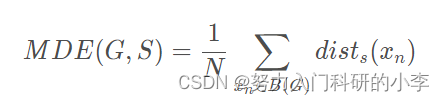原理
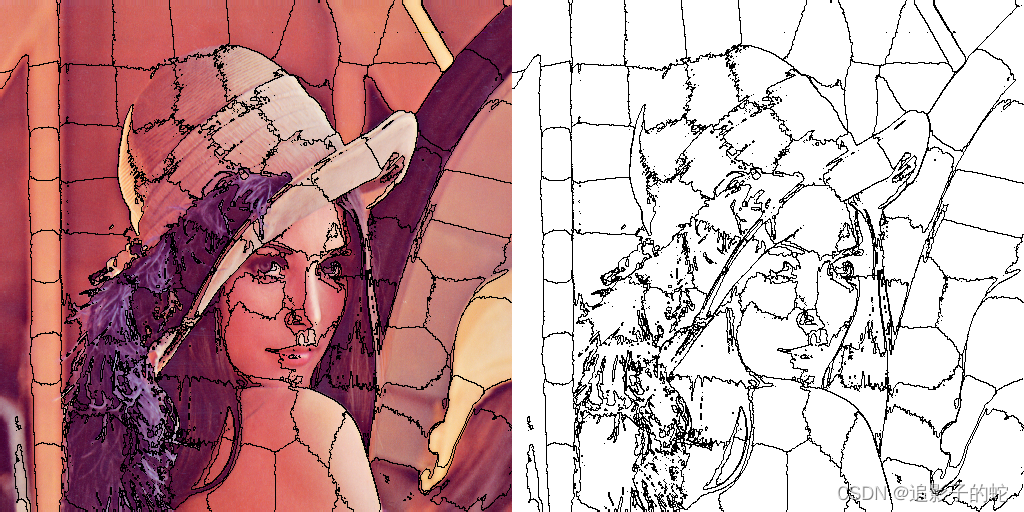
超像素概念是2003年Xiaofeng Ren提出和发展起来的图像分割技术,是指具有相似纹理、颜色、亮度等特征的相邻像素构成的有一定视觉意义的不规则像素块。它利用像素之间特征的相似性将像素分组,用少量的超像素代替大量的像素来表达图片特征,很大程度上降低了图像后处理的复杂度,所以通常作为分割算法的预处理步骤。
常见的超像素分割方法包括: Graph-based 、NCut 、Turbopixel 、 Quick-shift 、 Graph-cut a、Graph-cut b 以及 SLIC 。
其中,SLIC(simple linear iterativeclustering),即 简单线性迭代聚类 。
它是2010年提出的一种思想简单、实现方便的算法,将彩色图像转化为CIELAB颜色空间和XY坐标下的5维特征向量,然后对5维特征向量构造距离度量标准,对图像像素进行局部聚类的过程。
SLIC主要优点如下:
- 生成的超像素如同细胞一般紧凑整齐,邻域特征比较容易表达。这样基于像素的方法可以比较容易的改造为基于超像素的方法。
- 不仅可以分割彩色图,也可以兼容分割灰度图。
- 需要设置的参数非常少,默认情况下只需要设置一个预分割的超像素的数量。
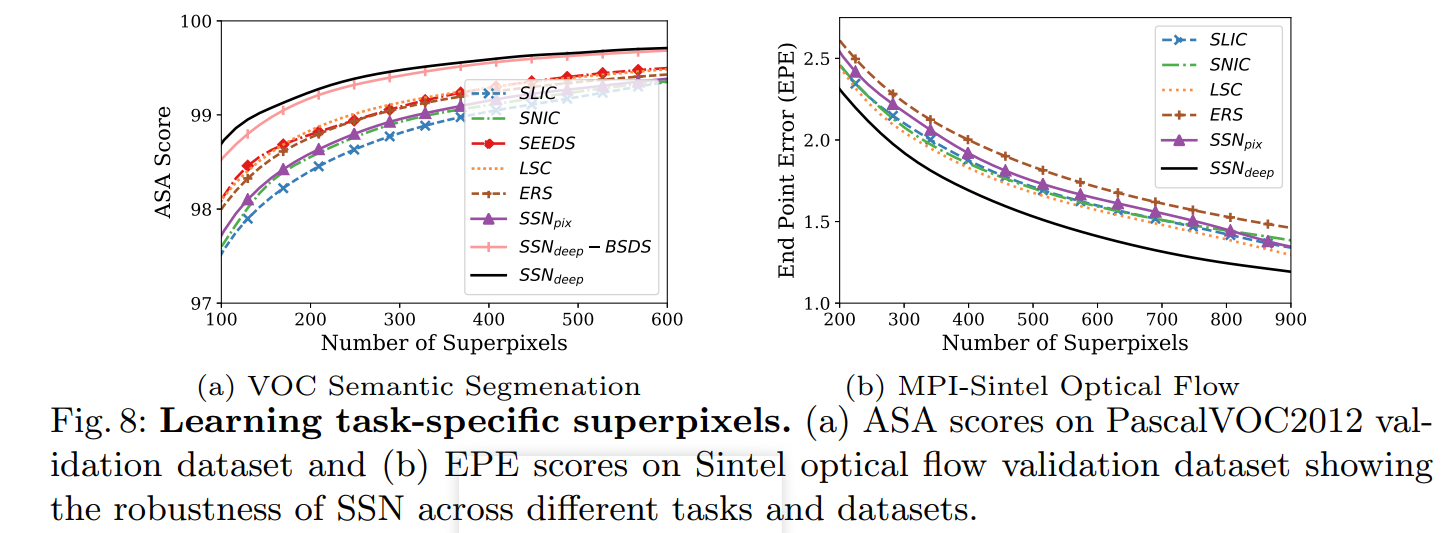
- 相比其他的超像素分割方法,SLIC在运行速度、生成超像素的紧凑度、轮廓保持方面都比较理想。
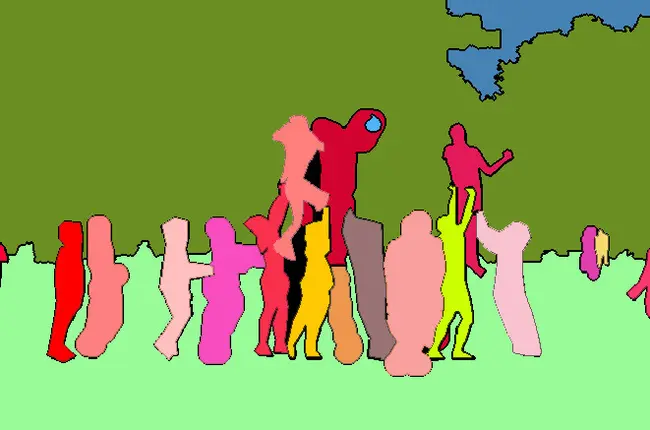
效果图
经过观察发现,在迭代至第10轮后,分割效果基本不再发生变化。
原图
K=64 时
第1轮迭代,效果图:

第20轮迭代,效果图:

K=128 时
第1轮迭代,效果图:

第20轮迭代,效果图:

K=256 时
第1轮迭代,效果图:

第20轮迭代,效果图:

K=1024 时
第1轮迭代,效果图:

第20轮迭代,效果图:
实现代码
代码是我上网找来的,稍微改动了一丢丢。
原代码出处:SLIC算法分割超像素原理及Python实现
import math
from skimage import io, color
import numpy as np
from tqdm import trangeclass Cluster(object):cluster_index = 1def __init__(self, h, w, l=0, a=0, b=0):self.update(h, w, l, a, b)self.pixels = []self.no = self.cluster_indexself.cluster_index += 1def update(self, h, w, l, a, b):self.h = hself.w = wself.l = lself.a = aself.b = bdef __str__(self):return "{},{}:{} {} {} ".format(self.h, self.w, self.l, self.a, self.b)def __repr__(self):return self.__str__()class SLICProcessor(object):@staticmethoddef open_image(path):"""Return:3D array, row col [LAB]"""rgb = io.imread(path)lab_arr = color.rgb2lab(rgb)return lab_arr@staticmethoddef save_lab_image(path, lab_arr):"""Convert the array to RBG, then save the image"""rgb_arr = color.lab2rgb(lab_arr)io.imsave(path, rgb_arr)def make_cluster(self, h, w):return Cluster(h, w,self.data[h][w][0],self.data[h][w][1],self.data[h][w][2])def __init__(self, filename, K, M):self.K = Kself.M = Mself.data = self.open_image(filename)self.image_height = self.data.shape[0]self.image_width = self.data.shape[1]self.N = self.image_height * self.image_widthself.S = int(math.sqrt(self.N / self.K))self.clusters = []self.label = {}self.dis = np.full((self.image_height, self.image_width), np.inf)def init_clusters(self):h = self.S / 2w = self.S / 2while h < self.image_height:while w < self.image_width:self.clusters.append(self.make_cluster(h, w))w += self.Sw = self.S / 2h += self.Sdef get_gradient(self, h, w):if w + 1 >= self.image_width:w = self.image_width - 2if h + 1 >= self.image_height:h = self.image_height - 2gradient = self.data[w + 1][h + 1][0] - self.data[w][h][0] + \self.data[w + 1][h + 1][1] - self.data[w][h][1] + \self.data[w + 1][h + 1][2] - self.data[w][h][2]return gradientdef move_clusters(self):for cluster in self.clusters:cluster_gradient = self.get_gradient(cluster.h, cluster.w)for dh in range(-1, 2):for dw in range(-1, 2):_h = cluster.h + dh_w = cluster.w + dwnew_gradient = self.get_gradient(_h, _w)if new_gradient < cluster_gradient:cluster.update(_h, _w, self.data[_h][_w][0], self.data[_h][_w][1], self.data[_h][_w][2])cluster_gradient = new_gradientdef assignment(self):for cluster in self.clusters:for h in range(cluster.h - 2 * self.S, cluster.h + 2 * self.S):if h < 0 or h >= self.image_height: continuefor w in range(cluster.w - 2 * self.S, cluster.w + 2 * self.S):if w < 0 or w >= self.image_width: continueL, A, B = self.data[h][w]Dc = math.sqrt(math.pow(L - cluster.l, 2) +math.pow(A - cluster.a, 2) +math.pow(B - cluster.b, 2))Ds = math.sqrt(math.pow(h - cluster.h, 2) +math.pow(w - cluster.w, 2))D = math.sqrt(math.pow(Dc / self.M, 2) + math.pow(Ds / self.S, 2))if D < self.dis[h][w]:if (h, w) not in self.label:self.label[(h, w)] = clustercluster.pixels.append((h, w))else:self.label[(h, w)].pixels.remove((h, w))self.label[(h, w)] = clustercluster.pixels.append((h, w))self.dis[h][w] = Ddef update_cluster(self):for cluster in self.clusters:sum_h = sum_w = number = 0for p in cluster.pixels:sum_h += p[0]sum_w += p[1]number += 1_h = sum_h / number_w = sum_w / numbercluster.update(_h, _w, self.data[_h][_w][0], self.data[_h][_w][1], self.data[_h][_w][2])def save_current_image(self, name):image_arr = np.copy(self.data)for cluster in self.clusters:for p in cluster.pixels:image_arr[p[0]][p[1]][0] = cluster.limage_arr[p[0]][p[1]][1] = cluster.aimage_arr[p[0]][p[1]][2] = cluster.bimage_arr[cluster.h][cluster.w][0] = 0image_arr[cluster.h][cluster.w][1] = 0image_arr[cluster.h][cluster.w][2] = 0self.save_lab_image(name, image_arr)def iterate_10times(self):self.init_clusters()self.move_clusters()for i in trange(20):self.assignment()self.update_cluster()name = 'Elegent_Girl_M{m}_K{k}_loop{loop}.jpg'.format(loop=i, m=self.M, k=self.K)self.save_current_image(name)if __name__ == '__main__':for k in [64, 128, 256, 1024]:p = SLICProcessor('800.jpg', k, 30)p.iterate_10times()
打印结果:
0%| | 0/20 [00:00<?, ?it/s]/home/user/anaconda2/lib/python2.7/site-packages/skimage/util/dtype.py:111: UserWarning: Possible precision loss when converting from float64 to uint8"%s to %s" % (dtypeobj_in, dtypeobj))
100%|##########| 20/20 [32:36<00:00, 97.83s/it]
100%|##########| 20/20 [24:37<00:00, 73.88s/it]
100%|##########| 20/20 [21:30<00:00, 64.55s/it]
100%|##########| 20/20 [18:49<00:00, 56.46s/it]Process finished with exit code 0