Java BIO 基本介绍
- I/O 模型简单的理解:就是用什么样的通道进行数据的发送和接收,很大程度上决定了程序通信的性能。
- Java 共支持 3 种网络编程模型 I/O 模式:BIO、NIO、AIO。
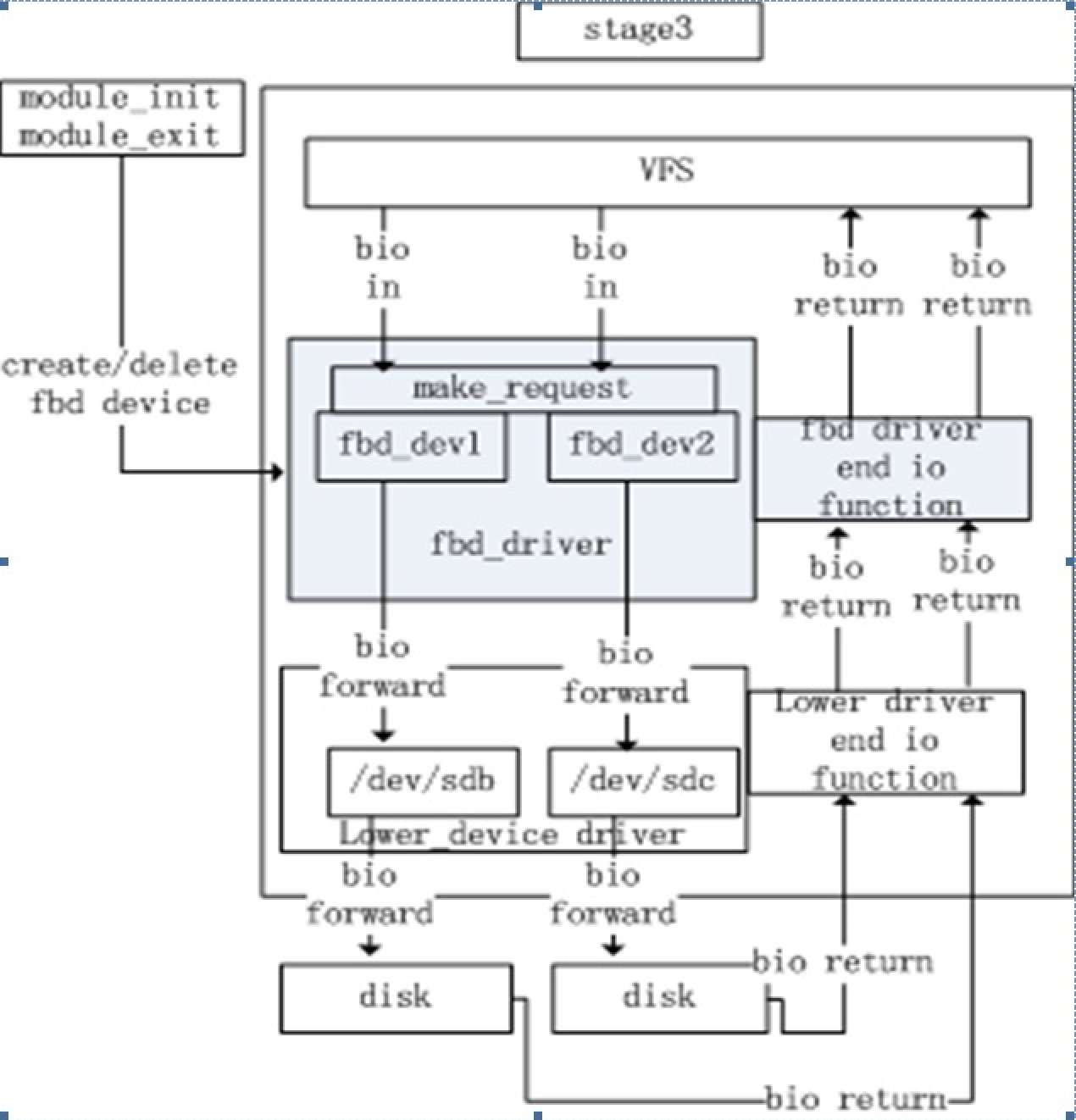
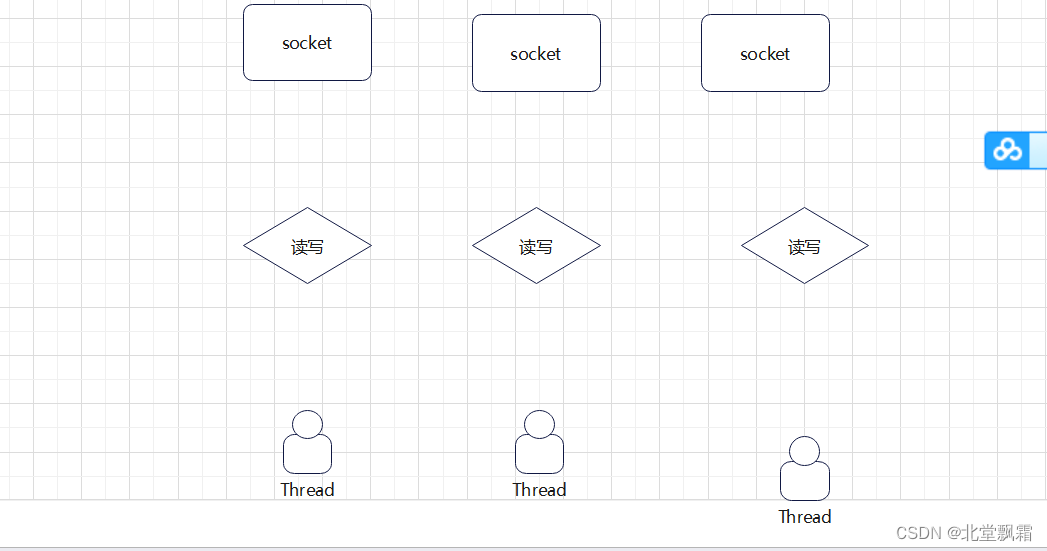
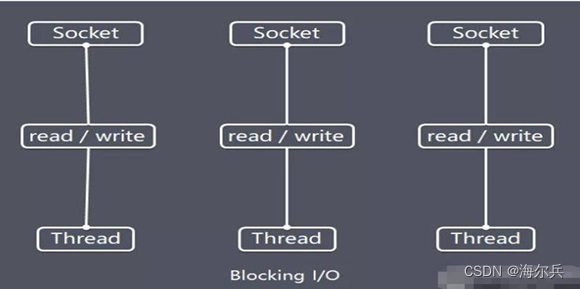
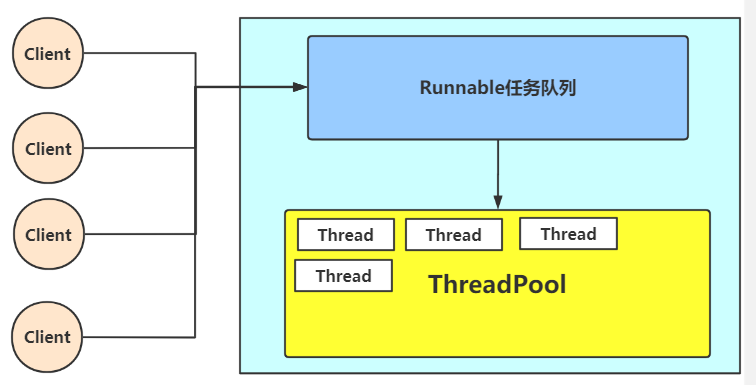
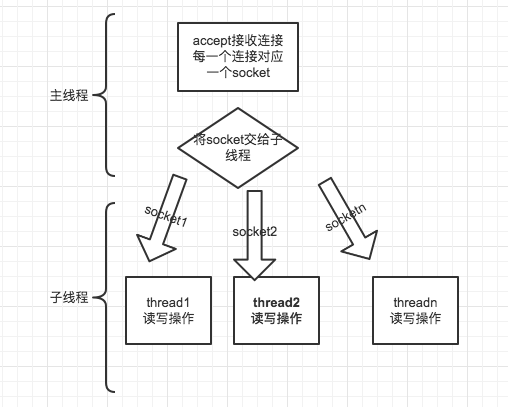
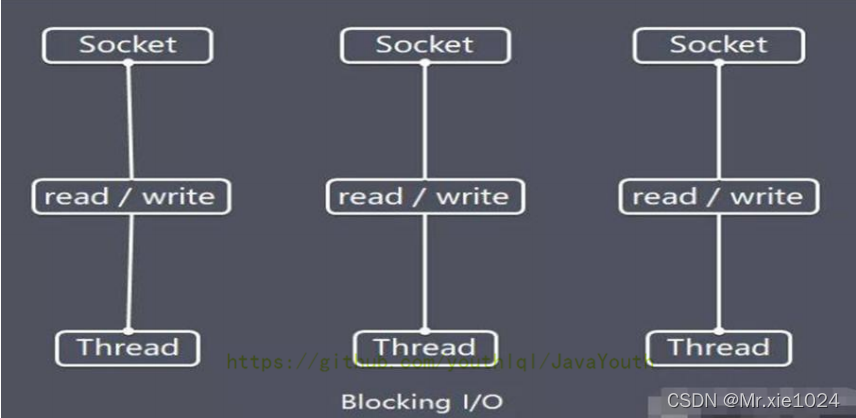
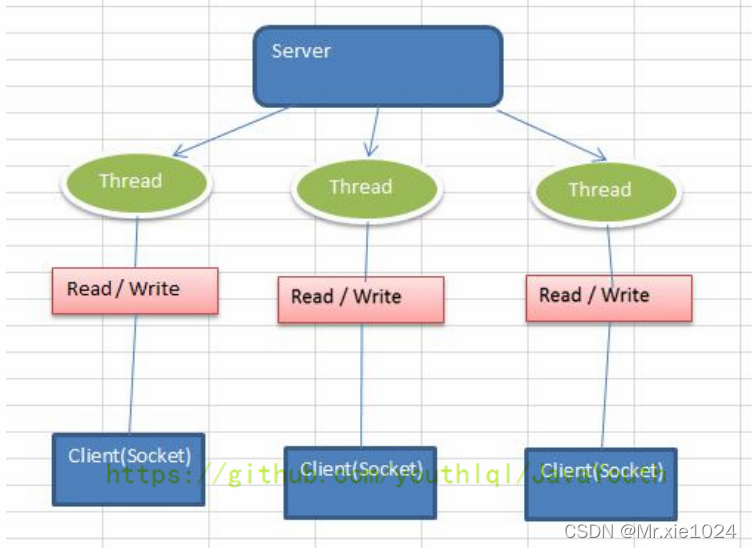
- Java BIO:同步并阻塞(传统阻塞型),服务器实现模式为一个连接一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程进行处理,如果这个连接不做任何事情会造成不必要的线程开销。【简单示意图】
Java BIO 模型
Java BIO 应用实例
实例说明:
- 使用 BIO 模型编写一个服务器端,监听 6666 端口,当有客户端连接时,就启动一个线程与之通讯。
- 要求使用线程池机制改善,可以连接多个客户端。
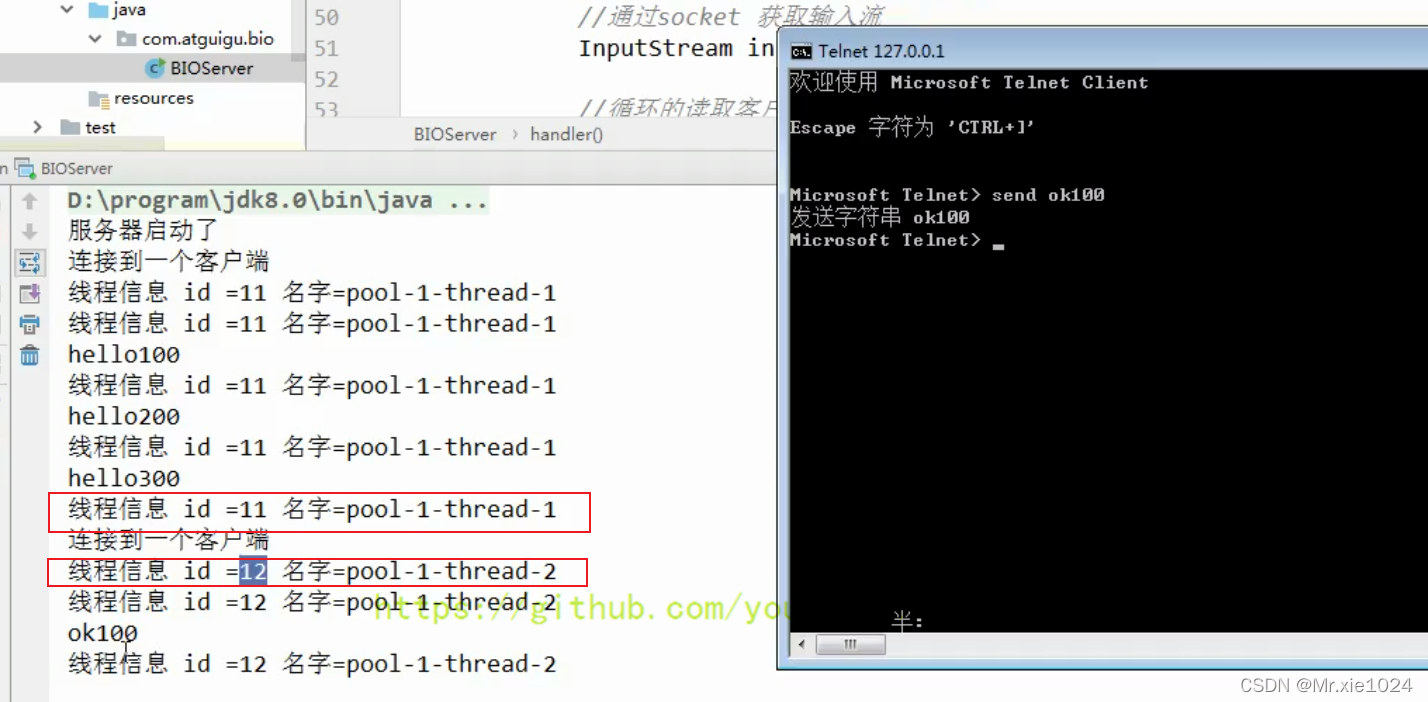
- 服务器端可以接收客户端发送的数据(telnet 方式即可)。
- 代码演示:
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class BIOServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//线程池机制//思路//1. 创建一个线程池//2. 如果有客户端连接,就创建一个线程,与之通讯(单独写一个方法)ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//创建ServerSocketServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(6666);System.out.println("服务器启动了");while (true) {System.out.println("线程信息id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + "名字 = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());//监听,等待客户端连接System.out.println("等待连接....");//会阻塞在accept()final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();System.out.println("连接到一个客户端");//就创建一个线程,与之通讯(单独写一个方法)newCachedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {public void run() {//我们重写//可以和客户端通讯handler(socket);}});}}//编写一个handler方法,和客户端通讯public static void handler(Socket socket) {try {System.out.println("线程信息id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + "名字 = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//通过socket获取输入流InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();//循环的读取客户端发送的数据while (true) {System.out.println("线程信息id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + "名字 = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("read....");int read = inputStream.read(bytes);if (read != -1) {System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, read));//输出客户端发送的数据} else {break;}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {System.out.println("关闭和client的连接");try {socket.close();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
问题:
- 每个请求都需要创建独立的线程,与对应的客户端进行数据 Read,业务处理,数据 Write。
- 当并发数较大时,需要创建大量线程来处理连接,系统资源占用较大。
- 连接建立后,如果当前线程暂时没有数据可读,则线程就阻塞在 Read 操作上,造成线程资源浪费。
Java NIO 基本介绍
-
Java NIO 全称 Java non-blocking IO,是指 JDK 提供的新 API。从 JDK1.4 开始,Java 提供了一系列改进的输入/输出的新特性,被统称为 NIO(即 NewIO),是同步非阻塞的。
-
NIO 相关类都被放在 java.nio 包及子包下,并且对原 java.io 包中的很多类进行改写。【基本案例】
-
NIO 有三大核心部分:Channel(通道)、Buffer(缓冲区)、Selector(选择器) 。
-
NIO 是面向缓冲区,或者面向块编程的。数据读取到一个它稍后处理的缓冲区,需要时可在缓冲区中前后移动,这就增加了处理过程中的灵活性,使用它可以提供非阻塞式的高伸缩性网络。
-
Java NIO 的非阻塞模式,使一个线程从某通道发送请求或者读取数据,但是它仅能得到目前可用的数据,如果目前没有数据可用时,就什么都不会获取,而不是保持线程阻塞,所以直至数据变的可以读取之前,该线程可以继续做其他的事情。非阻塞写也是如此,一个线程请求写入一些数据到某通道,但不需要等待它完全写入,这个线程同时可以去做别的事情。【后面有案例说明】
-
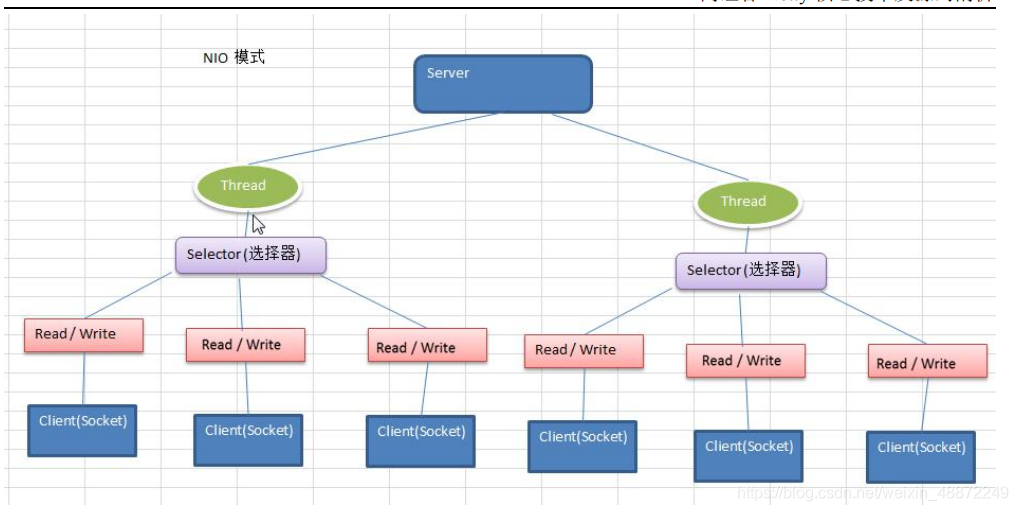
通俗理解:NIO 是可以做到用一个线程来处理多个操作的。假设有 10000 个请求过来,根据实际情况,可以分配 50 或者 100 个线程来处理。不像之前的阻塞 IO 那样,非得分配 10000 个。
-
HTTP 2.0 使用了多路复用的技术,做到同一个连接并发处理多个请求,而且并发请求的数量比 HTTP 1.1 大了好几个数量级。
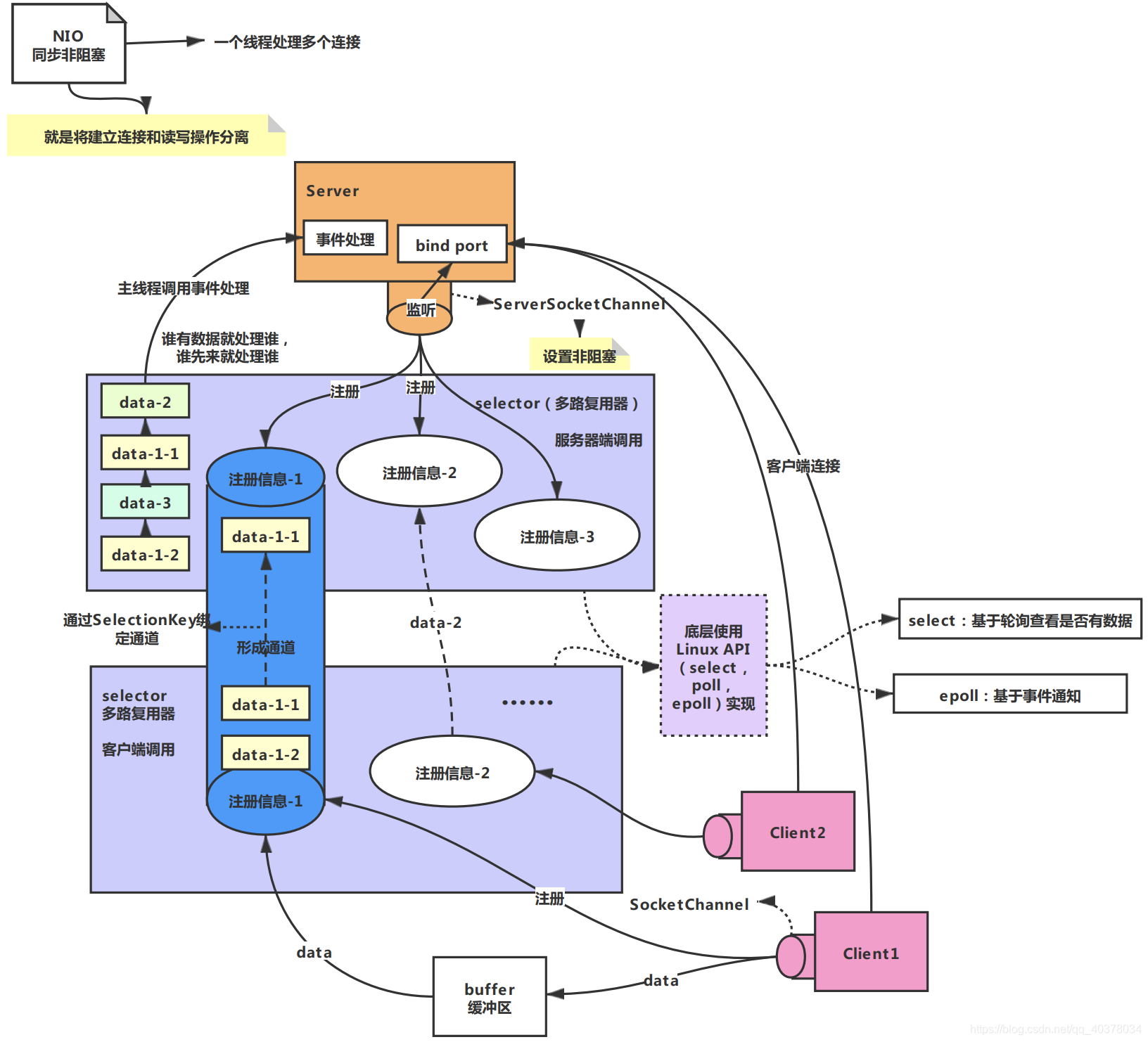
Java NIO 模型

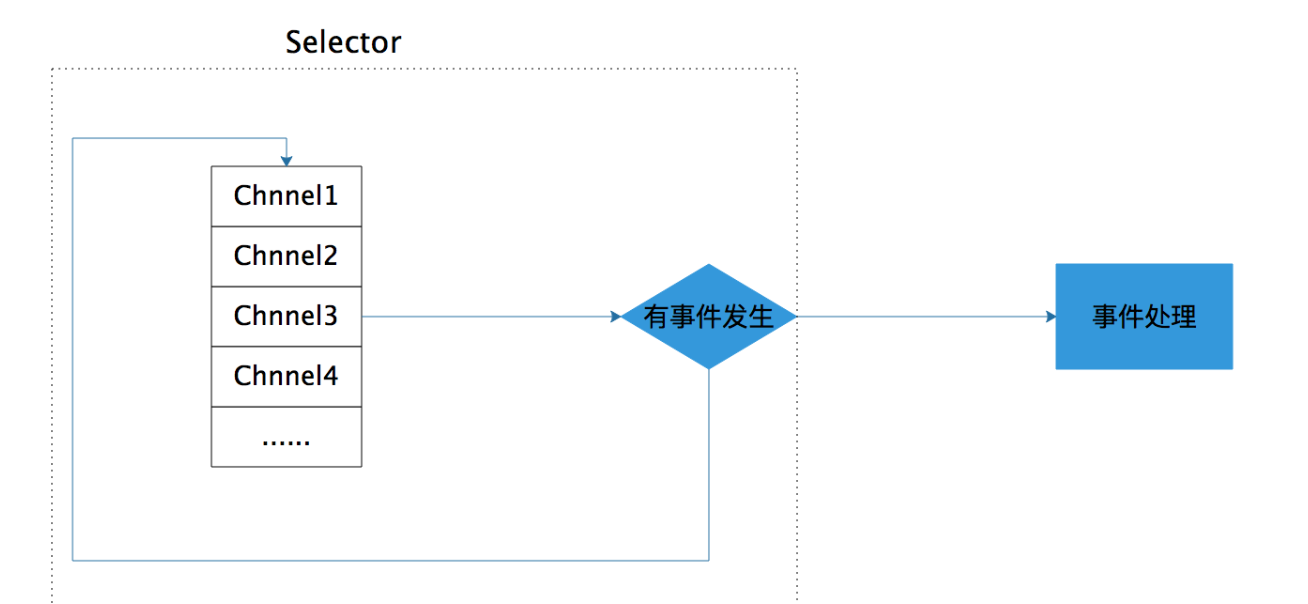
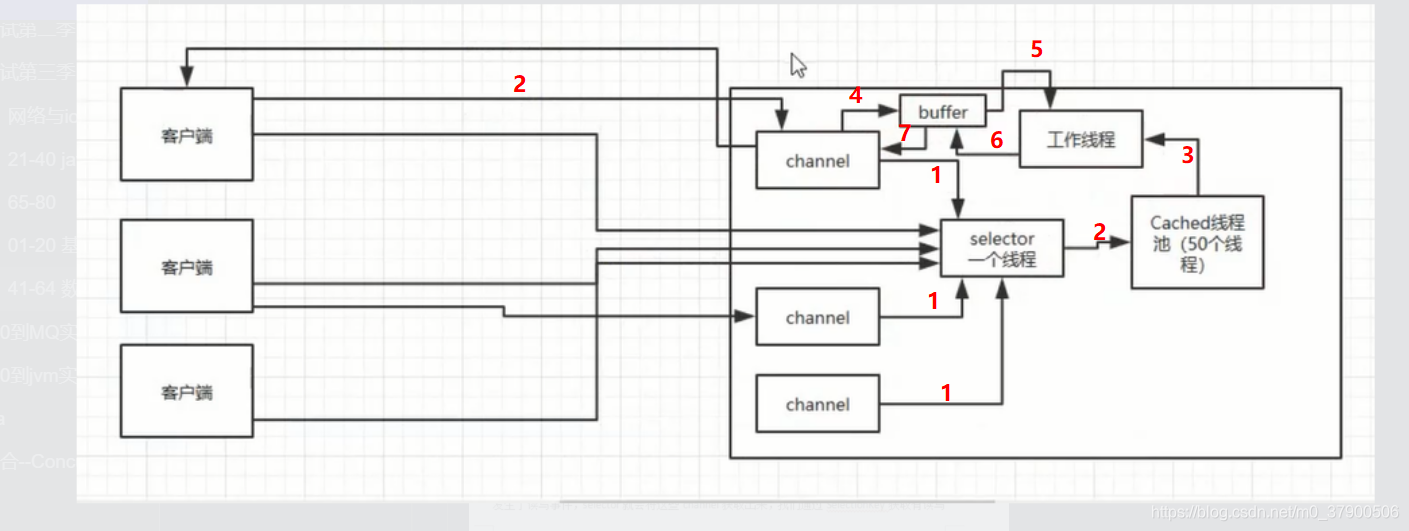
NIO 三大核心原理示意图
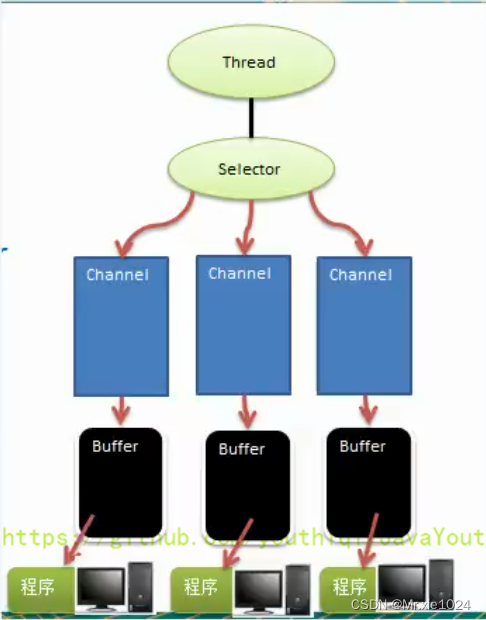
- 每个 Channel 都会对应一个 Buffer。
- Selector 对应一个线程,一个线程对应多个 Channel(连接)。
- 该图反应了有三个 Channel 注册到该 Selector //程序
- 程序切换到哪个 Channel 是由事件决定的,Event 就是一个重要的概念。
- Selector 会根据不同的事件,在各个通道上切换。
- Buffer 就是一个内存块,底层是有一个数组。
- 数据的读取写入是通过 Buffer,这个和 BIO是不同的,BIO 中要么是输入流,或者是输出流,不能双向,但是 NIO 的 Buffer 是可以读也可以写,需要 flip 方法切换 Channel 是双向的,可以返回底层操作系统的情况,比如 Linux,底层的操作系统通道就是双向的。
NIO网络编程应用实例 - 群聊系统
实例要求:
- 编写一个 NIO 群聊系统,实现服务器端和客户端之间的数据简单通讯(非阻塞)
- 实现多人群聊
- 服务器端:可以监测用户上线,离线,并实现消息转发功能
- 客户端:通过 Channel 可以无阻塞发送消息给其它所有用户,同时可以接受其它用户发送的消息(有服务器转发得到)
- 目的:进一步理解 NIO 非阻塞网络编程机制
- 示意图分析和代码

//服务端
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.Channel;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;public class GroupChatServer {//定义属性private Selector selector;private ServerSocketChannel listenChannel;private static final int PORT = 6667;//构造器//初始化工作public GroupChatServer() {try {//得到选择器selector = Selector.open();//ServerSocketChannellistenChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();//绑定端口listenChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));//设置非阻塞模式listenChannel.configureBlocking(false);//将该 listenChannel 注册到 selectorlistenChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public void listen() {try {//循环处理while (true) {int count = selector.select();if (count > 0) { //有事件处理// 遍历得到 selectionKey 集合Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {//取出 selectionkeySelectionKey key = iterator.next();//监听到 acceptif (key.isAcceptable()) {SocketChannel sc = listenChannel.accept();sc.configureBlocking(false);//将该 sc 注册到 seletorsc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);//提示System.out.println(sc.getRemoteAddress() + " 上线 ");}if (key.isReadable()) {//通道发送read事件,即通道是可读的状态// 处理读(专门写方法..)readData(key);}//当前的 key 删除,防止重复处理iterator.remove();}} else {System.out.println("等待....");}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//发生异常处理....}}//读取客户端消息public void readData(SelectionKey key) {SocketChannel channel = null;try {//得到 channelchannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();//创建 bufferByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);int count = channel.read(buffer);//根据 count 的值做处理if (count > 0) {//把缓存区的数据转成字符串String msg = new String(buffer.array());//输出该消息System.out.println("form客户端:" + msg);//向其它的客户端转发消息(去掉自己),专门写一个方法来处理sendInfoToOtherClients(msg, channel);}} catch (IOException e) {try {System.out.println(channel.getRemoteAddress() + "离线了..");//取消注册key.cancel();//关闭通道channel.close();} catch (IOException e2) {e2.printStackTrace();}}}//转发消息给其它客户(通道)private void sendInfoToOtherClients(String msg, SocketChannel self) throws IOException {System.out.println("服务器转发消息中...");//遍历所有注册到 selector 上的 SocketChannel,并排除 selffor (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()) {//通过 key 取出对应的 SocketChannelChannel targetChannel = key.channel();//排除自己if (targetChannel instanceof SocketChannel && targetChannel != self) {//转型SocketChannel dest = (SocketChannel) targetChannel;//将 msg 存储到 bufferByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes());//将 buffer 的数据写入通道dest.write(buffer);}}}public static void main(String[] args) {//创建服务器对象GroupChatServer groupChatServer = new GroupChatServer();groupChatServer.listen();}
}// 客户端:import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;public class GroupChatClient {//定义相关的属性private final String HOST = "127.0.0.1";//服务器的ipprivate final int PORT = 6667;//服务器端口private Selector selector;private SocketChannel socketChannel;private String username;//构造器,完成初始化工作public GroupChatClient() throws IOException {selector = Selector.open();//连接服务器socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(HOST, PORT));//设置非阻塞socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);//将 channel 注册到selectorsocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);//得到 usernameusername = socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString().substring(1);System.out.println(username + " is ok...");}//向服务器发送消息public void sendInfo(String info) {info = username + " 说:" + info;try {socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(info.getBytes()));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//读取从服务器端回复的消息public void readInfo() {try {int readChannels = selector.select();if (readChannels > 0) {//有可以用的通道Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {SelectionKey key = iterator.next();if (key.isReadable()) {//得到相关的通道SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();//得到一个 BufferByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);//读取sc.read(buffer);//把读到的缓冲区的数据转成字符串String msg = new String(buffer.array());System.out.println(msg.trim());}}iterator.remove(); //删除当前的 selectionKey,防止重复操作} else {//System.out.println("没有可以用的通道...");}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//启动我们客户端GroupChatClient chatClient = new GroupChatClient();//启动一个线程,每个 3 秒,读取从服务器发送数据new Thread() {public void run() {while (true) {chatClient.readInfo();try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();//发送数据给服务器端Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {String s = scanner.nextLine();chatClient.sendInfo(s);}}
}
NIO 零拷贝案例
案例要求:
- 使用传统的 IO 方法传递一个大文件
- 使用 NIO 零拷贝方式传递(transferTo)一个大文件
- 看看两种传递方式耗时时间分别是多少
NewIOServer.javaimport java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;//服务器
public class NewIOServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(7001);ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();ServerSocket serverSocket = serverSocketChannel.socket();serverSocket.bind(address);//创建bufferByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4096);while (true) {SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();int readcount = 0;while (-1 != readcount) {try {readcount = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);} catch (Exception ex) {// ex.printStackTrace();break;}//byteBuffer.rewind(); //倒带 position = 0 mark 作废}}}
}NewIOClient.javaimport java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;//客户端
public class NewIOClient {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 7001));String filename = "protoc-3.6.1-win32.zip";//得到一个文件channelFileChannel fileChannel = new FileInputStream(filename).getChannel();//准备发送long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//在 linux 下一个 transferTo 方法就可以完成传输//在 windows 下一次调用 transferTo 只能发送 8m, 就需要分段传输文件,而且要主要//传输时的位置=》课后思考...//transferTo 底层使用到零拷贝long transferCount = fileChannel.transferTo(0, fileChannel.size(), socketChannel);System.out.println("发送的总的字节数 = " + transferCount + " 耗时: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));//关闭fileChannel.close();}
}BIO、NIO、AIO 对比表
| - | BIO | NIO | AIO |
|---|---|---|---|
| IO模型 | 同步阻塞 | 同步非阻塞(多路复用) | 异步非阻塞 |
| 编程难度 | 简单 | 复杂 | 复杂 |
| 可靠性 | 差 | 好 | 好 |
| 吞吐量 | 低 | 高 | 高 |
举例说明
- 同步阻塞:到理发店理发,就一直等理发师,直到轮到自己理发。
- 同步非阻塞:到理发店理发,发现前面有其它人理发,给理发师说下,先干其他事情,一会过来看是否轮到自己.
- 异步非阻塞:给理发师打电话,让理发师上门服务,自己干其它事情,理发师自己来家给你理发