1.关于hash碰撞
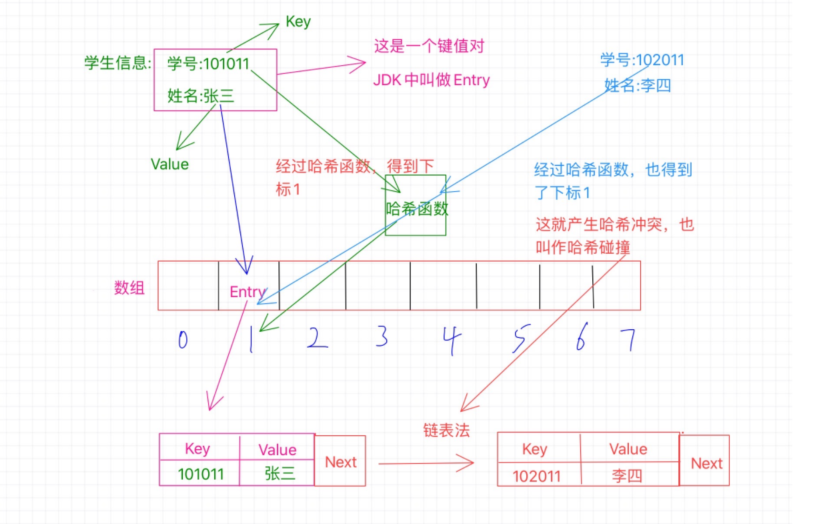
哈希碰撞是指,两个不同的输入得到了相同的输出;
hash碰撞不可避免,hash算法是把一个无限输入的集合映射到一个有限的集合里,必然会发生碰撞;
2.碰撞概率的问题描述的其他形式
-
n个球,(可重复的)随机放入k个桶里,至少有两个球在同一个桶里的概率;
-
给K个随机值,非负而且小于n,他们中至少有2个相等的概率;
3.碰撞概率的取决因素
hash碰撞的概率取决于两个因素(k, n 同上述)
-
hash的取值空间 k
-
hash的计算次数 n
4.hash碰撞概率的数学原型:生日问题
即: 一个班级需要有多少人,才能保证每个同学的生日都不一样?
结果:当一个班级有7人时,至少两人生日相同的概率在5%;
当一个班级有23人时,至少两人生日相同的概率就达到了50%;
当一个班级有50人时,至少两人生日相同的概率就达到了97%;
5.生日问题概率推导
要求一个班级n个人,至少两个人生日相同的概率 Pa
可以先求每个人生日都不同的概率 Pb
进而转换为:一个空的房间里,第一个人进去与其他人不同的概率(1-0);第二个人进入房间与其他人不同的概率(1- 1/365);第三个人进去与其他人不同的概率(1-2/365)… 以此类推,直到最后一个人进入房间与其他人不同的概率(1-n/365)
得:
P b ( n ) = ( 1 − 0 365 ) ⋅ ( 1 − 1 365 ) ⋅ ( 1 − 2 365 ) ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ( 1 − n − 1 365 ) (1) Pb(n) = (1-\frac{0}{365})\cdot(1-\frac{1}{365})\cdot(1-\frac{2}{365})\cdot\cdot\cdot(1-\frac{n-1}{365})\tag{1} Pb(n)=(1−3650)⋅(1−3651)⋅(1−3652)⋅⋅⋅(1−365n−1)(1)
进而:
P b ( n ) = ( 365 − 0 365 ) ⋅ ( 365 − 1 365 ) ⋅ ( 365 − 2 365 ) ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ( 365 − ( n − 1 ) 365 ) (2) Pb(n) = (\frac{365-0}{365})\cdot(\frac{365-1}{365})\cdot(\frac{365-2}{365})\cdot\cdot\cdot(\frac{365-(n-1)}{365})\tag{2} Pb(n)=(365365−0)⋅(365365−1)⋅(365365−2)⋅⋅⋅(365365−(n−1))(2)
化简:
P b ( n ) = 365 ! 36 5 n ( 365 − n ) ! (3) Pb(n) = \frac{365!}{365^n(365-n)!}\tag{3} Pb(n)=365n(365−n)!365!(3)
故至少两人生日概率相同Pa为:
P a ( n ) = 1 − P b ( n ) = 1 − 365 ! 36 5 n ( 365 − n ) ! (4) Pa(n) = 1-Pb(n) = 1-\frac{365!}{365^n(365-n)!}\tag{4} Pa(n)=1−Pb(n)=1−365n(365−n)!365!(4)
(4)式即为所求的公式,但是这个公式不便于计算,x趋于0时,根据泰勒公式:
lim x → 0 e x = 1 + x + 1 2 x 2 + 1 6 x 3 + 1 24 x 4 ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ (5) \lim_{x \to 0}e^x = 1+x+\frac{1}{2}x^2+\frac{1}{6}x^3+\frac{1}{24}x^4\cdot\cdot\cdot\tag{5} x→0limex=1+x+21x2+61x3+241x4⋅⋅⋅(5)
近似的有:
e x ≈ 1 + x (6) e^x \approx 1+x\tag{6} ex≈1+x(6)
观察(1)式,用(6)式代入得:
P b ( n ) ≈ ( e − 0 365 ) ⋅ ( e − 1 365 ) ⋅ ( e − 2 365 ) ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ( e − n − 1 365 ) (7) Pb(n) \approx (e^{-\frac{0}{365}})\cdot(e^{-\frac{1}{365}})\cdot(e^{-\frac{2}{365}})\cdot\cdot\cdot(e^{-\frac{n-1}{365}})\tag{7} Pb(n)≈(e−3650)⋅(e−3651)⋅(e−3652)⋅⋅⋅(e−365n−1)(7)
化简:
P b ( n ) ≈ e − n ( n − 1 ) 2 ⋅ 365 (8) Pb(n) \approx e^{-\frac{n(n-1)}{2\cdot365}}\tag{8} Pb(n)≈e−2⋅365n(n−1)(8)
故:
P a ( n ) ≈ 1 − e − n ( n − 1 ) 2 ⋅ 365 (9) Pa(n) \approx 1 - e^{-\frac{n(n-1)}{2\cdot365}}\tag{9} Pa(n)≈1−e−2⋅365n(n−1)(9)
6.hash碰撞概率推导
要求给K个随机值,非负而且小于n,他们中至少有2个相等的概率 Pa
由上述推导不难看出:
P a ( k , n ) = 1 − k ! k n ( k − n ) ! (10) Pa(k,n) = 1-\frac{k!}{k^n(k-n)!}\tag{10} Pa(k,n)=1−kn(k−n)!k!(10)
且由泰勒展开式,近似得:
P a ( k , n ) ≈ 1 − e − n ( n − 1 ) 2 ⋅ k (11) Pa(k,n) \approx 1 - e^{-\frac{n(n-1)}{2\cdot k}}\tag{11} Pa(k,n)≈1−e−2⋅kn(n−1)(11)
7.python作图
在生日概率问题中,k取365,做概率 Pa 关于班级人数n的函数图像:
准确表达式图像(4)式 (acc)
近似表达式图像(9)式 (fit)


代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import mathdef f_accurate(k, n):if n <= 0 or k <= 0:return -1if n > k:return 1var1 = 1for i in range(k - (n - 1), k + 1):var1 *= (i / k)return 1 - var1def f_fit(k, n):if n <= 0 or k <= 0:return -1if n > k:return 1var1 = (-1) * n * (n - 1) / (2 * k)var2 = math.pow(math.e, var1)return 1 - var2def f_plot_var_n(k, n):acc = []fit = []for i in range(1, n):acc.append(f_accurate(k, i))fit.append(f_fit(k, i))arr = np.array(range(1, n))acc = np.array(acc)fit = np.array(fit)plt.title("crash rate k = {}".format(k))plt.xlabel("n number")plt.ylabel("p(n) rate")plt.plot(arr, acc, color='blue', label='acc')plt.plot(arr, fit, color='red', label='fit')plt.legend()plt.show()def f_plot_var_k(k, n):acc = []fit = []for i in range(1, k):acc.append(f_accurate(i, n))fit.append(f_fit(i, n))arr = np.array(range(1, k))acc = np.array(acc)fit = np.array(fit)plt.title("crash rate n = {}".format(n))plt.xlabel("k number")plt.ylabel("p(k) rate")plt.plot(arr, acc, color='blue', label='acc')plt.plot(arr, fit, color='red', label='fit')plt.legend()plt.show()if __name__ == '__main__':k_value = 365n_value = 365# k_value = 10000# n_value = 100f_plot_var_n(k_value, n_value)# f_plot_var_k(k_value, n_value)可以看出近似表达式与准确表达式相差不大;
碰撞概率在n=23时,已经达到了50%,而取值空间为[0,365]
这对hash取值空间长度的取舍有参考意义;