使用tc-config.xml 配置Terracotta服务器时,要考虑的因素之一是在Terracotta服务器(L2-L2)之间,从客户端到服务器(L1-L2)以及从服务器到客户端(L2-L1)之间的运行状况检查属性的规范。 。 在高可用性方案中,Terracotta会检查这些属性的配置组合,以确保这些组合落在特定范围内。 这篇博客文章演示了如何使用Groovy解析和分析给定的tc-config.xml文件,以确定Terracotta是否将提供有关这些属性配置的WARN级消息。
Terracotta 4.3.2 BigMemory Max高可用性指南 ( PDF )的“ About HealthChecker ”部分描述了HealthChecker的目的:“ HealthChecker是一个类似于TCP keep-alive的连接监视器。 HealthChecker在Terracotta服务器实例之间(在高可用性环境中)以及Terracotta服务器实例与客户端之间运行。 通过使用HealthChecker,Terracotta节点可以确定对等节点是否可达,处于运行状态或处于GC操作中。 如果对等节点不可访问或发生故障,则使用HealthChecker的Terracotta节点可以采取纠正措施。”
《 Terracotta 4.3.2 BigMemory Max高可用性指南》在“ HealthChecker属性 ”部分下包含一个表格,该表格明确说明了用于计算以确定是否应记录有关配置错误的高可用性的警告的Terracotta属性。 为每个组合指定了类似命名的属性(服务器对客户端[L2L1]的l2.healthcheck.l1.*属性,服务器对服务器[L2L2]的l2.healthcheck.l2.*和l1.healthcheck.l2.*客户端到服务器[L1L2]的l1.healthcheck.l2.* )和对高可用性配置检查重要的属性(刚刚引用的属性名称的*部分)为ping.enabled , ping.idletime , ping.interval , ping.probes , socketConnect , socketConnectCount和socketConnectTimeout 。 这篇文章的相关Groovy脚本假定一个L2-L2,L1-L2和L2-L1的ping.enabled和socketConnect属性都配置为true (这是所有L2L2,L1L2,L2L1组合的默认属性) 。
Terracotta类com.tc.l2.ha.HASettingsChecker检测到这些属性的两种组合,这些组合导致以短语“未正确配置高可用性:…”开头的WARN级别的日志消息。 这两个警告消息分别指出:“未正确配置高可用性:L1L2HealthCheck小于L2-L2HealthCheck + ElectionTime + ClientReconnectWindow”和“未正确配置高可用性:L1L2HealthCheck大于L2-L2HealthCheck + ElectionTime”。
Terracotta类HASettingsChecker的方法interNodeHealthCheckTime(int,int,int,int,int)实施了《 高可用性指南 》“ 计算HealthChecker最大值 ”部分中概述的公式:
pingIdleTime + ((socketConnectCount) * (pingInterval * pingProbes + socketConnectTimeout * pingInterval))
以下Groovy脚本分析指示的tc-config.xml文件,并将相同的运行状况检查属性检查应用于该文件的<tc-properties>部分中定义的相关属性。 此处显示的Groovy脚本除了要解析和分析的有效tc-config.xml文件之外,没有任何外部依赖项。 如果脚本访问com.tc.properties.TCPropertiesConsts中定义的String常量,而不是定义它们自己的硬编码版本,则脚本将更短并且需要的维护更少。
checkTCServerProperties.groovy
#!/usr/bin/env groovydef cli = new CliBuilder(usage: 'checkTCServerProperties -f <pathToTcConfigXmlFile> [-v] [-h]',header: '\nAvailable options (use -h for help):\n',footer: '\nParses referenced tc-config.xml file and analyzes its health check parameters..\n')
import org.apache.commons.cli.Option
cli.with
{h(longOpt: 'help', 'Usage Information', required: false)f(longOpt: 'file', 'Path to tc-config.xml File', args: 1, required: true)v(longOpt: 'verbose', 'Specifies verbose output', args: 0, required: false)
}
def opt = cli.parse(args)if (!opt) return
if (opt.h) cli.usage()String tcConfigFileName = opt.f
boolean verbose = opt.vprintln "Checking ${tcConfigFileName}'s properties..."
def tcConfigXml = new XmlSlurper().parse(tcConfigFileName)
TreeMap<String, String> properties = new TreeSet<>()
tcConfigXml."tc-properties".property.each
{ tcProperty ->String tcPropertyName = tcProperty.@nameString tcPropertyValue = tcProperty.@valueproperties.put(tcPropertyName, tcPropertyValue)
}
if (verbose)
{properties.each{ propertyName, propertyValue ->println "${propertyName}: ${propertyValue}"}
}boolean isL2L1PingEnabled = extractBoolean(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l1.ping.enabled")
boolean isL2L2PingEnabled = extractBoolean(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l2.ping.enabled")
boolean isL1L2PingEnabled = extractBoolean(properties, "l1.healthcheck.l2.ping.enabled")
boolean isPingEnabled = isL2L1PingEnabled && isL2L2PingEnabled && isL1L2PingEnabled
println "Health Check Ping ${isPingEnabled ? 'IS' : 'is NOT'} enabled."
if (!isPingEnabled)
{System.exit(-1)
}Long pingIdleTimeL2L1 = extractLong(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l1.ping.idletime")
Long pingIdleTimeL2L2 = extractLong(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l2.ping.idletime")
Long pingIdleTimeL1L2 = extractLong(properties, "l1.healthcheck.l2.ping.idletime")Long pingIntervalL2L1 = extractLong(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l1.ping.interval")
Long pingIntervalL2L2 = extractLong(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l2.ping.interval")
Long pingIntervalL1L2 = extractLong(properties, "l1.healthcheck.l2.ping.interval")Long pingProbesL2L1 = extractLong(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l1.ping.probes")
Long pingProbesL2L2 = extractLong(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l2.ping.probes")
Long pingProbesL1L2 = extractLong(properties, "l1.healthcheck.l2.ping.probes")boolean socketConnectL2L1 = extractBoolean(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l1.socketConnect")
boolean socketConnectL2L2 = extractBoolean(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l2.socketConnect")
boolean socketConnectL1L2 = extractBoolean(properties, "l1.healthcheck.l2.socketConnect")if (!socketConnectL2L1 || !socketConnectL2L2 || !socketConnectL1L2)
{println "Socket connect is disabled."System.exit(-2)
}Long socketConnectTimeoutL2L1 = extractLong(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l1.socketConnectTimeout")
Long socketConnectTimeoutL2L2 = extractLong(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l2.socketConnectTimeout")
Long socketConnectTimeoutL1L2 = extractLong(properties, "l1.healthcheck.l2.socketConnectTimeout")Long socketConnectCountL2L1 = extractLong(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l1.socketConnectCount")
Long socketConnectCountL2L2 = extractLong(properties, "l2.healthcheck.l2.socketConnectCount")
Long socketConnectCountL1L2 = extractLong(properties, "l1.healthcheck.l2.socketConnectCount")Long maximumL2L1 = calculateMaximumTime(pingIdleTimeL2L1, pingIntervalL2L1, pingProbesL2L1, socketConnectCountL2L1, socketConnectTimeoutL2L1)
Long maximumL2L2 = calculateMaximumTime(pingIdleTimeL2L2, pingIntervalL2L2, pingProbesL2L2, socketConnectCountL2L2, socketConnectTimeoutL2L2)
Long maximumL1L2 = calculateMaximumTime(pingIdleTimeL1L2, pingIntervalL1L2, pingProbesL1L2, socketConnectCountL1L2, socketConnectTimeoutL1L2)if (verbose)
{println "L2-L1 Maximum Time: ${maximumL2L1}"println "L2-L2 Maximum Time: ${maximumL2L2}"println "L1-L2 Maximum Time: ${maximumL1L2}"
}long electionTime = 5000
long clientReconnectWindow = 120000long maximumL2L2Election = maximumL2L2 + electionTime
long maximumL2L2ElectionReconnect = maximumL2L2Election + clientReconnectWindowif (verbose)
{println "L2-L2 Maximum Time + ElectionTime: ${maximumL2L2Election}"println "L2-L2 Maximum Time + ElectionTime + Client Reconnect Window: ${maximumL2L2ElectionReconnect}"
}if (maximumL1L2 < maximumL2L2Election)
{print "WARNING: Will lead to 'High Availability Not Configured Properly: L1L2HealthCheck should be more than L2-L2HealthCheck + ElectionTime' "println "because ${maximumL1L2} < ${maximumL2L2Election}."
}
else if (maximumL1L2 > maximumL2L2ElectionReconnect)
{print "WARNING: Will lead to 'High Availability Not Configured Properly: L1L2HealthCheck should be less than L2-L2HealthCheck + ElectionTime + ClientReconnectWindow' "println "because ${maximumL1L2} > ${maximumL2L2ElectionReconnect}."
}/*** Extract a Boolean value for the provided property name from the provided* properties.** @return Boolean value associated with the provided property name.*/
boolean extractBoolean(TreeMap<String, String> properties, String propertyName)
{return properties != null && properties.containsKey(propertyName)? Boolean.valueOf(properties.get(propertyName)): false
}/*** Extract a Long value for the provided property name from the provided* properties.** @return Long value associated with the provided property name.*/
Long extractLong(TreeMap<String, String> properties, String propertyName)
{return properties != null && properties.containsKey(propertyName)? Long.valueOf(properties.get(propertyName)): 0
}/*** Provides the maximum time as calculated using the following formula:** Maximum Time =* (ping.idletime) + socketConnectCount ** [(ping.interval * ping.probes) + (socketConnectTimeout * ping.interval)]*/
Long calculateMaximumTime(Long pingIdleTime, Long pingInterval, Long pingProbes,Long socketConnectCount, Long socketConnectTimeout)
{return pingIdleTime + socketConnectCount * pingInterval * (pingProbes + socketConnectTimeout)
} 该脚本也将在GitHub上可用 。 在某个时候,我可能会在该GitHub版本中解决其某些弱点和局限性。 具体来说,如上所示,该脚本当前采用“选举时间”和“客户端重新连接窗口”的默认值,但是可以从tc-config.xml文件中进行解析。
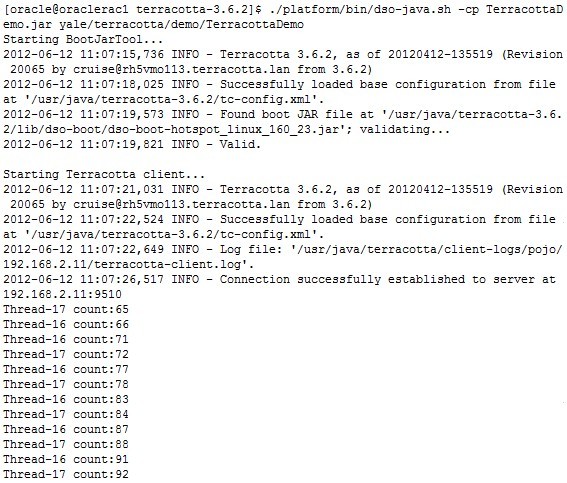
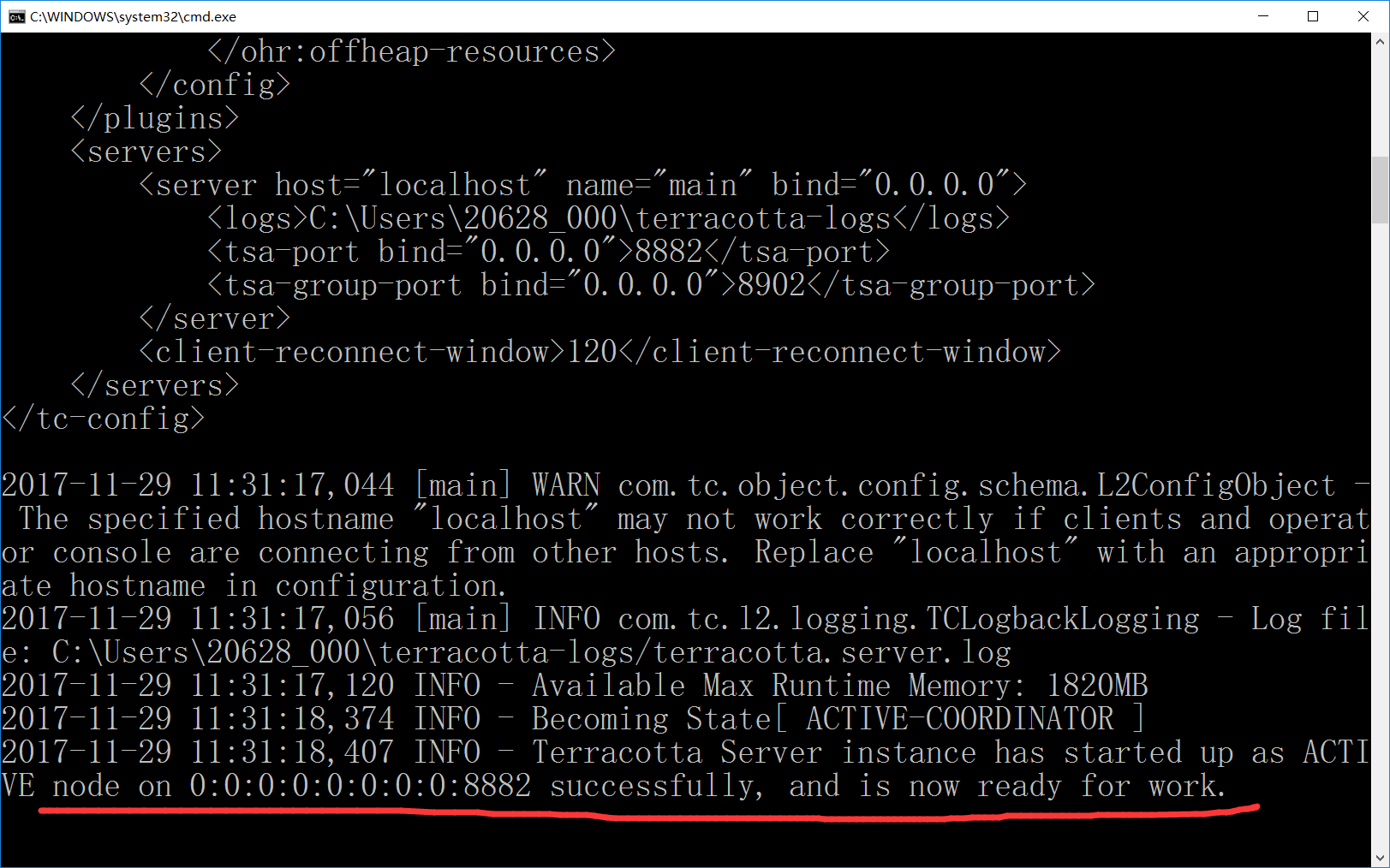
以下屏幕快照展示了该脚本针对各种tc-config.xml文件的操作。 第一个图像描述了未启用ping时脚本的行为。 第二张图描述了未启用套接字检查时脚本的行为。 第三幅和第四幅图像描述了高可用性配置的属性未正确配置时可能遇到的两个警告。 第五张图片描绘了脚本的完全成功执行,该脚本指示运行状况检查属性的配置在预期范围内。
Ping未启用 (非默认)
套接字未启用 (非默认)
HealthCheck属性警告#1
HealthCheck属性警告#2
已正确启用和配置HealthCheck属性
我使用了一个简单的电子表格来执行这些计算,并且效果很好。 但是,本文讨论的Groovy脚本允许自动分析候选tc-config.xml文件,而不需要将值复制并粘贴到电子表格中。 可以修改Groovy脚本以使用Terracotta提供的Java文件,如前所述。 还有其他一些增强功能可以使脚本更有用,例如从tc-config.xml文件解析客户端重新连接窗口和选举时间,而不是采用默认值。
翻译自: https://www.javacodegeeks.com/2017/03/using-groovy-quickly-analyze-terracotta-healthcheck-properties.html