reduce之前进行排序,只能保证每个reduce输出有序,不能保证全局有序。$hive> set mapred.reduce.task = 3;$hive> select * from stu3 sort by sid;
3. distribute by : 可以控制map的输出在reduce如何划分,可以按照指定字段将数据划分到不同reduce(桶文件)中,与group by,distribute by控制reduce如何处理数据,sort by控制reduce如何排序。$hive> select * from stu3 distribute by sid sort by sid;
4. cluster by : distribute by + sort by ;[限制条件] : 当distribute by 和sort by 处理字段相同的时候,可以使用cluster by 来代替distribute by和sort by。
=========================================================4.17
十九.hive变量:
变量的声明$hive> hive --define key=value$hive> select * from student where name = ${key}
二十.hive命令行中执行hadoop命令
centos : $> hadoop fs -lsr /$> hdfs dfs -lsr /hive : $hive> dfs -lsr /
二十一.hive表的数据类型与文件格式:
[数据类型]
---------------------数据类型 长度tinyint 1byte -- 字节类型smallint 2byte -- 短整数类型int 4byte -- 整数类型bigint 8byte -- 长整形float 4byte -- 单精度浮点型double 8byte -- 双精度浮点型string -- 字符序列boolean -- 布尔类型binary -- 字节数组timestamp -- 全类型 (整数、浮点数、字符串)[复杂(集合)数据类型]数据类型 描述 用法 实例---------------------------------------------------------------------------struct 类似于Java中的对象 字段.属性名 map 键值对 字段[key] array 数组 字段[下标]struct实例:1. 创建表create table t02 (id int , name string , s1 struct<sname:string,sage:int>) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' collection items terminated by ':'; -> struct字段的分隔符。2. 准备数据t02.txt---------------1,xm,xm:182,xw,xw:183. 加载数据load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/t02.txt' into table t02;4. 查询struct属性做为列select id,name,s1.sname from t02;运行结果:1 xiaoming xm2 xiaownag xw 作为条件select id,name from t02 where s1.sname = 'xm' and s1.sage > 18;运行结果: 1 xiaomingmap实例:1. 创建表 create table t03 (id int , name string , m1 map<string,int>) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' -> 指定字段的分隔符为tabcollection items terminated by ',' -> 指定map集合中元素的分割符map keys terminated by ':'; -> 指定map集合中元素的key与value的分隔符2. 准备数据t03.txt(1) 1 xm grade:3,class:5 2 xw grade:2,class:4t03.txt(2)3 xh grade:3,class:5,group:24 xv grade:2,class:43. 加载数据load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/t03.txt' into table t03;运行结果(1):1 xm {'grade':3,'class':5}2 xw {'grade':2,'class':4}运行结果(2):1 xm {'grade':3,'class':5}2 xw {'grade':2,'class':4}3 xh {'grade':3,'class':5,'group':2}4 xv {'grade':2,'class':4}4. 查询数据select id, name,m1['grade'] as grade , m1['class'] from t03;运行结果:1 xm 3 52 xw 2 43 xh 3 54 xv 2 4select id,name from t03 where m1['grade'] = 3 and m1['class'] = 5;运行结果:1 xm3 xh array实例:1. 创建表create table t04 (id int ,name string , a1 array<string>)row format delimited fields terminated by ','collection items terminated by ':';2. 准备数据t04.txt--------------1,xm,java:jsp:hadoop2,xw,c:c++:asp:ios3. 加载数据load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/t04.txt' into table t04;4. 查询数据select id,name,a1[0],a1[1] from t04 where a1[2] = 'hadoop';运行结果: 1 xm java jsp[数据文件格式]1. textfile--------------------hive默认的数据格式,导入数据时会将数据文件原封不动拷贝到hdfs上而不进行任何的处理。查看数据比较方便,磁盘开销大、数据解析时开销大。2. sequencefile--------------------二进制文件,以key value对的形式将数据序列化到数据文件中。存储方式: 按行存储可分割、可压缩(block压缩)sf文件是与hadoopAPI中的mapfile相互兼容。在进行大量分块操作时,按行存储的方式执行效率不高3. rcfile--------------------存储方式:将数据按行分块,每块按列存储压缩快 列读写快。(行转列)读取记录时涉及到的块是最少的在读取全部数据时,跟sequencefile相比没有明显的效率提升。4. orcfile--------------------存储方式:行转列压缩快,列读取快效率比rcfile高一些,其他特点与rcfile相同,相当于rcfile的升级版测试: 1. 创建三张表,分别使用不同的文件格式create table t_01(id int,name string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' stored as textfile;create table t_02(id int,name string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' stored as sequencefile;create table t_03(id int,name string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' stored as orcfile;2. 向三张表中分别导入数据。insert into table t_01 select id,name from student group by id,name ;insert into table t_02 select id,name from student group by id,name ;insert into table t_03 select id,name from student group by id,name ;insert select 与load不同之处:i s语句转成mr作业,load直接拷贝3. 观察三张表在hdfs上面数据文件的存储格式:$> hdfs dfs -lsr /drwxrwxrwx - centos supergroup 0 2020-04-17 15:45 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/t_01-rwxrwxrwx 1 centos supergroup 67 2020-04-17 15:45 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/t_01/000000_0drwxrwxrwx - centos supergroup 0 2020-04-17 15:46 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/t_02-rwxrwxrwx 1 centos supergroup 226 2020-04-17 15:46 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/t_02/000000_0drwxrwxrwx - centos supergroup 0 2020-04-17 15:47 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/t_03-rwxrwxrwx 1 centos supergroup 347 2020-04-17 15:47 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/t_03/000000_0$> hdfs dfs -cat /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/t_01/000000_0$> hdfs dfs -cat /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/t_02/000000_0$> hdfs dfs -cat /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/t_03/000000_0
二十二.数据操作
1.数据导入load data动态分区导入:insert into .. selectcreat table .. as select2.数据导出将表的文件夹从hive中下载到本地(不加local,导入到hdfs上)insert [overwrite] local directory 'path' select ...例:$hive> insert overwrite local directory '/home/centos/data/student' select id,name,age from student;
二十三.在hive中何时不会hql转换为mr执行
1. 全表查询: select * from student;
2. 分页查询:select * from student limit 0,10;
3. 如果在条件查询时,有时会将查询语句转成mrhive.fetch.task.conversion = minimal -> 所有查询都会转换为mrmore(默认) -> 尽量减少查询转为mr
分区表的查询可以不转为mr;
二十四.hive常用函数:
1. 数学函数round(double d,int n) 四舍五入 n是小数位数 floor(double d) 返回小于d的最大整数ceil(double d) 返回大于d的最小整数rand(int s) 返回随机数,s是随机因子bin(int d) 计算二进制d的string值2. 日期函数to_date(string time) 将字符串日期转成date类型select to_date('2020-4-22 10:50:02');current_date 返回当前日期year(date) 返回date参数中的年month(date) 返回date参数中的月day(date) 返回date参数中的日weekofyear(date) 返回date是该年的第几周datediff(date1,date2) 返回date1和date2相差的天数select datediff(current_date,to_date('2020-3-12'));date_add(date1,int1) 在date1天加int1的天数date_sub(date1,int1) 在date1天减int1的天数months_between(date1,date2) 返回date1和date2之间相差月数last_day(date1) 返回date1所在月份的最后一天next_day(date1,day1) 返回date1下一周的day1的日期trunc(date1,format) 日期截断,根据format 2020-4-22 'yyyy-mm' ->返回2020-4-13. 选择函数if(boolean,t1,t2); 如果boolean表达式成立,返回t1,不成立返回t2$hive> select id,if(age>18,1,0) as flag from student;case when _boolean then _value end; _boolean成立,则返回_value$hive>select id,name,case when age>18 then '>18' else '<=18' end a from student;isnull(v) : 如果v为null,则返回true,不为null则返回falsecoalesce(v0,v1,v2) 返回参数列表中的第一个非空值,如果所有值都为null,则返回null4. 字符串函数length(str) 返回str的长度concat(str1,str2) 拼接str1和str2$hive>select concat('abc','sdf');concat_ws(sep,str1,str2) 以sep作为分隔符对str1和str2进行拼接$hive>select concat_ws(',','sdf','zxc');lower(str) 将str转成小写 upper(str) 将str转成大写repeat(str,int1) str字符串重复int1次后的字符串$hive>select repeat('adh',1);reverse(str) 字符串反转rpad(str,len,pad) 以pad字符右填充str,至len长度$hive>select rpad('hello',8,'a');split(str,sep) 以sep作为分割符分割str,返回array$hive>select split('hello,a1,a2',',');substr(str,index,int1) 在index位置起截取int1长度的字符串 $hive>select substr('hello',2,3);replace(str1,str2,str3) 在str1中,将str2替换为str3$hive>select replace('hello','he','hy');5. 表生成函数explode(array) ->列转行操作,与聚合函数是相反的$hive>select explode(array(1,2,3));$hive>select explode(split('h1,h2,h3',','));explode(map)$hive>select explode(map(1,'a',2,'b',3,'c'));6. 聚合函数count(*/col) 统计行数avg(col) 统计平均值sum(col) 统计和min(col) 统计最小值max(col) 统计最大值练习2:
使用JSP/SSH框架 访问hive数据仓库,并将数据展示到web页面中。
JDBC + HiveServer2
二十五.hive中事务的使用
1.hive中的事务是如何实现的
2.hive数据仓库与关系型数据库事务的实现有什么差异
3.hive中事务应用场景
4.hive事务与关系型数据库的使用区别。事务ACID 四大特征:
A.原子性
C.一致性
I.隔离性
D.持久性关系型数据库处理并发事务时几个问题:
事务并发问题的解决方式:最高事务隔离级别: 串行化(将并发操作 加入互拆锁,使并发操作 变为串行化操作)hive 1.x 版本后加入了对事务的支持:关系型数据库(data) -> 非关系型数据库 的操作需要事务支持的事务的实现:预写日志 :保证原子性和持久性(原子性:要么都成功要么都失败; 持久性:将操作写入硬盘中)锁(lock) :互拆锁: 占用某资源时,为该资源加锁。(隔离性)【注意】:锁在并发环境中通过读写锁保证操作的互斥性,根据隔离级别的不同,锁的应用也不同。->-> data -> -> ->->在hive的metaData库中有专门一张表来存储锁的数据(hive_locks)
$hive> show locks;在hive中事务的使用准备工作:
---------------------------------在hive默认环境下,事务支持选项是关闭的。hive.support.concurrency = true (打开事务支持)[false (关闭事务支持)] hive.enforce.bucketing = true (桶表事务支持,hive2.0后的默认配置)hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode = nonstrict (非严格模式,使用事务时打开非严格模式)[strict (严格模式)] hive.txn.manager = org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.lockmgr.DbTxnManager [org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.lockmgr.DummyTxnManager(默认配置)] hive.compactor.initiator.on = true (事务元数据对象初始化)[false(默认配置)]hive.compactor.worker.threads = 1[0(默认配置)]如果使用beeline来操作hivehive.support.concurrency = truehive中使用事务注意事项
--------------------------------------1. begin,commit,rollback在hive中暂时不支持,所有的作业自动提交2. 数据格式为ORC格式3. 表必须是桶表4. hive的事务支持默认关闭,在使用是需要手动打开5. hive的事务管理器必须设置为 org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.lockmgr.DbTxnManage,不然无法支持hive的事务工作。6. hive目前支持快照级别的事务隔离。7. 已有的zookeeper管理hive锁的内存与Hive事务内存不冲突的。-zookeeper-hbase-flume kafka storm ….-spark(scala) -> 生态圈8.load data 语句在目前hive中不支持事。
二十六.操作:
$hive>insert into t_01 values (10,‘xiaofang’);
hive事务操作
------------------------------1.hive事务支持的配置:[客户端]set hive.support.concurrency = true;set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode = nonstrict;set hive.txn.manager = org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.lockmgr.DbTxnManager;[服务端]set hive.compactor.initiator.on = true;set hive.compactor.worker.threads = 1;2.创建一张测试表:$hive>create table test_txn(id int,name string) clustered by(id) into 2 buckets row format delimited fields terminated by ',' stored as orc tblproperties("transactional"="true","compactor.mapreduce.map.momory.mb"="2048","compactorthreshold.hive.compactor.delta.num.threshold"="4","compactorthreshold.hive.compactor.delta.pct.threshold"="0.5");解释:1."transactional"="true":指定该表为事务性表2."compactor.mapreduce.map.momory.mb"="2048":指定map作业可申请的内存大小为2kb(紧缩map作业)3."compactorthreshold.hive.compactor.delta.num.threshold"="4":增量目录轻度合并4."compactorthreshold.hive.compactor.delta.pct.threshold"="0.5"):如果增量文件与基础文件大小比率超过0.5,就会触发深度合并
二十七.操作:
create table tx1(id int,name string) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘,’;
load data local inpath ‘/home/centos/data/tx.txt’ into table tx1;
insert
3.对事务进行事务性操作(update、delete)对非事务性表进行update$hive>update student set name='xiaolv' where id=4;对事务性表进行update$hive>update test_txn set name='xiaohei' where id=4;对事务性表进行delete $hive>delete from test_txn where=4;$hive>dfs -lsr /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/test_txn;drwxr-xr-x - centos supergroup 0 2020-05-06 23:54 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/test_txn/delta_0000001_0000001_0000-rw-r--r-- 1 centos supergroup 668 2020-05-06 23:54 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/test_txn/delta_0000001_0000001_0000/bucket_00000-rw-r--r-- 1 centos supergroup 672 2020-05-06 23:54 /root/hive/warehouse/db1.db/test_txn/delta_0000001_0000001_0000/bucket_00001观察桶表的hdfs的目录结构多出来一个隐藏文件夹:预写日志(临时目录)桶目录中:每一次事务性操作都会创建一个操作目录,在此目录下而存放数据文件4.作业:并发性的事务操作的特点:并发执行=C 串行执行=S 不支持=NHive操作 关闭Concurrency 开启Concurrency 开启Transaction Mysql并行select 并行insert insert、select并行 select、insert并行 delete update 同时delete一条数据 同时delete多条数据 同时update一条数据 同时update多条数据 update同时select该条记录 delete同时update相同数据 delete同时update不同数据 delete同时执行select操作
二十八.hive的优化
0. 执行计划$hive> explain HQL;查看HQL语句的执行计划,有些stage是可以并行的,hive中默认一次只能执行一个stage,stage之间存在依赖关系。
1. fetch抓取$hive> set hive.fetch.task.conversion = [more] -> 某些简单查询不经过Mr。(默认)minimal -> 在where和limit时 不经过Mr none -> 无论执行什么HQL语句,都会转换为Mr。
2. 开启本地模式hive中默认分布式模式,我们可以通过配置将hive设置为本地模式,在做测试时,执行效率要高于分布式模式。$hive> set hive.exec.mode.local.auto = [false] -> 分布式模式true -> 本地模式$hive> set hive.exec.mode.local.auto.inputbytes.max = [134217728]; 启动本地模式的最大的文件输入大小为128M注意: 在修改时,一定是2的幂计算的结果(1,2,4,8,16,32,64...)$hive> set hive.exec.mode.local.auto.input.files.max = [4]; 本地模式的最大任务数为43. 合理利用文件存储格式: 创建表时,尽量使用orc数据格式(列式存储)。4. 压缩存储:hive的数据压缩格式 等同于 hadoop的数据压缩格式。map reduce 性能瓶颈:1.磁盘IO数据量越大,磁盘IO次数就会越多。可以通过压缩数据达到减少磁盘IO次数的目的。压缩格式:zlib: 默认压缩格式 -> org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodecgzip: 不可拆分,是hadoop自带的,压缩比率高,压缩速度比较快 -> org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodeclzo: 可拆分,(是hadoop自带的)需要手动安装,压缩率比较高,压缩速度很快 -> org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.lzo.LzoCodecsnappy: 不可拆分,(是hadoop自带的)需要安装,压缩率比较高,压缩速度很快 -> org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodecbzip2: 可拆分,是hadoop自带,压缩比率最高,压缩速度慢 -> org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.BZip2Codec 2.网络IO如何选择压缩方式:1. 是否支持拆分(切割 -> split)2. 压缩比率3. 压缩(解压缩)速度使用压缩格式:设置数据文件压缩格式:hive.exec.orc.default.compress = ZLIB;1. Job输出文件按照block以gzip的方式进行压缩:$hive> set mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress = true; 打开压缩支持(默认打开)$hive> set mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.type = block; //record按照block压缩$hive> set mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec = org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec; -> 指定压缩格式默认为org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec2. map的输出结果是gzip:$hive> set mapred.map.output.compress = true; //打开压缩支持,map输出时进行压缩$hive> set mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec = org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec; //map输出的压缩格式默认为org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec3. 对hive的输出结果以及中间步骤都进行压缩(包括1,2): 连用$hive> set hive.exec.compress.output = true; //设置mapreduce的压缩$hive> set hive.exec.compress.intermediate = true; //启用mapreduce压缩
5. 表优化1. join 多表查询:1.1 小表与大表join操作:MySQL :--------------------left : 大表 join 小表right : 小表 join 大表Hive:--------------------- 将key相对分散的,并且数据量小的表放在join左边,这样做可以减少发生内存溢出的几率。可以使用group语句让小表有限进入内存(map处理)。- 在hive2.0后,hive已对小表和大表的join操作进行了优化处理,join两边放大表或小表执行效率相差不大。[测试]:测试大表join小表和小表join大表这两种操作的执行效率。1. 建表$hive> create table big_table(id int,time int,uid string,keyword string,[click_num int,click_url string]) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';$hive> create table big_table(id int,time int,uid string,keyword string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';$hive> create table small_table(id int,time int,uid string,keyword string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';$hive> create table join_table(id int,time int,uid string,keyword string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';2. 载入数据1,10,1000,赵2,20,1001,李3,30,1011,孙4,40,1012,周5,50,1013,钱$hive> load data local inpath '/home/centos/data/' into table big_table|small_table;3. 关闭map join功能(默认是打开的)$hive> set hive.auto.convert.join = false;4. 执行小表join大表$hive> insert overwrite table join_table select b.id,b.uid,b.keyword,b.click_num,b.click_url from small_table s join big_table b on b.id = s.id;5. 执行大表join小表$hive> insert overwrite table join_table select s.id,s.uid,s.keyword,s.click_num,s.click_url from big_table b join small_table s on s.id = b.id;1.2 大表与大表的join操作:空key处理:1.空key过滤有时join操作会超时,这是因为某个key对应的数据量太大,而相同key所对应的数据会发送到相同reducer上面进行处理,从而导致内存不够。一般来讲这些key所对应的数据都是异常的数据,我们需要对这些数据进行过滤。create table null_id_table(id int,time int,uid string,keyword string,[click_num int,click_url string]) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';- 不过滤空key$hive> insert overwrite table join_table select n.* from null_id_table n left join small_table s on n.id = s.id;- 过滤空key $hive> insert overwrite table join_table select n.* from (select * from null_id_table where id is not null) n left join small_table s on n.id = s.id;2.空key转换有时虽然某个key为空的数据很多,虽然key为null,但是其他字段是需要展示到join结果集中的。这时可以给key为null的字段赋予一个随机值,将数据均匀分布到不同reducer上面。(1.减少内存溢出的发生 2.一定程度的避免数据倾斜)- 设置reduce的个数:$hive> set mapreduce.job.reduces = 5;- 不转换空key$hive> insert overwrite table join_table select n.* from null_id_table n left join small_table s on n.id = s.id; - 转换空key$hive> insert overwrite table join_table select n.* from null_id_table n left join small_table s on (case when n.id is null then concat('hive',rand()) else n.id end) = s.id;1.3 map端join操作:在hive中如果不指定mapjoin,那么hive解析器将join操作转换成common join(在reduce阶段完成join,比较容易发生数据倾斜)。可以使用mapjoin将小表全部加载到内存中在map端进行join,从而避免在reduce端进行join操作(数据倾斜)。[测试]1.开启mapjoin参数设置$hive> set hive.auto.convert.join = true;2.设置大表阙值(hive默认25M以下的表为小表)$hive> set hive.mapjoin.smalltable.filesize = 25000000;3.具体操作3.1 执行小表join大表$hive> insert overwrite table join_table select b.id,b.uid,b.keyword,b.click_num,b.click_url from small_table s join big_table b on b.id = s.id;3.2 执行大表join小表$hive> insert overwrite table join_table select s.id,s.uid,s.keyword,s.click_num,s.click_url from big_table b join small_table s on s.id = b.id;2. group by在默认的情况下,Map阶段同一key的数据分发给同一个reduce,如果某个key对应的数据量过大就会产生数据倾斜。并不是所有的聚合操作都需要在reduce端完成,很多聚合操作都可以先在map端进行部分聚合,最后在reduce端得出最终结果。开启map端聚合参数设置:1.是否在map端进行聚合,默认为true$hive> set hive.map.aggr = true;2.在map端进行聚合操作的记录数目:$hive> set hive.groupby.mapaggr.checkinterval = 100000;3.数据倾斜时,进行负载均衡(默认关闭) $hive> set hive.groupby.skewindata = true;3.count(distinct) 去重操作count(distinct)是为了防止数据量大的情况下,某一个reduce负载过大,导致整个job难以完成。1.执行去重id查询$hive> select count(distinct id) from big_table;2.采用group by去重id$hive> select count(a.id) from (select id from big_table group by id) a;4.笛卡尔积当hive设置严格模式时,不允许在HQL语句出现笛卡尔积,hive对笛卡尔积支持较弱。如果需要的话,可以设置reduce个数为1,不打开严格模式。5.行列过滤:列处理:在select中,只查询需要查询的列,尽量减少分区过滤,少用select *。行处理:在区分剪裁中,当使用外关联时,如果将副表的过滤条件写在where后面,name就会先全表管联,之后再过滤。[测试]先关联两张表,再用where条件进行过滤:select s.id from big_table b join small_table s on b.id = s.id where id<10;通过子查询后,再进行表关联select b.id from big_table b join (select id from small_table where id<10)s on b.id = s.id;6.动态分区:参数设置:1.打开动态分区:$hive> set hive.exec.dynamic.partition = true;2.设置为非严格模式$hive> set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode = nonstrict;3.在所有的Mr节点上,最大可创建的动态分区数:$hive> set hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions = 1000;4.在每个执行的Mr节点上,最大可创建的动态分区数:$hive> set hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions.pernode = 100;5.在整个Mr job 中,最大可创建的文件数:$hive> set hive.exec.max.created.files = 100000;6.当有空分区生成时,是否抛出异常,一般是不需要进行设置的。$hive> set hive.error.on.empty.partition = false;[测试]1.创建分区表2.加载数据到分区表3.创建目标分区表4.进行动态分区的优化参数设定5.通过insert..select完成分区6.查看分区表的分区情况:$hive> show partitions tablename;7.in/exists语句优化在hive中对in语句和exists语句有替代方案: left semi join使用in:$hive> select a.id,a.name,from a where a.id in (select b.id from b);使用exists:$hive> select a.id,a.name,from a where exists (select id from b where a.id = b.id);替代方案$hive> select a.id,a.name,from a left semi join b on a.id = b.id;8.排序选择:1.order by :全局排序,缺陷是只能使用一个reduce。2.sort by :单机排序,单个reduce进行排序。3.distribute by :分桶,保证同一个字段的值存在一个结果文件中。一般与sort by连用,保证每个reduce task结果是有序的。4.cluster by :对同一个字段分桶并排序,不能与sort by 连用。= distribute by + sort by.9.multi-group by : 4可以使用multi-group by 减少mr数量10.合理使用分桶: bucket
6. 数据倾斜 1.调整map数- Map数决定因素(split切片数量)[问题]Map的数量在hadoop中是根据什么决定的?[答]在通常情况下,job是根据输入目录产生多个map任务1.input的文件的总个数2.input的文件大小3.集群设置的文件的块大小一个mr job的MapTask数量是由输入切片InputSpilt决定。FileInputFormat.getSplit()可获取mr job的切片数。在hadoop中常用的配置:-dfs.blocksize=128M ->HDFS默认的数据块大小-mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize=1 ->最小切片大小-mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize=256M->在hive中设置mr作业中的最大切片大小mr的切片大小的计算公式:long splitSize=Math.max(minSize,Math.min(maxSize,blockSize));- 小数据文件处理(hadoop不擅于处理大量的小数据文件)配置:1.$hive>set hive.merge.mapfiles=true; -> 在map任务结束时合并小文件。2.$hive>set hive.merge.mapredfiles=false; -> 设置为true: 在mapreduce任务结束时合并小文件。3.$hive>set hive.merge.size.pre.task=256*1000*1000 -> 256M: 合并文件的大小4.$hive>set mapred.max.spilt.size=256*1000*1000; -> 每个map的最大切片大小(hive2中内置)5.$hive>set mapred.min.spilt.size.pre.node=1; -> 一个节点中spilt的最小值(hive2中内置)6.$hive>set hive.input.format=org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.CombineHiveInputFoemat; -> 执行map前进行小文件合并- 复杂的数据文件处理- input的文件都很大,任务逻辑复杂。在做以上操作时,map的执行效率会非常慢。在这时可以考虑增加map数量,来使每个map处理的数据量减少,从而提高任务的执行效率。- 增加map的方法:根据切片数的计算公式,得出,只要修改spilt.maxsize<dfs.blocksize切片数会增加,从而map的个数就会增加。1. 修改hadoop hdfs-site.xml dfs.blocksize=1282. $hive>set mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize=642.调整reduce个数:reduce数的决定因素?hadoop的分区数。hive中有一些属性确定reduce个数:配置: 2.1在hive中设置reduce个数 $hive>set hive.exec.reducers.bytes.per.reducer=256000000 -> 每个reduce任务处理的数据量。$hive>set hive.exec.reducers.max=1009 -> 每个job的最大reduce个数。2.2在hadoop中设置reduce个数修改[mapred-site.xml]mapreduce.job.reduces=15;注意:reduce的个数不是越多越好,1.如果reduce个数过多,启动和初始化reduce时会消耗过多的时间和资源。2.如果reduce个数过多,就会产生很多的输出文件(往往都是比较小的文件),这些输出文件有时会做为下一个job的输入文件,输入文件如果为多个小文件时,就会降低下个job的执行效率。3.并发执行Hive会将一个查询转化为多个阶段:map、reduce、抽样、合并、limit...在hive执行过程中可能还需要其他阶段。在默认情况下,hive一次只会执行一个阶段。但有时阶段与阶段之间是可以并发执行的,如果可以并发执行,整个job执行时间就可以缩短。配置:$hive>set hive.exec.parallel.thread.number=8; -> 并发执行的任务数$hive>set hive.exec.parallel=true; -> 打开任务并行执行4.严格模式防止用户做危险操作。5.jvm重用JVM重用是hadoop的调优内容,对hive性能影响很大,特别是对很难避免的小文件处理的情况或者task特别多的情况。处理时间短,资源消耗大。hadoop中修改mapred-site.xmlmapreduce.job.jvm.numtasks=10注意:如果出现了比较严重的数据倾斜,整个的job执行时间变长。6.执行计划-查看简易计划$hive> explain select * from usr;-查看详细计划$hive> explain extended select * from usr;7.推测执行根据自己经验,判断某些语句应该启用那些配置。
二十九.UDF:User define function 用户自定义函数
存储过程JDBC:Statement :SQL处理对象->静态sql语句的处理PreparedStatement :SQL预处理对象->动态SQL语句处理CallableStatement :SQL程序调用对象->外部程序(Java)调用DB中的过程函数函数往往在SQL中使用的。内置函数:用户自定义函数:在关系数据库中:单独创建一个对象:create function function_name() …函数体…在hive中:需要编写java程序 -> 将程序打包 -> 上传到hive/lib ->注册 -> 使用。1.function操作:-列出所有函数:show functions;-查看函数帮助:desc[ribe] function 函数名 ;$hive>desc function sum;-查看扩展帮助:desc[ribe] function extended 函数名 ;$hive>desc function extended sum;
2.函数调用:select concat(col1,col2) as x from table;注意:在hive中函数的调用一定是在hql语句中使用,不能够单独调用$hive>concat('a','b')->错误$hive>select concat('abc','def');OKabcdef3.函数类型UDF:输入一行或多行,输出一个值(可以返回复杂对象 array map struct)round()abs()UDAF:(User define aggregate function)用户自定义聚合函数一行或多行的n个列输入,输出一个值,一般是与group by联用count()$hive>select count(*) from t1;avg()UDTF:(User define table function)表生成函数n个输入,输出多行或多列array()$hive>select array(1,2,3);OK[1,2,3]explode()$hive>select explode(array(1,2,3));OK123select explode(array(1,2,3)) as el from emp;
4.自定义函数【例】编写一个自定义函数,将字符串转换为日期格式。1.依赖:hive-servicepom.xml<dependency><groupId>org.apache.hive</groupId><artifactId>hive-jdbc</artifactId><version>2.1.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId><artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId><version>2.7.3</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.apache.hive</groupId><artifactId>hive-exec</artifactId><version>2.1.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.apache.hive</groupId><artifactId>hive-service</artifactId><version>2.1.0</version></dependency>2.注解: @Description(name="xxx",value="yyy",extended="zzz")public class UDFxz extends UDF{try{SimpleDateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat();format.applyPattern("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");return format.parse(str);}catch(Exception ex){ex.printStackTrace();}return new Date();}}ToDate.java:package com.sk;import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDF;import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.Description;import java.text.ParseException;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.Date;@Description(//name函数起的函数名name="toDate",value="this is toDate function",extended = "ToDate('2020-6-4 10:50:10')->date obj or ToDate('1323345345334')")public class ToDate extends UDF {public Date evaluate(String str_date){//日期->字符串//SimpleDateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");//String str=format.format(new Date());Date date=new Date();try{SimpleDateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat();format.applyPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");date=format.parse(str_date);}catch(ParseException e){e.printStackTrace();}return date;}public Date evaluate(long mil){Date date=new Date(mil);return date;}}3.将函数打包成jaridea:maven projects -> Lifecycle -> package -> 右键 ->run maven Build4.通过hive命令将jar添加至hive的类路径$hive>add jar /home/centos/func/xxx.jar5.注册函数$hive>create temporary function to_date as 'com.sk.xx.func.toDate'6.调用1.add jar jar包路径最常用的一种方式,每次开启hive时,自定义函数都需要重新注册2.hive-site.xml hive.aux.jars.path -> file:///jarpath/jarname.jar3.hive安装目录下创建文件夹 auxlib 将jar放入4.hive-env.sh -> export HIVE_AUX_JARS_PATH = jar path 1.创建项目,导入pom依赖
2.编写UDF程序
3.将UDF打包,并且将UDF的jar文件上传至linux
4.add jar
5.create temporary function 函数名 as '包名.类名'