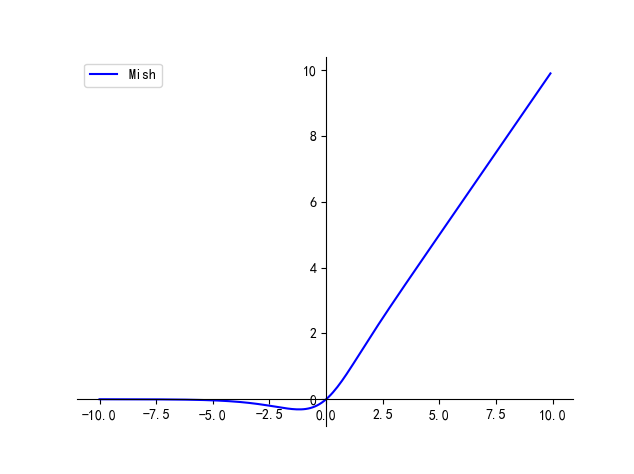
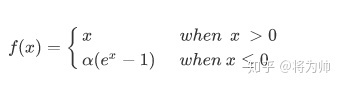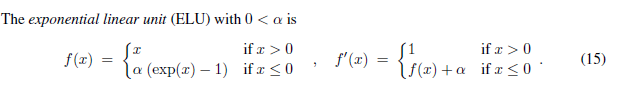一文理解常用激活函数
1. Sigmoid
公式:
Sigmoid ( x ) = 1 1 + exp ( − x ) \text{Sigmoid}(x) = \frac{1}{1 + \exp(-x)} Sigmoid(x)=1+exp(−x)1
Sigmoid的函数形状如下图所示:

对应的导数形式如下图所示:

Sigmoid函数的优点:
- 便于求导,可以看到Sigmoid的梯度是平滑的函数
- 能够压缩数据,数据会压缩在0-1之间
- 适合用于前向传播
Sigmoid函数的缺点:
- 容易出现梯度消失
- Sigmoid的输出不是0均值
- 幂函数计算相对比较耗时
2. Tanh
公式:
Tanh ( x ) = tanh ( x ) = exp ( x ) − exp ( − x ) exp ( x ) + exp ( − x ) \text{Tanh}(x) = \tanh(x) = \frac{\exp(x) - \exp(-x)}{\exp(x) + \exp(-x)} Tanh(x)=tanh(x)=exp(x)+exp(−x)exp(x)−exp(−x)
Tanh的函数形状如下图所示:

对应的导数形式如下图所示:

tanh函数的优点:
- 将数据收敛到-1~+1之间,并且输出是0均值
- 收敛速度比Sigmoid函数更快
tanh函数的缺点:
- 仍然存在梯度消失的问题
- 仍然存在幂指數运算,计算成本很高
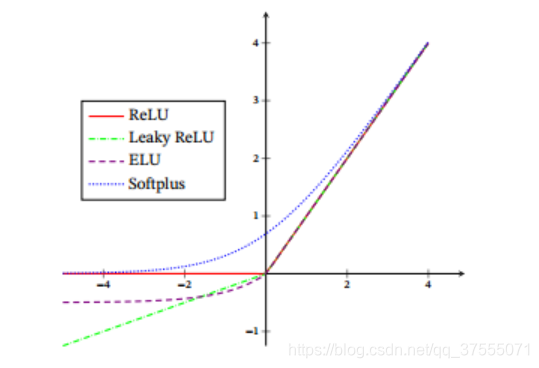
3. ReLU
公式:
f ( x ) = max ( 0 , x ) f(x)=\max(0, x) f(x)=max(0,x)
ReLU的函数形状如下图所示:

对应的导数形式如下图所示:

ReLU函数的优点:
- 收敛速度更快
- 解决了一部分梯度消失的问题
ReLU函数的缺点:
- 没有完全解决梯度消失的问题,在x轴为负的部分神经元的梯度始终为0,相当于神经元一旦失活后,就不会被激活
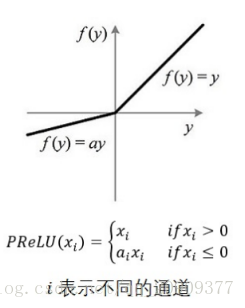
4. LeakyReLU
公式:
LeakyReLU ( x ) = max ( 0 , x ) + negative_slope ∗ min ( 0 , x ) \text{LeakyReLU}(x) = \max(0, x) + \text{negative\_slope} * \min(0, x) LeakyReLU(x)=max(0,x)+negative_slope∗min(0,x)
LeakyReLU的函数形状如下图所示:

对应的导数形式如下图所示:

LeakyReLU函数的优点:
- 解决了ReLU中神经一旦失活,就无法再次激活的问题
LeakyReLU函数的缺点:
- 无法为正负输入值提供一致的关系预测,可以看到不同区间的函数是不一致的
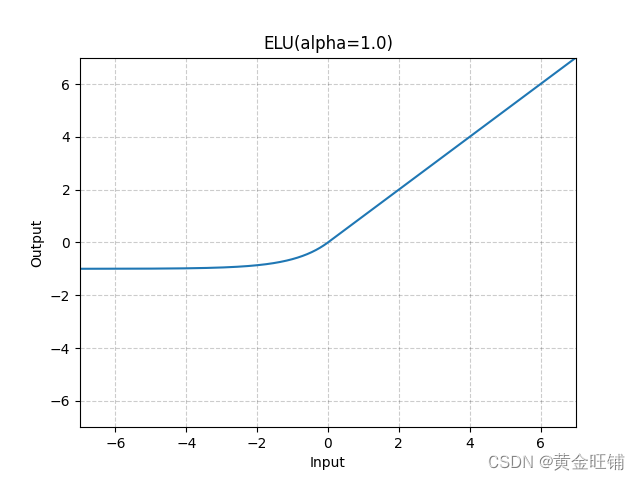
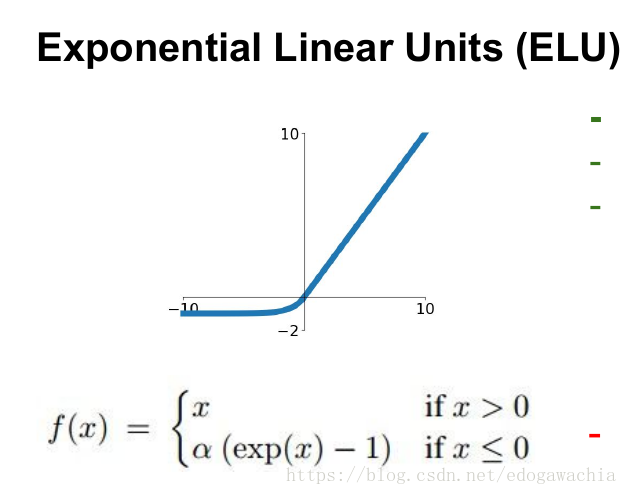
5. ELU
公式:
ELU ( x ) = max ( 0 , x ) + min ( 0 , α ∗ ( exp ( x ) − 1 ) ) \text{ELU}(x) = \max(0,x) + \min(0, \alpha * (\exp(x) - 1)) ELU(x)=max(0,x)+min(0,α∗(exp(x)−1))
ELU的函数形状如下图所示:

对应的导数形式如下图所示:

ELU函数的优点:
- 有ReLU所有的优点
ELU函数的缺点:
- 计算相较ReLU来说会比较复杂,效果也不一定比ELU好
6. GELU
公式:
GELU ( x ) = x ∗ Φ ( x ) \text{GELU}(x) = x * \Phi(x) GELU(x)=x∗Φ(x)
Φ ( x ) \Phi(x) Φ(x) is the Cumulative Distribution Function for Gaussian Distribution
GELU的函数形状如下图所示:

对应的导数形式如下图所示:
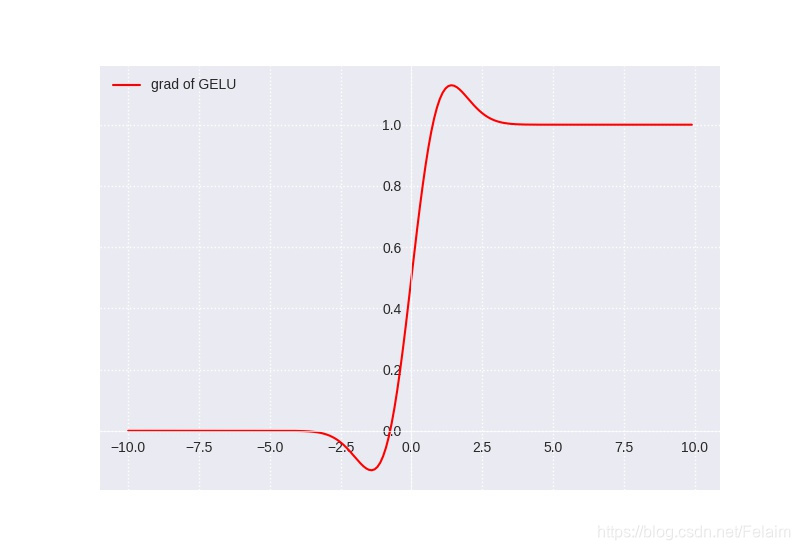
GELU函数的优点:
- 之前描述的所有的激活函数正则化和激活函数是分开进行的,GELU是同时进行正则化和激活函数
GELU函数的缺点:
- 暂无,等待补充
PS: 上述图例代码
import torch
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
import osfunc_pic_res = "./func_pic_res/"
if not os.path.exists(func_pic_res):os.makedirs(func_pic_res)def xyplot(x_vals, y_vals, name):plt.figure()plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (5, 3.5)plt.plot(x_vals.detach().numpy(), y_vals.detach().numpy(), label=name, linewidth=1.5, color='#FF0000')plt.grid(True, linestyle=':')plt.legend(loc='upper left')# dark_background, seaborn, ggplotplt.style.use("seaborn")ax = plt.gca()ax.spines['right'].set_color("none")ax.spines['top'].set_color("none")ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(("data", 0))ax.spines['left'].set_position(("data", 0))ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(0.5)ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(0.5)ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')plt.savefig(func_pic_res + "{}.jpg".format(name))# sigmoid激活函数
def test_Sigmoid():x = torch.arange(-10.0, 10.0, 0.1, requires_grad=True)y = x.sigmoid()xyplot(x, y, 'Sigmoid')# 导数y.sum().backward()xyplot(x, x.grad, 'grad of Sigmoid')def test_Tanh():x = torch.arange(-10.0, 10.0, 0.1, requires_grad=True)y = x.tanh()xyplot(x, y, 'Tanh')# 导数y.sum().backward()xyplot(x, x.grad, 'grad of Tanh')def test_ReLU():x = torch.arange(-10.0, 10.0, 0.1, requires_grad=True)y = x.relu()xyplot(x, y, 'ReLU')# 导数y.sum().backward()xyplot(x, x.grad, 'grad of ReLU')def test_LeakyReLU():x = torch.arange(-10.0, 10.0, 0.1, requires_grad=True)y = F.leaky_relu(x, negative_slope=0.1, inplace=False)xyplot(x, y, 'LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1)')# 导数y.sum().backward()xyplot(x, x.grad, 'grad of LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1)')def test_ELU():x = torch.arange(-10.0, 10.0, 0.1, requires_grad=True)y = F.elu(x, alpha=0.3, inplace=False)xyplot(x, y, 'ELU(alpha=0.3)')# 导数y.sum().backward()xyplot(x, x.grad, 'grad of ELU(alpha=0.3)')def test_GELU():x = torch.arange(-10.0, 10.0, 0.1, requires_grad=True)y = F.gelu(x)xyplot(x, y, 'GELU')# 导数y.sum().backward()xyplot(x, x.grad, 'grad of GELU')if __name__ == "__main__":test_Sigmoid()test_Tanh()test_ReLU()test_LeakyReLU()test_ELU()test_GELU()