1、顺序栈
一组地址连续的存储单元加一个标识栈顶元素的指针。
#define MaxSize 50 //定义栈中最大元素个数
typedef struct{ ElemType data[MaxSize];//存放栈中的元素int Top;//栈顶指针
}SqStack;
栈空:s.top==-1
栈满:s.top==MaxSize-1
栈长:s.top+1
2、顺序栈的方法
(1)初始化InitStack
void InitStack(SqStack &S){S.top=-1; //初始化栈顶指针
}
(2)栈判空StackEmpty
bool StackEmpty(SqStack &S){if(S.top==-1){return true;else return false;}
}
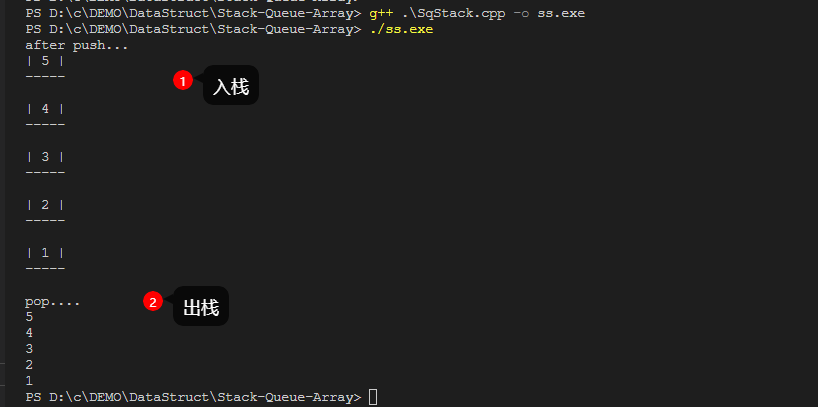
(3)进栈Push 入栈判满,出栈判空
bool Push(SqStack &S,ElemType x){if(s.top==MaxSize-1)return false;S.top++;S.data[S.top]==x;return true;}
(4)出栈Pop
bool Pop(SqStack &S,ElemType &x){if(s.top==-1)return false;x=s.data[s.top--];reurn true;}
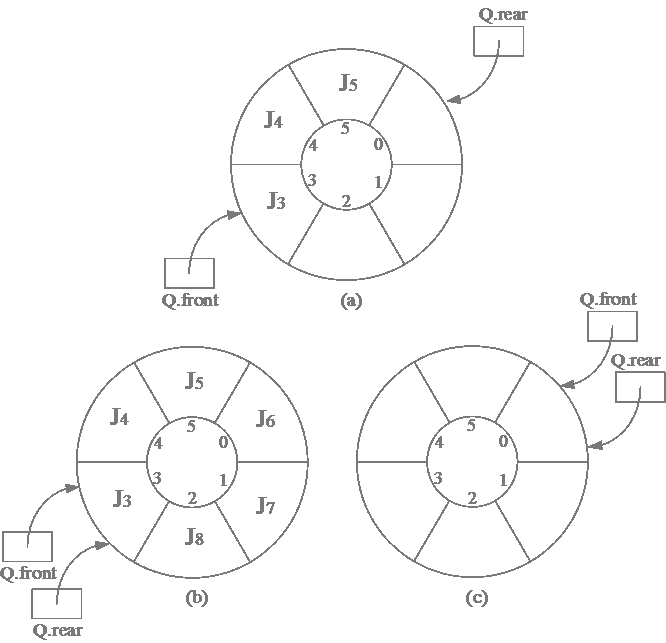
3、共享栈
两个顺序栈共享一个一维空间,将两个栈的栈底分别设置到两端
4、栈的链式存储结构
typedef struct LinkNode{ElemType data;struct LinKNode *next;
}*LiStack5、n个不同元素进栈,出栈元素不同排列 的个数为
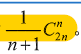
6、判断出入栈的操作序列是否合法
思路:(1)入栈次数必须大于等于出栈次数
bool isStandStack(char a[ ]){int i=0;int count_In=0,count_Out=0while(i<a.length&&count_In>=count_Out){if(a[i]='I')count_In++; elsecount_out++;i++;}if(count_in==count_out)return true;elsereturn false;}
7、用栈的思想判断单链表元素 是否对称
思想:设置一个长度为单链表一半的数组作为栈,将每个元素存入,当再次遇到此元素时,弹出,最后如果数组为空,则说明对称。
bool dc(LinkList L,int n){int i=0; char s[n/2];p=L->next;//p指向第一个结点while(i<n/2){s[i++]=p->data;p=p->next;}i--;if(n%2==1) //如果是奇数,指针后移一个元素p=p->next;while(p!=null&&s[i]==p->data){ //如果下一个结点不为空且当前结点i--;p=p->next;}if(i=-1)return true;elsereturn false;
}
8、 共享栈入栈出栈的操作算法
思想:共享栈相当于两个栈,需要区分是那个栈入栈;入栈判满。共享栈判满方式是top2-top11;
出栈判空,共享栈判空一是top1-1,二是top2==maxSize;
#define maxSize 100;
#define element int
typedef struct{element stack[maxSize];int top1,top2;
}stk;
stk s;
(1)入栈
bool push(int i,element x){ //i是栈号if(!(i=1||i=2)){printf("栈号不匹配!");exit(0);}if(top2-top1==1){printf("栈满!\0");return 0;}switch(i){case 1:s.stack[++s.top1]=x;return 1;break;case 2:s.stack[--s.top2]=x;return 1;break;}
}
(2)出栈
bool pop(int i,element &x){if(!(i=1||i=2)){printf("栈号不匹配!");exit(0);}switch(i){case 1:if(s.top1==-1){printf("栈1空,无法出栈");return 0;}else{x=s.stack[s.top1--];return 1;}break;case 2:if(s.top1==maxSize){printf("栈2空,无法出栈");return 0;}else{x=s.stack[s.top2++];return 1;}break; }
}


![[转载]静息态fMRI、DTI、VBM](http://simg.sinajs.cn/blog7style/images/common/sg_trans.gif)
![[spm操作] VBM分析中,modulation的作用](http://52brain.com/data/attachment/forum/201703/28/022631c8j8h668saiszbw8.png)



