Android的App可以读写的位置为:
一、内置data目录下对应app名称的目录;
二、扩展SD卡(包括虚拟的内置SD卡和外置SD卡);
一、先说说内置data目录下文件的读写。
内置data目录即内部存储,指的是应用内部独有的存储,这部分存储的文件、数据,只能被应用自身访问到,其他应用都没有权限访问。
一般情况下,/data开头的路径都是内部存储。而一般应用所能够访问到的就是下面几个路径,称为应用内部私有存储。
应用内部私有存储:
/data/user/0/<包名>
/data/user/0/<包名>/files #存放文件数据
/data/user/0/<包名>/databases #存放Sqlite的数据库文件
/data/user/0/<包名>/shared_prefs #存放SharedPreference的数据
/data/user/0/<包名>/cache #存放缓存文件
一旦App被卸载,系统将会移除内部存储中相关应用的数据。
方式1:内置API读写
这个位置的读写有提供一套单独的API来读写,无需申明特殊权限。
代码中有个openFileInput的方法,这个方法是Android内置的,需放在Activity中才能执行。
如下:
//读取内置data目录下文件public String readDataFile(String fileName) {String res = "";try {FileInputStream fin = openFileInput(fileName);int length = fin.available();byte[] buffer = new byte[length];fin.read(buffer);res = new String(buffer);fin.close();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();Log.e("Exception", "readDataFile Error!" + e.getMessage());}return res;}//写入内置data目录下文件private void writeDataFile(String fileName, String content) {try {FileOutputStream fut = openFileOutput(fileName, Context.MODE_PRIVATE | Context.MODE_APPEND);byte[] bytes = content.getBytes();fut.write(bytes);fut.close();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();Log.e("Exception", "writeDataFile Error!" + e.getMessage());}}测试代码:
String fileName="test.txt";
writeDataFile(fileName, "Hello Android");
String txt = readDataFile(fileName);
Log.e("txt", txt);方式2:获取对应的data路径后,通过普通的方法读写data中的文件。
手动获取拼接data目录下文件路径,然后用通用的文件读写方式进行读写。
通用读写文件的辅助类,FileHelper.java
package com.rc114.scanner;import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.net.URLDecoder;public class FileHelper {public static String combinePath(String path1, String path2) {File file1 = new File(path1);File file2 = new File(file1, path2);return file2.getPath();}/*** 读取文件** @param filepath 文件路径*/public static String readFile(String filepath) {String encoding = "UTF-8";return readFile(filepath, encoding);}/*** 读取文件,指定编码** @param filepath 文件路径*/public static String readFile(String filepath, String encoding) {try {filepath = URLDecoder.decode(filepath, "utf-8");File file = new File(filepath);Long filelength = file.length();byte[] filecontent = new byte[filelength.intValue()];FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);in.read(filecontent);in.close();return new String(filecontent, encoding);} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "";}/*** 将字符串写入文件** @param filepath* @param text* @param isAppend*/public static void writeFile(String filepath, String text, boolean isAppend) {try {filepath = URLDecoder.decode(filepath, "utf-8");File file = new File(filepath);File parentFile = file.getParentFile();if (!parentFile.exists()) {parentFile.mkdirs();}if (!file.exists()) {file.createNewFile();}FileOutputStream f = new FileOutputStream(filepath, isAppend);f.write(text.getBytes());f.close();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void writeFile(String filepath, String text, String encodeing) {try {filepath = URLDecoder.decode(filepath, "utf-8");File file = new File(filepath);File parentFile = file.getParentFile();if (!parentFile.exists()) {parentFile.mkdirs();}if (!file.exists()) {file.createNewFile();}// FileOutputStream f = new FileOutputStream(filepath, "GBK");// f.write(text.getBytes());// f.close();OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(filepath), encodeing);writer.append(text);writer.close();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
测试代码:
//获取data目录下对应包名根目录
String dataDir = Environment.getDataDirectory().getPath() + "/data/" + packageName;//拼接待读写文件路径
String filepath = FileHelper.combinePath(dataDir, "test.txt");//写入文件
FileHelper.writeFile(filepath, "Hello", "utf-8");//读取文件
String txt = FileHelper.readFile(filepath);Log.e("txt", txt);二、扩展SD卡文件读写
扩展SD卡文件即外部存储,指的是是公共的存储,这部分存储理论上是全局可见的,所有的应用都可以访问这部分数据,一般情况下,路径都是以/storage开头的,比如说/storage/emulated/0就是属于外部存储,这个路径的实际的挂载点是/data/media。又比如外置sdcard的路径为/storage/13FC-0F0B。 相比较内部存储一定会存在,外部存储可能是sdcard或者通过otg挂载的U盘形式,所以可能出现没有挂载的情况,所以所有的外部存储要在使用前通过下面的方式判断是否有被挂载。
/*检查外部存储是否可写*/public boolean isExternalStorageWritable() {String state = Environment.getExternalStorageState();if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(state)) {return true;}return false;}/*检查外部存储是否可读*/public boolean isExternalStorageReadable() {String state = Environment.getExternalStorageState();if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(state) ||Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED_READ_ONLY.equals(state)) {return true;}return false;}访问外部存储需在AndroidManifest.xml文件中申明权限:
<!-- 存储权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MANAGE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MOUNT_UNMOUNT_FILESYSTEMS" tools:ignore="ProtectedPermissions" />安卓6.0以后,谷歌要求危险权限必须动态获取,所以还要使用requestPermissions在运行时获取权限。
private static String[] PERMISSIONS_STORAGE = {Manifest.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE,Manifest.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE};private static int REQUEST_PERMISSION_CODE = 100;//获取权限private void getPermission() {if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT > Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {if (ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, Manifest.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, PERMISSIONS_STORAGE, REQUEST_PERMISSION_CODE);} else {boolean writable = isExternalStorageWritable();boolean readable = isExternalStorageReadable();Log.e("外部存储读写", "写:" + writable + "-读:" + readable);File root = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();//取得外部存储根路径File[] files = root.listFiles();if (files != null) {for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {if (files[i].isDirectory()) {Log.e("文件夹", files[i].toString());}}}}}}@Overridepublic void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, @NonNull String[] permissions, @NonNull int[] grantResults) {super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults);if (requestCode == REQUEST_PERMISSION_CODE) {for (int i = 0; i < permissions.length; i++) {Log.i("MainActivity", "申请的权限为:" + permissions[i] + ",申请结果:" + grantResults[i]);}}}在Activity的onCreate事件中执行getPermission()方法,动态获取存储权限。
完成了上面的操作后,在代码:
File root = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();//取得外部存储根路径
File[] files = root.listFiles();
中,root.listFiles()可能会返回null,还是无法读取或写入文件。
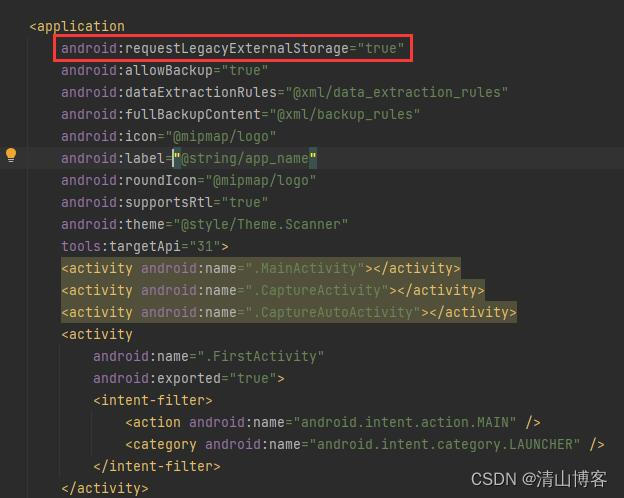
查了下资料,Android 10 或更高版本,还需要做一个配置:在AndroidManifest.xml中,还需增加:android:requestLegacyExternalStorage="true"
利用上面的FileHelper.java类,测试写入一个文件:
File root = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();
FileHelper.writeFile(FileHelper.combinePath(root.getPath(), "text.txt"), "Hello", false);测试遍历根目录:
File root = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();
File[] files = root.listFiles();
if (files != null) {for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {if (files[i].isDirectory()) {Log.e("文件夹", files[i].toString());}if (files[i].isFile()) {Log.e("文件", files[i].toString());}}
}输出结果:
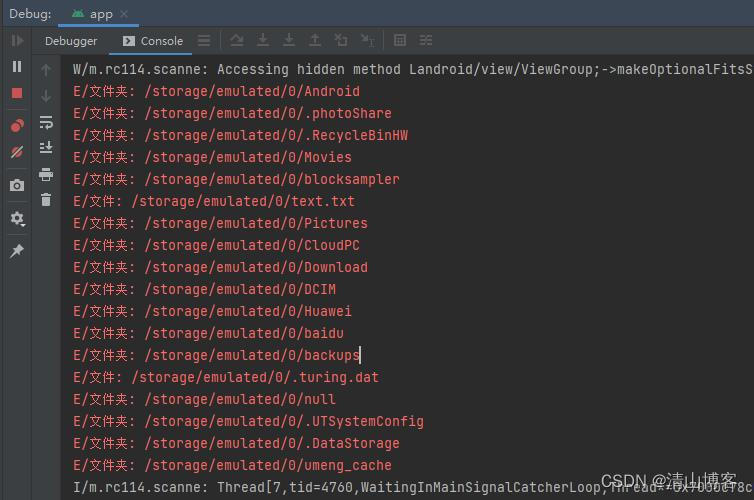
至此,完成了外部存储的读写功能。
参考资料:
1.Android中的内部存储和外部存储_build hero的博客-CSDN博客_android 外部存储
2.android - Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory() deprecation alternatives - Stack Overflow