文章目录
- 大纲
- lambda表达式
- 一般内部类
- 局部内部类
- 匿名内部类
- 基于函数式接口的lambda表达式
- JDK8中自带的函数式接口
- Predicate判断
- Consumer消费
- Supplier供应商
- Function方法
- 其他接口
- 方法引用和构造器引用
- 静态方法引用
- 非静态方法引用
- 构造器引用
- lambda表达式中的异常处理
- Currying in java
- Java Stream API
- 使用stream流操作Collections
- 创建stream流
- 方法一:Stream.generate
- 方法二:Stream.of
- 方法三:streamFromCollections
- 方法四:Stream.builder
- 操作stream
- foreach
- map
- collect
- filter
- findFirst
- peek
- flatmap
- stream流操作nio
- ParallelStream
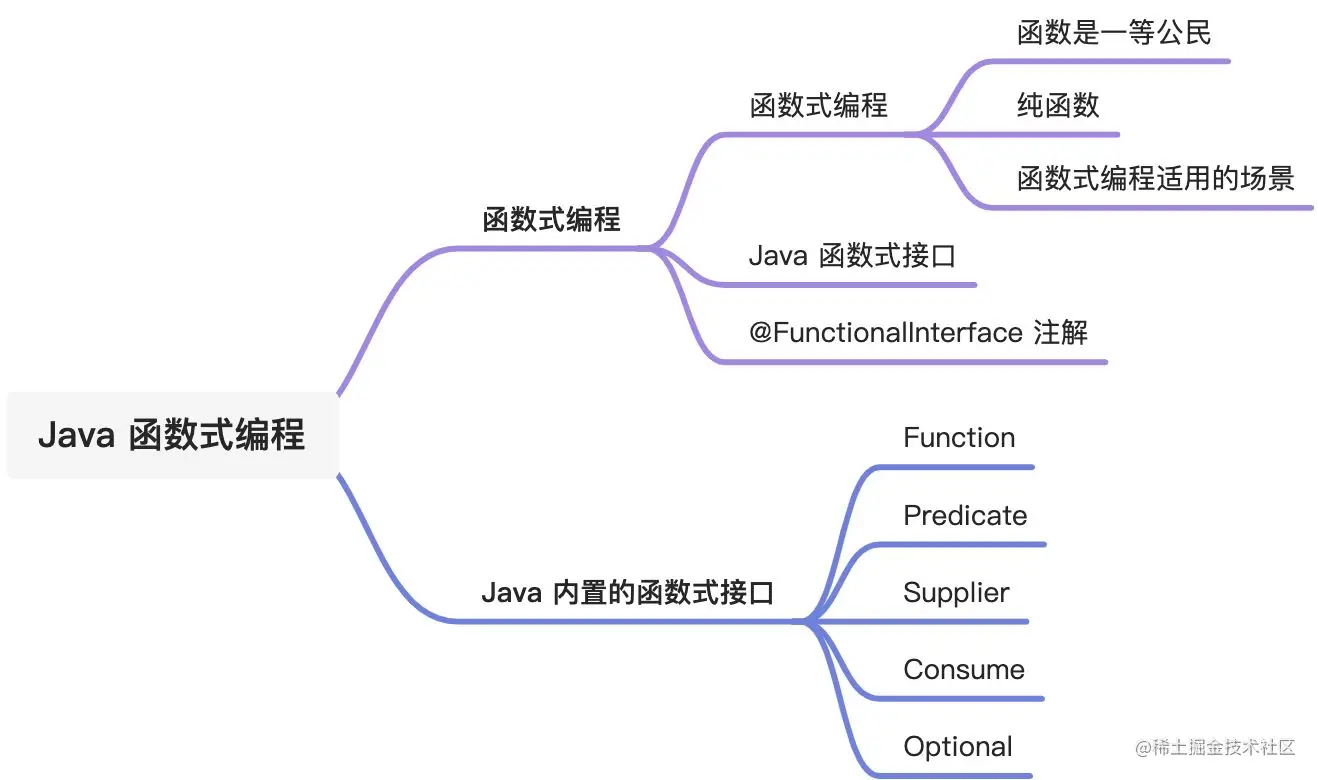
大纲
函数式编程学习的重点
- Lambda表达式
- Java Stream API
Lambda表达式
- 基于匿名类
- 基于函数式接口
- JDK8自带的函数式接口
- 方法引用和构造器引用
Java Stream API
- 操作Collections
- 操作NIO2.0
- 线程解析
lambda表达式
实现的接口
public interface PriceDashboard {Price getPrice(String symbol);
}
一般内部类
内部类可以调用外部属性
@Slf4j
public class DemoPart1Test {private Map<String, Price> stockPrices = new HashMap<>();private int accessCount = 0;public void init() {stockPrices.put("APPL", Price.builder().currPrice(new BigDecimal("130.06")).build());}private class PriceDashboardNewImpl implements PriceDashboard {@Overridepublic Price getPrice(String symbol) {log.info("log this inner class action");return stockPrices.get(symbol);
// log.info("about to reference by this");
// return DemoPartOneTest.this.stockPrices.get(symbol);}}public static void main(String[] args) {DemoPart1Test test = new DemoPart1Test();test.init();PriceDashboard priceDashboard = test.new PriceDashboardNewImpl();log.info(priceDashboard.getPrice("APPL").toString());}
}
局部内部类
定义在成员方法中,在代码块之外无法使用
@Slf4j
public class DemoPart2Test {private Map<String, Price> stockPrices = new HashMap<>();private int accessCount = 0;public void init() {stockPrices.put("APPL", Price.builder().currPrice(new BigDecimal("130.06")).build());}public PriceDashboard priceBoard() {class PriceDashboardInMethodImpl implements PriceDashboard {@Overridepublic Price getPrice(String symbol) {log.info("log this in-method action");return stockPrices.get(symbol);}}return new PriceDashboardInMethodImpl();}public static void main(String[] args) {DemoPart2Test test = new DemoPart2Test();test.init();PriceDashboard priceDashboard = test.priceBoard();log.info(priceDashboard.getPrice("APPL").toString());}
}
匿名内部类
一般写法
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-9ZbfOXVE-1652065085743)(WEBRESOURCE3802f4261394549afbff028b2afb4ee0)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1b4973d2119644eb9f40594cc73cdbb4.png)
函数式写法
public PriceDashboard anonPriceBoard() {return symbol -> {log.info("log this in-method anonymous action");return stockPrices.get(symbol);};
}
基于函数式接口的lambda表达式
函数式接口的使用只能存在一个抽象方法,存在多余的抽象方法则编译不通过。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface PriceCalculation {BigDecimal increase(BigDecimal curr, BigDecimal inc);static void staticMethod() {System.out.println("static method");}default void defaultMethod() {System.out.println("default method");}
}
静态方法的调用可以通过接口名称直接调用,而default方法只能通过实现类来调用。
public class PriceCalculationImpl implements PriceCalculation{@Overridepublic BigDecimal increase(BigDecimal curr, BigDecimal inc) {return curr.add(inc);}@Overridepublic void defaultMethod() {System.out.println("customized default");}public static void main(String[] args) {//static methodPriceCalculation.staticMethod();//default methodnew PriceCalculationImpl().defaultMethod();}
}
举例:
// 接口一
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Demo0ParamInterf {String print();
}// 接口二
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Demo1ParamInterf {void print(int a);
}// 接口三
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Demo2ParamInterf {int print(int a, int b);
}// 接口四
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Demo3ParamInterf {int print();//equals is Object methodboolean equals(Object a);//Object.clone is not public, so not functional
// Object clone();
}
表达式
public class DemoParamTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Demo0ParamInterf impl0 = () -> "0 param";Demo1ParamInterf impl1 = (a) -> System.out.println(a);Demo2ParamInterf impl2 = (a, b) -> {int c = a * b;int d = Math.floorMod(c, a - 1);return d;};}
}
JDK8中自带的函数式接口
Predicate判断
接口
/*** Represents a predicate (boolean-valued function) of one argument.** <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a>* whose functional method is {@link #test(Object)}.** @param <T> the type of the input to the predicate** @since 1.8*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Predicate<T> {/*** Evaluates this predicate on the given argument.** @param t the input argument* @return {@code true} if the input argument matches the predicate,* otherwise {@code false}*/boolean test(T t);/*** Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical* AND of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed* predicate, if this predicate is {@code false}, then the {@code other}* predicate is not evaluated.** <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.** @param other a predicate that will be logically-ANDed with this* predicate* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical* AND of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate* @throws NullPointerException if other is null*/default Predicate<T> and(Predicate<? super T> other) {Objects.requireNonNull(other);return (t) -> test(t) && other.test(t);}/*** Returns a predicate that represents the logical negation of this* predicate.** @return a predicate that represents the logical negation of this* predicate*/default Predicate<T> negate() {return (t) -> !test(t);}/*** Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical* OR of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed* predicate, if this predicate is {@code true}, then the {@code other}* predicate is not evaluated.** <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.** @param other a predicate that will be logically-ORed with this* predicate* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical* OR of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate* @throws NullPointerException if other is null*/default Predicate<T> or(Predicate<? super T> other) {Objects.requireNonNull(other);return (t) -> test(t) || other.test(t);}/*** Returns a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}.** @param <T> the type of arguments to the predicate* @param targetRef the object reference with which to compare for equality,* which may be {@code null}* @return a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}*/static <T> Predicate<T> isEqual(Object targetRef) {return (null == targetRef)? Objects::isNull: object -> targetRef.equals(object);}/*** Returns a predicate that is the negation of the supplied predicate.* This is accomplished by returning result of the calling* {@code target.negate()}.** @param <T> the type of arguments to the specified predicate* @param target predicate to negate** @return a predicate that negates the results of the supplied* predicate** @throws NullPointerException if target is null** @since 11*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")static <T> Predicate<T> not(Predicate<? super T> target) {Objects.requireNonNull(target);return (Predicate<T>)target.negate();}
}使用
@Slf4j
public class DemoPredicateTest {@Testpublic void SimplePredicate() {Predicate<Integer> isAdult = age -> (age > 18);log.info(String.valueOf(isAdult.test(20)));log.info(String.valueOf(isAdult.test(16)));}@Testpublic void AndPredicate() {Predicate<Integer> isAdult = new Predicate<Integer>() {@Overridepublic boolean test(Integer age) {log.info("we are young once");return age > 18;}};Predicate<Integer> isRetired = age -> {log.info("yes, pension");return age > 70;};log.info(String.valueOf(isAdult.and(isRetired).test(25)));
// log.info(String.valueOf(isRetired.and(isAdult).test(25)));}@Testpublic void OrPredicate() {Predicate<Integer> cannotRead = age -> (age < 4);Predicate<Integer> cannotCode = age -> (age > 99);log.info("Should quit coding at 35? {}",cannotRead.or(cannotCode).test(35));}@Testpublic void NegatePredicate(){Predicate<Integer> isAdult = age -> (age >18);log.info(String.valueOf(isAdult.negate().test(16)));}@Testpublic void compositePredicate(){Predicate<Integer> cannotRead = age -> (age < 4);Predicate<Integer> cannotCode = age -> (age > 99);//composite them togetherPredicate<Integer> compositePredicate = cannotRead.or(cannotCode).negate();//now you can pass this composite predicate around in your programlog.info("Should quit coding at 35? {}", compositePredicate.test(35));}}
Consumer消费
接口
/*** Represents an operation that accepts a single input argument and returns no* result. Unlike most other functional interfaces, {@code Consumer} is expected* to operate via side-effects.** <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a>* whose functional method is {@link #accept(Object)}.** @param <T> the type of the input to the operation** @since 1.8*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T> {/*** Performs this operation on the given argument.** @param t the input argument*/void accept(T t);/*** Returns a composed {@code Consumer} that performs, in sequence, this* operation followed by the {@code after} operation. If performing either* operation throws an exception, it is relayed to the caller of the* composed operation. If performing this operation throws an exception,* the {@code after} operation will not be performed.** @param after the operation to perform after this operation* @return a composed {@code Consumer} that performs in sequence this* operation followed by the {@code after} operation* @throws NullPointerException if {@code after} is null*/default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) {Objects.requireNonNull(after);return (T t) -> { accept(t); after.accept(t); };}
}
使用
@Slf4j
public class DemoConsumerTest {@Testpublic void LogConsumer() {Consumer<Object> logConsumer = o -> {log.info(o.toString());};logConsumer.accept("Print something");logConsumer.accept(System.currentTimeMillis());}@Testpublic void AndThen() {Consumer<List<String>> upperCaseConsumer = strings -> {for (int i = 0; i < strings.size(); i++) {strings.set(i, strings.get(i).toUpperCase());}};Consumer<List<String>> logConsumer = strings -> strings.forEach(str -> System.out.println(str));List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList("foo", "bar", "baz");upperCaseConsumer.andThen(logConsumer).accept(list);}
}
Supplier供应商
接口
/*** Represents a supplier of results.** <p>There is no requirement that a new or distinct result be returned each* time the supplier is invoked.** <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a>* whose functional method is {@link #get()}.** @param <T> the type of results supplied by this supplier** @since 1.8*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier<T> {/*** Gets a result.** @return a result*/T get();
}
使用
@Slf4j
public class DemoSupplierTest {@Testpublic void RandomSupplier() {Supplier<Double> doubleSupplier = Math::random;Consumer<Double> logConsumer = num -> log.info(String.valueOf(num));logConsumer.accept(doubleSupplier.get());}
}
Function方法
接口
/*** Represents a function that accepts one argument and produces a result.** <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a>* whose functional method is {@link #apply(Object)}.** @param <T> the type of the input to the function* @param <R> the type of the result of the function** @since 1.8*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T, R> {/*** Applies this function to the given argument.** @param t the function argument* @return the function result*/R apply(T t);/*** Returns a composed function that first applies the {@code before}* function to its input, and then applies this function to the result.* If evaluation of either function throws an exception, it is relayed to* the caller of the composed function.** @param <V> the type of input to the {@code before} function, and to the* composed function* @param before the function to apply before this function is applied* @return a composed function that first applies the {@code before}* function and then applies this function* @throws NullPointerException if before is null** @see #andThen(Function)*/default <V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before) {Objects.requireNonNull(before);return (V v) -> apply(before.apply(v));}/*** Returns a composed function that first applies this function to* its input, and then applies the {@code after} function to the result.* If evaluation of either function throws an exception, it is relayed to* the caller of the composed function.** @param <V> the type of output of the {@code after} function, and of the* composed function* @param after the function to apply after this function is applied* @return a composed function that first applies this function and then* applies the {@code after} function* @throws NullPointerException if after is null** @see #compose(Function)*/default <V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {Objects.requireNonNull(after);return (T t) -> after.apply(apply(t));}/*** Returns a function that always returns its input argument.** @param <T> the type of the input and output objects to the function* @return a function that always returns its input argument*/static <T> Function<T, T> identity() {return t -> t;}
}
使用
@Slf4j
public class DemoFunctionTest {@Testpublic void ArithmeticFunction() {Function<Integer, Integer> doubled = x -> x * 2;System.out.println(doubled.apply(3));Function<Integer, Integer> halved = x -> x / 2;System.out.println(halved.apply(10));Function<Integer, Integer> inched = x -> x + 2;System.out.println(inched.apply(20));}@Testpublic void TypeTransformationFunction() {Function<String, Integer> lengthFunction = str -> str.length();System.out.println(lengthFunction.apply("woyouhuile"));}@Testpublic void CompositeFunction() {Function<Integer, Integer> doubled = x -> x * 2;Function<Integer, Integer> inched = x -> x + 2;System.out.println(doubled.compose(inched).apply(10));System.out.println(doubled.andThen(inched).apply(10));}// 通过使用identity的方式,把方法本身作为一个对象传入了map中value中@Testpublic void IdentityFunction() {List<Stock> stocks = Lists.newArrayList(Stock.builder().name("APPLE").symbol("APPL").build(),Stock.builder().name("Amazon").symbol("AMZN").build(),Stock.builder().name("Starbucks").symbol("SBUX").build());Map<String, Stock> map = stocks.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Stock::getSymbol, Function.identity()));System.out.println(map);}
}
其他接口
在java.util包中存在其他函数式接口
bitfunction就是接收两个参数返回一个参数的接口
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-YXJ4DICe-1652065085744)(WEBRESOURCE1f90b7416add7831d258c6377e9c30cf)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bae72322538545ef9fbc757919555a2f.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-zZDZLzOs-1652065085744)(WEBRESOURCEf4ad6069ee16657aeace3d14366c1c5a)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ac3fe935c8314f18b5c03c3668fc8c0f.png)
因为通用的函数式接口存在包装类的装箱与拆箱的操作,因此定义了许多不同的函数式接口进行使用,在数据量大的时候减少消耗。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-SNCx248R-1652065085744)(WEBRESOURCEc2ebfcc60455dac446180a3de330bf49)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4a6a117ad65c4550af1ca4a3c5ffacf8.png)
方法引用和构造器引用
静态方法引用
使用类名::方法名的方式引用
public class DemoStaticMethodReferenceTest {@Testpublic void printStringTest() {Thread t = new Thread(() -> printString());Thread t1 = new Thread(DemoStaticMethodReferenceTest::printString);t.start();}public static void printString() {System.out.println("string");}//ClassName::staticMethodName
}
非静态方法引用
定义一个比较器
public class StockComparator implements Comparator<Stock> {@Overridepublic int compare(Stock o1, Stock o2) {return o1.getSymbol().compareTo(o2.getSymbol());}
}
使用@Builder注解,可以使用build的方式创建类
@Data
@Builder
public class Stock {public Stock() {}public Stock(String symbol, String name) {this.symbol = symbol;this.name = name;}private String symbol;private String name;
}
使用
public class DemoInstanceMethodReferenceTest {@Testpublic void orderStockTest() {List<Stock> stocks = Lists.newArrayList(Stock.builder().name("APPLE").symbol("APPL").build(),Stock.builder().name("Amazon").symbol("AMZN").build(),Stock.builder().name("Starbucks").symbol("SBUX").build());StockComparator stockComparator = new StockComparator();stocks.stream().sorted((o1, o2) -> o1.getSymbol().compareTo(o2.getSymbol()))//.sorted(stockComparator::compare).collect(Collectors.toList());stocks.stream()
// .forEach(stock -> System.out.println(stock));.forEach(System.out::println);}//instanceReference::methodName}
构造器引用
接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface StockCreator {Stock getStock();
}@FunctionalInterface
public interface StockCreator2 {Stock getStock(String symbol, String name);
}
根据参数的类型以及数量,引用对应的构造器。不对应时,无法使用构造器引用。
public class DemoConstructorReferenceTest {@Testpublic void stockConstructorTest() {StockCreator creator1 = Stock::new;StockCreator2 creator2 = Stock::new;Supplier<Stock> creator3 = Stock::new;Stock stock1 = creator1.getStock();Stock stock2 = creator2.getStock("APPL", "APPLE Inc");Stock stock3 = creator3.get();}//ClassName::new
}
lambda表达式中的异常处理
需要抛出异常的方法
public class ComplexComputer {public String encrypt(String input) throws GeneralSecurityException, InterruptedException {Thread.sleep(1000L);return "encoded";}
}
根据场景选择何时的异常处理逻辑可以使用@SneakyThrows或者try/catch在方法底层抛出异常,或者向上抛出,用exceptionhandle处理。
public class DemoThrowExceptionTest {public ComplexComputer complexComputer = new ComplexComputer();@Testpublic void forLoopTest() throws GeneralSecurityException, InterruptedException {List<String> items = Lists.newArrayList("foo", "bar", "baz");for (String item : items) {complexComputer.encrypt(item);}}@Testpublic void throwIOExceptionTest() {List<String> items = Lists.newArrayList("foo", "bar", "baz");items.forEach(new Consumer<String>() {@SneakyThrows@Overridepublic void accept(String item) {complexComputer.encrypt(item);}});}
}
Currying in java
科利化是函数式编程一个重要的特性,意思是把接受多个参数的函数变为接受单一参数的函数。
科里方程如下
Named after Haskell Curryfunction curry(f) {return function(a) {return function(b) {return f(a, b);};};
}f(a,b) -> f(a)(b)
科利化的使用
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jJmav0UZ-1652065085745)(WEBRESOURCE82fb0170acaa43d3d7395e03ec21f05f)]
函数式改造之后
@Test
public void testSimpleStockModelCreation() {BiFunction<String, String, StockModelA> StockModelCreator = (symbol, name) -> new StockModelA(symbol, name);Function<String, Function<String, StockModelA>> CurryingStockModelInnerClassCreator =symbol -> name -> new StockModelA(symbol, name);}
使用科利化构造器引用之后,传入对应的值
@Test
public void testMoreAttrStockModelCreation() {Function<String, Function<String, Function<String, Function<BigDecimal, Function<BigDecimal, StockModelB>>>>>curryingStockModelCreator =symbol -> name -> desc -> currPrice -> prevPrice -> new StockModelB(symbol, name, desc, currPrice, prevPrice);StockModelB demoStockModel = curryingStockModelCreator.apply("SYMBOL").apply("NAME").apply("DESCRIPTION").apply(new BigDecimal("1.00")).apply(new BigDecimal("0.99"));
}
部分属性不变时
@Test
public void testPartialModelCreation() {Function<String, Function<String, Function<String, Function<BigDecimal, Function<BigDecimal, StockModelB>>>>>curryingStockModelCreator =symbol -> name -> desc -> currPrice -> prevPrice -> new StockModelB(symbol, name, desc, currPrice, prevPrice);Function<BigDecimal, Function<BigDecimal, StockModelB>>partialStockModelCreator =currPrice -> prevPrice -> curryingStockModelCreator.apply("SYMBOL").apply("NAME").apply("DESCRIPTION").apply(currPrice).apply(prevPrice);StockModelB fromPartialCreated = partialStockModelCreator.apply(new BigDecimal("1.00")).apply(new BigDecimal("0.99"));System.out.println(fromPartialCreated);
}
Java Stream API
stream流是可以更方便的使用lambda表达式操作集合的数据结构,并且实现了并行计算等功能。只有在真正需要计算的时候才会执行,“延迟计算”。
stream-category
Stream- intermiate 中间操作,返回流但是不会计算- stateless 无状态操作,元素的处理不会受之前或之后元素的影响- stateful 有状态操作,只有在拿到了所有元素之后才能继续- terminal 终结操作,会进行计算- short-circuiting 短路操作,遇到符合的元素就可以得到结果- un-short-circuiting 非短路操作,只有所有元素都拿到才能计算结果
使用stream流操作Collections
创建stream流
方法一:Stream.generate
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-d7CkUMI0-1652065085745)(WEBRESOURCEefd8335e784f5aeb459180a567ce2dfb)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/eac223b45dba415a937d791bab2778cb.png)
使用limit限制无限流生成的数据
@Test
public void streamGenerate() {Stream<Double> stream = Stream.generate(Math::random);stream.limit(5).forEach(System.out::println);
}
方法二:Stream.of
@Test
public void streamOf() {Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of("foo");Stream<String> stream2 = Stream.of("foo", "bar", "baz");//stream2 and stream3 are equivalentStream<String> stream3 = Arrays.stream(new String[]{"foo", "bar", "baz"});
}
方法三:streamFromCollections
因为map不是继承collection接口,所以要使用stream流遍历时需要entrySet()方法。
@Test
public void streamFromCollections() {List<Stock> stocks = Lists.newArrayList(Stock.builder().name("APPLE").symbol("APPL").build(),Stock.builder().name("Amazon").symbol("AMZN").build(),Stock.builder().name("Starbucks").symbol("SBUX").build());Stream<Stock> stream1 = stocks.stream();Map map = new HashMap();map.entrySet().stream();
}
方法四:Stream.builder
@Test
public void streamBuilder() {Stream.Builder<Stock> builder = Stream.builder();builder.accept(Stock.builder().name("APPLE").symbol("APPL").build());builder.accept(Stock.builder().name("Amazon").symbol("AMZN").build());builder.accept(Stock.builder().name("Starbucks").symbol("SBUX").build());Stream<Stock> stockStream = builder.build();
}
操作stream
foreach
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-wImV5202-1652065085746)(WEBRESOURCE91923ba241b76a610a9e1fdf11b701bd)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ca1abb99904e4e6fb2a1f0fb78e6f35a.png)
@Test
public void streamForEach() {List<Stock> stocks = Lists.newArrayList(Stock.builder().name("APPLE").symbol("APPL").build(),Stock.builder().name("Amazon").symbol("AMZN").build(),Stock.builder().name("Starbucks").symbol("SBUX").build());stocks.stream().forEach(stock -> stock.setSymbol(stock.getSymbol().toLowerCase()));System.out.println(stocks);//directly on Iterable and Mapstocks.forEach(stock -> stock.setSymbol(stock.getSymbol() + "Iterable"));System.out.println(stocks);Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap();map.forEach((k, v)->{});
}
map
map是stream流的中间操作,会返回一个流供下一步操作。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ejZYq8w8-1652065085746)(WEBRESOURCE547d27123b8fc862417e8fd7d97abed6)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0b918c8c068348c09e3b7de294acf89b.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-iXR2gqw4-1652065085747)(WEBRESOURCE1eb5415c0541d1a80c39fae9cc143242)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/cc806d9e6c134021a3de6fc15b337454.png)
@Test
public void streamMap() {Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("foo", "bar", "baz");Stream<Stock> stockStream = stream.map(str -> Stock.builder().name(str).build());stockStream.forEach(System.out::println);
}
输出结果
Stock(symbol=null, name=foo)
Stock(symbol=null, name=bar)
Stock(symbol=null, name=baz)
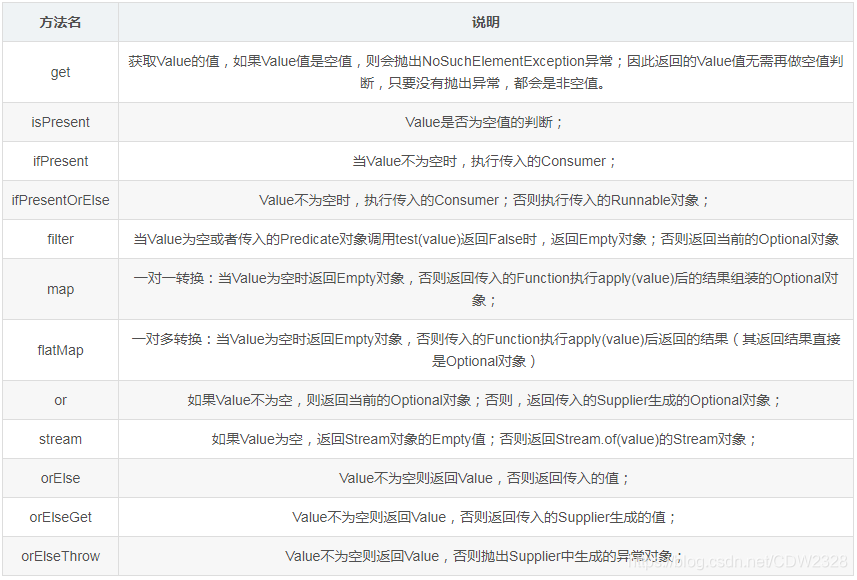
collect
把处理好的stream流的元素收集起来,返回一个数据集合。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-TUH6C4so-1652065085747)(WEBRESOURCEa3fe625e961cf016ea5a98ab1e5ddab3)]
Collector中定义了三个泛型,T是规约操作的输入类型,A是中间暂存所用的类型,R是规约操作输出的类型。
public interface Collector<T, A, R> {// 创建可变的结果容器Supplier<A> supplier();// 将数据元素合并到结果容器中BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator();// 将部分结果合并到一个结果容器中BinaryOperator<A> combiner();// 将结果类型转换Function<A, R> finisher();Set<Characteristics> characteristics();public static<T, R> Collector<T, R, R> of(Supplier<R> supplier,BiConsumer<R, T> accumulator,BinaryOperator<R> combiner,Characteristics... characteristics) {Objects.requireNonNull(supplier);Objects.requireNonNull(accumulator);Objects.requireNonNull(combiner);Objects.requireNonNull(characteristics);Set<Characteristics> cs = (characteristics.length == 0)? Collectors.CH_ID: Collections.unmodifiableSet(EnumSet.of(Collector.Characteristics.IDENTITY_FINISH,characteristics));return new Collectors.CollectorImpl<>(supplier, accumulator, combiner, cs);}public static<T, A, R> Collector<T, A, R> of(Supplier<A> supplier,BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator,BinaryOperator<A> combiner,Function<A, R> finisher,Characteristics... characteristics) {Objects.requireNonNull(supplier);Objects.requireNonNull(accumulator);Objects.requireNonNull(combiner);Objects.requireNonNull(finisher);Objects.requireNonNull(characteristics);Set<Characteristics> cs = Collectors.CH_NOID;if (characteristics.length > 0) {cs = EnumSet.noneOf(Characteristics.class);Collections.addAll(cs, characteristics);cs = Collections.unmodifiableSet(cs);}return new Collectors.CollectorImpl<>(supplier, accumulator, combiner, finisher, cs);}enum Characteristics {CONCURRENT,UNORDERED,IDENTITY_FINISH}
}
使用
@Test
public void streamCollectToList() {Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("foo", "bar", "baz");Stream<Stock> stockStream = stream.map(str -> Stock.builder().name(str).build());List<Stock> stocks = stockStream.collect(Collectors.toList());
}@Test
public void streamCollectJoining() {Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("foo", "bar", "baz");String result = stream.collect(Collectors.joining("|"));// 使用 | 将元素进行分割System.out.println(result);
}@Test
public void streamCollectGroupBy() {List<Student> students = getStudentsData();//group student by class 按照班级名称对流中的元素进行分组Map<String, List<Student>> byClass =students.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getClassName));System.out.println(byClass);
}@Test
public void streamCollectGroupByWithCustomizedDownstream() {List<Student> students = getStudentsData();//sum student score by classMap<String, Integer> sumScoreByClass =students.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getClassName,Collectors.summingInt(Student::getScore)));System.out.println(sumScoreByClass);//get student with highest score for each classMap<String, Optional<Student>> highestScoreByClass = students.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getClassName,Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Student::getScore))));System.out.println(highestScoreByClass);
}
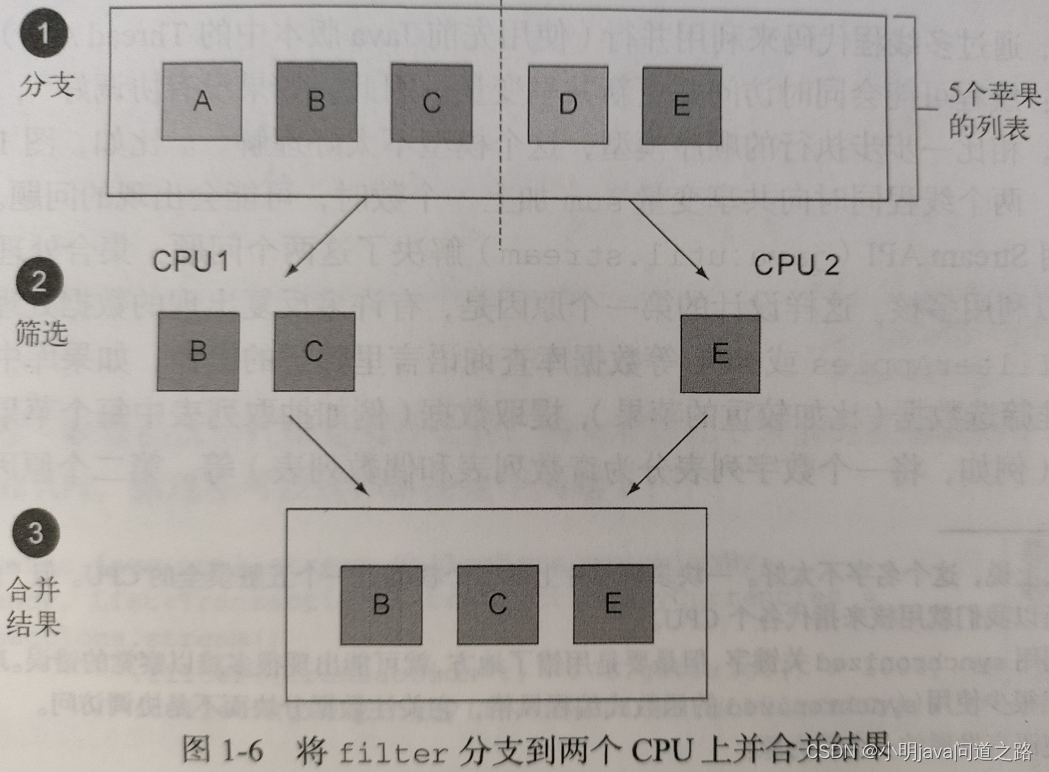
filter
stream流的中间操作,filter中实现了一个Predicate接口。对传入的元素进行判断,断言成功则返回,不成功便丢弃。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-v31gTL2w-1652065085747)(WEBRESOURCEa8fcb41e76f5e8d4d3d9505c33630b47)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2ed443e2e9514679bd3faa4ed9ccdfd1.png)
@Test
public void streamFilter() {List<Student> students = getStudentsData();// 筛选成绩大于80的学生Stream<Student> scoreOver80Stream = students.stream().filter(student -> student.getScore() > 80);System.out.println(scoreOver80Stream.collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
findFirst
短路操作。
@Test
public void streamFindFirst() {List<Student> students = getStudentsData();Optional<Student> firstGuy = students.stream().filter(student -> student.getScore() > 80).findFirst();System.out.println(firstGuy);
}
// 不使用Optional
@Test
public void streamFindFirst() {List<Student> students = getStudentsData();Student firstGuy = students.stream().filter(student -> student.getScore() > 80).findFirst().orElse(new Student());System.out.println(firstGuy);
}
peek
与foreach类似,都实现了consumer接口,但是属于中间操作,操作结束之后会把元素重新返回流中。
@Test
public void streamPeek() {List<Student> students = getStudentsData();students.stream().peek(student -> student.setScore(student.getScore() + 10)).peek(System.out::println);// 在指定终结操作之前都不会打印,“延迟计算”
// .collect(Collectors.toList());
}
flatmap
Function.identity()是返回元素本身
@Test
public void streamFlatMap() {String paragraph = "this is a demo paragraph to calculate char occurrences";String[] words = paragraph.split(" ");Map<String, Long> occurrence = Arrays.stream(words).map(str -> str.split("")).flatMap(strAarray -> Arrays.stream(strAarray))// 整合为一个流.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Function.identity(), Collectors.counting()));// 按照元素自己进行计数分类System.out.println(occurrence);
}
stream流操作nio
// 文件读取
@Test
public void FilesLinesTest() {Path path = new File(getClass().getResource("/stream/nio_datasource_1.txt").getFile()).toPath();try (Stream<String> content = Files.lines(path, Charset.defaultCharset())) {List<String> orderedList = content.map(String::toUpperCase).sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(orderedList);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
// 深度遍历文件夹
@Test
public void FilesWalkTest() {Path rootPath = new File(getClass().getResource("/stream/a").getFile()).toPath();try (Stream<Path> matched = Files.walk(rootPath, 3)) {List<Path> matchedPathList = matched.collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(matchedPathList);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
// 查找文件
@Test
public void FilesFindTest() throws IOException {Path rootPath = new File(getClass().getResource("/stream/a").getFile()).toPath();try (Stream<Path> matched = Files.find(rootPath, 3, (path, attr) -> path.endsWith("bar.txt"))) {List<Path> matchedPathList = matched.collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(matchedPathList);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
ParallelStream
// 使用AtomicInteger保证线程安全
public static AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger();@Test
public void simpleParallel() {List<Student> students = getLotsOfStudents();List<Student> studentList = students.parallelStream().peek(student -> counter.getAndIncrement()).collect(Collectors.toList());
// System.out.println(studentList);System.out.println(students.size());System.out.println(counter);
}