文章目录
- 1.spi总线驱动
- 1.1spi简介
- 1.2spi时序解析
- 1.3spi驱动框架
- 1.4spi设备驱动的API
- 1.5spi驱动的实例
- 1.6m74hc595设备树的填充
- 1.6.1m74hc595操作数码管的原理图
- 1.6.2控制器的设备树
- 1.6.3编写自己的设备树
- 1.7spi相关的结构体及函数
- 1.8spi驱动的实例2
- 1.9让数码管流水显示0-f
1.spi总线驱动
1.1spi简介
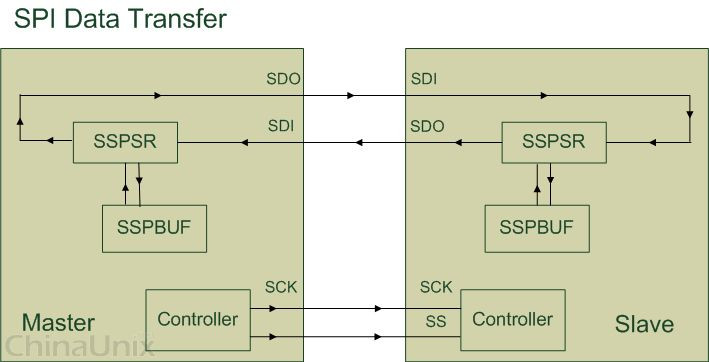
SPI 是串行外设接口(Serial Peripheral Interface)的缩写。是 Motorola 公司推出的一种同步串行接口技术,是一种高速的,全双工,同步的通信总线。SPI优点支持全双工通信通信简单数据传输速率快1):高速、同步、全双工、非差分、总线式2):主从机通信模式缺点没有指定的流控制,没有应答机制确认是否接收到数据,所以跟IIC总线协议比较在数据的可靠性上有一定的缺陷。
1.2spi时序解析
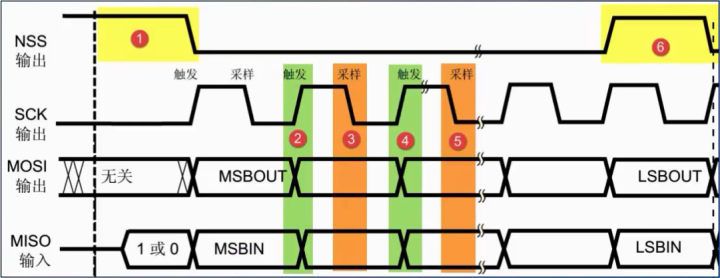
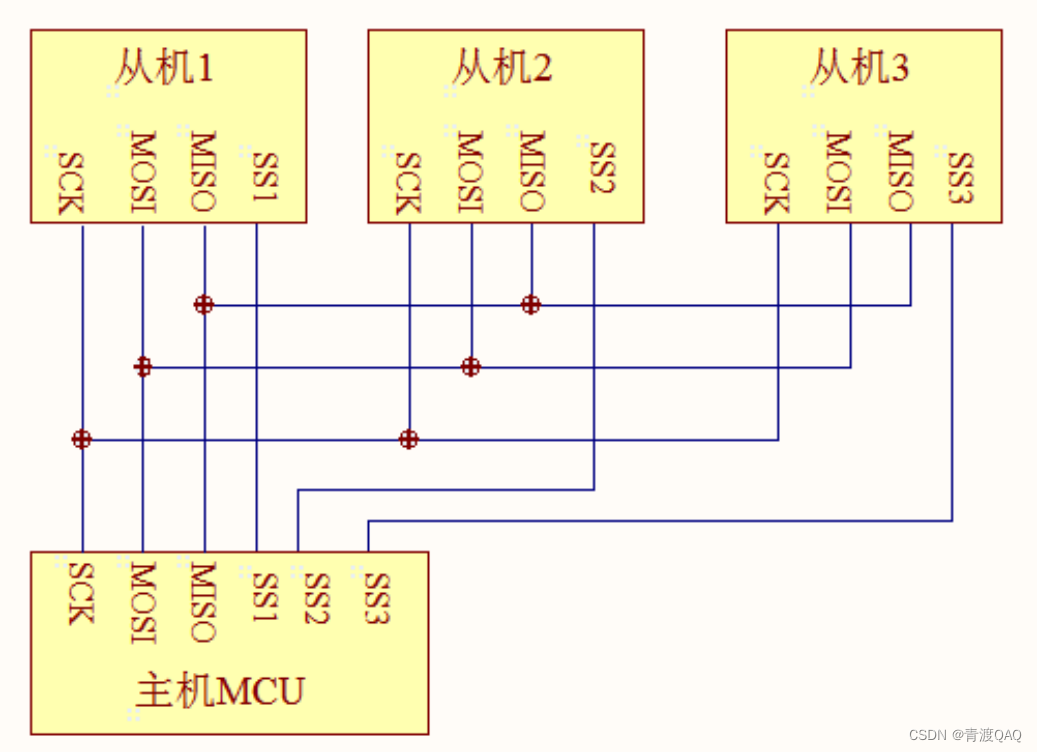
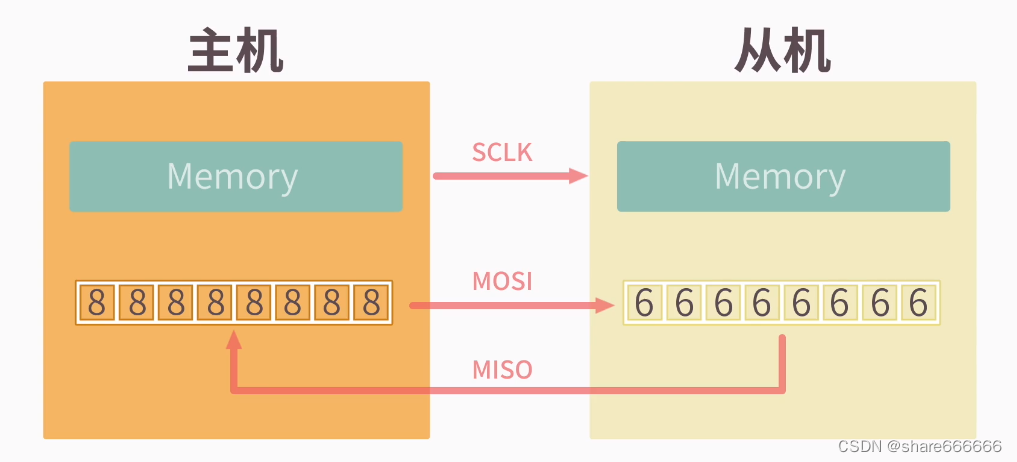
可以一主机多从机,具体和那个从机通讯通过cs片选决定。MISO :主机输入,从机输出MOSI :主机输出,从机输入CLK :时钟线(只能主机控制)CS :片选线数据传输的四种方式:
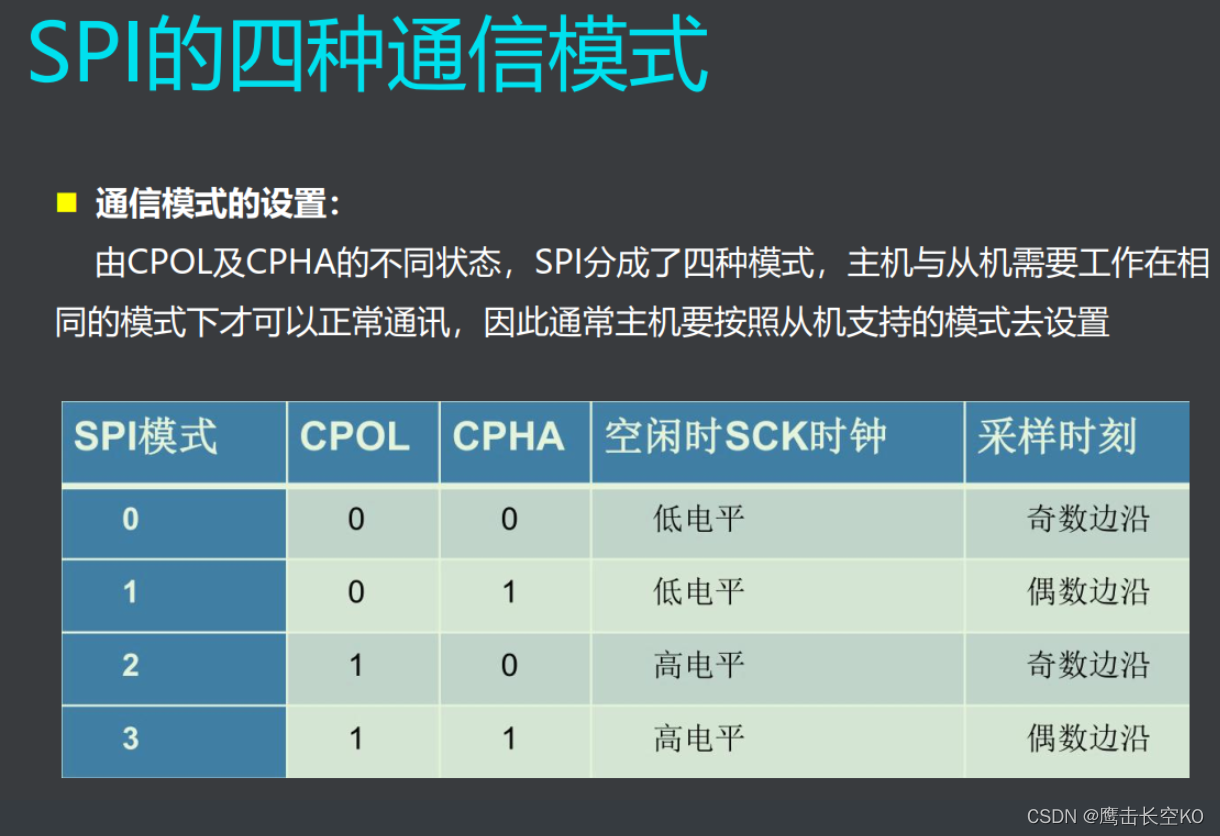
CPOL(时钟极性) : 0:时钟起始位低电平 1:时钟起始为高电平
CPHA(时钟相位) :0:第一个时钟周期采样 1:第二个时钟周期采样

例如:
CPOL=0,CPHA=0:此时空闲态时,SCLK处于低电平,数据采样是在第1个边沿,
也就是 SCLK由低电平到高电平的跳变,所以数据采样是在上升沿,数据发送
是在下降沿。
CPOL=0,CPHA=1:此时空闲态时,SCLK处于低电平,数据发送是在第1个边沿,
也就是 SCLK由低电平到高电平的跳变,所以数据采样是在下降沿,数据发送
是在上升沿。
CPOL=1,CPHA=0:此时空闲态时,SCLK处于高电平,数据采集是在第1个边沿,
也就是 SCLK由高电平到低电平的跳变,所以数据采集是在下降沿,数据发送
是在上升沿。
CPOL=1,CPHA=1:此时空闲态时,SCLK处于高电平,数据发送是在第1个边沿,
也就是 SCLK由高电平到低电平的跳变,所以数据采集是在上升沿,数据发送
是在下降沿。
1.3spi驱动框架

配置spi核心层和spi控制器驱动到内核中
spi控制器驱动配置:
Device Drivers —>
[*] SPI support ---> <*> STMicroelectronics STM32 SPI controllerspi核心层配置:
CONFIG_SPI_MASTER=y重新编译内核
make uImage LOADADDR=0xc2000000将编译好的内核拷贝到tftpboot目录下
1.4spi设备驱动的API
1.分配并初始化对象struct spi_driver {int (*probe)(struct spi_device *spi);int (*remove)(struct spi_device *spi);struct device_driver driver;};struct device_driver {const char *name;const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;}
2.注册 #define spi_register_driver(driver) \__spi_register_driver(THIS_MODULE, driver)
3.注销void spi_unregister_driver(struct spi_driver *sdrv)
4.一键注册的宏module_spi_driver(结构体变量名);
1.5spi驱动的实例
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/spi/spi.h>
int m74hc595_probe(struct spi_device* spi)
{printk("%s:%d\n", __func__, __LINE__);return 0;
}
int m74hc595_remove(struct spi_device* spi)
{printk("%s:%d\n", __func__, __LINE__);return 0;
}struct of_device_id oftable[] = {{.compatible = "hqyj,m74hc595",},{}
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of,oftable);struct spi_driver m74hc595 = {.probe = m74hc595_probe,.remove = m74hc595_remove,.driver = {.name = "m74hc595",.of_match_table = oftable,},
};
module_spi_driver(m74hc595);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
1.6m74hc595设备树的填充
1.6.1m74hc595操作数码管的原理图

1.6.2控制器的设备树
spi4: spi@44005000 {#address-cells = <1>;#size-cells = <0>;compatible = "st,stm32h7-spi";reg = <0x44005000 0x400>;interrupts = <GIC_SPI 84 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;clocks = <&rcc SPI4_K>;resets = <&rcc SPI4_R>;dmas = <&dmamux1 83 0x400 0x01>,<&dmamux1 84 0x400 0x01>;dma-names = "rx", "tx";power-domains = <&pd_core>;status = "disabled";};
1.6.3编写自己的设备树
&spi4 {pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";pinctrl-0 = <&spi4_pins_b>;pinctrl-1 = <&spi4_sleep_pins_b>;cs-gpios = <&gpioe 11 0>;status = "okay";m74hc595@0 {compatible = "hqyj,m74hc595";reg = <0>; //片选编号spi-max-frequency = <10000000>; //10MHZ };
};
1.7spi相关的结构体及函数
int spi_write(struct spi_device *spi, const void *buf, size_t len) //发数据
int spi_read(struct spi_device *spi, void *buf, size_t len) //接收数据
int spi_write_then_read(struct spi_device *spi, //同时收发const void *txbuf, unsigned n_tx,void *rxbuf, unsigned n_rx);
1.8spi驱动的实例2
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/spi/spi.h>int m74hc595_probe(struct spi_device* spi)
{unsigned char buf[] = {0x4,0x6d};printk("%s:%d\n", __func__, __LINE__);spi_write(spi,buf,2);return 0;
}
int m74hc595_remove(struct spi_device* spi)
{printk("%s:%d\n", __func__, __LINE__);return 0;
}struct of_device_id oftable[] = {{.compatible = "hqyj,m74hc595",},{}
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of,oftable);struct spi_driver m74hc595 = {.probe = m74hc595_probe,.remove = m74hc595_remove,.driver = {.name = "m74hc595",.of_match_table = oftable,},
};
module_spi_driver(m74hc595);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
1.9让数码管流水显示0-f
m74hc595.h
#ifndef __M74HC595_H__
#define __M74HC595_H__#define SEG_WHICH _IOW('k',0,int)
#define SEG_DAT _IOW('k',1,int)
#endif
m74hc595.c
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/spi/spi.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include "m74hc595.h"
/*&spi4 { pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep"; pinctrl-0 = <&spi4_pins_b>; pinctrl-1 = <&spi4_sleep_pins_b>; cs-gpios = <&gpioe 11 0>;status = "okay";m74hc595@0{compatible = "m74hc595";reg = <0>;spi-max-frequency = <10000000>;};
};
*/
#define NAME "m74hc595"
int major = 0;
struct class *cls;
struct device *dev;
struct spi_device *gspi;
u8 code[] = {0x3f, //00x06, //10x5b, //20x4f, //30x66, //40x6d, //50x7d, //60x07, //70x7f, //80x6f, //90x77, //A0x7c, //b0x39, //c0x5e, //d0x79, //e0x71, //f
};u8 which[] = {0x1, //sg00x2, //sg10x4, //sg20x8, //sg3
};int m74hc595_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{printk("%s:%d\n",__func__,__LINE__);return 0;
}
long m74hc595_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long args)
{ switch(cmd){case SEG_WHICH:spi_write(gspi,&which[args],1);break;case SEG_DAT:spi_write(gspi,&code[args],1);break;default: printk("ioctl error\n");break;}return 0;
}int m74hc595_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{printk("%s:%d\n",__func__,__LINE__);return 0;
}
struct file_operations fops = {.open = m74hc595_open,.unlocked_ioctl = m74hc595_ioctl,.release = m74hc595_close,
};int m74hc595_probe(struct spi_device *spi)
{u8 buf[2] = {0xf,0x0};printk("%s:%d\n",__func__,__LINE__);gspi = spi;spi_write(gspi,buf,ARRAY_SIZE(buf));major = register_chrdev(0,NAME,&fops);if(major < 0){printk("register chrdev error\n");return major;}cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE,NAME);if(IS_ERR(cls)){printk("class create error\n");return PTR_ERR(cls);}dev = device_create(cls,NULL,MKDEV(major,0),NULL,NAME);if(IS_ERR(dev)){printk("device create error\n");return PTR_ERR(dev);}return 0;
}int m74hc595_remove(struct spi_device *spi)
{printk("%s:%d\n",__func__,__LINE__);device_destroy(cls,MKDEV(major,0));class_destroy(cls);unregister_chrdev(major,NAME);return 0;
}const struct of_device_id of_match[] = {{.compatible = "hqyj,m74hc595",},{},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of,of_match);struct spi_driver m74hc595 = {.probe = m74hc595_probe,.remove = m74hc595_remove,.driver = {.name = "m74hc595",.of_match_table = of_match,},
};
module_spi_driver(m74hc595);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
test.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include "m74hc595.h"int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{int which=0;int data=0;int fd;fd = open("/dev/m74hc595",O_RDWR);if(fd < 0){perror("open error");return -1;}while(1){ioctl(fd,SEG_WHICH,which++);ioctl(fd,SEG_DAT,data++);if(which >= 4)which=0;if(data >= 16)data = 0;sleep(1);}close(fd);return 0;
}