一、官方手册中的描述
1、Manual/Coroutines
函数在调用时, “从调用到返回” 都发生在一帧之内,想要处理 “随时间推移进行的事务”, 相比Update,使用协程来执行此类任务会更方便。
协程在创建时,通常是一个 “返回值类型 为 IEnumerator”、“函数体中包含 yield return 语句 ” 的函数。
yiled return 可以暂停协程的执行,并在恰当时候恢复。具体在何时恢复,由 yield 的返回值决定。
启动协程,必须使用 MonoBehaviour 的 StartCoroutine 方法。
停止协程,可以使用 MonoBehaviour 的 StopCoroutine 方法 或 StopAllCoroutine 方法。
注意:以下情况也可能使协程停止:
1)、销毁启动协程的组件(GameObject.Destory(component);) ==> 协程停止
2)、禁用启动协程的组件(component.enabled = false;)==> 协程不停止
3)、销毁启动协程的组件所在的物体(GameObject.Destory(gameobject);) ==> 协程停止
4)、隐藏启动协程的组件所在的物体(gameobject.SetActive(false);) ==> 协程停止
2、MonoBehaviour.StartCoroutine
StartCoroutine 方法总是立刻返回一个 Coroutine 对象(同步返回)。
无法保证协同程序按其启动顺序结束,即使他们在同一帧中完成也是如此(异步无序完成)。
可以在一个协程中启动另一个协程(支持协程嵌套)。
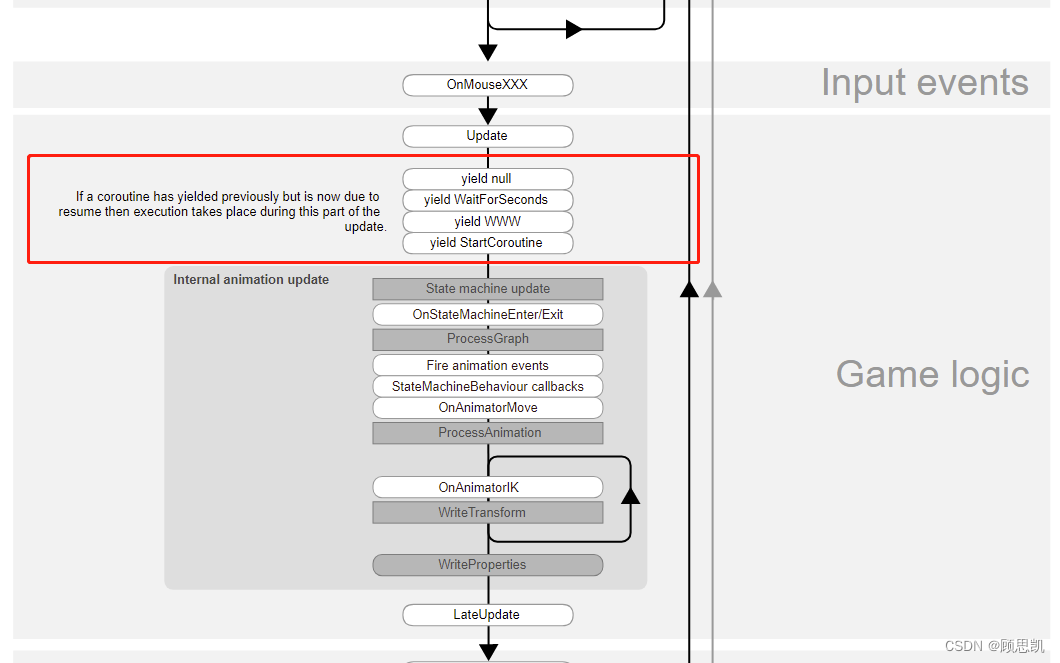
二、Unity中的 yield 语句类型
1、yield break; //打断协程运行
2、yield return null; //挂起协程,并从下一帧继续
3、yield return + “任意数字”; //挂起协程,并从下一帧继续
4、yield return + “bool值”; //挂起协程,并从下一帧继续
5、yield return + “任意字符串”; //挂起协程,并从下一帧继续
6、yield return + “普通Object”; //挂起协程,并从下一帧继续
7、yield return + “任意实现了 IEnumerator 接口的对象”。重要!(可嵌套)
Unity 中,常见的、直接或间接实现了 IEnumerator 接口的类有:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CustomYieldInstruction (abstarct) ——|> IEnumerator (interface)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WaitUnitil (sealed) ——|> CustomYieldInstruction
WaitWhile (sealed) ——|> CustomYieldInstruction
WaitForSecondsRealtime (非sealed,但未发现子类) ——|> CustomYieldInstruction
WWW (非sealed,但未发现子类) ——|> CustomYieldInstruction
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
随着Unity更新或在一些可选的Package中,可能有更多。。。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8、yield return + “任意继承了 YieldInstruction 类 ([UsedByNativeCode],源码C#层中无具体实现) 的对象”。重要!(可嵌套)
Unity 中,常见的、直接或间接继承了 YieldInstruction 类的类有:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WaitForSeconds (sealed) ——|> YieldInstruction
Coroutine (sealed) ——|> YieldInstruction (Coroutine 是 StartCoroutine方法的返回值,意味着协程中可嵌套协程)
WaitForEndOfFrame (sealed) ——|> YieldInstruction
WaitForFixedUpdate (sealed) ——|> YieldInstruction
AsyncOperation ——|> YieldInstruction
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AssetBundleCreateRequest (非sealed,但未发现子类) ——|> AsyncOperation
AssetBundleRecompressOperation (非sealed,但未发现子类) ——|> AsyncOperation
AssetBundleRequest (非sealed,但未发现子类) ——|> AsyncOperation
ResourceRequest (非sealed,但未发现子类) ——|> AsyncOperation
UnityEngine.Networking.UnityWebRequestAsyncOperation (非sealed,但未发现子类) ——|> AsyncOperation
UnityEngine.iOS.OnDemandResourcesRequest (sealed) ——|> AsyncOperation
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
随着Unity更新或在一些可选的Package中,可能有更多。。。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
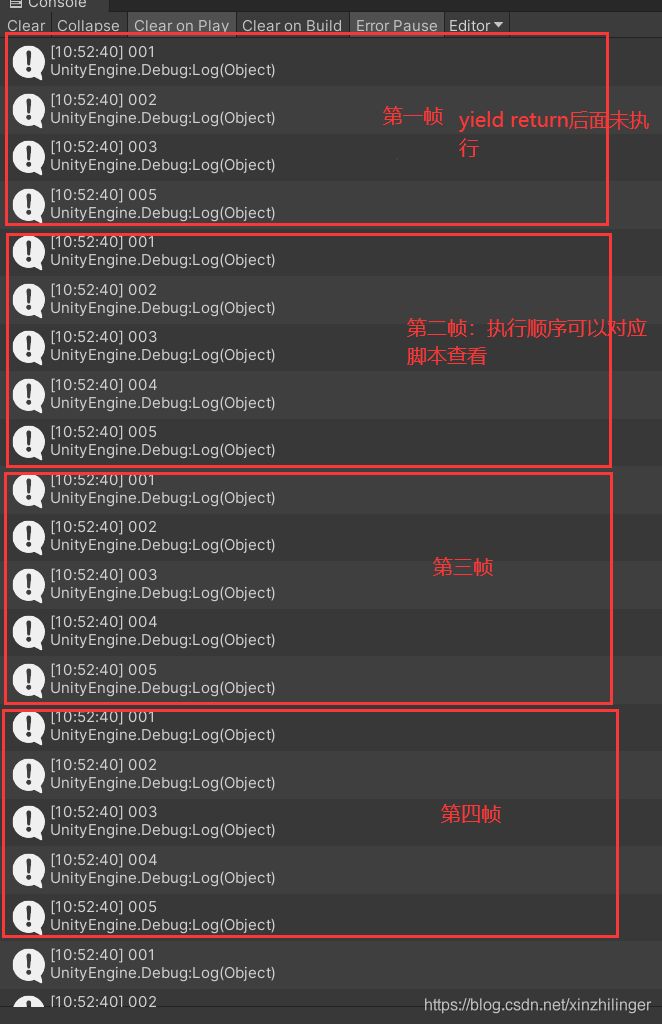
***测试验证 第2、3、4、5、6条 如下:
using System.Collections;
using UnityEngine;public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{void Start(){StartCoroutine(Func1());}IEnumerator Func1(){Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return null;Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return 0;Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return 1;Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return 99; //其他整数Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return 0.5f; //浮点数值Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return false; //bool值Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return "Hi NRatel!"; //字符串Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return new Object(); //任意对象Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);}
}
***测试验证 第7条 如下:
using System.Collections;
using UnityEngine;public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{void Start(){StartCoroutine(Func1());}IEnumerator Func1(){Debug.Log("Func1");yield return Func2();}IEnumerator Func2(){Debug.Log("Func2");yield return Func3();}IEnumerator Func3(){Debug.Log("Func3");yield return null;}
}
三、Unity协程实现原理
1、C# 的迭代器。
现在已经知道:协程肯定与IEnumerator有关,因为启动协程时需要一个 IEnumerator 对象。
而 IEnumerator 是C#实现的 迭代器模式 中的 枚举器(用于迭代的游标)。
迭代器相关接口定义如下:
namespace System.Collections
{//可枚举(可迭代)对象接口public interface IEnumerable{IEnumerator GetEnumerator();}//迭代游标接口public interface IEnumerator{object Current { get; }bool MoveNext();void Reset();}
}参考 MSDN C#文档中对于 IEnumerator、IEnumerable、迭代器 的描述。
利用 IEnumerator 对象,可以对与之关联的 IEnumerable 集合 进行迭代:
1)、通过 IEnumerator 的 Current 方法,可以获取集合中位于枚举数当前位置的元素。
2)、通过 IEnumerator 的 MoveNext 方法,可以将枚举数推进到集合的下一个元素。如果 MoveNext 越过集合的末尾, 则枚举器将定位在集合中最后一个元素之后, 同时 MoveNext 返回 false。 当枚举器位于此位置时, 对 MoveNext 的后续调用也将返回 false 。如果最后一次调用 MoveNext 时返回 false,则 Current 未定义(结果为null)。
3)、通过 IEnumerator 的 Reset 方法,可以将“迭代游标” 设置为其初始位置,该位置位于集合中第一个元素之前。
2、C# 的 yield 关键字。
C#编译器在生成IL代码时,会将一个返回值类型为 IEnumerator 的方法(其中包含一系列的 yield return 语句),构建为一个实现了 IEnumerator 接口的对象。
注意,yield 是C#的关键字,而非Unity定义!IEnumerator 对象 也可以直接用于迭代,并非只能被Unity的 StartCoroutine 使用!
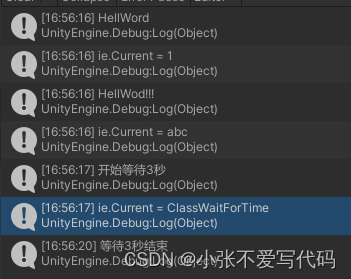
using System.Collections;
using UnityEngine;public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{void Start(){IEnumerator e = Func();while (e.MoveNext()){Debug.Log(e.Current);}}IEnumerator Func(){yield return 1;yield return "Hi NRatel!";yield return 3;}
}
对上边C#代码生成的Dll进行反编译,查看IL代码:


3、Unity 的协程。
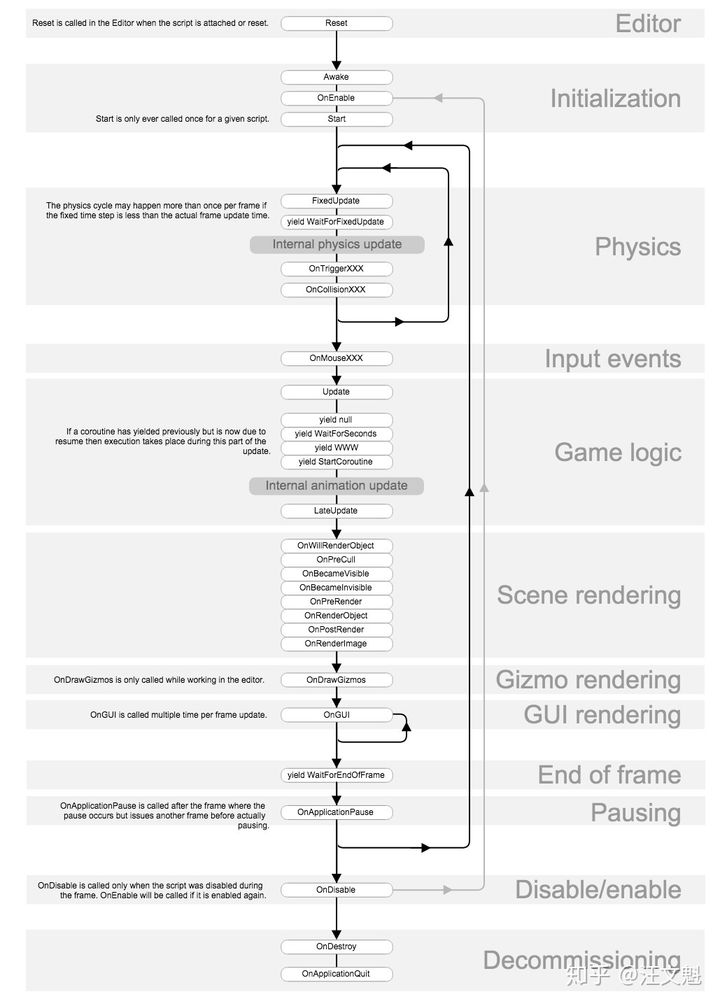
Unity 协程是在逐帧迭代的,这点可以从 Unity 脚本生命周期 中看出。

可以大胆猜测一下,实现出自己的协程(功能相似,能够说明逐帧迭代的原理,不是Unity源码):
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{private Dictionary<IEnumerator, IEnumerator> recoverDict; //key:当前迭代器 value:子迭代器完成后需要恢复的父迭代器private IEnumerator enumerator;private void Start(){//Unity自身的协程//StartCoroutine(Func1());//自己实现的协程StarMyCoroutine(Func1());}private void StarMyCoroutine(IEnumerator e){recoverDict = new Dictionary<IEnumerator, IEnumerator>();enumerator = e;recoverDict.Add(enumerator, null); //完成后不需要恢复任何迭代器}private void LateUpdate(){if (enumerator != null){DoEnumerate(enumerator);}}private void DoEnumerate(IEnumerator e){object current;if (e.MoveNext()){current = e.Current;}else{//迭代结束IEnumerator recoverE = recoverDict[e];if (recoverE != null){recoverDict.Remove(e);}//恢复至父迭代器, 若没有则会至为nullenumerator = recoverE;return;}//null,什么也不做,下一帧继续if (current == null) { return; }Type type = current.GetType();//基础类型,什么也不做,下一帧继续if (current is System.Int32) { return; }if (current is System.Boolean) { return; }if (current is System.String) { return; }//IEnumerator 类型, 等待内部嵌套的IEnumerator迭代完成再继续if (current is IEnumerator){//切换至子迭代器enumerator = current as IEnumerator;recoverDict.Add(enumerator, e);return;}//YieldInstruction 类型, 猜测也是类似IEnumerator的实现if (current is YieldInstruction){//省略实现return;}}IEnumerator Func1(){Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return null;Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return "Hi NRatel!";Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return 3;Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return new WaitUntil(() =>{return Time.frameCount == 20;});Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);yield return Func2();Debug.Log("Time.frameCount: " + Time.frameCount);}IEnumerator Func2(){Debug.Log("XXXXXXXXX");yield return null;Debug.Log("YYYYYYYYY");yield return Func3(); //嵌套 IEnumerator}IEnumerator Func3(){Debug.Log("AAAAAAAA");yield return null;Debug.Log("BBBBBBBB");yield return null;}
}对比结果,基本可以达成协程作用,包括 IEnumerator 嵌套。
但是 Time.frameCount 的结果不同,想来实现细节必然是有差别的。

四、部分Unity源码分析
1、CustomYieldInstruction 类
可以继承该类,并实现自己的、需要异步等待的类。
原理:
当协程中 yield return “一个CustomYieldInstruction的子类”; 其实就相当于在原来的 迭代器A 中,插入了一个 新的迭代器B。
当迭代程序进入 B ,如果 keepWaiting 为 true,MoveNext() 就总是返回 true。
上面已经说过,迭代器在迭代时,MoveNext() 返回false 才标志着迭代完成!
那么,B 就总是完不成,直到 keepWaiting 变为 false。
这样 A 运行至 B处就 处于了 等待B完成的状态,相当于A挂起了。
猜测 YieldInstruction 也是类似的实现。
// Unity C# reference source
// Copyright (c) Unity Technologies. For terms of use, see
// https://unity3d.com/legal/licenses/Unity_Reference_Only_Licenseusing System.Collections;namespace UnityEngine
{public abstract class CustomYieldInstruction : IEnumerator{public abstract bool keepWaiting{get;}public object Current{get{return null;}}public bool MoveNext() { return keepWaiting; } public void Reset() {}}
}2、WaitUntil 类
语义为 “等待...直到满足...”
继承自 CustomYieldInstruction,需要等待时让 m_Predicate 返回 false (keepWating为true)。
// Unity C# reference source
// Copyright (c) Unity Technologies. For terms of use, see
// https://unity3d.com/legal/licenses/Unity_Reference_Only_Licenseusing System;namespace UnityEngine
{public sealed class WaitUntil : CustomYieldInstruction{Func<bool> m_Predicate;public override bool keepWaiting { get { return !m_Predicate(); } }public WaitUntil(Func<bool> predicate) { m_Predicate = predicate; }}
}3、WaitWhile 类
语义为 “等待...如果满足...”
继承自 CustomYieldInstruction,需要等待时让 m_Predicate 返回 true (keepWating为true)。
与 WaitUntil 的实现恰好相反。
// Unity C# reference source
// Copyright (c) Unity Technologies. For terms of use, see
// https://unity3d.com/legal/licenses/Unity_Reference_Only_Licenseusing System;namespace UnityEngine
{public sealed class WaitWhile : CustomYieldInstruction{Func<bool> m_Predicate;public override bool keepWaiting { get { return m_Predicate(); } }public WaitWhile(Func<bool> predicate) { m_Predicate = predicate; }}
}