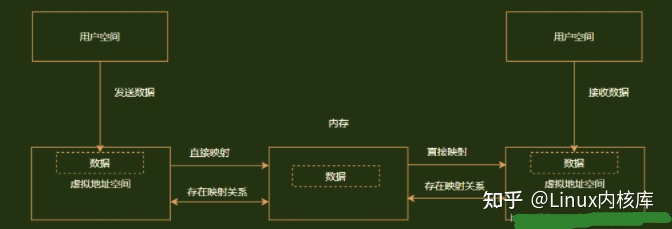
linux进程虚拟地址空间中存在一段称为mmap的内存区,当申请用户内存较大时,如大于128kb,系统一般会通过mmap系统调用直接映射一片内存区,使用结束后再通过ummap系统调用归还。关于mmap的原理网上有很多文档,这里不再赘述,主要给出驱动程序如何编写mmap函数,并通过缺页异常形式进行具体页的映射,具体参考这位博主:
https://blog.csdn.net/xxxxxlllllxl/article/details/17303231,
博文中使用kmalloc分配内存,在物理地址上连续,这里使用vmalloc开辟一段连续线性地址空间进行mmap

驱动程序:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#define CHR_DEV_NAME "my_chr_dev"static struct cdev chr_dev;
static dev_t ndev;
char * addr;
#define VMALLOC_SIZE PAGE_SIZE //映射一页至用户空间
typedef struct {char buf[100];int num;
}map_t;map_t *pmap;char map_char[10]={};static int chr_open(struct inode *nd, struct file *filp)
{//int a = PAGE_SIZE;int major = MAJOR(nd->i_rdev);int minor = MINOR(nd->i_rdev);printk("chr_open,major=%d,minor=%d\n",major,minor);return 0;
}static ssize_t chr_read(struct file *f, char __user *u, size_t sz, loff_t *off)
{printk("In the chr_read() function!\n");return 0;
}
static int eccdev_vma_fault(//struct vm_area_struct *vma, //此参数在高版本内核不存在struct vm_fault *vmf /**< Fault data. */)
{printk("go to mmap\n");unsigned long offset = (vmf->pgoff )<< PAGE_SHIFT;//虚拟地址偏移struct page *page;printk("offset = %lu\n",offset);page = vmalloc_to_page(addr+offset);//将虚拟地址转为实际物理页面if(!page){printk("page error\n");return VM_FAULT_SIGBUS;}get_page(page); //获取实际物理页面vmf->page = page;return 0;
}struct vm_operations_struct chr_vm_ops = {.fault = eccdev_vma_fault,};static int chr_mmap(struct file *filp, struct vm_area_struct *vma)
{printk("mmap \n");vma->vm_ops = &chr_vm_ops;vma->vm_flags |= VM_DONTDUMP; /* Pages will not be swapped out */// vma->vm_private_data = priv;return 0;
}
struct file_operations chr_ops =
{.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = chr_open,.read = chr_read,.mmap = chr_mmap
};static int demo_init(void)
{int ret;addr = (char *)vmalloc(VMALLOC_SIZE); //调用vmalloc( )分配一段内存区间if( addr == NULL )printk("vmalloc failed! \n");else{printk("vmalloc successfully! addr = 0x%lx\n", (unsigned long)addr);}sprintf(addr,"nihaolinux , this is a mmap test");printk("addr=%s\n",addr);/*pmap = kmalloc(sizeof(map_t),GFP_KERNEL);if(!pmap){ printk("kmalloc failed\n");return -ENOMEM;}sprintf(pmap->buf,"hello");pmap->num = 111;sprintf(map_char,"nihao");*/cdev_init(&chr_dev,&chr_ops);ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&ndev, 0, 1, CHR_DEV_NAME);if(ret < 0)return ret;printk("demo_init():major=%d,minor=%d\n", MAJOR(ndev),MINOR(ndev));ret = cdev_add(&chr_dev, ndev, 1);if(ret < 0)return ret;return 0;
}static void demo_exit(void)
{vfree(addr);printk("Removing chr_dev module...\n");cdev_del(&chr_dev);unregister_chrdev_region(ndev, 1);
}module_init(demo_init);
module_exit(demo_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Xuhongzhi");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A char device driver as an example");
用户程序:
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>#include <string.h>#include <stdio.h>
#define DEVICE_FILENAME "/dev/my_chr_dev"int main()
{int fd;char *ptrdata = NULL;fd = open(DEVICE_FILENAME, O_RDWR|O_NDELAY);if(fd >= 0){ptrdata=(char*)mmap(0,4096,PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE,MAP_SHARED,fd,0);// memcpy(ptrdata,"hihi",3);printf("%s \n", ptrdata);munmap(ptrdata, 4096);/*ptrdata=(char*)mmap(0,4096,PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE,MAP_SHARED,fd,4096);printf("%s", ptrdata);munmap(ptrdata, 4096);*/close(fd);}return 0;
}
运行结果