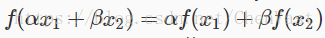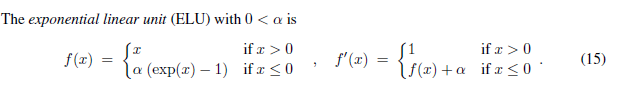文章目录
- 前言
- 一、解决问题
- 二、基本原理
- 三、添加方法
- 四、总结
前言
作为当前先进的深度学习目标检测算法YOLOv7,已经集合了大量的trick,但是还是有提高和改进的空间,针对具体应用场景下的检测难点,可以不同的改进方法。此后的系列文章,将重点对YOLOv7的如何改进进行详细的介绍,目的是为了给那些搞科研的同学需要创新点或者搞工程项目的朋友需要达到更好的效果提供自己的微薄帮助和参考。由于出到YOLOv7,YOLOv5算法2020年至今已经涌现出大量改进论文,这个不论对于搞科研的同学或者已经工作的朋友来说,研究的价值和新颖度都不太够了,为与时俱进,以后改进算法以YOLOv7为基础,此前YOLOv5改进方法在YOLOv7同样适用,所以继续YOLOv5系列改进的序号。另外改进方法在YOLOv5等其他算法同样可以适用进行改进。希望能够对大家有帮助。
具体改进办法请关注后私信留言!关注免费领取深度学习算法学习资料!
一、解决问题
之前改进从改进的部位来分的话从输入端、主干特征提取网络(backbone)、特征融合网络(neck)、检测头等四个方面进行改进,从改进的方法包括添加注意力机制、损失函数改进、改变网络结构、替换主干特征提取网络、改进非极大值抑制、k-means++聚类算法等方面进行改进,本文尝试通过改进更为专用于视觉任务的激活函数来网络进行改进。原激活函数为SiLU激活函数,改进激活函数来提高检测效果。此前💡🎈☁️34. 更换激活函数为FReLU💡🎈☁️46. 改进激活函数为ACON💡🎈☁️47. 改进激活函数为GELU有一定效果。本文将尝试更多类型的激活函数,大家可以通过实验进行验证。
二、基本原理
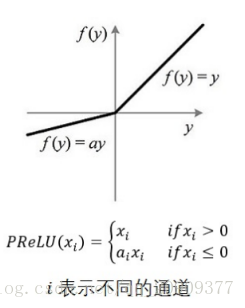
原理部分以及需要写激活函数图代码,可以参考【学习经验分享NO.16】超全代码-python画Sigmoid,ReLU,Tanh等十多种激活函数曲线及其梯度曲线(持续更新)
三、添加方法
pytorch框架里activation.py中已经定义了很多种激活函数,都可以用。相关代码如下所示。
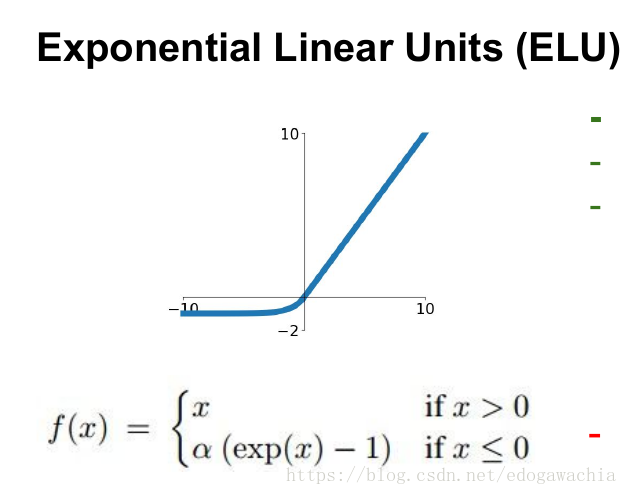
class ReLU(Module):r"""Applies the rectified linear unit function element-wise::math:`\text{ReLU}(x) = (x)^+ = \max(0, x)`Args:inplace: can optionally do the operation in-place. Default: ``False``Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/ReLU.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.ReLU()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)An implementation of CReLU - https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.05201>>> m = nn.ReLU()>>> input = torch.randn(2).unsqueeze(0)>>> output = torch.cat((m(input),m(-input)))"""__constants__ = ['inplace']inplace: booldef __init__(self, inplace: bool = False):super(ReLU, self).__init__()self.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.relu(input, inplace=self.inplace)def extra_repr(self) -> str:inplace_str = 'inplace=True' if self.inplace else ''return inplace_strclass RReLU(Module):r"""Applies the randomized leaky rectified liner unit function, element-wise,as described in the paper:`Empirical Evaluation of Rectified Activations in Convolutional Network`_.The function is defined as:.. math::\text{RReLU}(x) =\begin{cases}x & \text{if } x \geq 0 \\ax & \text{ otherwise }\end{cases}where :math:`a` is randomly sampled from uniform distribution:math:`\mathcal{U}(\text{lower}, \text{upper})`.See: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1505.00853.pdfArgs:lower: lower bound of the uniform distribution. Default: :math:`\frac{1}{8}`upper: upper bound of the uniform distribution. Default: :math:`\frac{1}{3}`inplace: can optionally do the operation in-place. Default: ``False``Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/RReLU.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.RReLU(0.1, 0.3)>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input).. _`Empirical Evaluation of Rectified Activations in Convolutional Network`:https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.00853"""__constants__ = ['lower', 'upper', 'inplace']lower: floatupper: floatinplace: booldef __init__(self,lower: float = 1. / 8,upper: float = 1. / 3,inplace: bool = False):super(RReLU, self).__init__()self.lower = lowerself.upper = upperself.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.rrelu(input, self.lower, self.upper, self.training, self.inplace)def extra_repr(self):inplace_str = ', inplace=True' if self.inplace else ''return 'lower={}, upper={}{}'.format(self.lower, self.upper, inplace_str)class Hardtanh(Module):r"""Applies the HardTanh function element-wise.HardTanh is defined as:.. math::\text{HardTanh}(x) = \begin{cases}1 & \text{ if } x > 1 \\-1 & \text{ if } x < -1 \\x & \text{ otherwise } \\\end{cases}The range of the linear region :math:`[-1, 1]` can be adjusted using:attr:`min_val` and :attr:`max_val`.Args:min_val: minimum value of the linear region range. Default: -1max_val: maximum value of the linear region range. Default: 1inplace: can optionally do the operation in-place. Default: ``False``Keyword arguments :attr:`min_value` and :attr:`max_value`have been deprecated in favor of :attr:`min_val` and :attr:`max_val`.Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/Hardtanh.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.Hardtanh(-2, 2)>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['min_val', 'max_val', 'inplace']min_val: floatmax_val: floatinplace: booldef __init__(self,min_val: float = -1.,max_val: float = 1.,inplace: bool = False,min_value: Optional[float] = None,max_value: Optional[float] = None) -> None:super(Hardtanh, self).__init__()if min_value is not None:warnings.warn("keyword argument min_value is deprecated and rename to min_val")min_val = min_valueif max_value is not None:warnings.warn("keyword argument max_value is deprecated and rename to max_val")max_val = max_valueself.min_val = min_valself.max_val = max_valself.inplace = inplaceassert self.max_val > self.min_valdef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.hardtanh(input, self.min_val, self.max_val, self.inplace)def extra_repr(self) -> str:inplace_str = ', inplace=True' if self.inplace else ''return 'min_val={}, max_val={}{}'.format(self.min_val, self.max_val, inplace_str)class ReLU6(Hardtanh):r"""Applies the element-wise function:.. math::\text{ReLU6}(x) = \min(\max(0,x), 6)Args:inplace: can optionally do the operation in-place. Default: ``False``Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/ReLU6.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.ReLU6()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""def __init__(self, inplace: bool = False):super(ReLU6, self).__init__(0., 6., inplace)def extra_repr(self) -> str:inplace_str = 'inplace=True' if self.inplace else ''return inplace_strclass Sigmoid(Module):r"""Applies the element-wise function:.. math::\text{Sigmoid}(x) = \sigma(x) = \frac{1}{1 + \exp(-x)}Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/Sigmoid.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.Sigmoid()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return torch.sigmoid(input)class Hardsigmoid(Module):r"""Applies the Hardsigmoid function element-wise.Hardsigmoid is defined as:.. math::\text{Hardsigmoid}(x) = \begin{cases}0 & \text{if~} x \le -3, \\1 & \text{if~} x \ge +3, \\x / 6 + 1 / 2 & \text{otherwise}\end{cases}Args:inplace: can optionally do the operation in-place. Default: ``False``Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/Hardsigmoid.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.Hardsigmoid()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['inplace']inplace: booldef __init__(self, inplace : bool = False) -> None:super(Hardsigmoid, self).__init__()self.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.hardsigmoid(input, self.inplace)class Tanh(Module):r"""Applies the Hyperbolic Tangent (Tanh) function element-wise.Tanh is defined as:.. math::\text{Tanh}(x) = \tanh(x) = \frac{\exp(x) - \exp(-x)} {\exp(x) + \exp(-x)}Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/Tanh.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.Tanh()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return torch.tanh(input)class SiLU(Module):r"""Applies the Sigmoid Linear Unit (SiLU) function, element-wise.The SiLU function is also known as the swish function... math::\text{silu}(x) = x * \sigma(x), \text{where } \sigma(x) \text{ is the logistic sigmoid.}.. note::See `Gaussian Error Linear Units (GELUs) <https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.08415>`_where the SiLU (Sigmoid Linear Unit) was originally coined, and see`Sigmoid-Weighted Linear Units for Neural Network Function Approximationin Reinforcement Learning <https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.03118>`_ and `Swish:a Self-Gated Activation Function <https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.05941v1>`_where the SiLU was experimented with later.Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/SiLU.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.SiLU()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['inplace']inplace: booldef __init__(self, inplace: bool = False):super(SiLU, self).__init__()self.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.silu(input, inplace=self.inplace)def extra_repr(self) -> str:inplace_str = 'inplace=True' if self.inplace else ''return inplace_strclass Mish(Module):r"""Applies the Mish function, element-wise.Mish: A Self Regularized Non-Monotonic Neural Activation Function... math::\text{Mish}(x) = x * \text{Tanh}(\text{Softplus}(x)).. note::See `Mish: A Self Regularized Non-Monotonic Neural Activation Function <https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.08681>`_Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/Mish.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.Mish()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['inplace']inplace: booldef __init__(self, inplace: bool = False):super(Mish, self).__init__()self.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.mish(input, inplace=self.inplace)def extra_repr(self) -> str:inplace_str = 'inplace=True' if self.inplace else ''return inplace_strclass Hardswish(Module):r"""Applies the hardswish function, element-wise, as described in the paper:`Searching for MobileNetV3`_... math::\text{Hardswish}(x) = \begin{cases}0 & \text{if~} x \le -3, \\x & \text{if~} x \ge +3, \\x \cdot (x + 3) /6 & \text{otherwise}\end{cases}Args:inplace: can optionally do the operation in-place. Default: ``False``Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/Hardswish.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.Hardswish()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input).. _`Searching for MobileNetV3`:https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02244"""__constants__ = ['inplace']inplace: booldef __init__(self, inplace : bool = False) -> None:super(Hardswish, self).__init__()self.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.hardswish(input, self.inplace)class ELU(Module):r"""Applies the Exponential Linear Unit (ELU) function, element-wise, as describedin the paper: `Fast and Accurate Deep Network Learning by Exponential LinearUnits (ELUs) <https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.07289>`__.ELU is defined as:.. math::\text{ELU}(x) = \begin{cases}x, & \text{ if } x > 0\\\alpha * (\exp(x) - 1), & \text{ if } x \leq 0\end{cases}Args:alpha: the :math:`\alpha` value for the ELU formulation. Default: 1.0inplace: can optionally do the operation in-place. Default: ``False``Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/ELU.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.ELU()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['alpha', 'inplace']alpha: floatinplace: booldef __init__(self, alpha: float = 1., inplace: bool = False) -> None:super(ELU, self).__init__()self.alpha = alphaself.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.elu(input, self.alpha, self.inplace)def extra_repr(self) -> str:inplace_str = ', inplace=True' if self.inplace else ''return 'alpha={}{}'.format(self.alpha, inplace_str)class CELU(Module):r"""Applies the element-wise function:.. math::\text{CELU}(x) = \max(0,x) + \min(0, \alpha * (\exp(x/\alpha) - 1))More details can be found in the paper `Continuously Differentiable Exponential Linear Units`_ .Args:alpha: the :math:`\alpha` value for the CELU formulation. Default: 1.0inplace: can optionally do the operation in-place. Default: ``False``Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/CELU.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.CELU()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input).. _`Continuously Differentiable Exponential Linear Units`:https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.07483"""__constants__ = ['alpha', 'inplace']alpha: floatinplace: booldef __init__(self, alpha: float = 1., inplace: bool = False) -> None:super(CELU, self).__init__()self.alpha = alphaself.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.celu(input, self.alpha, self.inplace)def extra_repr(self) -> str:inplace_str = ', inplace=True' if self.inplace else ''return 'alpha={}{}'.format(self.alpha, inplace_str)class SELU(Module):r"""Applied element-wise, as:.. math::\text{SELU}(x) = \text{scale} * (\max(0,x) + \min(0, \alpha * (\exp(x) - 1)))with :math:`\alpha = 1.6732632423543772848170429916717` and:math:`\text{scale} = 1.0507009873554804934193349852946`... warning::When using ``kaiming_normal`` or ``kaiming_normal_`` for initialisation,``nonlinearity='linear'`` should be used instead of ``nonlinearity='selu'``in order to get `Self-Normalizing Neural Networks`_.See :func:`torch.nn.init.calculate_gain` for more information.More details can be found in the paper `Self-Normalizing Neural Networks`_ .Args:inplace (bool, optional): can optionally do the operation in-place. Default: ``False``Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/SELU.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.SELU()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input).. _Self-Normalizing Neural Networks: https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02515"""__constants__ = ['inplace']inplace: booldef __init__(self, inplace: bool = False) -> None:super(SELU, self).__init__()self.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.selu(input, self.inplace)def extra_repr(self) -> str:inplace_str = 'inplace=True' if self.inplace else ''return inplace_strclass GLU(Module):r"""Applies the gated linear unit function:math:`{GLU}(a, b)= a \otimes \sigma(b)` where :math:`a` is the first halfof the input matrices and :math:`b` is the second half.Args:dim (int): the dimension on which to split the input. Default: -1Shape:- Input: :math:`(\ast_1, N, \ast_2)` where `*` means, any number of additionaldimensions- Output: :math:`(\ast_1, M, \ast_2)` where :math:`M=N/2`Examples::>>> m = nn.GLU()>>> input = torch.randn(4, 2)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['dim']dim: intdef __init__(self, dim: int = -1) -> None:super(GLU, self).__init__()self.dim = dimdef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.glu(input, self.dim)def extra_repr(self) -> str:return 'dim={}'.format(self.dim)class GELU(Module):r"""Applies the Gaussian Error Linear Units function:.. math:: \text{GELU}(x) = x * \Phi(x)where :math:`\Phi(x)` is the Cumulative Distribution Function for Gaussian Distribution.Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/GELU.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.GELU()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.gelu(input)class Hardshrink(Module):r"""Applies the Hard Shrinkage (Hardshrink) function element-wise.Hardshrink is defined as:.. math::\text{HardShrink}(x) =\begin{cases}x, & \text{ if } x > \lambda \\x, & \text{ if } x < -\lambda \\0, & \text{ otherwise }\end{cases}Args:lambd: the :math:`\lambda` value for the Hardshrink formulation. Default: 0.5Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/Hardshrink.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.Hardshrink()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['lambd']lambd: floatdef __init__(self, lambd: float = 0.5) -> None:super(Hardshrink, self).__init__()self.lambd = lambddef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.hardshrink(input, self.lambd)def extra_repr(self) -> str:return '{}'.format(self.lambd)class LeakyReLU(Module):r"""Applies the element-wise function:.. math::\text{LeakyReLU}(x) = \max(0, x) + \text{negative\_slope} * \min(0, x)or.. math::\text{LeakyRELU}(x) =\begin{cases}x, & \text{ if } x \geq 0 \\\text{negative\_slope} \times x, & \text{ otherwise }\end{cases}Args:negative_slope: Controls the angle of the negative slope. Default: 1e-2inplace: can optionally do the operation in-place. Default: ``False``Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)` where `*` means, any number of additionaldimensions- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input.. image:: ../scripts/activation_images/LeakyReLU.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['inplace', 'negative_slope']inplace: boolnegative_slope: floatdef __init__(self, negative_slope: float = 1e-2, inplace: bool = False) -> None:super(LeakyReLU, self).__init__()self.negative_slope = negative_slopeself.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.leaky_relu(input, self.negative_slope, self.inplace)def extra_repr(self) -> str:inplace_str = ', inplace=True' if self.inplace else ''return 'negative_slope={}{}'.format(self.negative_slope, inplace_str)class LogSigmoid(Module):r"""Applies the element-wise function:.. math::\text{LogSigmoid}(x) = \log\left(\frac{ 1 }{ 1 + \exp(-x)}\right)Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/LogSigmoid.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.LogSigmoid()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.logsigmoid(input)class Softplus(Module):r"""Applies the Softplus function :math:`\text{Softplus}(x) = \frac{1}{\beta} *\log(1 + \exp(\beta * x))` element-wise.SoftPlus is a smooth approximation to the ReLU function and can be usedto constrain the output of a machine to always be positive.For numerical stability the implementation reverts to the linear functionwhen :math:`input \times \beta > threshold`.Args:beta: the :math:`\beta` value for the Softplus formulation. Default: 1threshold: values above this revert to a linear function. Default: 20Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/Softplus.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.Softplus()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['beta', 'threshold']beta: intthreshold: intdef __init__(self, beta: int = 1, threshold: int = 20) -> None:super(Softplus, self).__init__()self.beta = betaself.threshold = thresholddef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.softplus(input, self.beta, self.threshold)def extra_repr(self) -> str:return 'beta={}, threshold={}'.format(self.beta, self.threshold)class Softshrink(Module):r"""Applies the soft shrinkage function elementwise:.. math::\text{SoftShrinkage}(x) =\begin{cases}x - \lambda, & \text{ if } x > \lambda \\x + \lambda, & \text{ if } x < -\lambda \\0, & \text{ otherwise }\end{cases}Args:lambd: the :math:`\lambda` (must be no less than zero) value for the Softshrink formulation. Default: 0.5Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/Softshrink.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.Softshrink()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['lambd']lambd: floatdef __init__(self, lambd: float = 0.5) -> None:super(Softshrink, self).__init__()self.lambd = lambddef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.softshrink(input, self.lambd)def extra_repr(self) -> str:return str(self.lambd)class MultiheadAttention(Module):r"""Allows the model to jointly attend to informationfrom different representation subspaces as described in the paper:`Attention Is All You Need <https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762>`_.Multi-Head Attention is defined as:.. math::\text{MultiHead}(Q, K, V) = \text{Concat}(head_1,\dots,head_h)W^Owhere :math:`head_i = \text{Attention}(QW_i^Q, KW_i^K, VW_i^V)`.Args:embed_dim: Total dimension of the model.num_heads: Number of parallel attention heads. Note that ``embed_dim`` will be splitacross ``num_heads`` (i.e. each head will have dimension ``embed_dim // num_heads``).dropout: Dropout probability on ``attn_output_weights``. Default: ``0.0`` (no dropout).bias: If specified, adds bias to input / output projection layers. Default: ``True``.add_bias_kv: If specified, adds bias to the key and value sequences at dim=0. Default: ``False``.add_zero_attn: If specified, adds a new batch of zeros to the key and value sequences at dim=1.Default: ``False``.kdim: Total number of features for keys. Default: ``None`` (uses ``kdim=embed_dim``).vdim: Total number of features for values. Default: ``None`` (uses ``vdim=embed_dim``).batch_first: If ``True``, then the input and output tensors are providedas (batch, seq, feature). Default: ``False`` (seq, batch, feature).Examples::>>> multihead_attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim, num_heads)>>> attn_output, attn_output_weights = multihead_attn(query, key, value)"""__constants__ = ['batch_first']bias_k: Optional[torch.Tensor]bias_v: Optional[torch.Tensor]def __init__(self, embed_dim, num_heads, dropout=0., bias=True, add_bias_kv=False, add_zero_attn=False,kdim=None, vdim=None, batch_first=False, device=None, dtype=None) -> None:factory_kwargs = {'device': device, 'dtype': dtype}super(MultiheadAttention, self).__init__()self.embed_dim = embed_dimself.kdim = kdim if kdim is not None else embed_dimself.vdim = vdim if vdim is not None else embed_dimself._qkv_same_embed_dim = self.kdim == embed_dim and self.vdim == embed_dimself.num_heads = num_headsself.dropout = dropoutself.batch_first = batch_firstself.head_dim = embed_dim // num_headsassert self.head_dim * num_heads == self.embed_dim, "embed_dim must be divisible by num_heads"if self._qkv_same_embed_dim is False:self.q_proj_weight = Parameter(torch.empty((embed_dim, embed_dim), **factory_kwargs))self.k_proj_weight = Parameter(torch.empty((embed_dim, self.kdim), **factory_kwargs))self.v_proj_weight = Parameter(torch.empty((embed_dim, self.vdim), **factory_kwargs))self.register_parameter('in_proj_weight', None)else:self.in_proj_weight = Parameter(torch.empty((3 * embed_dim, embed_dim), **factory_kwargs))self.register_parameter('q_proj_weight', None)self.register_parameter('k_proj_weight', None)self.register_parameter('v_proj_weight', None)if bias:self.in_proj_bias = Parameter(torch.empty(3 * embed_dim, **factory_kwargs))else:self.register_parameter('in_proj_bias', None)self.out_proj = NonDynamicallyQuantizableLinear(embed_dim, embed_dim, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)if add_bias_kv:self.bias_k = Parameter(torch.empty((1, 1, embed_dim), **factory_kwargs))self.bias_v = Parameter(torch.empty((1, 1, embed_dim), **factory_kwargs))else:self.bias_k = self.bias_v = Noneself.add_zero_attn = add_zero_attnself._reset_parameters()def _reset_parameters(self):if self._qkv_same_embed_dim:xavier_uniform_(self.in_proj_weight)else:xavier_uniform_(self.q_proj_weight)xavier_uniform_(self.k_proj_weight)xavier_uniform_(self.v_proj_weight)if self.in_proj_bias is not None:constant_(self.in_proj_bias, 0.)constant_(self.out_proj.bias, 0.)if self.bias_k is not None:xavier_normal_(self.bias_k)if self.bias_v is not None:xavier_normal_(self.bias_v)def __setstate__(self, state):# Support loading old MultiheadAttention checkpoints generated by v1.1.0if '_qkv_same_embed_dim' not in state:state['_qkv_same_embed_dim'] = Truesuper(MultiheadAttention, self).__setstate__(state)def forward(self, query: Tensor, key: Tensor, value: Tensor, key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,need_weights: bool = True, attn_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,average_attn_weights: bool = True) -> Tuple[Tensor, Optional[Tensor]]:r"""Args:query: Query embeddings of shape :math:`(L, E_q)` for unbatched input, :math:`(L, N, E_q)` when ``batch_first=False``or :math:`(N, L, E_q)` when ``batch_first=True``, where :math:`L` is the target sequence length,:math:`N` is the batch size, and :math:`E_q` is the query embedding dimension ``embed_dim``.Queries are compared against key-value pairs to produce the output.See "Attention Is All You Need" for more details.key: Key embeddings of shape :math:`(S, E_k)` for unbatched input, :math:`(S, N, E_k)` when ``batch_first=False``or :math:`(N, S, E_k)` when ``batch_first=True``, where :math:`S` is the source sequence length,:math:`N` is the batch size, and :math:`E_k` is the key embedding dimension ``kdim``.See "Attention Is All You Need" for more details.value: Value embeddings of shape :math:`(S, E_v)` for unbatched input, :math:`(S, N, E_v)` when``batch_first=False`` or :math:`(N, S, E_v)` when ``batch_first=True``, where :math:`S` is the sourcesequence length, :math:`N` is the batch size, and :math:`E_v` is the value embedding dimension ``vdim``.See "Attention Is All You Need" for more details.key_padding_mask: If specified, a mask of shape :math:`(N, S)` indicating which elements within ``key``to ignore for the purpose of attention (i.e. treat as "padding"). For unbatched `query`, shape should be :math:`(S)`.Binary and byte masks are supported.For a binary mask, a ``True`` value indicates that the corresponding ``key`` value will be ignored forthe purpose of attention. For a byte mask, a non-zero value indicates that the corresponding ``key``value will be ignored.need_weights: If specified, returns ``attn_output_weights`` in addition to ``attn_outputs``.Default: ``True``.attn_mask: If specified, a 2D or 3D mask preventing attention to certain positions. Must be of shape:math:`(L, S)` or :math:`(N\cdot\text{num\_heads}, L, S)`, where :math:`N` is the batch size,:math:`L` is the target sequence length, and :math:`S` is the source sequence length. A 2D mask will bebroadcasted across the batch while a 3D mask allows for a different mask for each entry in the batch.Binary, byte, and float masks are supported. For a binary mask, a ``True`` value indicates that thecorresponding position is not allowed to attend. For a byte mask, a non-zero value indicates that thecorresponding position is not allowed to attend. For a float mask, the mask values will be added tothe attention weight.average_attn_weights: If true, indicates that the returned ``attn_weights`` should be averaged acrossheads. Otherwise, ``attn_weights`` are provided separately per head. Note that this flag only has aneffect when ``need_weights=True.``. Default: True (i.e. average weights across heads)Outputs:- **attn_output** - Attention outputs of shape :math:`(L, E)` when input is unbatched,:math:`(L, N, E)` when ``batch_first=False`` or :math:`(N, L, E)` when ``batch_first=True``,where :math:`L` is the target sequence length, :math:`N` is the batch size, and :math:`E` is theembedding dimension ``embed_dim``.- **attn_output_weights** - Only returned when ``need_weights=True``. If ``average_attn_weights=True``,returns attention weights averaged across heads of shape :math:`(L, S)` when input is unbatched or:math:`(N, L, S)`, where :math:`N` is the batch size, :math:`L` is the target sequence length, and:math:`S` is the source sequence length. If ``average_weights=False``, returns attention weights perhead of shape :math:`(num_heads, L, S)` when input is unbatched or :math:`(N, num_heads, L, S)`... note::`batch_first` argument is ignored for unbatched inputs."""is_batched = query.dim() == 3if self.batch_first and is_batched:query, key, value = [x.transpose(1, 0) for x in (query, key, value)]if not self._qkv_same_embed_dim:attn_output, attn_output_weights = F.multi_head_attention_forward(query, key, value, self.embed_dim, self.num_heads,self.in_proj_weight, self.in_proj_bias,self.bias_k, self.bias_v, self.add_zero_attn,self.dropout, self.out_proj.weight, self.out_proj.bias,training=self.training,key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask, need_weights=need_weights,attn_mask=attn_mask, use_separate_proj_weight=True,q_proj_weight=self.q_proj_weight, k_proj_weight=self.k_proj_weight,v_proj_weight=self.v_proj_weight, average_attn_weights=average_attn_weights)else:attn_output, attn_output_weights = F.multi_head_attention_forward(query, key, value, self.embed_dim, self.num_heads,self.in_proj_weight, self.in_proj_bias,self.bias_k, self.bias_v, self.add_zero_attn,self.dropout, self.out_proj.weight, self.out_proj.bias,training=self.training,key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask, need_weights=need_weights,attn_mask=attn_mask, average_attn_weights=average_attn_weights)if self.batch_first and is_batched:return attn_output.transpose(1, 0), attn_output_weightselse:return attn_output, attn_output_weightsclass PReLU(Module):r"""Applies the element-wise function:.. math::\text{PReLU}(x) = \max(0,x) + a * \min(0,x)or.. math::\text{PReLU}(x) =\begin{cases}x, & \text{ if } x \geq 0 \\ax, & \text{ otherwise }\end{cases}Here :math:`a` is a learnable parameter. When called without arguments, `nn.PReLU()` uses a singleparameter :math:`a` across all input channels. If called with `nn.PReLU(nChannels)`,a separate :math:`a` is used for each input channel... note::weight decay should not be used when learning :math:`a` for good performance... note::Channel dim is the 2nd dim of input. When input has dims < 2, then there isno channel dim and the number of channels = 1.Args:num_parameters (int): number of :math:`a` to learn.Although it takes an int as input, there is only two values are legitimate:1, or the number of channels at input. Default: 1init (float): the initial value of :math:`a`. Default: 0.25Shape:- Input: :math:`( *)` where `*` means, any number of additionaldimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input.Attributes:weight (Tensor): the learnable weights of shape (:attr:`num_parameters`)... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/PReLU.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.PReLU()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['num_parameters']num_parameters: intdef __init__(self, num_parameters: int = 1, init: float = 0.25,device=None, dtype=None) -> None:factory_kwargs = {'device': device, 'dtype': dtype}self.num_parameters = num_parameterssuper(PReLU, self).__init__()self.weight = Parameter(torch.empty(num_parameters, **factory_kwargs).fill_(init))def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.prelu(input, self.weight)def extra_repr(self) -> str:return 'num_parameters={}'.format(self.num_parameters)class Softsign(Module):r"""Applies the element-wise function:.. math::\text{SoftSign}(x) = \frac{x}{ 1 + |x|}Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/Softsign.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.Softsign()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.softsign(input)class Tanhshrink(Module):r"""Applies the element-wise function:.. math::\text{Tanhshrink}(x) = x - \tanh(x)Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)`, where :math:`*` means any number of dimensions.- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the input... image:: ../scripts/activation_images/Tanhshrink.pngExamples::>>> m = nn.Tanhshrink()>>> input = torch.randn(2)>>> output = m(input)"""def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.tanhshrink(input)class Softmin(Module):r"""Applies the Softmin function to an n-dimensional input Tensorrescaling them so that the elements of the n-dimensional output Tensorlie in the range `[0, 1]` and sum to 1.Softmin is defined as:.. math::\text{Softmin}(x_{i}) = \frac{\exp(-x_i)}{\sum_j \exp(-x_j)}Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)` where `*` means, any number of additionaldimensions- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the inputArgs:dim (int): A dimension along which Softmin will be computed (so every slicealong dim will sum to 1).Returns:a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input, withvalues in the range [0, 1]Examples::>>> m = nn.Softmin()>>> input = torch.randn(2, 3)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['dim']dim: Optional[int]def __init__(self, dim: Optional[int] = None) -> None:super(Softmin, self).__init__()self.dim = dimdef __setstate__(self, state):self.__dict__.update(state)if not hasattr(self, 'dim'):self.dim = Nonedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.softmin(input, self.dim, _stacklevel=5)def extra_repr(self):return 'dim={dim}'.format(dim=self.dim)class Softmax(Module):r"""Applies the Softmax function to an n-dimensional input Tensorrescaling them so that the elements of the n-dimensional output Tensorlie in the range [0,1] and sum to 1.Softmax is defined as:.. math::\text{Softmax}(x_{i}) = \frac{\exp(x_i)}{\sum_j \exp(x_j)}When the input Tensor is a sparse tensor then the unspecifedvalues are treated as ``-inf``.Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)` where `*` means, any number of additionaldimensions- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the inputReturns:a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input withvalues in the range [0, 1]Args:dim (int): A dimension along which Softmax will be computed (so every slicealong dim will sum to 1)... note::This module doesn't work directly with NLLLoss,which expects the Log to be computed between the Softmax and itself.Use `LogSoftmax` instead (it's faster and has better numerical properties).Examples::>>> m = nn.Softmax(dim=1)>>> input = torch.randn(2, 3)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['dim']dim: Optional[int]def __init__(self, dim: Optional[int] = None) -> None:super(Softmax, self).__init__()self.dim = dimdef __setstate__(self, state):self.__dict__.update(state)if not hasattr(self, 'dim'):self.dim = Nonedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.softmax(input, self.dim, _stacklevel=5)def extra_repr(self) -> str:return 'dim={dim}'.format(dim=self.dim)class Softmax2d(Module):r"""Applies SoftMax over features to each spatial location.When given an image of ``Channels x Height x Width``, it willapply `Softmax` to each location :math:`(Channels, h_i, w_j)`Shape:- Input: :math:`(N, C, H, W)` or :math:`(C, H, W)`.- Output: :math:`(N, C, H, W)` or :math:`(C, H, W)` (same shape as input)Returns:a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input withvalues in the range [0, 1]Examples::>>> m = nn.Softmax2d()>>> # you softmax over the 2nd dimension>>> input = torch.randn(2, 3, 12, 13)>>> output = m(input)"""def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:assert input.dim() == 4 or input.dim() == 3, 'Softmax2d requires a 3D or 4D tensor as input'return F.softmax(input, -3, _stacklevel=5)class LogSoftmax(Module):r"""Applies the :math:`\log(\text{Softmax}(x))` function to an n-dimensionalinput Tensor. The LogSoftmax formulation can be simplified as:.. math::\text{LogSoftmax}(x_{i}) = \log\left(\frac{\exp(x_i) }{ \sum_j \exp(x_j)} \right)Shape:- Input: :math:`(*)` where `*` means, any number of additionaldimensions- Output: :math:`(*)`, same shape as the inputArgs:dim (int): A dimension along which LogSoftmax will be computed.Returns:a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input withvalues in the range [-inf, 0)Examples::>>> m = nn.LogSoftmax()>>> input = torch.randn(2, 3)>>> output = m(input)"""__constants__ = ['dim']dim: Optional[int]def __init__(self, dim: Optional[int] = None) -> None:super(LogSoftmax, self).__init__()self.dim = dimdef __setstate__(self, state):self.__dict__.update(state)if not hasattr(self, 'dim'):self.dim = Nonedef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:return F.log_softmax(input, self.dim, _stacklevel=5)def extra_repr(self):return 'dim={dim}'.format(dim=self.dim)第二步:common.py构建模块。重构Conv模块。将SILU改为ELU,即为选择了ELU激活函数。如图所示。
同理,可以将ELU激活函数换为ReLU、RReLU、Hardtanh、ReLU6、Sigmoid、Tanh、Mish、Hardswish、ELU、CELU、GLU、GELU、Hardshrink、LeakyReLU、LogSigmoid、Softplus、Softshrink、PReLU、Softmin等数十种激活函数。

第三步:将train.py中改为本文的yaml文件即可,开始训练,即可将原Conv中的激活函数改为其他的函数。
四、总结
预告一下:下一篇内容将继续分享深度学习算法相关改进方法。有兴趣的朋友可以关注一下我,有问题可以留言或者私聊我哦
PS:该方法不仅仅是适用改进YOLOv5,也可以改进其他的YOLO网络以及目标检测网络,比如YOLOv7、v6、v4、v3,Faster rcnn ,ssd等。
最后,有需要的请关注私信我吧。关注免费领取深度学习算法学习资料!
YOLO系列算法改进方法 | 目录一览表
💡🎈☁️1. 添加SE注意力机制
💡🎈☁️2.添加CBAM注意力机制
💡🎈☁️3. 添加CoordAtt注意力机制
💡🎈☁️4. 添加ECA通道注意力机制
💡🎈☁️5. 改进特征融合网络PANET为BIFPN
💡🎈☁️6. 增加小目标检测层
💡🎈☁️7. 损失函数改进
💡🎈☁️8. 非极大值抑制NMS算法改进Soft-nms
💡🎈☁️9. 锚框K-Means算法改进K-Means++
💡🎈☁️10. 损失函数改进为SIOU
💡🎈☁️11. 主干网络C3替换为轻量化网络MobileNetV3
💡🎈☁️12. 主干网络C3替换为轻量化网络ShuffleNetV2
💡🎈☁️13. 主干网络C3替换为轻量化网络EfficientNetv2
💡🎈☁️14. 主干网络C3替换为轻量化网络Ghostnet
💡🎈☁️15. 网络轻量化方法深度可分离卷积
💡🎈☁️16. 主干网络C3替换为轻量化网络PP-LCNet
💡🎈☁️17. CNN+Transformer——融合Bottleneck Transformers
💡🎈☁️18. 损失函数改进为Alpha-IoU损失函数
💡🎈☁️19. 非极大值抑制NMS算法改进DIoU NMS
💡🎈☁️20. Involution新神经网络算子引入网络
💡🎈☁️21. CNN+Transformer——主干网络替换为又快又强的轻量化主干EfficientFormer
💡🎈☁️22. 涨点神器——引入递归门控卷积(gnConv)
💡🎈☁️23. 引入SimAM无参数注意力
💡🎈☁️24. 引入量子启发的新型视觉主干模型WaveMLP(可尝试发SCI)
💡🎈☁️25. 引入Swin Transformer
💡🎈☁️26. 改进特征融合网络PANet为ASFF自适应特征融合网络
💡🎈☁️27. 解决小目标问题——校正卷积取代特征提取网络中的常规卷积
💡🎈☁️28. ICLR 2022涨点神器——即插即用的动态卷积ODConv
💡🎈☁️29. 引入Swin Transformer v2.0版本
💡🎈☁️30. 引入10月4号发表最新的Transformer视觉模型MOAT结构
💡🎈☁️31. CrissCrossAttention注意力机制
💡🎈☁️32. 引入SKAttention注意力机制
💡🎈☁️33. 引入GAMAttention注意力机制
💡🎈☁️34. 更换激活函数为FReLU
💡🎈☁️35. 引入S2-MLPv2注意力机制
💡🎈☁️36. 融入NAM注意力机制
💡🎈☁️37. 结合CVPR2022新作ConvNeXt网络
💡🎈☁️38. 引入RepVGG模型结构
💡🎈☁️39. 引入改进遮挡检测的Tri-Layer插件 | BMVC 2022
💡🎈☁️40. 轻量化mobileone主干网络引入
💡🎈☁️41. 引入SPD-Conv处理低分辨率图像和小对象问题
💡🎈☁️42. 引入V7中的ELAN网络
💡🎈☁️43. 结合最新Non-local Networks and Attention结构
💡🎈☁️44. 融入适配GPU的轻量级 G-GhostNet
💡🎈☁️45. 首发最新特征融合技术RepGFPN(DAMO-YOLO)
💡🎈☁️46. 改进激活函数为ACON
💡🎈☁️47. 改进激活函数为GELU
💡🎈☁️48. 构建新的轻量网络—Slim-neck by GSConv(2022CVPR)
💡🎈☁️49. 模型剪枝、蒸馏、压缩
💡🎈☁️50. 超越ConvNeXt!Conv2Former:用于视觉识别的Transformer风格的ConvNet
💡🎈☁️51.融入多分支空洞卷积结构RFB-Bottleneck改进PANet构成新特征融合网络
💡🎈☁️52.将YOLOv8中的C2f模块融入YOLOv5
💡🎈☁️53.融入CFPNet网络中的ECVBlock模块,提升小目标检测能力