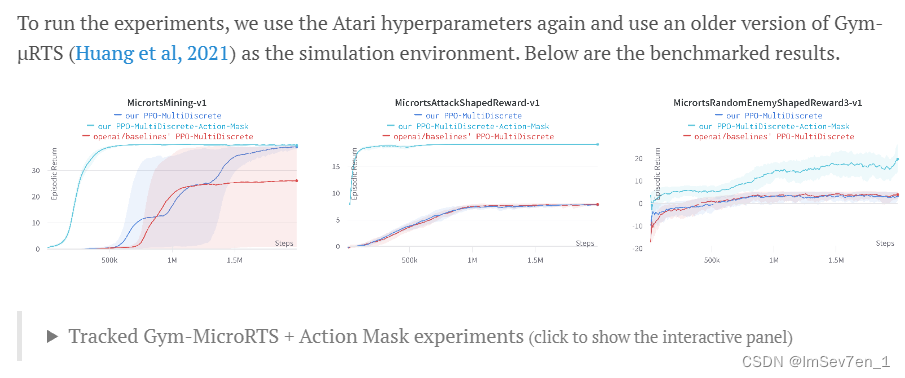
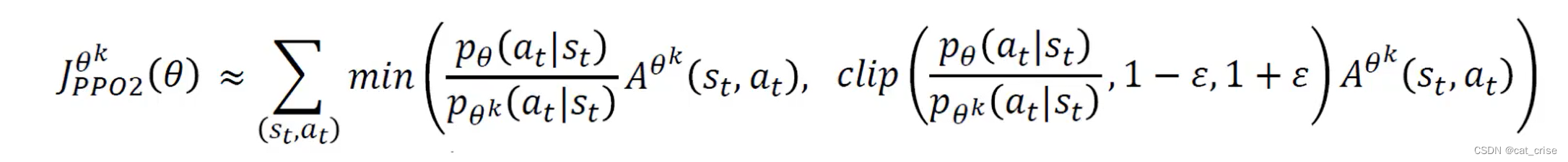哈哈初学,复现龙龙老师的实例!
state:是平衡小车上的杆子,观测状态由 4 个连续的参数组成:推车位置 [-2.4,2.4],车速 [-∞,∞],杆子角度 [~-41.8°,~41.8°] 与杆子末端速度 [-∞,∞]。
游戏结束:当极点与垂直方向的夹角超过15度时,或者推车从中心移出2.4个单位以上
向推车施加+1或-1的力来控制系统
杆保持直立的每个时间步长都提供+1的奖励
代码分析
经验池缓存
批训练条件:
Transition = namedtuple('Transition', ['state', 'action', 'a_log_prob', 'reward', 'next_state'])
trans = Transition(state, action, action_prob, reward, next_state)
agent.store_transition(trans)
self.buffer.append(transition)
if done: # 合适的时间点训练网络(回合结束done=True才训练)if len(agent.buffer) >= batch_size:agent.optimize() # 训练网络break
数据迭代次数:round()函数不设四舍五入位数,默认计算到整数。
# 对缓冲池数据大致迭代10遍for _ in range(round(10*len(self.buffer)/batch_size)):
奖励计算
Rs = []for r in reward[::-1]:R = r + gamma * RRs.insert(0, R) #在List 列表前添加新的RRs = tf.constant(Rs, dtype=tf.float32) #将List转换为Tensor格式
重要性采样:old_action_log_prob为Actor策略网络得出的已经生成的buffer动作概率(策略采样offline);pi_a为index对应的(历史)buffer中的状态再进行Actor网络在线得出的动作概率(目标策略online)
ratio = (pi_a / tf.gather(old_action_log_prob, index, axis=0))
PPO2误差:
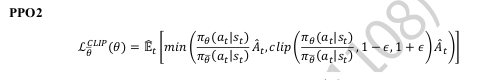
ratio = (pi_a / tf.gather(old_action_log_prob, index, axis=0))
surr1 = ratio * advantage
surr2 = tf.clip_by_value(ratio, 1 - epsilon, 1 + epsilon) * advantage
# PPO误差函数
policy_loss = -tf.reduce_mean(tf.minimum(surr1, surr2))
函数备注:
tf.reshape(tensor,[-1,1])将张量变为一维列向量
tf.reshape(tensor,[1,-1])将张量变为一维行向量
tf.gather 可以根据索引号收集数据的目的。
如:考虑班级成绩册的例子,共有 4 个班
级,每个班级 35 个学生,8 门科目,保存成绩册的张量 shape 为[4,35,8]。例如在班级的维度上面我们可以像下面这样收集1和2班级的成绩册。
x = tf.random.uniform([4,35,8],maxval=100,dtype=tf.int32)
y=tf.gather(x,[0,1],axis=0)
buffer.append(transition) 在列表后面添加存储数据。
range()返回从0到4的5个数构成的list,而arange()返回一个array对象。不过他们的元素都是一样的。
Transition = namedtuple('Transition', ['state', 'action', 'a_log_prob', 'reward', 'next_state'])
下面的函数的作用为从数组x中取出n个元素,false表示每个元素不一样
**np.random.choice**(x,n,replace=false)
np.arange(len(self.buffer)) :生成长度的数组,这里为0~39,40个数(buffer的数目),后面会用这些抽取的随机数作为训练样本的索引下标。
中间prob概率截图
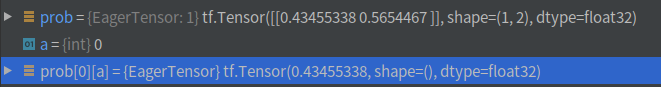
a = tf.random.categorical(tf.math.log(prob), 1)[0]
变量监视:






PPO实战代码
import matplotlib
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
matplotlib.rcParams['font.size'] = 18
matplotlib.rcParams['figure.titlesize'] = 18
matplotlib.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [9, 7]
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = ['Microsoft YaHei']
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=Falseplt.figure()import gym,os
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers,optimizers,losses
from collections import namedtuple
#from torch.utils.data import SubsetRandomSampler,BatchSamplerenv = gym.make('CartPole-v1') # 创建游戏环境
env.seed(2222)
tf.random.set_seed(2222)
np.random.seed(2222)
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
assert tf.__version__.startswith('2.')gamma = 0.98 # 激励衰减因子
epsilon = 0.2 # PPO误差超参数0.8~1.2
batch_size = 32 # batch size# 创建游戏环境
env = gym.make('CartPole-v0').unwrapped
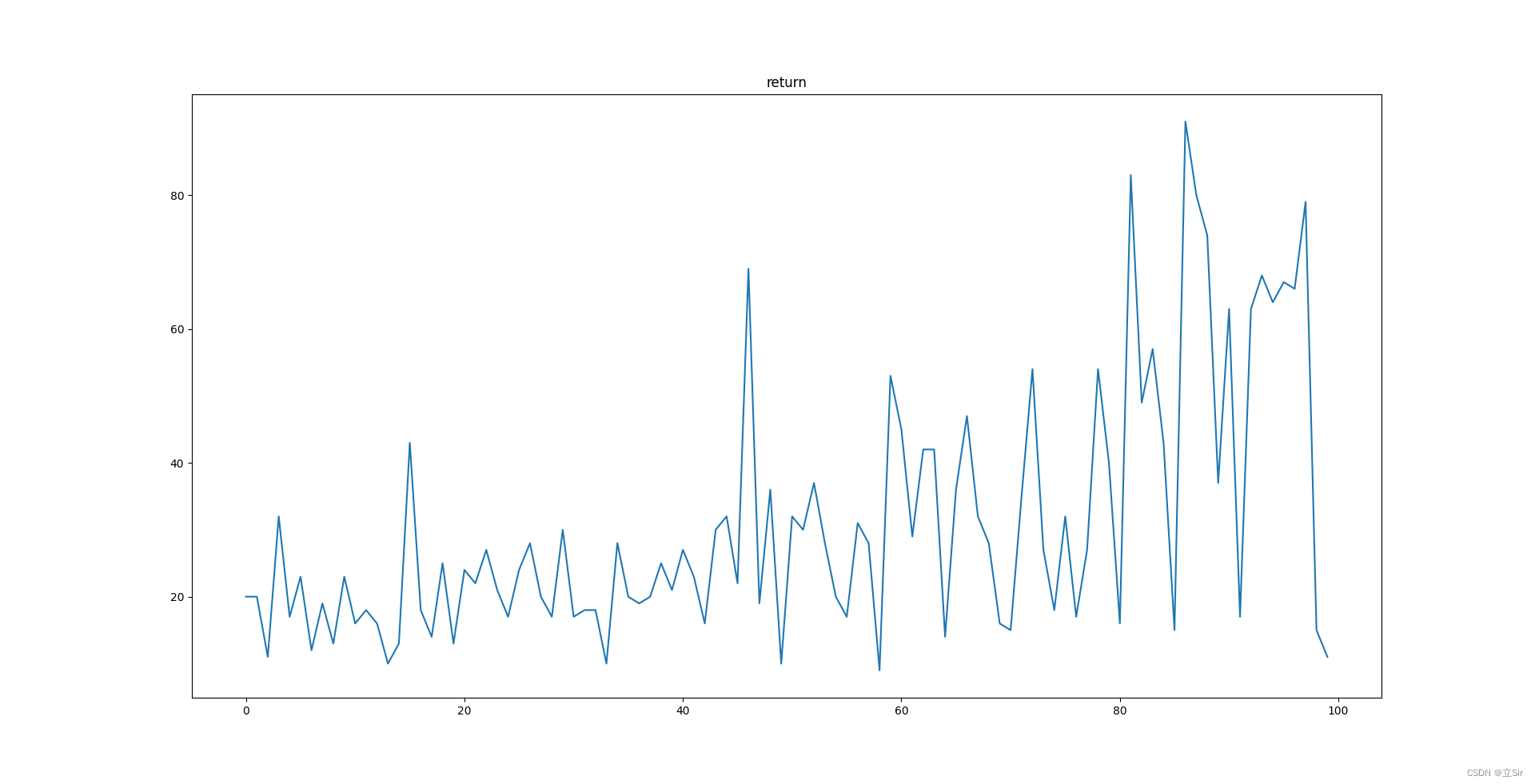
Transition = namedtuple('Transition', ['state', 'action', 'a_log_prob', 'reward', 'next_state'])class Actor(keras.Model):def __init__(self):super(Actor, self).__init__()# 策略网络,也叫Actor网络,输出为概率分布pi(a|s)self.fc1 = layers.Dense(100, kernel_initializer='he_normal')self.fc2 = layers.Dense(2, kernel_initializer='he_normal')def call(self, inputs):x = tf.nn.relu(self.fc1(inputs))x = self.fc2(x)x = tf.nn.softmax(x, axis=1) # 转换成概率return xclass Critic(keras.Model):def __init__(self):super(Critic, self).__init__()# 偏置b的估值网络,也叫Critic网络,输出为v(s)self.fc1 = layers.Dense(100, kernel_initializer='he_normal')self.fc2 = layers.Dense(1, kernel_initializer='he_normal')def call(self, inputs):x = tf.nn.relu(self.fc1(inputs))x = self.fc2(x)return xclass PPO():# PPO算法主体def __init__(self):super(Actor, self).__init__()self.actor = Actor() # 创建Actor网络self.critic = Critic() # 创建Critic网络self.buffer = [] # 数据缓冲池self.actor_optimizer = optimizers.Adam(1e-3) # Actor优化器self.critic_optimizer = optimizers.Adam(3e-3) # Critic优化器def select_action(self, s):# 送入状态向量,获取策略: [4]s = tf.constant(s, dtype=tf.float32)# s: [4] => [1,4]s = tf.expand_dims(s, axis=0)# 获取策略分布: [1, 2]prob = self.actor(s)# 从类别分布中采样1个动作, shape: [1]a = tf.random.categorical(tf.math.log(prob), 1)[0]a = int(a) # Tensor转数字return a, float(prob[0][a]) # 返回动作及其概率def get_value(self, s):# 送入状态向量,获取策略: [4]s = tf.constant(s, dtype=tf.float32)# s: [4] => [1,4]s = tf.expand_dims(s, axis=0)# 获取策略分布: [1, 2]v = self.critic(s)[0]return float(v) # 返回v(s)def store_transition(self, transition):# 存储采样数据self.buffer.append(transition)def optimize(self):# 优化网络主函数# 从缓存中取出样本数据,转换成Tensorstate = tf.constant([t.state for t in self.buffer], dtype=tf.float32)action = tf.constant([t.action for t in self.buffer], dtype=tf.int32)action = tf.reshape(action,[-1,1])reward = [t.reward for t in self.buffer]old_action_log_prob = tf.constant([t.a_log_prob for t in self.buffer], dtype=tf.float32)old_action_log_prob = tf.reshape(old_action_log_prob, [-1,1])# 通过MC方法循环计算R(st)R = 0Rs = []for r in reward[::-1]:R = r + gamma * RRs.insert(0, R)Rs = tf.constant(Rs, dtype=tf.float32)# 对缓冲池数据大致迭代10遍for _ in range(round(10*len(self.buffer)/batch_size)):# 随机从缓冲池采样batch size大小样本index = np.random.choice(np.arange(len(self.buffer)), batch_size, replace=False)# 构建梯度跟踪环境with tf.GradientTape() as tape1, tf.GradientTape() as tape2:# 取出R(st),[b,1]v_target = tf.expand_dims(tf.gather(Rs, index, axis=0), axis=1)# 计算v(s)预测值,也就是偏置b,我们后面会介绍为什么写成vv = self.critic(tf.gather(state, index, axis=0))delta = v_target - v # 计算优势值advantage = tf.stop_gradient(delta) # 断开梯度连接# 由于TF的gather_nd与pytorch的gather功能不一样,需要构造# gather_nd需要的坐标参数,indices:[b, 2]# pi_a = pi.gather(1, a) # pytorch只需要一行即可实现a = tf.gather(action, index, axis=0) # 取出batch的动作at# batch的动作分布pi(a|st)pi = self.actor(tf.gather(state, index, axis=0))indices = tf.expand_dims(tf.range(a.shape[0]), axis=1)indices = tf.concat([indices, a], axis=1)pi_a = tf.gather_nd(pi, indices) # 动作的概率值pi(at|st), [b]pi_a = tf.expand_dims(pi_a, axis=1) # [b]=> [b,1]# 重要性采样ratio = (pi_a / tf.gather(old_action_log_prob, index, axis=0))surr1 = ratio * advantagesurr2 = tf.clip_by_value(ratio, 1 - epsilon, 1 + epsilon) * advantage# PPO误差函数policy_loss = -tf.reduce_mean(tf.minimum(surr1, surr2))# 对于偏置v来说,希望与MC估计的R(st)越接近越好value_loss = losses.MSE(v_target, v)# 优化策略网络grads = tape1.gradient(policy_loss, self.actor.trainable_variables)self.actor_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, self.actor.trainable_variables))# 优化偏置值网络grads = tape2.gradient(value_loss, self.critic.trainable_variables)self.critic_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, self.critic.trainable_variables))self.buffer = [] # 清空已训练数据def main():agent = PPO()returns = [] # 统计总回报total = 0 # 一段时间内平均回报for i_epoch in range(1000): # 训练回合数state = env.reset() # 复位环境for t in range(500): # 最多考虑500步# 通过最新策略与环境交互action, action_prob = agent.select_action(state)next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)# 构建样本并存储trans = Transition(state, action, action_prob, reward, next_state)agent.store_transition(trans)state = next_state # 刷新状态total += reward # 累积激励env.render()if done: # 合适的时间点训练网络if len(agent.buffer) >= batch_size:agent.optimize() # 训练网络breakif i_epoch % 20 == 0: # 每20个回合统计一次平均回报returns.append(total/20)total = 0print(i_epoch, returns[-1])print(np.array(returns))plt.figure()plt.plot(np.arange(len(returns))*20, np.array(returns))plt.plot(np.arange(len(returns))*20, np.array(returns), 's')plt.xlabel('回合数')plt.ylabel('总回报')plt.savefig('ppo-tf-cartpole.svg')if __name__ == '__main__':main()print("end")
- List item