hugegraph查询使用Gremlin语法,打开 hugegraph-studio http://10.0.0.50:18088,更详细的方法参考 http://kelvinlawrence.net/book/Gremlin-Graph-Guide.html#fuzzyregs
导入数据,jar包参考 https://git.gtapp.xyz/ml/graph-user,导入的数据为user白名单数据,下文中示例如无说明,均使用此数据。
java -jar target/graph-cases-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar -u http://10.0.0.50:8080 -i input_0.json
基本查询
1.has 类的step
方法V(), E(), hasLabel(labels,...), hasId(ids,...), has(key, value), has(label, key, value), has(keys,...),hasNot(keys,...), values(keys,...)等。
| 方法 | 语义 |
|---|---|
| V() | 获取所有顶点 |
| E() | 获取所有边 |
| hasLabel(label1,…,labelN) | 返回label为label1, …, labelN的顶点/边 |
| hasId(id1, …, idN) | 返回id为id1,…,idN的顶点/边 |
| has(key, value) | 返回key属性值为value的顶点/边 |
| has(label, key, value) | 返回标签为label,key属性值为value的顶点/边 |
| has(key1,…,keyN) | 返回拥有属性key1,…,keyN的顶点/边 |
| hasNot(key1,…,keyN) | 返回没有属性key1,…,keyN的顶点/边 |
| values(key1,…,keyN) | 返回key1,…,keyN属性的值 |
| next() | 将查询结果存入一个变量,方便以后使用 |
示例如下:
g.V() # 返回所有顶点g.E() # 返回所有边g.V().hasLabel("user") # 返回label为‘user’的顶点g.V().hasId("000749e1c17ad7bad7cfb7fa2a42b7b0") # 返回id为‘000749e1c17ad7bad7cfb7fa2a42b7b0’的顶点
# 返回属性lastRequestTime的值为‘2018-10-09T13:01:06.672143’的顶点
g.V().has("user", "lastRequestTime", "2018-10-09T13:01:06.672143")
# 等价于
g.V().hasLabel("user").has("lastRequestTime", "2018-10-09T13:01:06.672143")
上面两个语句,语法没问题,但是很傻逼好像不能用,报错为
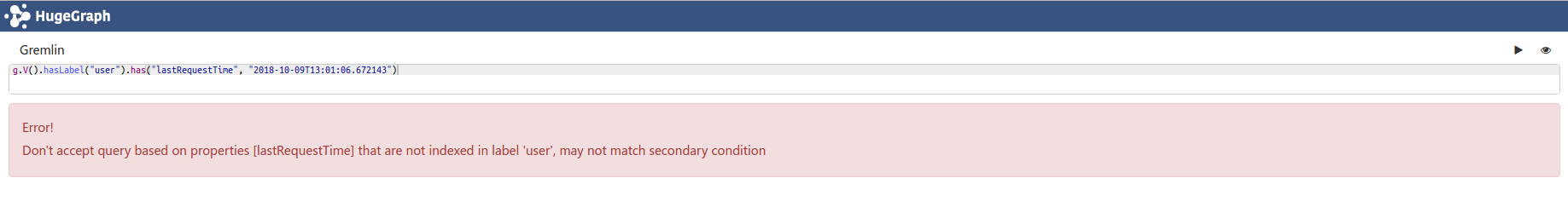
但是中间加一个limit(200)又没报错了,真他妈傻逼
g.V().limit(200).has("user", "lastRequestTime", "2018-10-09T13:01:06.672143")
# 等价于
g.V().limit(200).hasLabel("user").has("lastRequestTime", "2018-10-09T13:01:06.672143")
g.E().limit(200).has('count') # 返回拥有count属性的边g.E().limit(200).values("count") # 返回边的count属性值
# 将100个顶点存入变量aus,取出第2个
aus = g.V().next(100)
aus[1]
2.label,id,节点/边及其属性操作
label() 查询顶点/边的label
id() 查询顶点/边的id
properties() 查询属性,对每个顶点/边返回一个mapping
values(key1,...,keyN)取出节点/边的属性,返回列表。
valueMap()输出属性的key-value对。
select(key1,...,keyN)从map中取出需要的属性
dedup() 去重
local(traversal) 对当前状态的每个元素进行traversal操作,返回集合
limit(N) 限制输出数据个数N
range(n1, n2) 切片输出n1到n2
tail(N) 尾部截取N个数据
# valueMap()示例
g.V().hasId('07f09b432f95611329d2a4b2426bb59e').valueMap() # valueMap()传入参数true则同时输出id和label
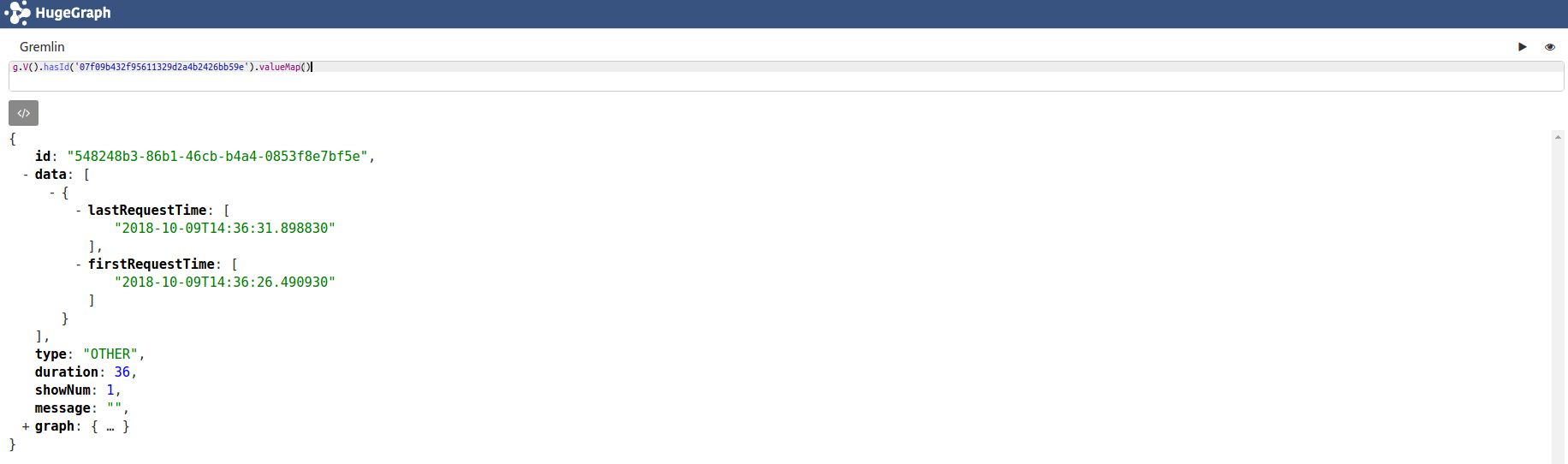
# select示例
g.V().hasId('07f09b432f95611329d2a4b2426bb59e').valueMap(true).select('lastRequestTime', "firstRequestTime").unfold()
g.V().hasLabel('user').limit(20).id() # 查询顶点的id返回列表g.V().hasLabel('user').limit(20).label() # 查询顶点的label返回列表g.V().hasLabel('user').limit(20).properties() # 返回顶点的属性,形式为[{}, {}]g.V().hasLabel('user').limit(20).values("lastRequestTime") # 返回顶点lastRequestTime属性值的列表g.V().hasLabel('user').limit(20).properties().key().dedup() # 查询顶点所有属性的keyg.V().hasLabel('user').limit(20).properties().value().dedup() # 查询顶点所有属性的值
g.V().hasLabel('captchaId').limit(20).local(__.in().count()) # 返回20个顶点captchaId顶点的in边个数
3.排序order().by()
order().by()表示按…排序。by()传入一个属性key或者一个遍历。incr升序,desc降序。
g.V().hasLabel("user").limit(2000).sample(20).order().by("lastRequestTime")g.V().hasLabel("user").limit(2000).sample(20).order().by(out("userIp").count())
4.逻辑判断
类似其他语法中有比较值或值的范围的语句,gremlin中这类比较语句的Predicates,有eq(), neq(), gt, gte, lt, lte, inside, outside, between, within, without。
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| eq() | 等于 |
| neq() | 不等于 |
| gt() | 大于 |
| gte() | 大于或等于 |
| lt() | 小于 |
| lte() | 小于或等于 |
| inside(a, b) | 是否在开区间(a, b) |
| outside(a,b) | 是否在开区间(a,b)外 |
| between(a, b) | 是否在区间[a, b)内 |
| within | 是否在list/range中 |
| without | 是否在/list/range外 |
示例如下
g.E().limit(2000).has('count', eq(1)).count() # 边count属性值等于1的个数g.E().limit(2000).has('count', within(1..14)).count() # 边count属性在1..14序列中的个数,1..14相当于range(1,15)g.V().hasLabel("user").limit(200).has('lastRequestTime', between("2018-10-09T13", '2018-10-09T14')) # lastRequestTime属性值在"2018-10-09T13", '2018-10-09T14'之间的顶点。
5.条件和过滤 where() filter() match()
where()、filter()用来过滤遍历过程中当前阶段的对象。match() 模式匹配,返回map<模式变量,匹配上的数据> has类型的step也是特殊形式的过滤,如hasId()
示例如下
where()单独使用有三种方式:where(P);where(string, P);where(traversal)
g1 = g.V('0000018201b74cf860dbbba88664ccf1').as("a").out("userCaptchaId").in('userCaptchaId').as("b") # 表示与user访问过相同的captcha_id的user的集合(包括它本身)。g1.count()返回[9156]
g1.where(neq('a')).count() # 返回[9155],此时where(neq('a"))剔除了它本身;g1.where("a", neq("b")).count() # 返回[9155];g1.where(values("lastRequestTime").is(neq("2018-10-09T13:01:06.672143"))).count() # 返回[9155]。
where()与by()配合使用。
g1.where("a", gt("b")).by("lastRequestTime").count() # 取出a的lastRequestTime属性值大于b的lastRequestTime属性值的顶点,计数。
where()与as()+select()配合使用。
as()为某一阶段的对象添加标签,select()可以通过标签取出对象,如g1.select("a").dedup()取出顶点0000018201b74cf860dbbba88664ccf1。
g1.select("a", 'b').by("lastRequestTime").where("b", gte("a")) # 返回的是符合条件的对象‘a’、‘b’的属性lastRequestTime对照组map。
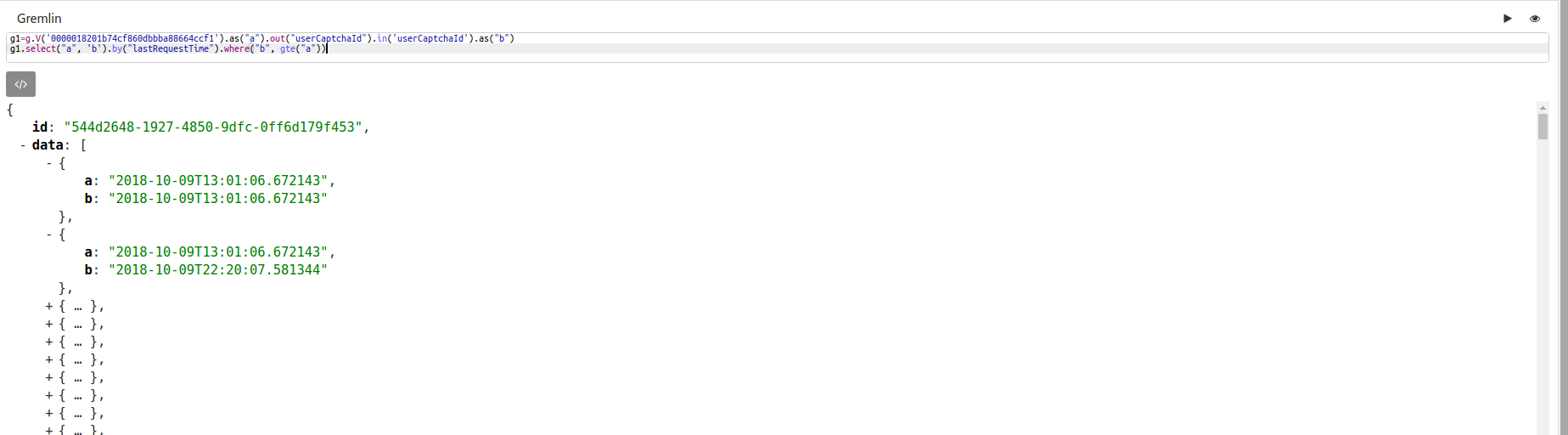
match(traversal1, traversal2),传入模式匹配查询片段(traversal fragments),每个片段会产生变量,返回map<String, Object>。
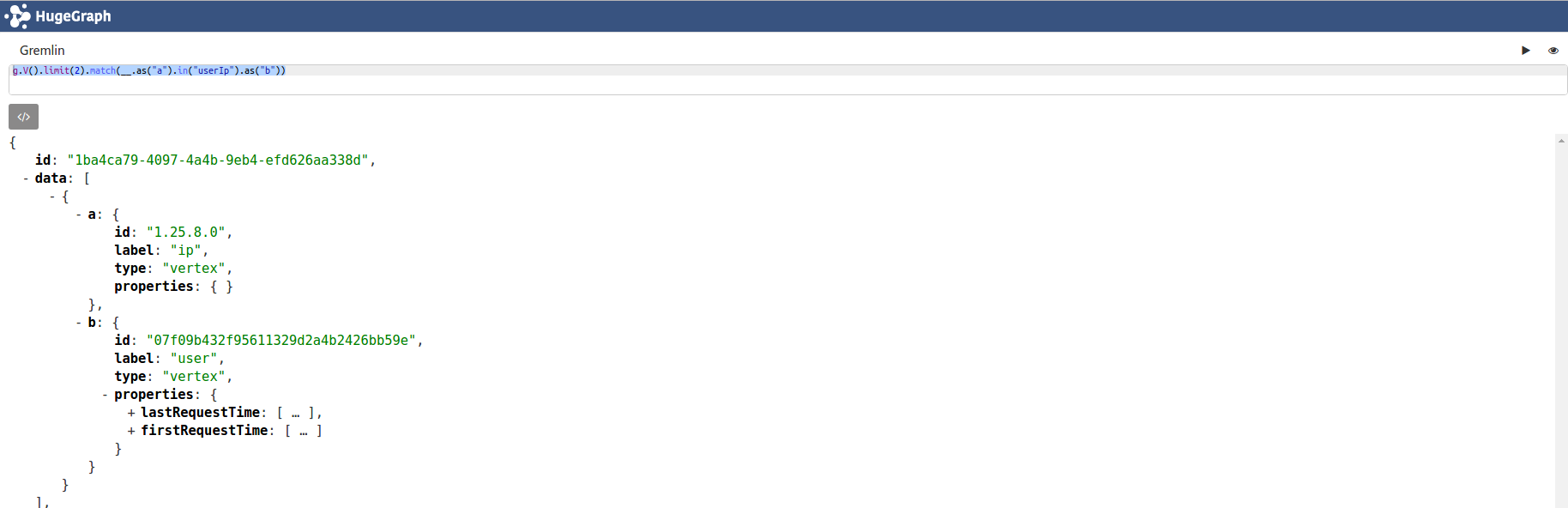
# 对每个顶点,用以下模式取匹配
# 模式1:‘a’对应当前顶点,且有userIp标签的in边
# 模式2:‘b’对应userIp标签的边连接的user顶点
g.V().limit(2).match(__.as("a").in("userIp").as("b"))
filter()用法
lambda方式,filter{it.get()...};traversal方式,filter(traversal)
6.group聚合操作
操作group().by().by(traversal) 根据某个元素(可以是label,顶点某个属性等)对数据分组,并对每一组中的数据作traversal操作 。groupCount().by() 根据某个元素对数据分组,并对每一组数据计数。
统计边的权重分布
g.E().limit(2000).groupCount().by("count")
上面语句中,groupCount().by("count")对边,按照属性count的值分组,计算每组的个数。
查询user的出度
g.V().hasLabel('user').limit(2000).group().by(__.id()).by(out().count())
语句中group().by(__.id())表是按照当前阶段对象的id进行分组,by(out().count())表示对分组后数据的每一组按照当前对象的out方向的边计数。其中,__.id()中__与identity()的用法相同,指当前阶段的节点/边的所有信息(这里是标签为user的顶点的集合),这里的__.id()也可以换成id()和identity()。后面out().count()中的out()也是承接当前阶段的对象(这里表示每一组的顶点)。
查询user的边类型为‘userIp’的出度。
g.V().hasLabel('user').limit(2000).group().by(__.id()).by(out('userIp').count())
查询user的边类型为‘userIp’的出度,根据出度排序取最后10个。
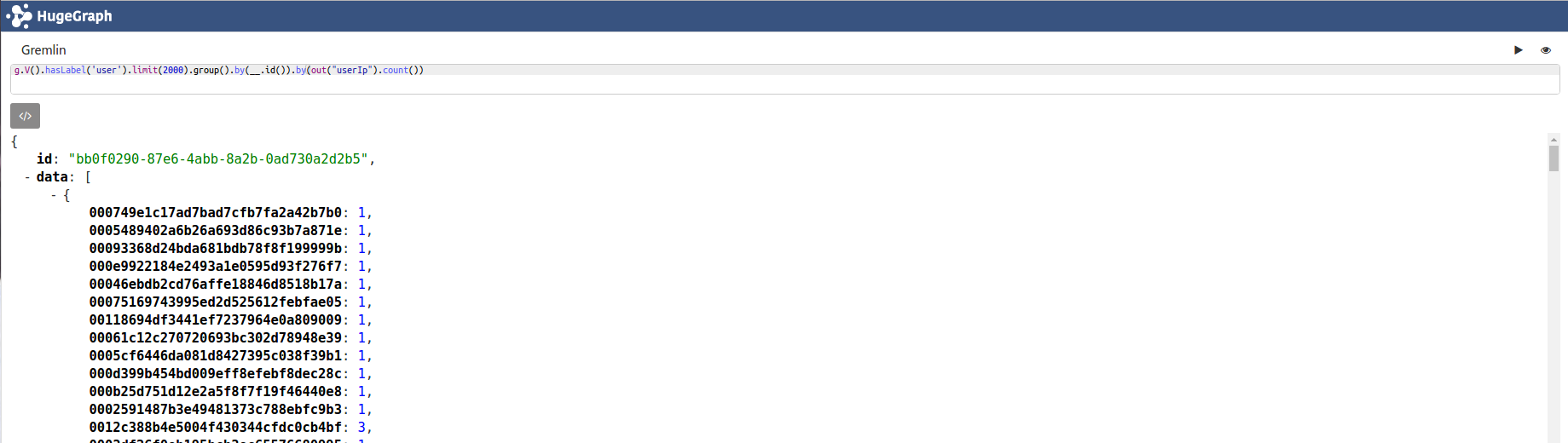
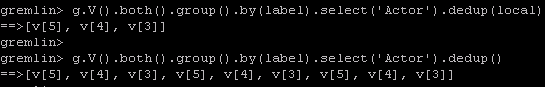
g.V().hasLabel('user').limit(2000).group().by(__.id()).by(out("userIp").count()).order(local).by(values).unfold().tail(10).fold()
上面语句中,order(local).by(values)表示对当前返回的对象按value值排序,其中local指当前返回值,它是一个字典,如下图所示;unfold()将字典,展开成list(dict());fold()将对象装在一个list中;tail(10)取出最后10个元素。
group操作耗时
| 顶点数 | 耗时(毫秒) | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 155 | |
| 20000 | 1251 | |
| 200000 | 12812 | 出现request失败问题 |
| 2000000 | 出现error:Too many records(must <=800000) for the query |
7.边的遍历查询
方法in(), out(), inE(), outE(), inV(), outV(), both()等,所有方法都可以传入边的label,表示沿着该label的边walking。
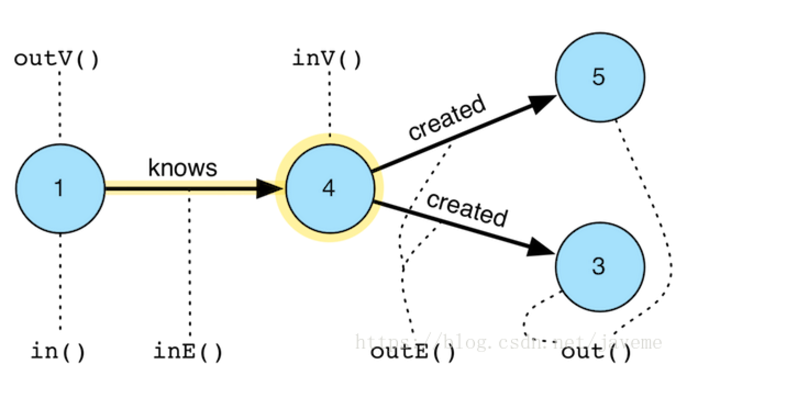
当前阶段为顶点时,如图中的顶点4,in(label), out(label), inE(label), outE(label)用法如上图,both(label)根据指定的EdgeLabel访问双向顶点。
当前节点为边时,如图中的边knows,inV(), outV()用法如上图,bothV()访问边的双向顶点,otherV()访问边的伙伴顶点,即相对于基准顶点而言的另一端的顶点。
示例如下:
g.V("62756445cd524543f5a16418cd920ffd").inE().order().by('count', decr).limit(20)
语义:顶点"62756445cd524543f5a16418cd920ffd"的所有in边,按边属性count,decr排序,限制输出20条
g.V().hasId("0022982a926bbd786bf50c2b11e92442").in("userCaptchaId").out("userCaptchaId")
语义:与captchaId顶点"0022982a926bbd786bf50c2b11e92442"有共同user顶点的,captchaId顶点的集合
g.E().limit(200).filter {it.get().value("count") == 1}
g.V("62756445cd524543f5a16418cd920ffd").inE().limit(100).outV().hasLabel('user').group().by(count())
语义:顶点"62756445cd524543f5a16418cd920ffd"的100个in边对应label为user的顶点
g.V().hasId("0022982a926bbd786bf50c2b11e92442").in("userCaptchaId").out("userCaptchaId").where(out("userCaptchaId").count().is(gte(2)))
语义:与captchaId顶点"0022982a926bbd786bf50c2b11e92442"有两个及其以上同样访问者(user)的captchaId顶点的集合
9.获取遍历的路径 Path()
path()获取图walking时的路径,沿途的顶点信息。by()筛选输出节点/边的信息。from().to()截取路径中的某一段。hasNext()两个顶点之间的边是否存在。
示例如下:
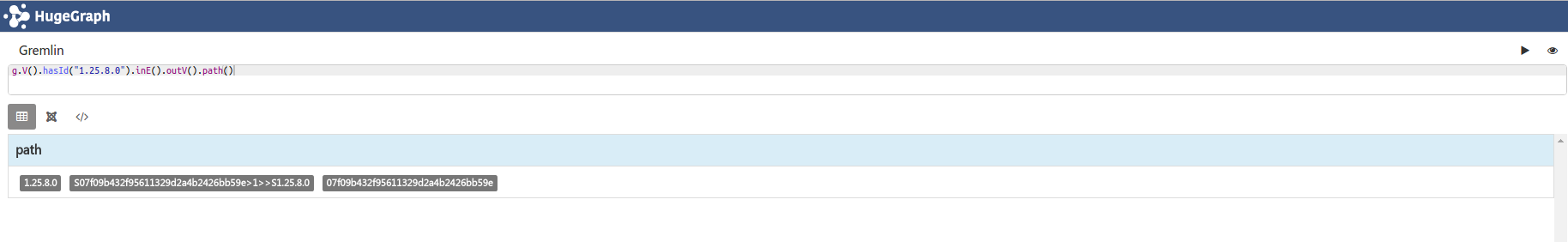
# 示例path()
g.V().hasId("1.25.8.0").inE().outV().path() # 顶点从“1.25.8.0”出发,通过该顶点的in边到达边的out顶点的路径
返回顶点“1.25.8.0”,路径“S07f09b432f95611329d2a4b2426bb59e>1>>S1.25.8.0”,顶点“07f09b432f95611329d2a4b2426bb59e”的id。
# 示例by()
g.V().hasId("1.25.8.0").inE().outV().path().by(id).by("count").by('lastRequestTime') # 分别返回id,count属性值,lastRequestTime属性值
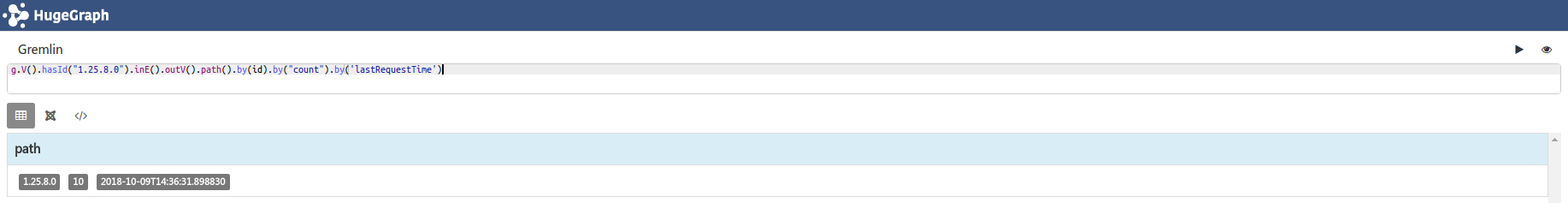
注意三个by()分别对应v-e-v,不传入参数则表示输出顶点或边的id。by()可以传入属性key、一个遍历。如by('count')、by(values("lastRequestTime", "firstRequestTime"))、by(out().count())等。
from().to()在返回的path中截取一段
# 示例from().to()
g.V().hasId("1.25.8.0").inE().as("a").outV().as("b").path().from("a").to("b").by(id).by('lastRequestTime') # 在返回的v-e-v路径中,截取e-v输出。
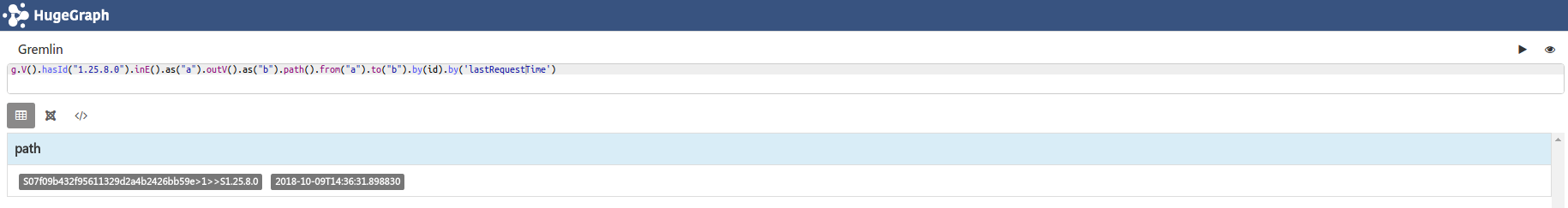
# 示例hasNext()
g.V().hasId("1.25.8.0").in().hasId('07f09b432f95611329d2a4b2426bb59e').hasNext() # 查看顶点“1.25.8.0”和顶点“07f09b432f95611329d2a4b2426bb59e”之间的边是否存在,返回bool值
10.顶点之间的最短路径
repeat().until()配合使用输出两个顶点之间的所有路径,使用repeat…until…结构不需要指定随机游走的步数。也可以使用times()指定步数,通常指定2/3步。emit()获取循环中的结果,节省查询时间。cyclicPath()返回环形路径,SimplePath()返回单向路径
由于user白名单构成的图数据中ip,UA和captchaId都没有out边,无法out().out().out()查询,故这里使用airport数据示例
g.V().has(k1, v1).repeat(out().simplePath()).until(has(k2, v2)).path().by(id()).limit(20)g.V().has('code','AUS').repeat(out()).times(2).has('code','SYD').path().by('code')
g.V().has('code','SAF').repeat(out()).emit().path().by('code').limit(10)
11.统计运算
关键词 sum(), max(), min(), mean()
g.E().limit(2000).not(values("count").is(inside(0, 20))).values("count") # `返回列表`[29,29,29,21,21,21,28,28,28,20,20,24,24,24,27,27,27]`
sum()对列表中所有数字求和
g.E().limit(2000).not(values("count").is(inside(0, 20))).values("count").sum() # `返回`[427]`
max()对列表中所有数字求最大值
g.E().limit(2000).not(values("count").is(inside(0, 20))).values("count").max() # `返回`[29]`
min()对列表中所有数字求最小值
g.E().limit(2000).not(values("count").is(inside(0, 20))).values("count").max() # `返回`[20]`
mean()对列表中所有数字求均值
g.E().limit(2000).not(values("count").is(inside(0, 20))).values("count").mean() # `返回`[25.11764705882353]`
12.随机采样coin和sample
coin(), sample()对数据采样。coin(0.1)是依0.1概率采样,sample(N)直接抽样N个样本。
g.V().hasLabel("user").limit(200).coin(0.5)g.V().hasLabel("user").limit(200).sample(20)
13.正则表达式做模糊查找
contains 包含;=~ 正则匹配,后接正则表达式
g.V().hasLabel('user').limit(20).hasId("0000018201b74cf860dbbba88664ccf1", "0000146ae2b2f5c8d17b088b74cc4192").filter{it.get().property("lastRequestTime").value().contains('2018-10-09T13')}g.V().hasLabel('user').limit(20).hasId("0000018201b74cf860dbbba88664ccf1", "0000146ae2b2f5c8d17b088b74cc4192").filter{it.get().property("lastRequestTime").value()==~'^2018-10-09.*'}
2.增加节点/边/属性
addV(label)增加顶点,addE(label)增加边,它们配合property使用同时增加边和顶点的属性。但是property() step 好像不能增加一个图scheme中本来没有的属性, 例如给ip增加risk_level属性。
g.V().limit(20).addV("ip").property(id, "127.0.0.2").dedup() # 增加ip顶点,id为127.0.0.2g.V().limit(20).addV("ip").property(id, "127.0.0.3").property("risk_level", "sb").dedup() # 增加risk_level属性报错,Undefined property key: 'risk_level'g.V().limit(20).addV("user").property(id, "user1").property('lastRequestTime', "time1").property("firstRequestTime", "time2") # 增加user顶点,id为user1# 在user1增加out边,到127.0.0.1
aa = g.V().hasId('127.0.0.1')
g.V().hasId('user1').addE("userIp").to(aa).property("count", 20)
3.删掉节点/边/属性
查询需要删除的顶点/边/属性,直接在后面加drop() step 删除。
g.E().drop() # 删除图中所有的边g.V().drop() # 删除图中所有的顶点
子查询
choose实现if…else…逻辑
# 如果lastRequestTime属性值大于2018-10-09T09:07:30.520245,输出lastRequestTime属性值,否则输出firstRequestTime属性值。
g.V().hasLabel("user").limit(2000).sample(20).choose(values('lastRequestTime').is(gt("2018-10-09T09:07:30.520245")), values('lastRequestTime'), values("firstRequestTime"))
union合并查询结果
g.V().hasLabel('ip').limit(20).hasId('1.25.8.0').as("a").union(select("a"), __.in().count())g.V("0012c388b4e5004f430344cfdc0cb4bf").union(constant("hello"), constant("wold")).fold()
数值计算
hugegraph不支持math() step,故无法将一个函数运用在某个属性值上。
其他要注意的问题
1.查询语句换行避免使用反斜杠,从“.”号后面换行。
g.V().hasLabel('airport').has('region',within('US-TX','US-LA','US-AZ','US-OK')).order().by('region',incr).valueMap().select('code','region')
2.保留关键词的冲突,当in() step不是直接跟在当前状态之后,则要使用__.in(),而不是in()。
g.V().has('code','AUS').union(in(),out())g.V().has("code", "AUS").union(__.in(), out())
集合操作
union, project, store, cap, aggregate, withSideEffect
union合并两个对象到一个列表
project("a", "b").by().by()创建一个map(“a”, “b”),a,b的具体内容取决于project step后的两个by()
store 创建一个set
cap将缓存的集合,返回到结果输出
aggregate("name") 创建一个临时的集合,赋给对象name
unfold 将集合展开,可以和repeat结合使用, repeat(unfold()).times(2), repeat(unfold()).until(count(local).is(1))
local 如果需要对集合中的内容做做一些操作,如排序、切片,需要用到local。这里使用local表示当前集合 order(local)、tail(local, 3)、range(local, 3, 5)、dedup(local)
sideEffect{} 使用lambda函数, sideEffect{print if.get().values("code").stratsWidth("Dal")}.count()





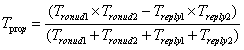


![DWM1000 测距原理简单分析 之 SS-TWR代码分析2 -- [蓝点无限]](https://img2018.cnblogs.com/blog/149290/201811/149290-20181119213011345-441600695.png)




![DWM1000 测距原理简单分析 之 SS-TWR代码分析1 -- [蓝点无限]](https://img2018.cnblogs.com/blog/149290/201811/149290-20181119212300721-444635258.png)