斐波那契堆的介绍
斐波那契堆(Fibonacci heap)是一种可合并堆,可用于实现合并优先队列。它比二项堆具有更好的平摊分析性能,它的合并操作的时间复杂度是O(1)。
与二项堆一样,它也是由一组堆最小有序树组成,并且是一种可合并堆。
与二项堆不同的是,斐波那契堆中的树不一定是二项树;而且二项堆中的树是有序排列的,但是斐波那契堆中的树都是有根而无序的。
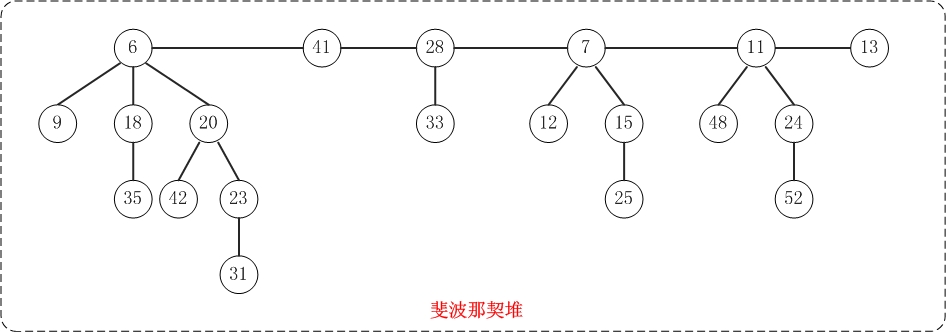
斐波那契堆的基本操作
1. 基本定义
/// <summary>/// 斐波那契堆/// </summary>public class FibHeap{private int keyNum; // 堆中节点的总数private FibNode min; // 最小节点(某个最小堆的根节点)private class FibNode{public int key; // 关键字(键值)public int degree; // 度数public FibNode left; // 左兄弟public FibNode right; // 右兄弟public FibNode child; // 第一个孩子节点public FibNode parent; // 父节点public bool marked; // 是否被删除第一个孩子public FibNode(int key){this.key = key;this.degree = 0;this.marked = false;this.left = this;this.right = this;this.parent = null;this.child = null;}}}
FibNode是斐波那契堆的节点类,它包含的信息较多。key是用于比较节点大小的,degree是记录节点的度,left和right分别是指向节点的左右兄弟,child是节点的第一个孩子,parent是节点的父节点,marked是记录该节点是否被删除第1个孩子(marked在删除节点时有用)。
FibHeap是斐波那契堆对应的类。min是保存当前堆的最小节点,keyNum用于记录堆中节点的总数,maxDegree用于记录堆中最大度,而cons在删除节点时来暂时保存堆数据的临时空间。

上面是斐波那契堆的两种不同结构图的对比。从中可以看出,斐波那契堆是由一组最小堆组成,这些最小堆的根节点组成了双向链表(后文称为"根链表");斐波那契堆中的最小节点就是"根链表中的最小节点"!
PS. 上面这幅图的结构和测试代码中的"基本信息"测试函数的结果是一致的;你可以通过测试程序来亲自验证!
2. 插入操作
插入操作非常简单:插入一个节点到堆中,直接将该节点插入到"根链表的min节点"之前即可;若被插入节点比"min节点"小,则更新"min节点"为被插入节点。
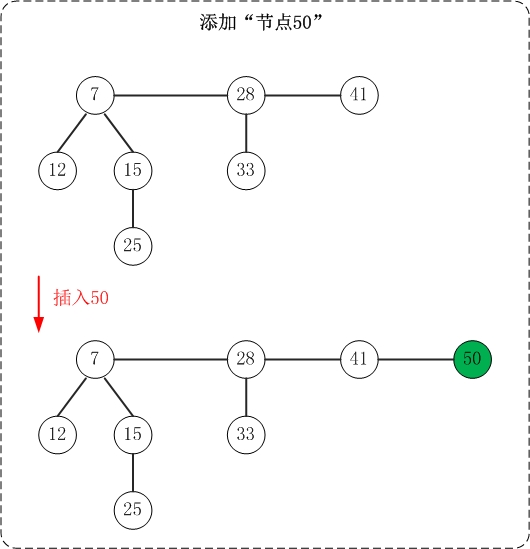
上面是插入操作的示意图。
斐波那契堆的根链表是"双向链表",这里将min节点看作双向联表的表头(后文也是如此)。在插入节点时,每次都是"将节点插入到min节点之前(即插入到双链表末尾)"。此外,对于根链表中最小堆都只有一个节点的情况,插入操作就很演化成双向链表的插入操作。
此外,插入操作示意图与测试程序中的"插入操作"相对应,感兴趣的可以亲自验证。
插入操作代码
/** 将node堆结点加入root结点之前(循环链表中)* a …… root* a …… node …… root*/private void addNode(FibNode node, FibNode root){node.left = root.left;root.left.right = node;node.right = root;root.left = node;}/** 将节点node插入到斐波那契堆中*/private void insert(FibNode node){if (keyNum == 0)min = node;else{addNode(node, min);if (node.key < min.key)min = node;}keyNum++;}/* * 新建键值为key的节点,并将其插入到斐波那契堆中*/public void insert(int key){FibNode node;node = new FibNode(key);if (node == null)return;insert(node);}
3. 合并操作
合并操作和插入操作的原理非常类似:将一个堆的根链表插入到另一个堆的根链表上即可。简单来说,就是将两个双链表拼接成一个双向链表。
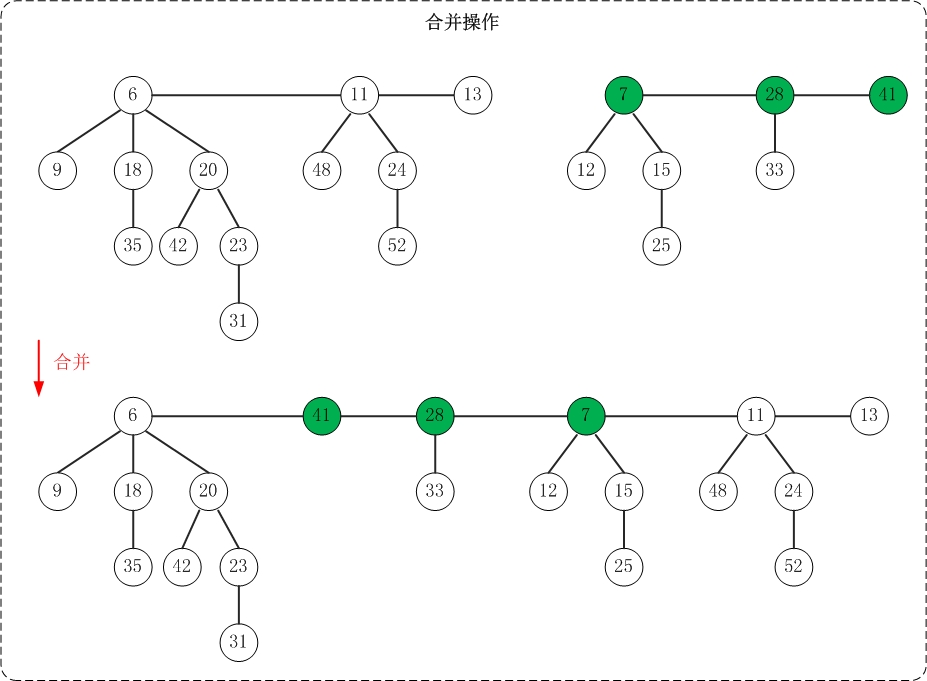
上面是合并操作的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"合并操作"相对应!
合并操作代码
/** 将双向链表b链接到双向链表a的后面*/private void catList(FibNode a, FibNode b){FibNode tmp;tmp = a.right;a.right = b.right;b.right.left = a;b.right = tmp;tmp.left = b;}/** 将other合并到当前堆中*/public void union(FibHeap other){if (other == null)return;if ((this.min) == null){ // this无"最小节点"this.min = other.min;this.keyNum = other.keyNum;other = null;}else if ((other.min) == null){ // this有"最小节点" && other无"最小节点"other = null;}else{ // this有"最小节点" && other有"最小节点"// 将"other中根链表"添加到"this"中catList(this.min, other.min);if (this.min.key > other.min.key)this.min = other.min;this.keyNum += other.keyNum;other = null; ;}}
4. 取出最小节点
抽取最小结点的操作是斐波那契堆中较复杂的操作。
(1)将要抽取最小结点的子树都直接串联在根表中;
(2)合并所有degree相等的树,直到没有相等的degree的树。

上面是取出最小节点的示意图。图中应该写的非常明白了,若有疑问,看代码。
此外,该操作示意图与测试程序中的"删除最小节点"相对应!有兴趣的可以亲自验证。
取出最小节点代码
/** 将node链接到root根结点*/private void link(FibNode node, FibNode root){// 将node从双链表中移除 removeNode(node);// 将node设为root的孩子if (root.child == null)root.child = node;elseaddNode(node, root.child);node.parent = root;root.degree++;node.marked = false;}/* * 合并斐波那契堆的根链表中左右相同度数的树*/private void consolidate(){// 计算log2(keyNum),floor意味着向上取整!// ex. log2(13) = 3,向上取整为4。int maxDegree = (int)Math.Floor(Math.Log(keyNum) / Math.Log(2.0));int D = maxDegree + 1;FibNode[] cons = new FibNode[D + 1];for (int i = 0; i < D; i++)cons[i] = null;// 合并相同度的根节点,使每个度数的树唯一while (min != null){FibNode x = extractMin(); // 取出堆中的最小树(最小节点所在的树)int d = x.degree; // 获取最小树的度数// cons[d] != null,意味着有两棵树(x和y)的"度数"相同。while (cons[d] != null){FibNode y = cons[d]; // y是"与x的度数相同的树" if (x.key > y.key){ // 保证x的键值比y小FibNode tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;}link(y, x); // 将y链接到x中cons[d] = null;d++;}cons[d] = x;}min = null;// 将cons中的结点重新加到根表中for (int i = 0; i < D; i++){if (cons[i] != null){if (min == null)min = cons[i];else{addNode(cons[i], min);if ((cons[i]).key < min.key)min = cons[i];}}}}/** 移除最小节点*/public void removeMin(){if (min == null)return;FibNode m = min;// 将min每一个儿子(儿子和儿子的兄弟)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中while (m.child != null){FibNode child = m.child;removeNode(child);if (child.right == child)m.child = null;elsem.child = child.right;addNode(child, min);child.parent = null;}// 将m从根链表中移除 removeNode(m);// 若m是堆中唯一节点,则设置堆的最小节点为null;// 否则,设置堆的最小节点为一个非空节点(m.right),然后再进行调节。if (m.right == m)min = null;else{min = m.right;consolidate();}keyNum--;m = null;}
5. 减小节点值
减少斐波那契堆中的节点的键值,这个操作的难点是:如果减少节点后破坏了"最小堆"性质,如何去维护呢?下面对一般性情况进行分析。
(1) 首先,将"被减小节点"从"它所在的最小堆"剥离出来;然后将"该节点"关联到"根链表"中。 倘若被减小的节点不是单独一个节点,而是包含子树的树根。则是将以"被减小节点"为根的子树从"最小堆"中剥离出来,然后将该树关联到根链表中。
(2) 接着,对"被减少节点"的原父节点进行"级联剪切"。所谓"级联剪切",就是在被减小节点破坏了最小堆性质,并被切下来之后;再从"它的父节点"进行递归级联剪切操作。
而级联操作的具体动作则是:若父节点(被减小节点的父节点)的marked标记为false,则将其设为true,然后退出。
否则,将父节点从最小堆中切下来(方式和"切被减小节点的方式"一样);然后递归对祖父节点进行"级联剪切"。
marked标记的作用就是用来标记"该节点的子节点是否有被删除过",它的作用是来实现级联剪切。而级联剪切的真正目的是为了防止"最小堆"由二叉树演化成链表。
(3) 最后,别忘了对根链表的最小节点进行更新。
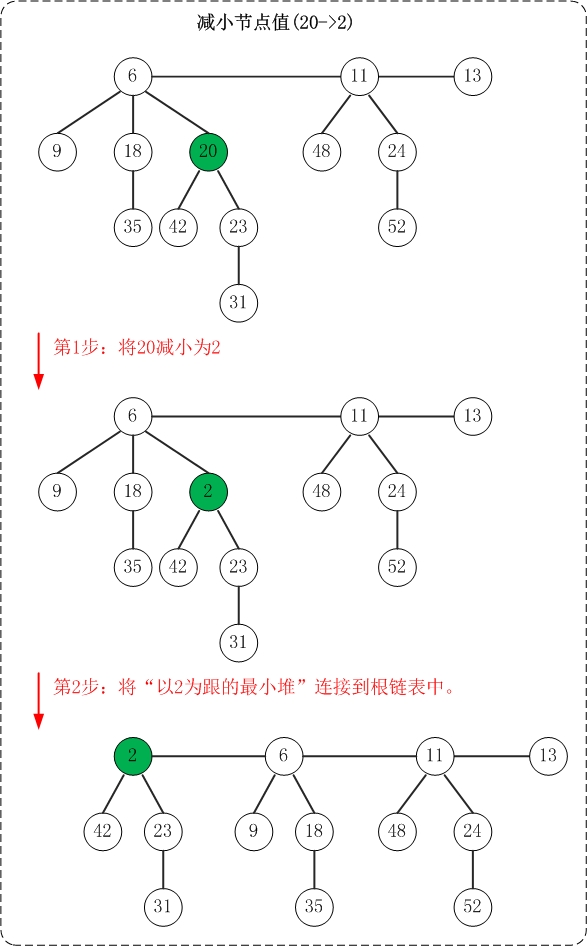
上面是减小节点值的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"减小节点"相对应!
减小节点值的代码
/* * 修改度数*/private void renewDegree(FibNode parent, int degree){parent.degree -= degree;if (parent.parent != null)renewDegree(parent.parent, degree);}/* * 将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,* 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员。*/private void cut(FibNode node, FibNode parent){removeNode(node);renewDegree(parent, node.degree);// node没有兄弟if (node == node.right)parent.child = null;elseparent.child = node.right;node.parent = null;node.left = node.right = node;node.marked = false;// 将"node所在树"添加到"根链表"中 addNode(node, min);}/* * 对节点node进行"级联剪切"** 级联剪切:如果减小后的结点破坏了最小堆性质,* 则把它切下来(即从所在双向链表中删除,并将* 其插入到由最小树根节点形成的双向链表中),* 然后再从"被切节点的父节点"到所在树根节点递归执行级联剪枝*/private void cascadingCut(FibNode node){FibNode parent = node.parent;if (parent != null){if (node.marked == false)node.marked = true;else{cut(node, parent);cascadingCut(parent);}}}/* * 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值减少为key*/private void decrease(FibNode node, int key){if (min == null || node == null)return;if (key > node.key){Console.WriteLine("decrease failed: the new key{0} is no smaller than current key{1}\n", key, node.key);return;}FibNode parent = node.parent;node.key = key;if (parent != null && (node.key < parent.key)){// 将node从父节点parent中剥离出来,并将node添加到根链表中 cut(node, parent);cascadingCut(parent);}// 更新最小节点if (node.key < min.key)min = node;}
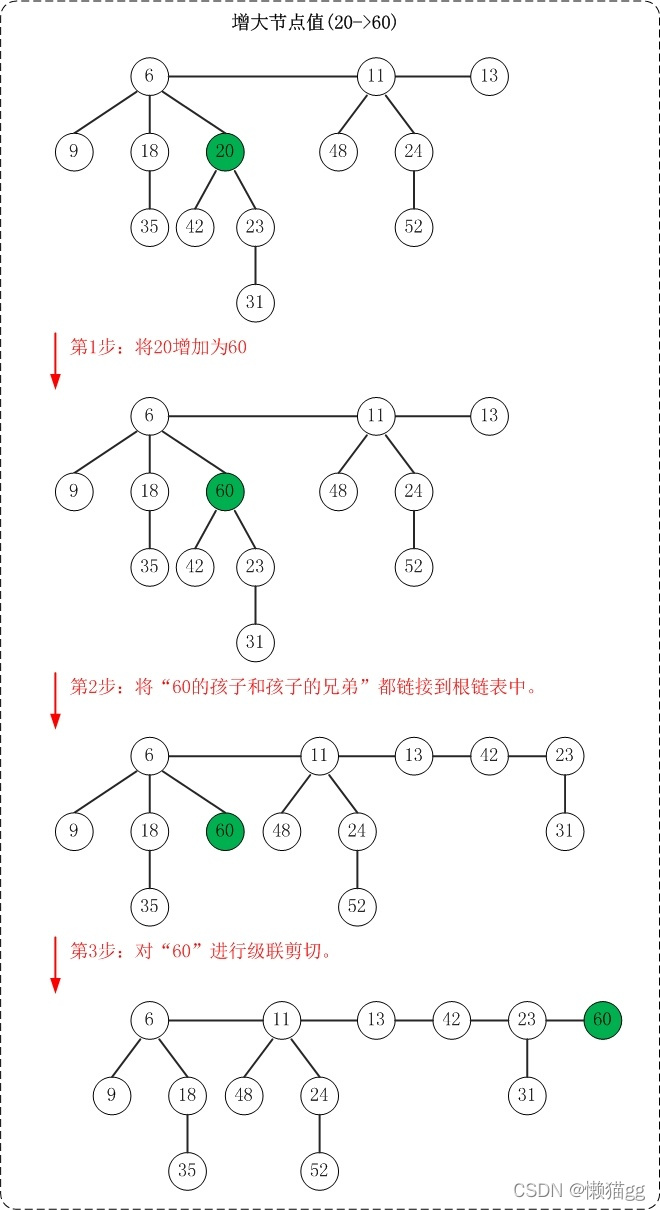
6. 增加节点值
增加节点值和减少节点值类似,这个操作的难点也是如何维护"最小堆"性质。思路如下:
(1) 将"被增加节点"的"左孩子和左孩子的所有兄弟"都链接到根链表中。
(2) 接下来,把"被增加节点"添加到根链表;但是别忘了对其进行级联剪切。

上面是增加节点值的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"增大节点"相对应!
增加节点值的代码
/* * 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值增加为key*/private void increase(FibNode node, int key){if (min == null || node == null)return;if (key <= node.key){Console.WriteLine("increase failed: the new key{0} is no greater than current key {1}\n", key, node.key);return;}// 将node每一个儿子(不包括孙子,重孙,...)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中while (node.child != null){FibNode child = node.child;removeNode(child); // 将child从node的子链表中删除if (child.right == child)node.child = null;elsenode.child = child.right;addNode(child, min); // 将child添加到根链表中child.parent = null;}node.degree = 0;node.key = key;// 如果node不在根链表中,// 则将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,// 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员,// 然后进行"级联剪切"// 否则,则判断是否需要更新堆的最小节点FibNode parent = node.parent;if (parent != null){cut(node, parent);cascadingCut(parent);}else if (min == node){FibNode right = node.right;while (right != node){if (node.key > right.key)min = right;right = right.right;}}}
7. 删除节点
删除节点,本文采用了操作是:"取出最小节点"和"减小节点值"的组合。
(1) 先将被删除节点的键值减少。减少后的值要比"原最小节点的值"即可。
(2) 接着,取出最小节点即可。
删除节点值的代码
/** 删除结点node*/private void remove(FibNode node){int m = min.key;decrease(node, m - 1);removeMin();}
注意:关于斐波那契堆的"更新"、"打印"、"销毁"等接口就不再单独介绍了。后文的源码中有给出它们的实现代码,Please RTFSC(Read The Fucking Source Code)!
斐波那契堆的实现(完整源码)
斐波那契堆的实现文件
/// <summary>/// 斐波那契堆/// </summary>public class FibHeap{private int keyNum; // 堆中节点的总数private FibNode min; // 最小节点(某个最小堆的根节点)private class FibNode{public int key; // 关键字(键值)public int degree; // 度数public FibNode left; // 左兄弟public FibNode right; // 右兄弟public FibNode child; // 第一个孩子节点public FibNode parent; // 父节点public bool marked; // 是否被删除第一个孩子public FibNode(int key){this.key = key;this.degree = 0;this.marked = false;this.left = this;this.right = this;this.parent = null;this.child = null;}}public FibHeap(){this.keyNum = 0;this.min = null;}/* * 将node从双链表移除*/private void removeNode(FibNode node){node.left.right = node.right;node.right.left = node.left;}/** 将node堆结点加入root结点之前(循环链表中)* a …… root* a …… node …… root*/private void addNode(FibNode node, FibNode root){node.left = root.left;root.left.right = node;node.right = root;root.left = node;}/** 将节点node插入到斐波那契堆中*/private void insert(FibNode node){if (keyNum == 0)min = node;else{addNode(node, min);if (node.key < min.key)min = node;}keyNum++;}/* * 新建键值为key的节点,并将其插入到斐波那契堆中*/public void insert(int key){FibNode node;node = new FibNode(key);if (node == null)return;insert(node);}/** 将双向链表b链接到双向链表a的后面*/private void catList(FibNode a, FibNode b){FibNode tmp;tmp = a.right;a.right = b.right;b.right.left = a;b.right = tmp;tmp.left = b;}/** 将other合并到当前堆中*/public void union(FibHeap other){if (other == null)return;if ((this.min) == null){ // this无"最小节点"this.min = other.min;this.keyNum = other.keyNum;other = null;}else if ((other.min) == null){ // this有"最小节点" && other无"最小节点"other = null;}else{ // this有"最小节点" && other有"最小节点"// 将"other中根链表"添加到"this"中catList(this.min, other.min);if (this.min.key > other.min.key)this.min = other.min;this.keyNum += other.keyNum;other = null; ;}}/** 将"堆的最小结点"从根链表中移除,* 这意味着"将最小节点所属的树"从堆中移除!*/private FibNode extractMin(){FibNode p = min;if (p == p.right)min = null;else{removeNode(p);min = p.right;}p.left = p.right = p;return p;}/** 将node链接到root根结点*/private void link(FibNode node, FibNode root){// 将node从双链表中移除 removeNode(node);// 将node设为root的孩子if (root.child == null)root.child = node;elseaddNode(node, root.child);node.parent = root;root.degree++;node.marked = false;}/* * 合并斐波那契堆的根链表中左右相同度数的树*/private void consolidate(){// 计算log2(keyNum),floor意味着向上取整!// ex. log2(13) = 3,向上取整为4。int maxDegree = (int)Math.Floor(Math.Log(keyNum) / Math.Log(2.0));int D = maxDegree + 1;FibNode[] cons = new FibNode[D + 1];for (int i = 0; i < D; i++)cons[i] = null;// 合并相同度的根节点,使每个度数的树唯一while (min != null){FibNode x = extractMin(); // 取出堆中的最小树(最小节点所在的树)int d = x.degree; // 获取最小树的度数// cons[d] != null,意味着有两棵树(x和y)的"度数"相同。while (cons[d] != null){FibNode y = cons[d]; // y是"与x的度数相同的树" if (x.key > y.key){ // 保证x的键值比y小FibNode tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;}link(y, x); // 将y链接到x中cons[d] = null;d++;}cons[d] = x;}min = null;// 将cons中的结点重新加到根表中for (int i = 0; i < D; i++){if (cons[i] != null){if (min == null)min = cons[i];else{addNode(cons[i], min);if ((cons[i]).key < min.key)min = cons[i];}}}}/** 移除最小节点*/public void removeMin(){if (min == null)return;FibNode m = min;// 将min每一个儿子(儿子和儿子的兄弟)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中while (m.child != null){FibNode child = m.child;removeNode(child);if (child.right == child)m.child = null;elsem.child = child.right;addNode(child, min);child.parent = null;}// 将m从根链表中移除 removeNode(m);// 若m是堆中唯一节点,则设置堆的最小节点为null;// 否则,设置堆的最小节点为一个非空节点(m.right),然后再进行调节。if (m.right == m)min = null;else{min = m.right;consolidate();}keyNum--;m = null;}/** 获取斐波那契堆中最小键值;失败返回-1*/public int minimum(){if (min == null)return -1;return min.key;}/* * 修改度数*/private void renewDegree(FibNode parent, int degree){parent.degree -= degree;if (parent.parent != null)renewDegree(parent.parent, degree);}/* * 将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,* 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员。*/private void cut(FibNode node, FibNode parent){removeNode(node);renewDegree(parent, node.degree);// node没有兄弟if (node == node.right)parent.child = null;elseparent.child = node.right;node.parent = null;node.left = node.right = node;node.marked = false;// 将"node所在树"添加到"根链表"中 addNode(node, min);}/* * 对节点node进行"级联剪切"** 级联剪切:如果减小后的结点破坏了最小堆性质,* 则把它切下来(即从所在双向链表中删除,并将* 其插入到由最小树根节点形成的双向链表中),* 然后再从"被切节点的父节点"到所在树根节点递归执行级联剪枝*/private void cascadingCut(FibNode node){FibNode parent = node.parent;if (parent != null){if (node.marked == false)node.marked = true;else{cut(node, parent);cascadingCut(parent);}}}/* * 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值减少为key*/private void decrease(FibNode node, int key){if (min == null || node == null)return;if (key > node.key){Console.WriteLine("decrease failed: the new key{0} is no smaller than current key{1}\n", key, node.key);return;}FibNode parent = node.parent;node.key = key;if (parent != null && (node.key < parent.key)){// 将node从父节点parent中剥离出来,并将node添加到根链表中 cut(node, parent);cascadingCut(parent);}// 更新最小节点if (node.key < min.key)min = node;}/* * 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值增加为key*/private void increase(FibNode node, int key){if (min == null || node == null)return;if (key <= node.key){Console.WriteLine("increase failed: the new key{0} is no greater than current key {1}\n", key, node.key);return;}// 将node每一个儿子(不包括孙子,重孙,...)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中while (node.child != null){FibNode child = node.child;removeNode(child); // 将child从node的子链表中删除if (child.right == child)node.child = null;elsenode.child = child.right;addNode(child, min); // 将child添加到根链表中child.parent = null;}node.degree = 0;node.key = key;// 如果node不在根链表中,// 则将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,// 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员,// 然后进行"级联剪切"// 否则,则判断是否需要更新堆的最小节点FibNode parent = node.parent;if (parent != null){cut(node, parent);cascadingCut(parent);}else if (min == node){FibNode right = node.right;while (right != node){if (node.key > right.key)min = right;right = right.right;}}}/* * 更新斐波那契堆的节点node的键值为key*/private void update(FibNode node, int key){if (key < node.key)decrease(node, key);else if (key > node.key)increase(node, key);elseConsole.WriteLine("No need to update!!!\n");}public void update(int oldkey, int newkey){FibNode node;node = search(oldkey);if (node != null)update(node, newkey);}/** 在最小堆root中查找键值为key的节点*/private FibNode search(FibNode root, int key){FibNode t = root; // 临时节点FibNode p = null; // 要查找的节点if (root == null)return root;do{if (t.key == key){p = t;break;}else{if ((p = search(t.child, key)) != null)break;}t = t.right;} while (t != root);return p;}/** 在斐波那契堆中查找键值为key的节点*/private FibNode search(int key){if (min == null)return null;return search(min, key);}/** 在斐波那契堆中是否存在键值为key的节点。* 存在返回true,否则返回false。*/public bool contains(int key){return search(key) != null ? true : false;}/** 删除结点node*/private void remove(FibNode node){int m = min.key;decrease(node, m - 1);removeMin();}public void remove(int key){if (min == null)return;FibNode node = search(key);if (node == null)return;remove(node);}/* * 销毁斐波那契堆*/private void destroyNode(FibNode node){if (node == null)return;FibNode start = node;do{destroyNode(node.child);// 销毁node,并将node指向下一个node = node.right;node.left = null;} while (node != start);}public void destroy(){destroyNode(min);}/** 打印"斐波那契堆"** 参数说明:* node -- 当前节点* prev -- 当前节点的前一个节点(父节点or兄弟节点)* direction -- 1,表示当前节点是一个左孩子;* 2,表示当前节点是一个兄弟节点。*/private void print(FibNode node, FibNode prev, int direction){FibNode start = node;if (node == null)return;do{if (direction == 1)Console.WriteLine("{0}({1}) is {2}'s child\n", node.key, node.degree, prev.key);elseConsole.WriteLine("{0}({1}) is {2}'s next\n", node.key, node.degree, prev.key);if (node.child != null)print(node.child, node, 1);// 兄弟节点prev = node;node = node.right;direction = 2;} while (node != start);}public void print(){if (min == null)return;int i = 0;FibNode p = min;Console.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆的详细信息: ==\n");do{i++;Console.WriteLine("{0}. {1}({2}) is root\n", i, p.key, p.degree);print(p.child, p, 1);p = p.right;} while (p != min);Console.Write("\n");}}
斐波那契堆的测试程序
public class TestFibHeap{// 共8个private int[] a = { 12, 7, 25, 15, 28, 33, 41, 1 };// 共14个private int[] b = {18, 35, 20, 42, 9,31, 23, 6, 48, 11,24, 52, 13, 2 };// 验证"基本信息(斐波那契堆的结构)"public void testBasic(){FibHeap hb = new FibHeap();// 斐波那契堆hbConsole.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");for (int i = 0; i < b.Length; i++){Console.Write("{0} ", b[i]);hb.insert(b[i]);}Console.WriteLine("\n");Console.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");hb.removeMin();hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb }// 验证"插入操作"public void testInsert(){FibHeap ha = new FibHeap();// 斐波那契堆haConsole.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(ha)中依次添加: ");for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++){Console.Write("{0} ", a[i]);ha.insert(a[i]);}Console.WriteLine("\n");Console.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(ha)删除最小节点\n");ha.removeMin();ha.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆ha Console.WriteLine("== 插入50\n");ha.insert(50);ha.print();}// 验证"合并操作"public void testUnion(){FibHeap ha = new FibHeap();FibHeap hb = new FibHeap();// 斐波那契堆haConsole.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(ha)中依次添加: ");for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++){Console.Write("{0} ", a[i]);ha.insert(a[i]);}Console.WriteLine("\n");Console.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(ha)删除最小节点\n");ha.removeMin();ha.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆ha// 斐波那契堆hbConsole.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");for (int i = 0; i < b.Length; i++){Console.Write("{0} ", b[i]);hb.insert(b[i]);}Console.WriteLine("\n");Console.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");hb.removeMin();hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb// 将"斐波那契堆hb"合并到"斐波那契堆ha"中。Console.WriteLine("== 合并ha和hb\n");ha.union(hb);ha.print();}// 验证"删除最小节点"public void testRemoveMin(){FibHeap ha = new FibHeap();FibHeap hb = new FibHeap();// 斐波那契堆haConsole.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(ha)中依次添加: ");for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++){Console.Write("{0} ", a[i]);ha.insert(a[i]);}Console.WriteLine("\n");Console.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(ha)删除最小节点\n");ha.removeMin();//ha.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆ha// 斐波那契堆hbConsole.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");for (int i = 0; i < b.Length; i++){Console.Write("{0} ", b[i]);hb.insert(b[i]);}Console.WriteLine("\n");Console.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");hb.removeMin();//hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb// 将"斐波那契堆hb"合并到"斐波那契堆ha"中。Console.WriteLine("== 合并ha和hb\n");ha.union(hb);ha.print();Console.WriteLine("== 删除最小节点\n");ha.removeMin();ha.print();}// 验证"减小节点"public void testDecrease(){FibHeap hb = new FibHeap();// 斐波那契堆hbConsole.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");for (int i = 0; i < b.Length; i++){Console.Write("{0} ", b[i]);hb.insert(b[i]);}Console.WriteLine("\n");Console.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");hb.removeMin();hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb Console.WriteLine("== 将20减小为2\n");hb.update(20, 2);hb.print();}// 验证"增大节点"public void testIncrease(){FibHeap hb = new FibHeap();// 斐波那契堆hbConsole.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");for (int i = 0; i < b.Length; i++){Console.Write("{0} ", b[i]);hb.insert(b[i]);}Console.WriteLine("\n");Console.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");hb.removeMin();hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb Console.WriteLine("== 将20增加为60\n");hb.update(20, 60);hb.print();}// 验证"删除节点"public void testDelete(){FibHeap hb = new FibHeap();// 斐波那契堆hbConsole.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");for (int i = 0; i < b.Length; i++){Console.Write("{0} ", b[i]);hb.insert(b[i]);}Console.WriteLine("\n");Console.WriteLine("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");hb.removeMin();hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb Console.WriteLine("== 删除节点20\n");hb.remove(20);hb.print();}public void test(){// 验证"基本信息(斐波那契堆的结构)" testBasic();// 验证"插入操作" testInsert();// 验证"合并操作" testUnion();// 验证"删除最小节点" testRemoveMin();// 验证"减小节点" testDecrease();// 验证"增大节点" testIncrease();// 验证"删除节点" testDelete();}}
斐波那契堆的测试程序
斐波那契堆的测试程序包括了"插入"、"合并"、"增大"、"减小"、"删除"、"基本信息"等几种功能的测试代码。默认是运行的"基本信息(验证斐波那契堆的结构)"测试代码,你可以根据自己的需要来对相应的功能进行验证!
下面是基本信息测试代码的运行结果:
== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: 18 35 20 42 9 31 23 6 48 11 24 52 13 2 == 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点 == 斐波那契堆的详细信息: ==1. 6(3) is root9(0) is 6's child18(1) is 9's next35(0) is 18's child20(2) is 18's next42(0) is 20's child23(1) is 42's next31(0) is 23's child2. 11(2) is root48(0) is 11's child24(1) is 48's next52(0) is 24's child3. 13(0) is root













![[渝粤教育] 郑州航空工业管理学院 电工电子技术基础 参考 资料](http://nos.netease.com/edu-image/b67bf012c1684a0683fd4f83987f56e0.png)