一、移除链表元素
OJ链接![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/submissions/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/submissions/
1.1. | 解题思路 |
创建一个新的哨兵头节点 guard,创建尾节点 tail,创建 cur 用于遍历原链表数据。
对原链表进行遍历,若 cur->val != val,则将 cur 尾插到 tail 的后面,最后将 guard -> next 作为返回值。
1.2. | 题解代码 |
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){struct ListNode* guard=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* tail=guard;struct ListNode* cur=head;while(cur){if(cur->val!=val){tail->next=cur;tail=tail->next;}cur=cur->next;}tail->next=NULL;head=guard->next;free(guard);guard=NULL;return head;
}二、反转链表
OJ链接![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
2.1. | 解题思路 |
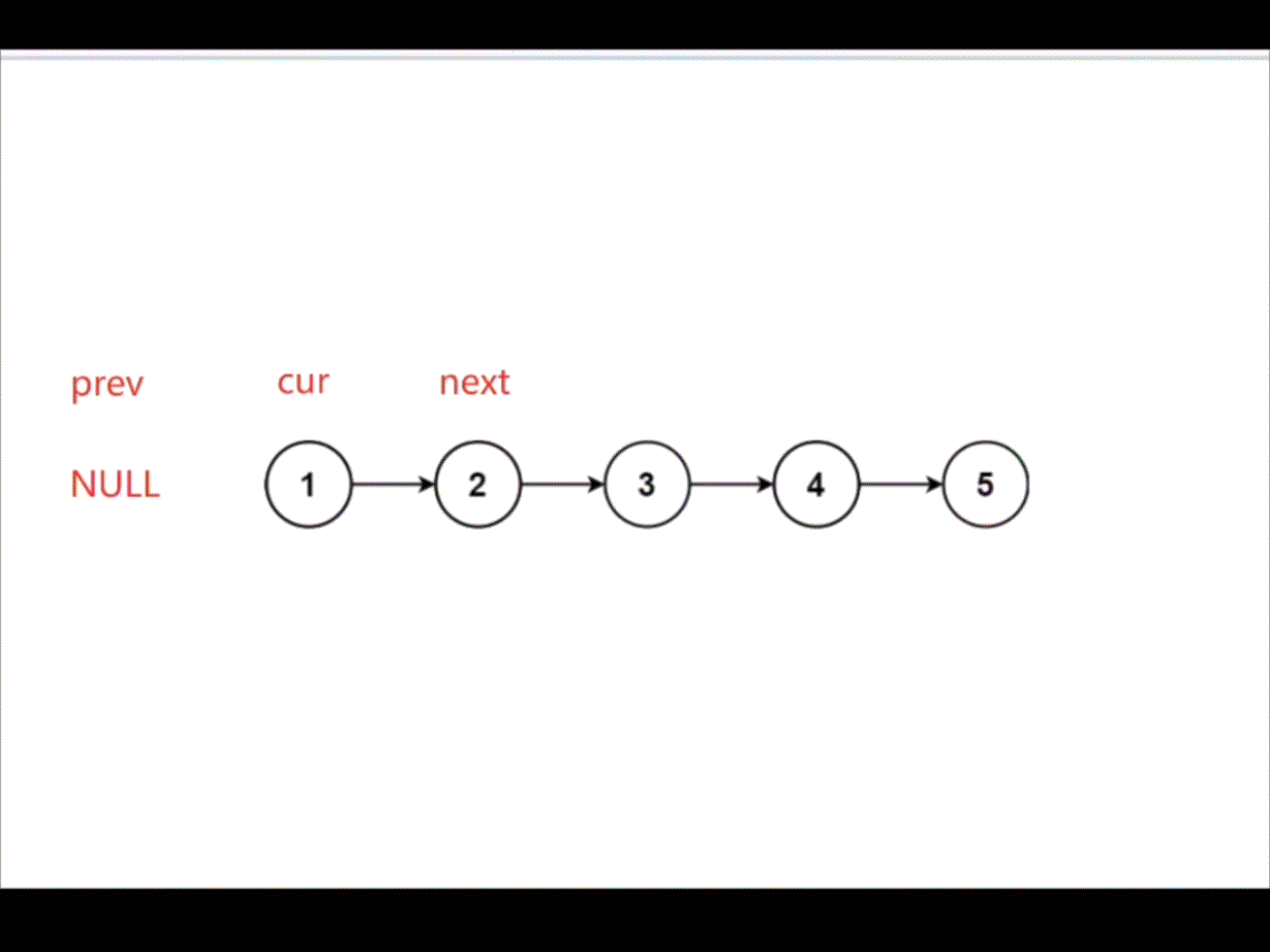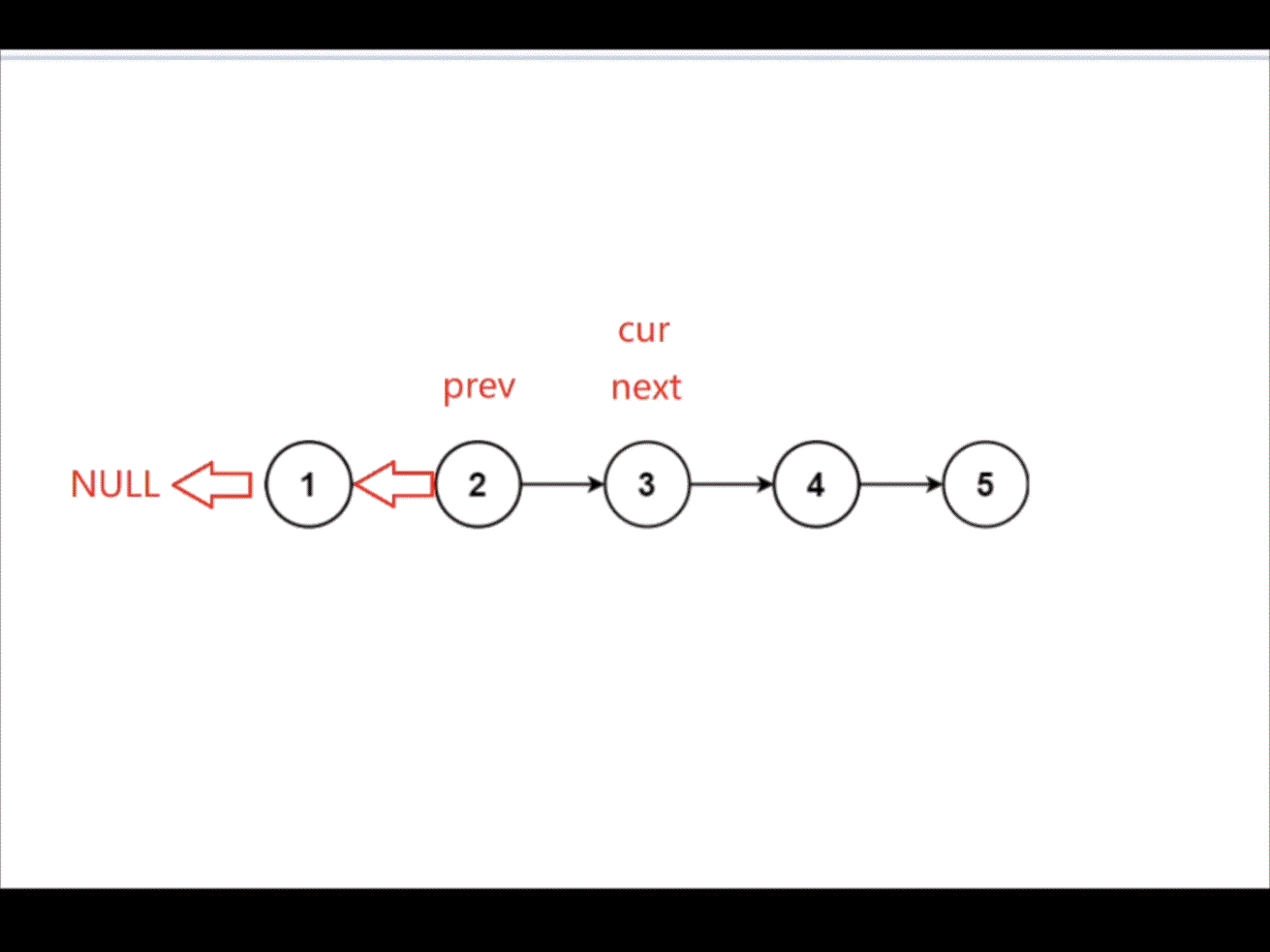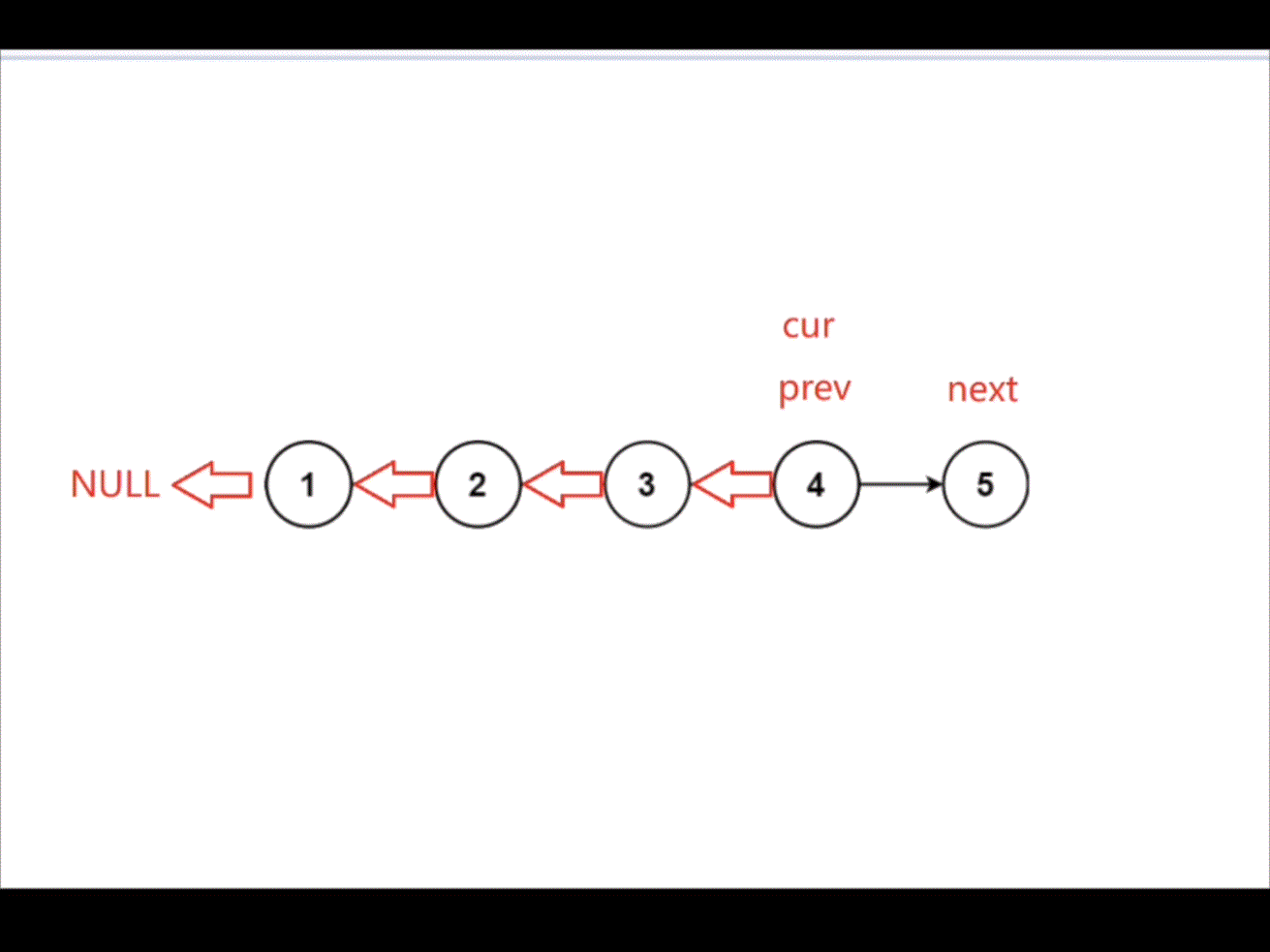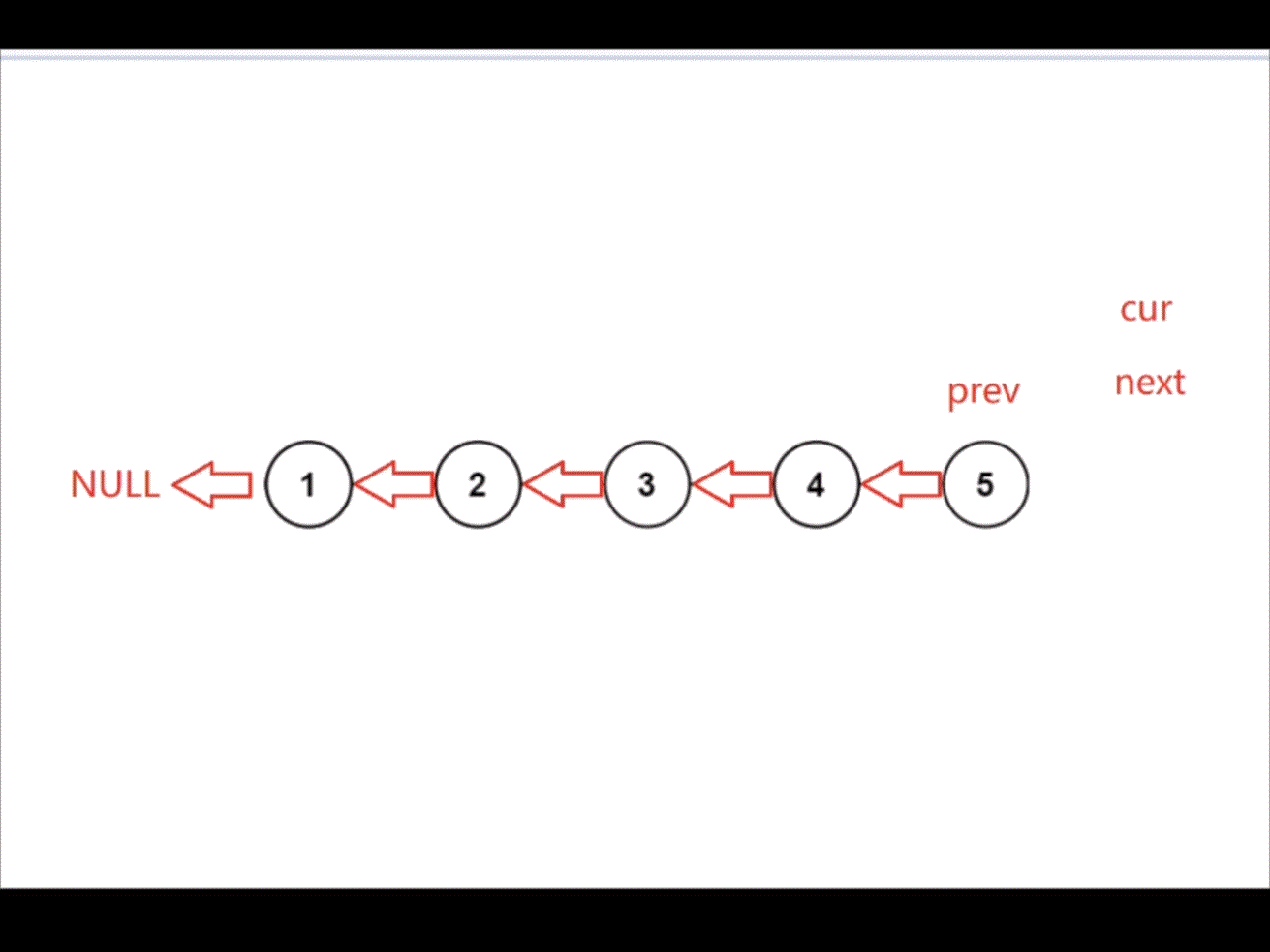
创建变量 prev,cur,next。用 cur 遍历链表,将 cur->next 指向 prev 从而达到反转链表的效果。
2.2. | 题解代码 |
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){struct ListNode* cur=head;struct ListNode* prev=NULL;struct ListNode* next=NULL;while(cur){next=cur->next;cur->next=prev;prev=cur;cur=next;}return prev;
}三、链表的中间结点
OJ链接![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/
3.1. | 解题思路 |
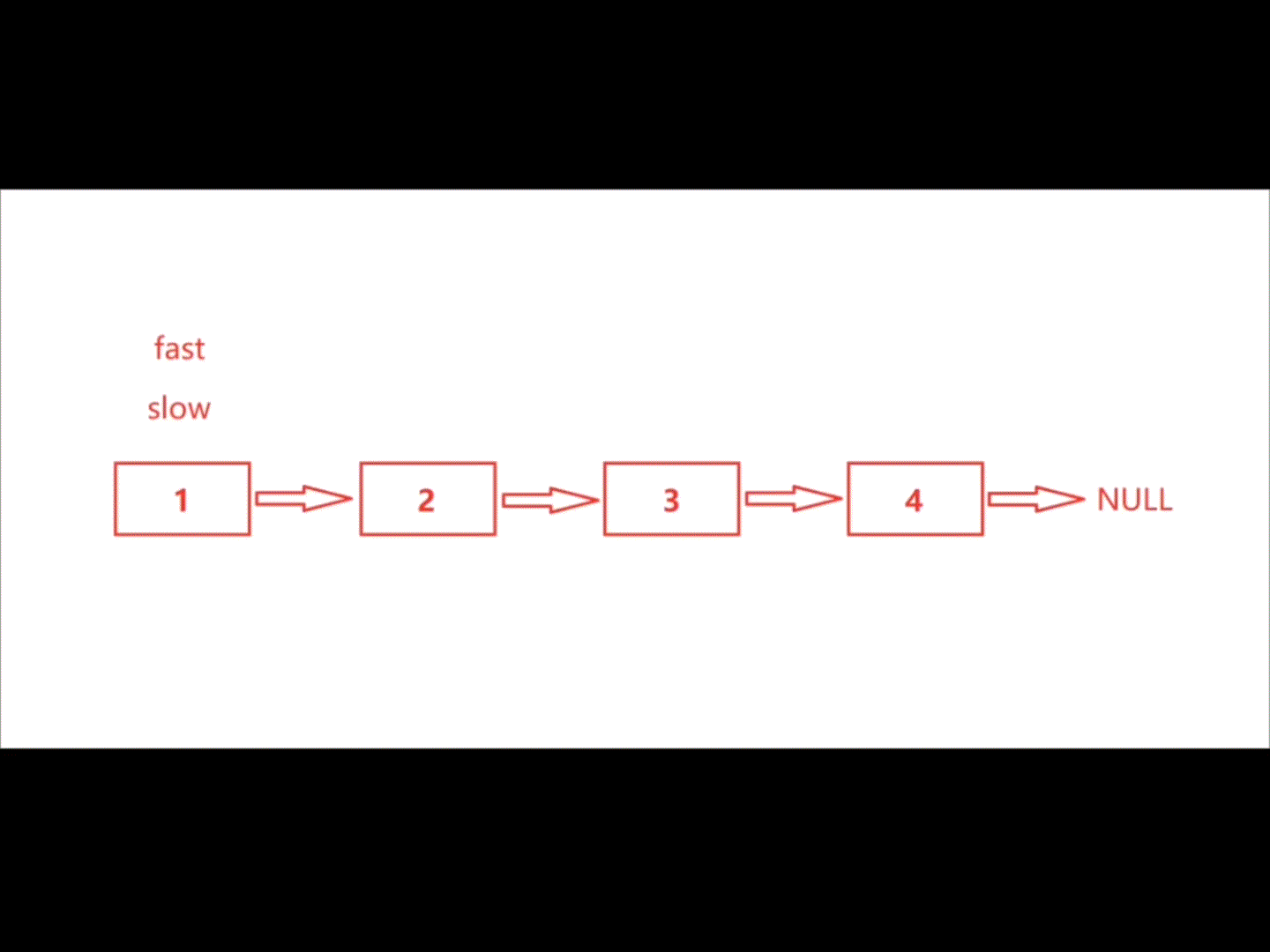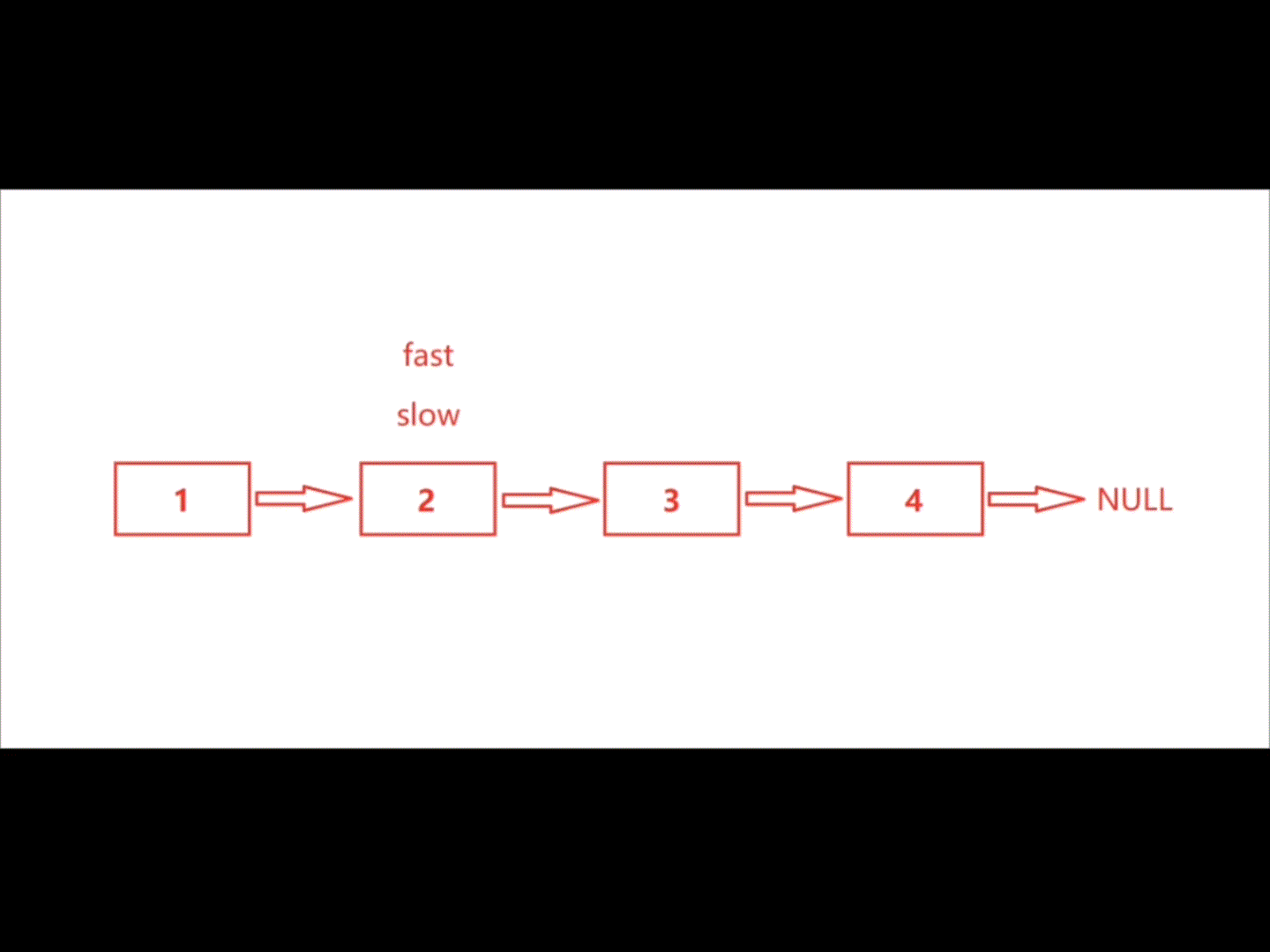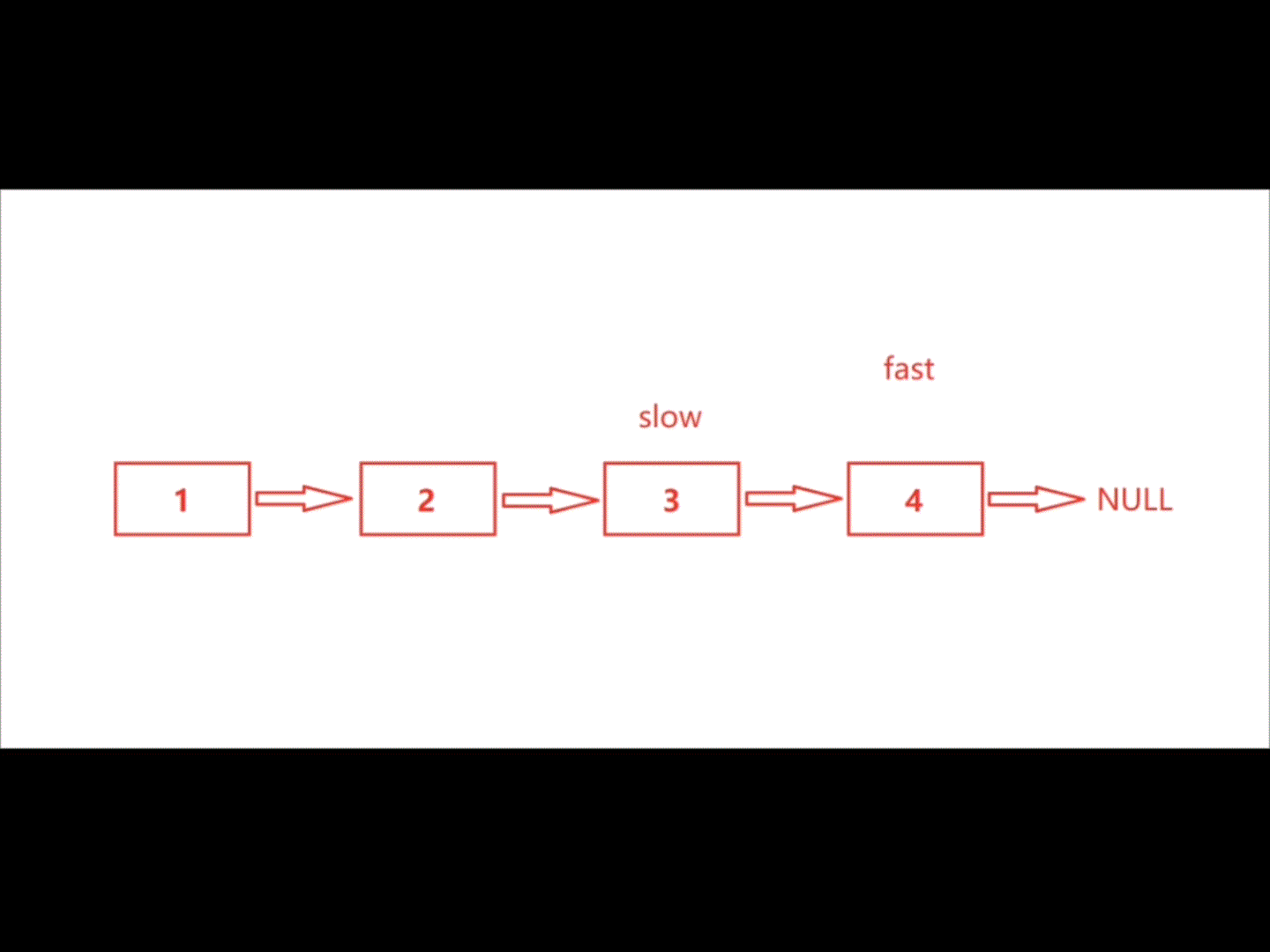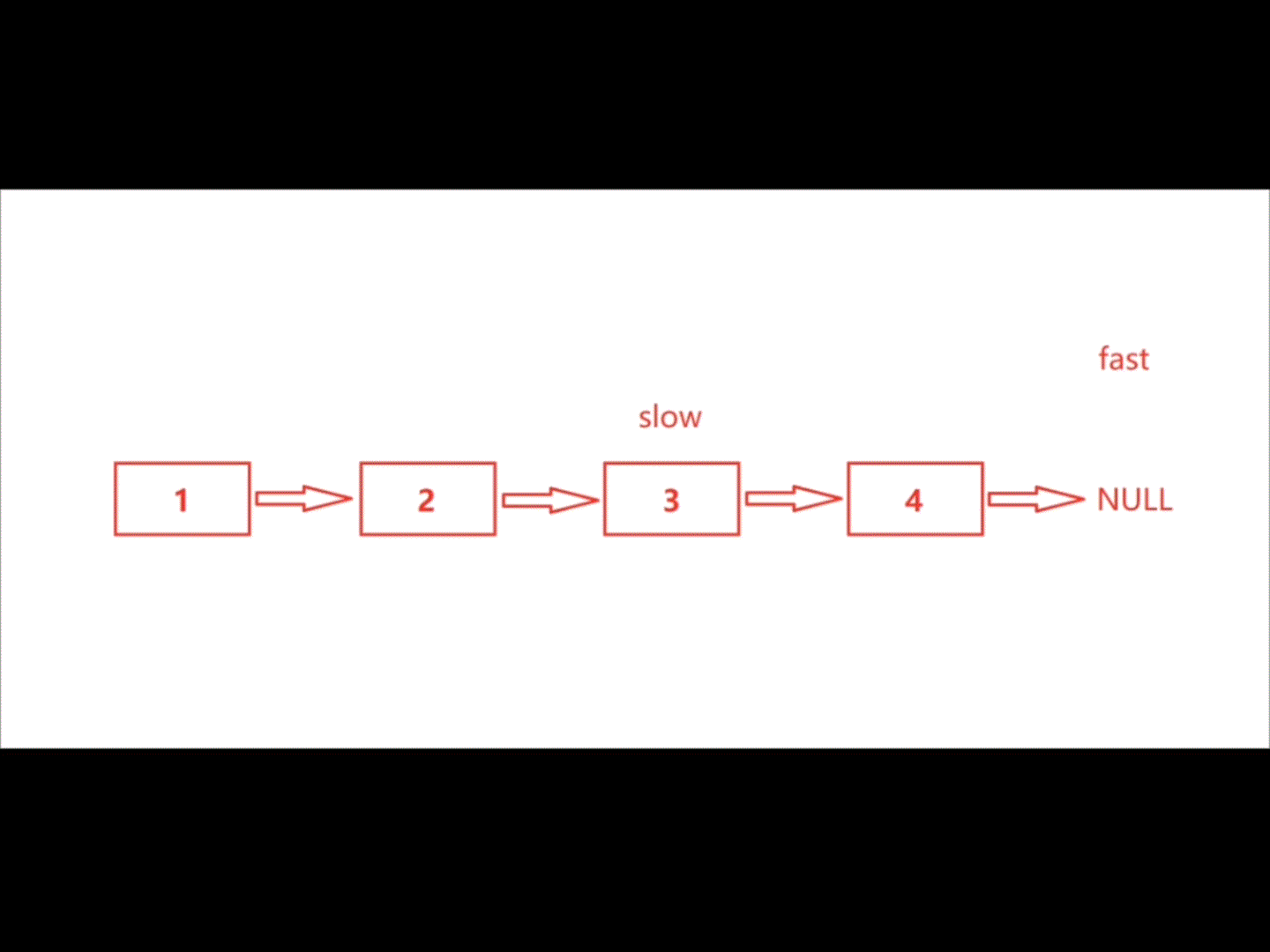
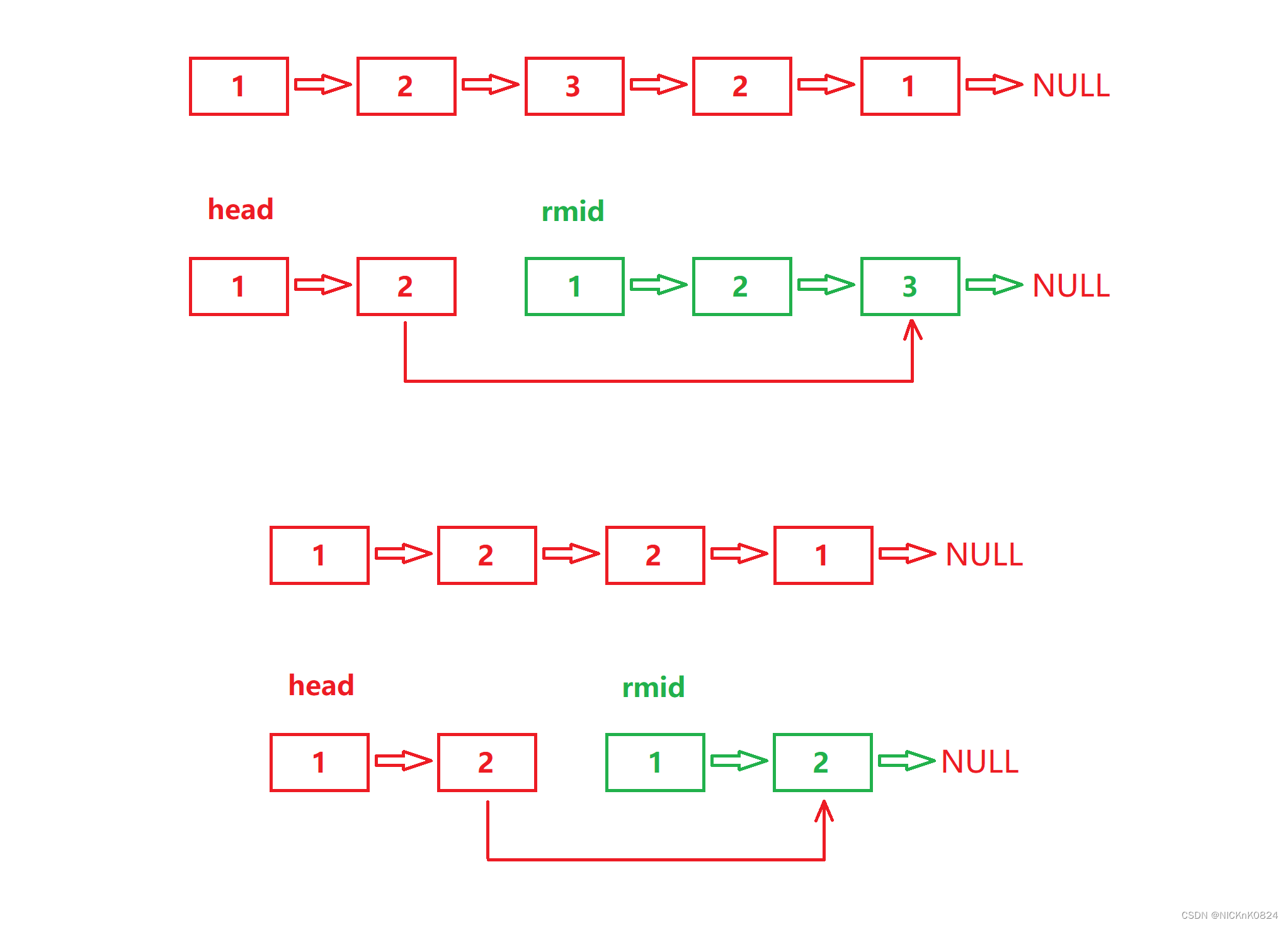
利用快慢指针解决此题正合适,慢指针走一步,快指针走两步。最后快指针走完时,慢指针的位置恰好在链表中间结点处。
注:此题要分两种情况讨论,① 链表长度为奇数,② 链表长度为偶数
| 奇数 |
| 偶数 |
注:链表长度为奇数和链表长度为偶数的结束条件不一样,需要分情况讨论
3.2. | 题解代码 |
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){struct ListNode* fast=head;struct ListNode* slow=head;while(fast&&fast->next){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next->next;}return slow;
}四、链表中倒数第k个结点
OJ链接![]() https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/529d3ae5a407492994ad2a246518148a?tpId=13&&tqId=11167&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/529d3ae5a407492994ad2a246518148a?tpId=13&&tqId=11167&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking
4.1. | 解题思路 |
创建一个快指针一个慢指针,先让快指针走k步,再让快指针和慢指针同时走,一次走一步,当快指针指向NULL时,慢指针指向的就是链表中倒数第k个结点。
4.2. | 题解代码 |
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {struct ListNode* fast=pListHead;struct ListNode* slow=pListHead;while(k--){if(fast==NULL){return NULL;}fast=fast->next;}while(fast){fast=fast->next;slow=slow->next;}return slow;
}五、合并两个有序链表
OJ链接![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
5.1. | 解题思路 |
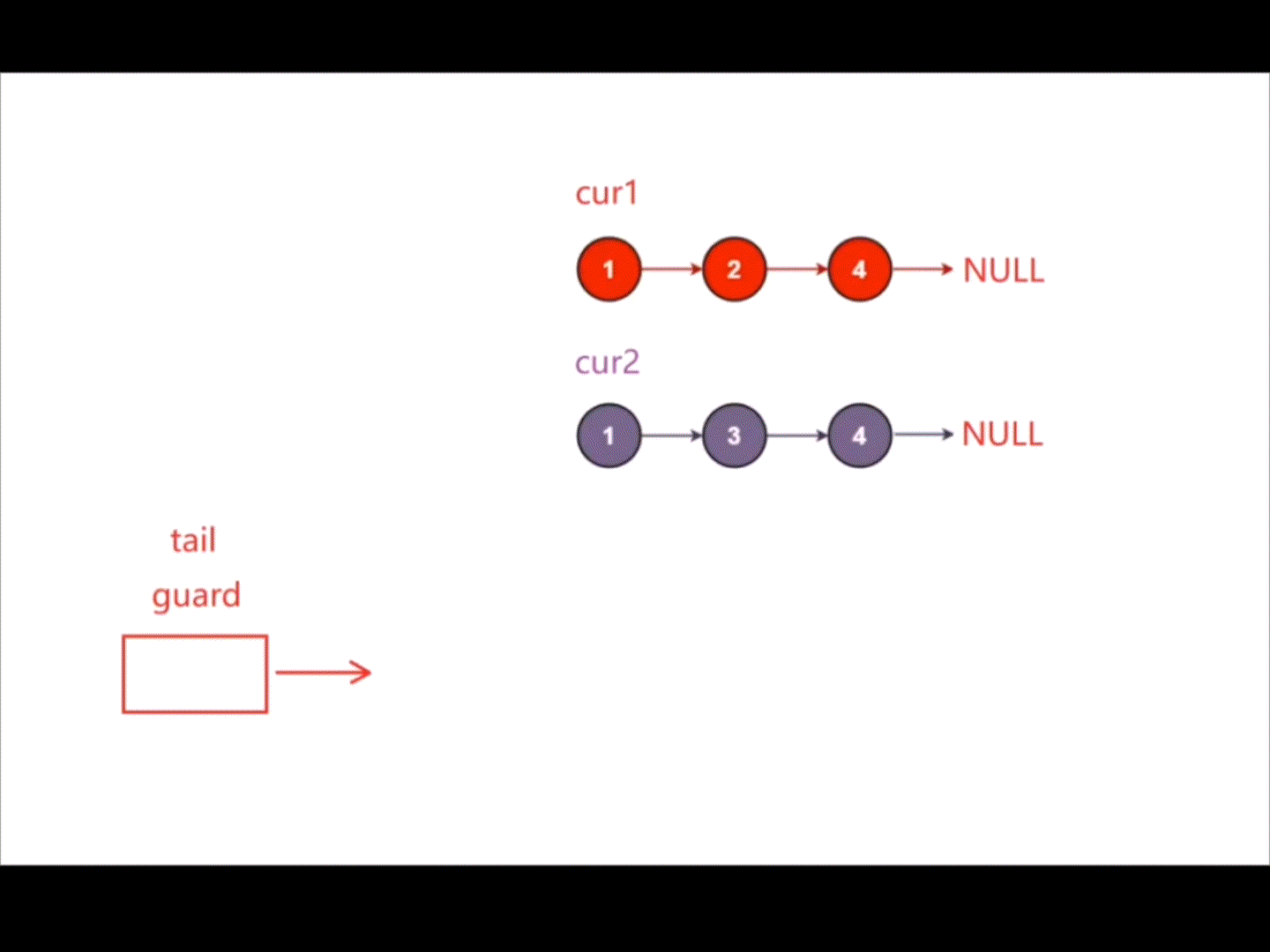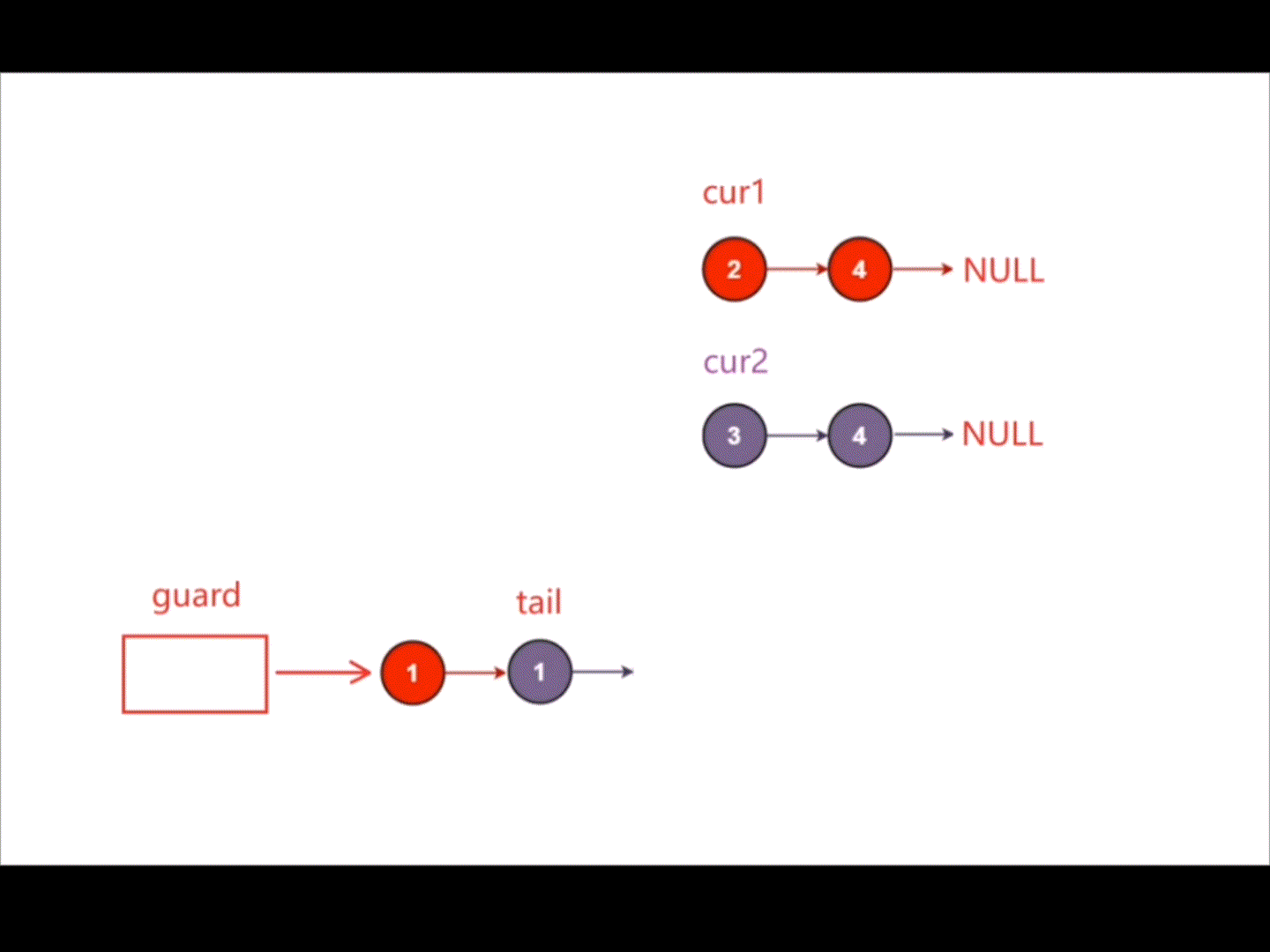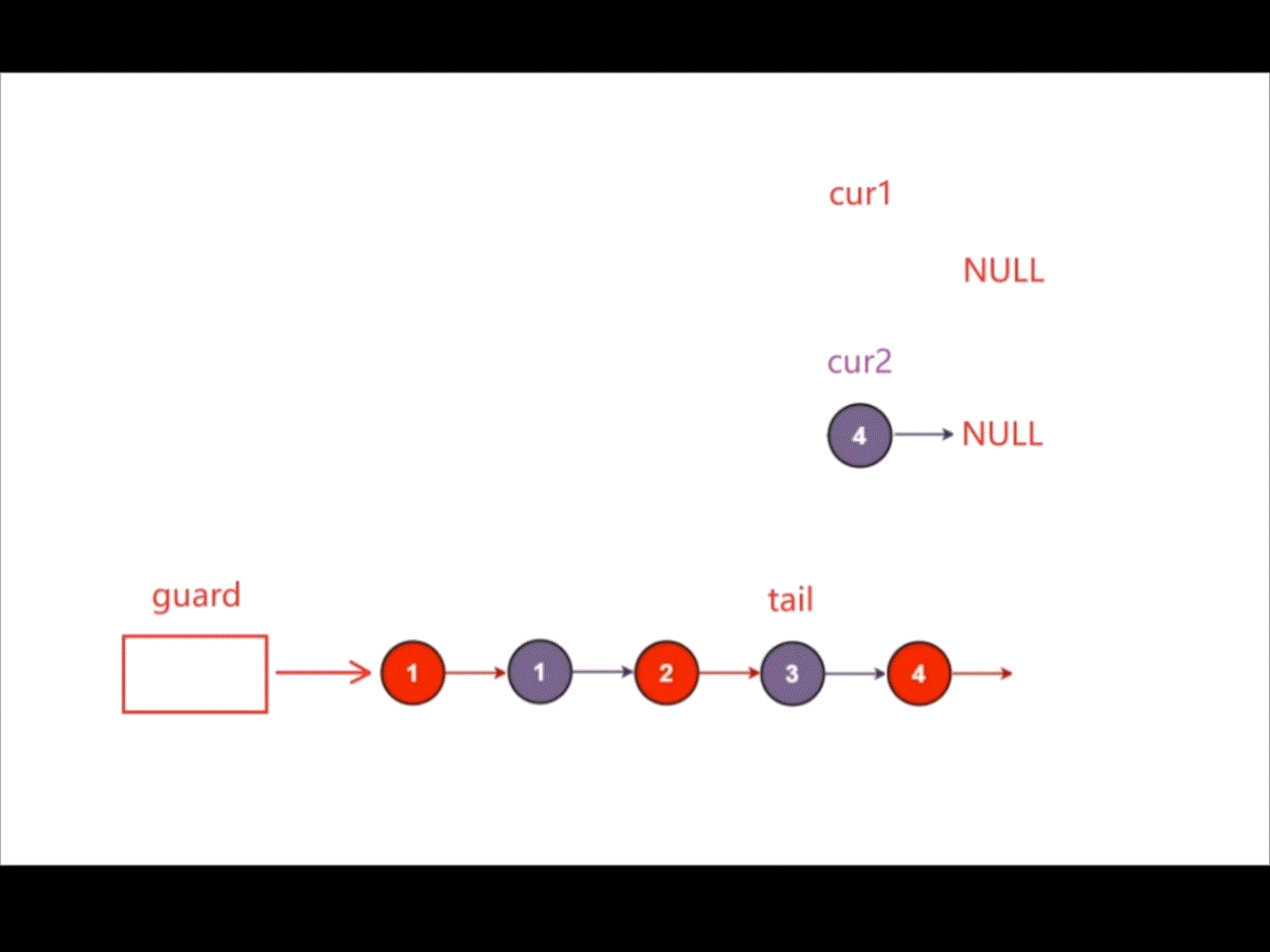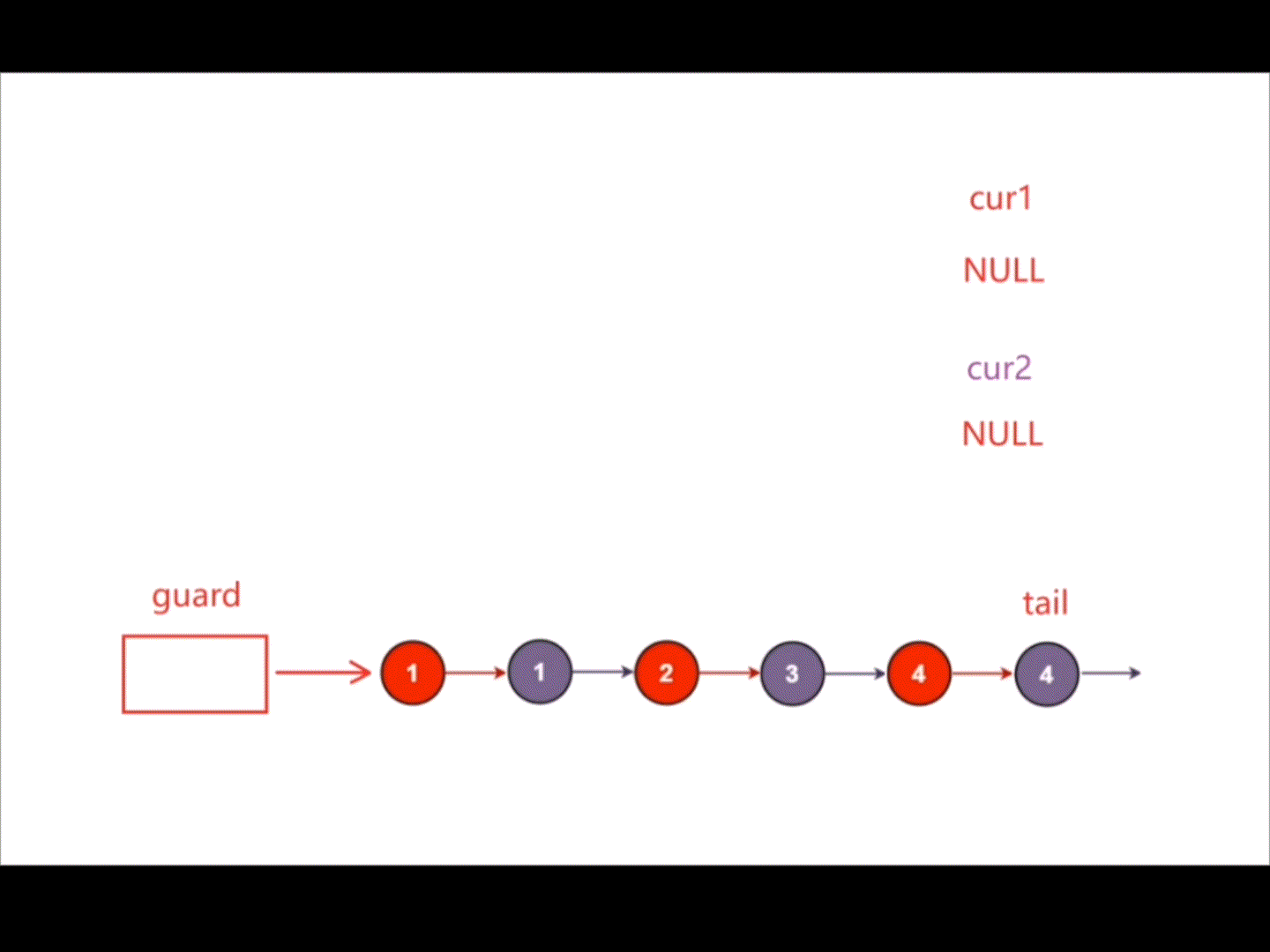
创建一个新的带头结点的链表,创建指针cur1指向链表1,创建指针cur2指向链表2,对比指针cur1指向结点的数据和指针cur2指向结点的数据,将小的那个尾插在新链表后,当指针cur1和指针cur2其中一个指向NULL时,说明其中一个链表已经结束,将另一个未结束的链表直接尾插在新链表后即可。
5.2. | 题解代码 |
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){struct ListNode* guard=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));guard->next=NULL;struct ListNode* tail=guard;struct ListNode* cur1=list1;struct ListNode* cur2=list2;while(cur1&&cur2){if(cur1->val<cur2->val){tail->next=cur1;cur1=cur1->next;}else{tail->next=cur2;cur2=cur2->next;}tail=tail->next;}if(cur1){tail->next=cur1;}if(cur2){tail->next=cur2;}struct ListNode* head=guard->next;free(guard);guard=NULL;return head;
}六、链表分割
OJ链接![]() https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/0e27e0b064de4eacac178676ef9c9d70?tpId=8&&tqId=11004&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/cracking-the-coding-interview/question-ranking
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/0e27e0b064de4eacac178676ef9c9d70?tpId=8&&tqId=11004&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/cracking-the-coding-interview/question-ranking
6.1. | 解题思路 |
创建两个新的带头结点的链表,一个链表的头结点是lessGuard,另一个链表的头结点是greaterGuard。创建指针cur遍历原链表,将原链表中结点的数值小于x的尾插在lessGuard后,将原链表中结点的数值大于x的尾插在greaterGuard后,最后让lessTail->next指向greaterGuard->next,再让greaterTail->next指向NULL。
6.2. | 题解代码 |
class Partition {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {struct ListNode* lessGuard,*greaterGuard,*lessTail,*greaterTail;lessGuard=lessTail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));greaterGuard=greaterTail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));lessGuard->next=NULL;greaterGuard->next=NULL;struct ListNode* cur=pHead;while(cur){if(cur->val<x){lessTail->next=cur;lessTail=lessTail->next;}else{greaterTail->next=cur;greaterTail=greaterTail->next;}cur=cur->next;}lessTail->next=greaterGuard->next;greaterTail->next=NULL;pHead=lessGuard->next;free(lessGuard);lessGuard=NULL;free(greaterGuard);greaterGuard=NULL;return pHead;}
};七、链表的回文结构
OJ链接![]() https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa?tpId=49&&tqId=29370&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/2016test/question-ranking
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa?tpId=49&&tqId=29370&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/2016test/question-ranking
7.1. | 解题思路 |
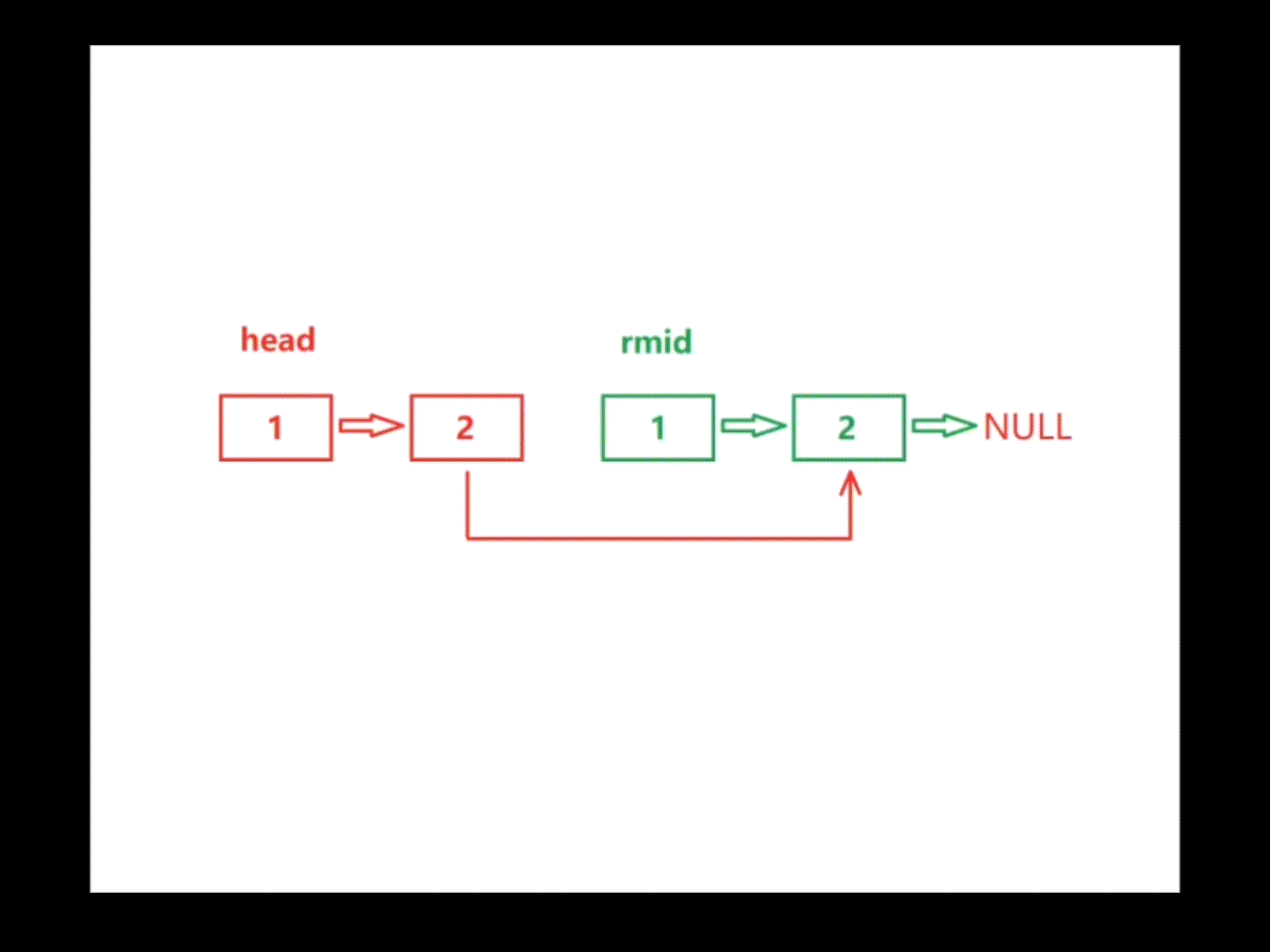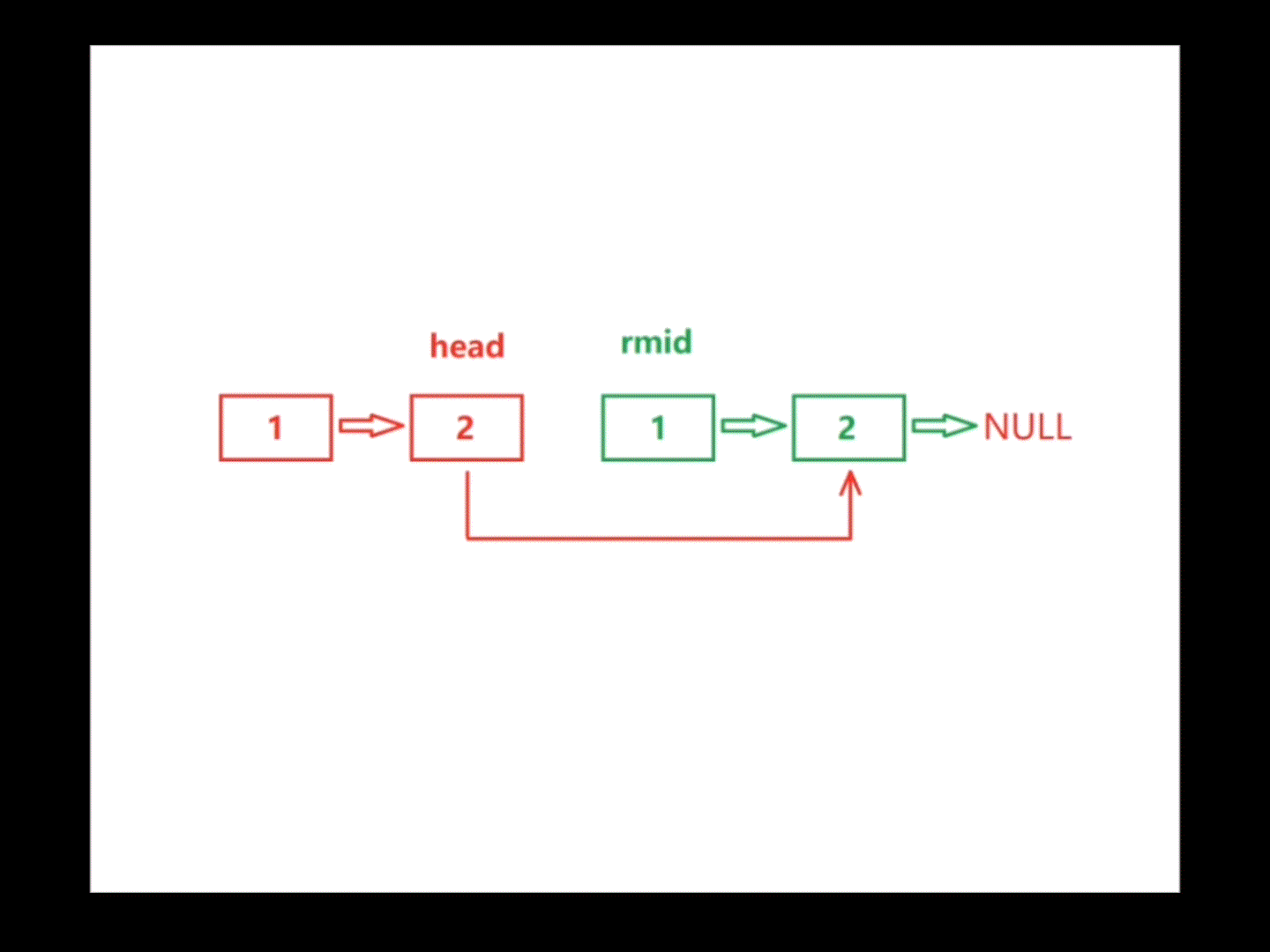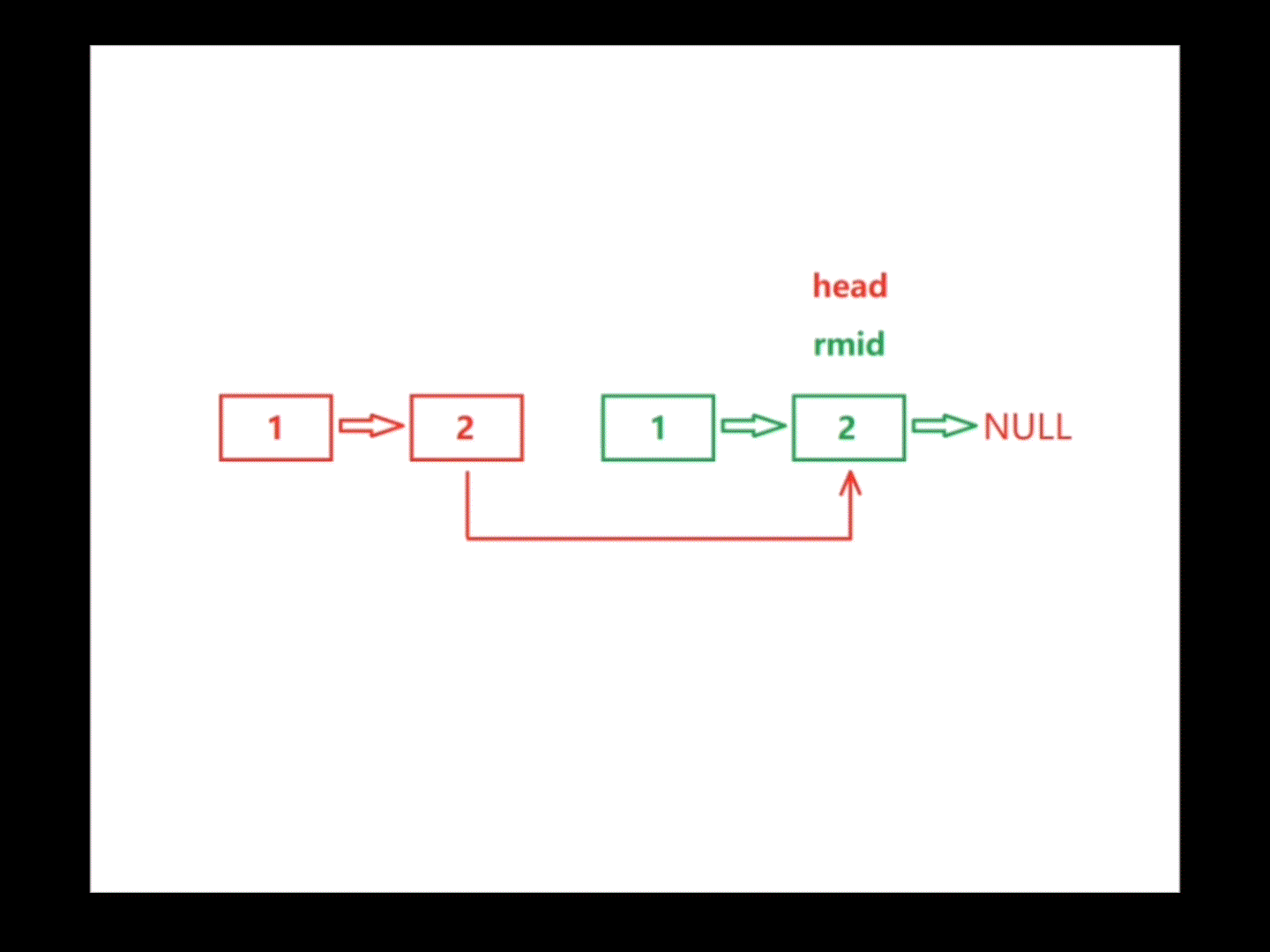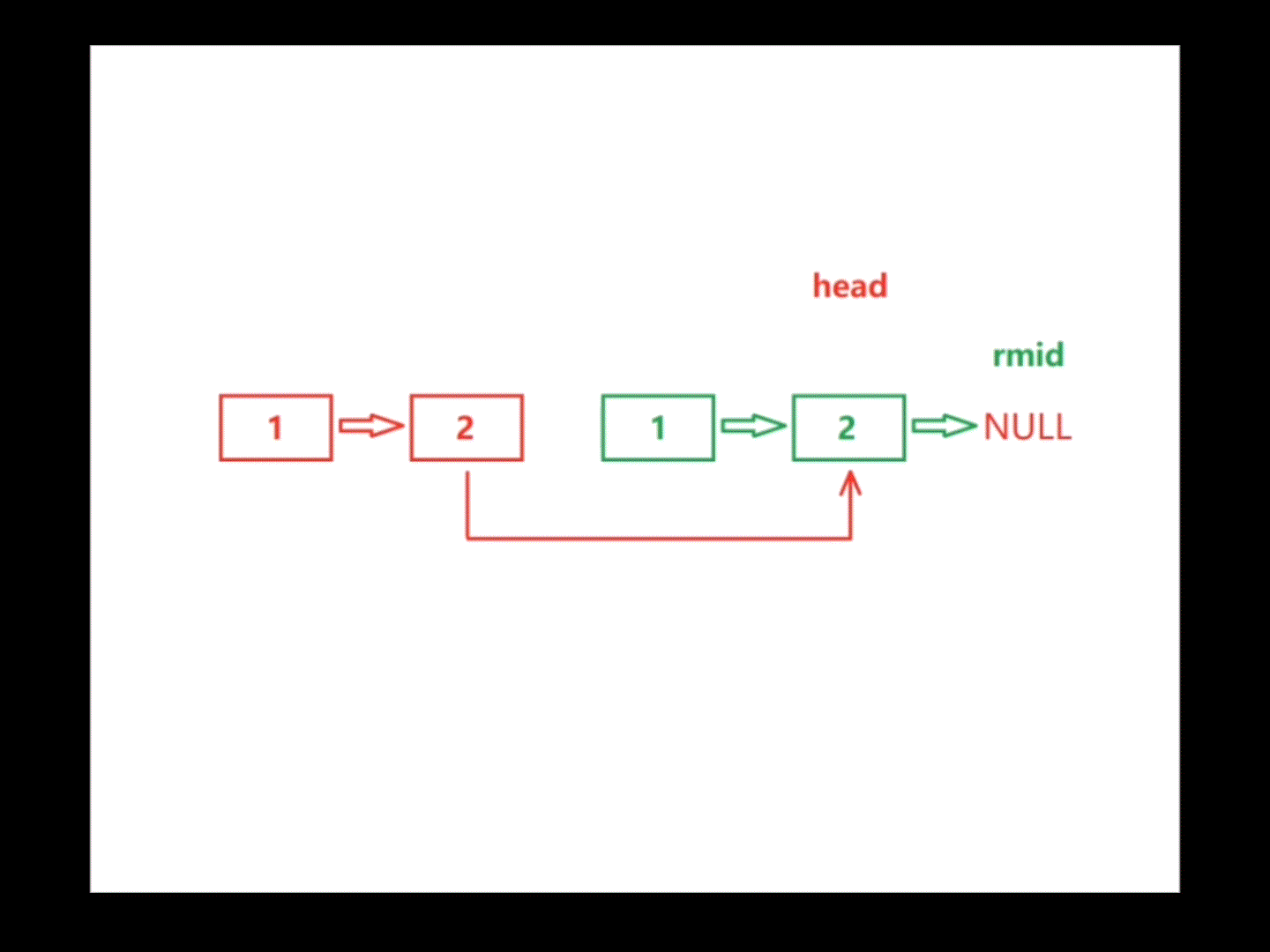
首先在链表中找到中间结点,然后反转中间结点以后的所有结点(包括中间结点),利用指针head和指针rmid遍历链表,遍历过程中若存在head->val != rmid->val,则该链表不属于回文结构,return false;若将链表遍历完全都没有return false,则该链表属于回文结构,return true。注:遍历链表的结束条件因链表的长度是奇是偶而不同
7.2. | 题解代码 |
class PalindromeList {
public:struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){struct ListNode* cur=head;struct ListNode* prev=NULL;struct ListNode* next=NULL;while(cur){next=cur->next;cur->next=prev;prev=cur;cur=next;}return prev;
}struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){struct ListNode* fast=head;struct ListNode* slow=head;while(fast&&fast->next){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next->next;}return slow;
}bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* mid=middleNode(head);struct ListNode* rmid=reverseList(mid);while(head&&rmid){if(head->val!=rmid->val){return false;}head=head->next;rmid=rmid->next;}return true;}
};八、相交链表
OJ链接![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/
8.1. | 解题思路 |
首先分别遍历两个链表记录链表的长度,再判断两个链表的尾结点地址是否相等,相等则两链表相交,不相等则不相交。创建指针curA和指针curB,让长的链表的cur先走gap步(gap=abs(lenA-lenB)),再让两个链表同时走,每次走一步,当第一次curA==curB,此时的结点为两个链表的相交结点。
8.2. | 题解代码 |
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {if(headA==NULL||headB==NULL){return NULL;}struct ListNode* curA=headA;struct ListNode* curB=headB;int lenA=1;while(curA->next){lenA++;curA=curA->next;}int lenB=1;while(curB->next){lenB++;curB=curB->next;}if(curA!=curB){return NULL;}int gap=abs(lenA-lenB);struct ListNode* longList=headA;struct ListNode* shortList=headB;if(lenA<lenB){longList=headB;shortList=headA;}while(gap--){longList=longList->next;}while(longList!=shortList){longList=longList->next;shortList=shortList->next;}return longList;
}九、判断链表是否带环
OJ链接![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
9.1. | 解题思路 |
创建一个快指针fast,一个慢指针slow,fast一次走两步,slow一次走一步。若链表带环,当slow进环时,fast已经在环中了,此时变为fast追逐slow,当fast追上slow时,表明链表带环;若链表不带环,则fast最终会指向NULL或fast->next指向NULL(取决于链表的长度是奇数还是偶数)。
9.2. | 题解代码 |
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode* fast=head;struct ListNode* slow=head;while(fast&&fast->next){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next->next;if(fast==slow){return true;}}return false;
}十、判断链表是否带环 + 返回入环的第一个结点
OJ链接![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
10.1. | 解题思路 |
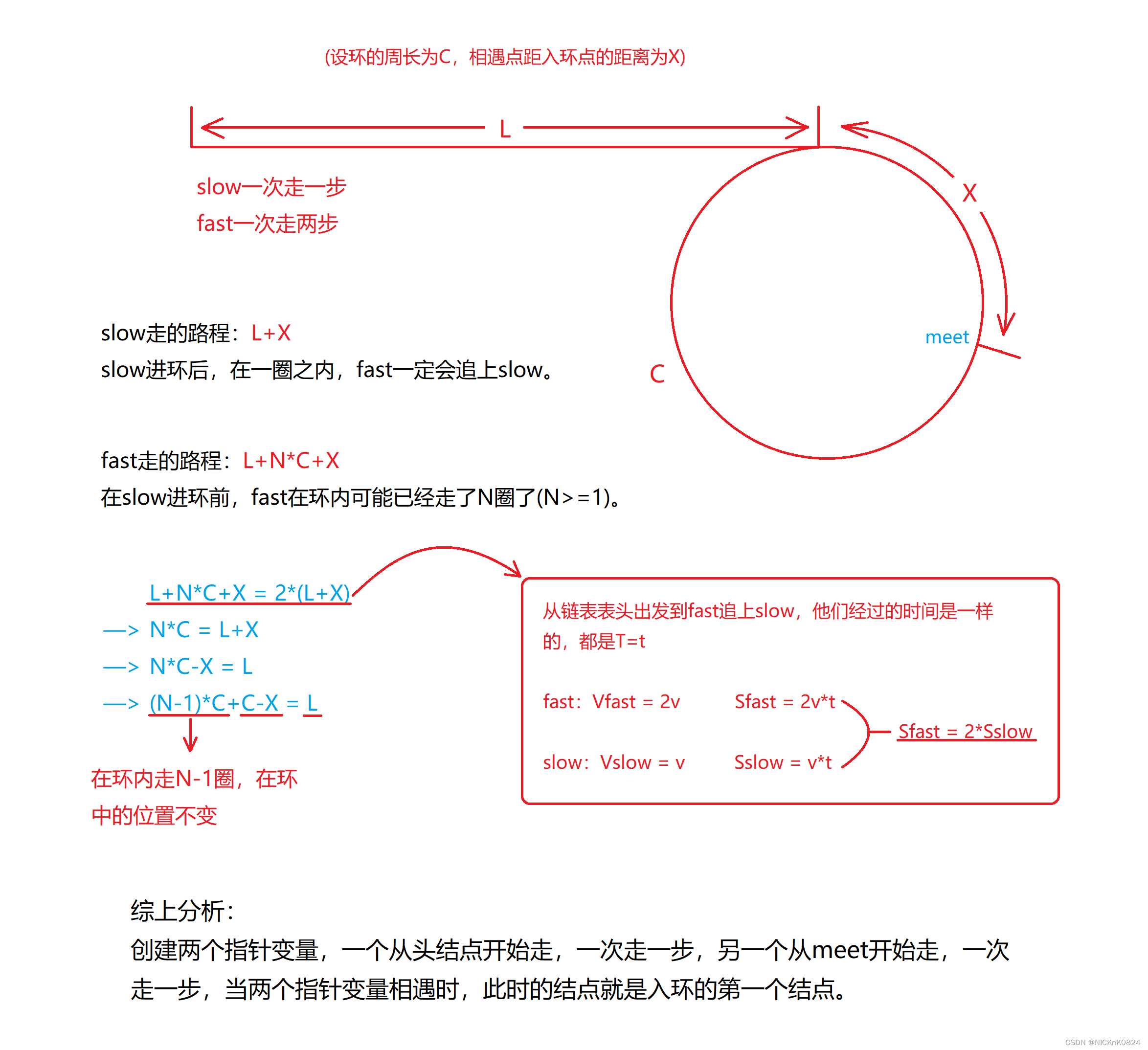
| 方法一:公式推导法 |
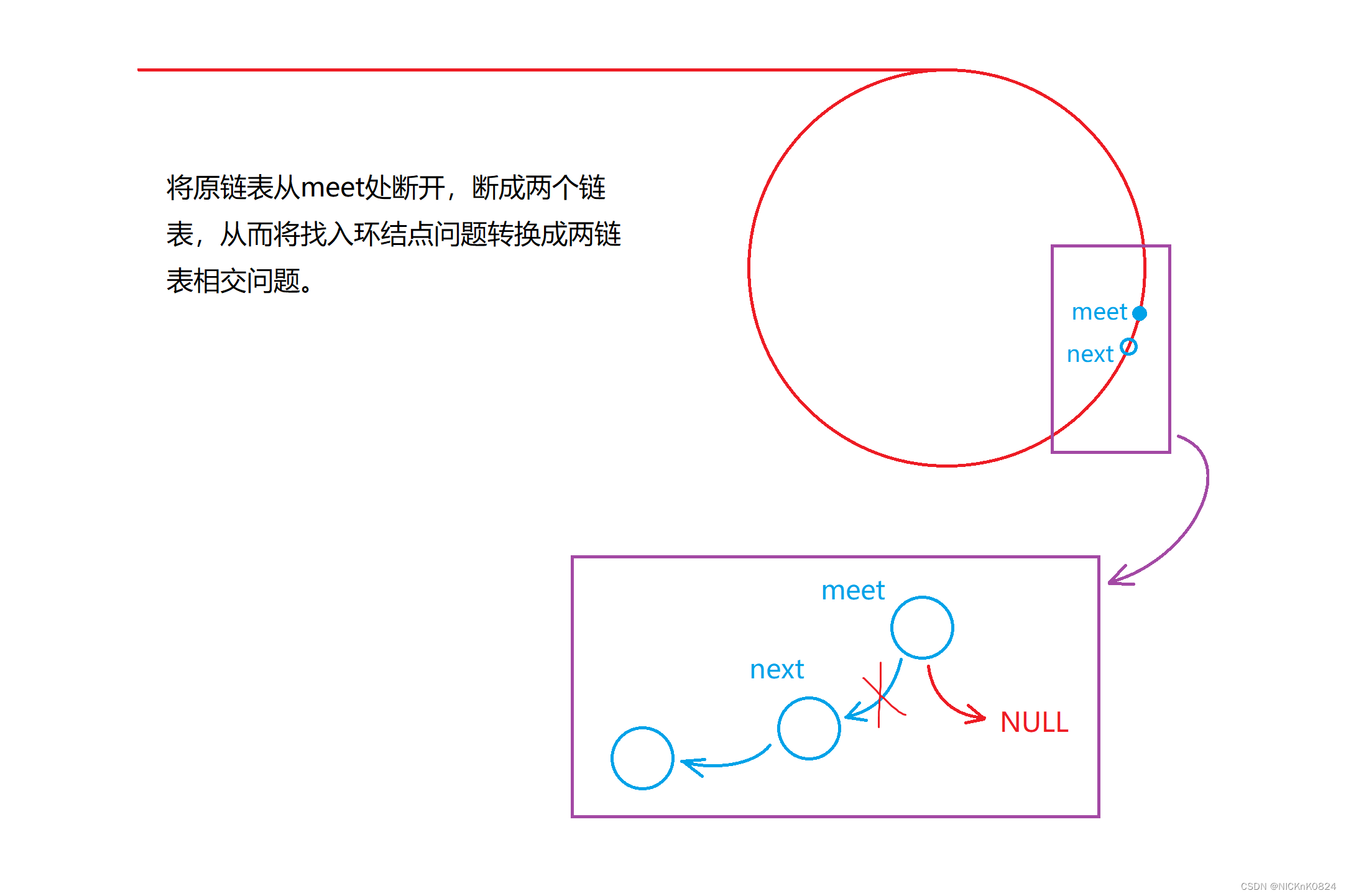
| 方法二:链表相交结点法 |
10.2. | 题解代码 |
//方法一:公式推导法struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode* fast=head;struct ListNode* slow=head;while(fast&&fast->next){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next->next;if(fast==slow){struct ListNode* meet=fast;while(meet!=head){meet=meet->next;head=head->next;}return meet;}}return NULL;
}//方法二:链表相交结点法struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {if(headA==NULL||headB==NULL){return NULL;}struct ListNode* curA=headA;struct ListNode* curB=headB;int lenA=1;while(curA->next){lenA++;curA=curA->next;}int lenB=1;while(curB->next){lenB++;curB=curB->next;}if(curA!=curB){return NULL;}int gap=abs(lenA-lenB);struct ListNode* longList=headA;struct ListNode* shortList=headB;if(lenA<lenB){longList=headB;shortList=headA;}while(gap--){longList=longList->next;}while(longList!=shortList){longList=longList->next;shortList=shortList->next;}return longList;
}struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode* fast=head;struct ListNode* slow=head;while(fast&&fast->next){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next->next;if(fast==slow){struct ListNode* meet=fast;struct ListNode* next=meet->next;meet->next=NULL;struct ListNode* entryNode=getIntersectionNode(head,next);meet->next=next;return entryNode;}}return NULL;
}十一、复制带随机指针的链表
OJ链接![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/description/
11.1. | 解题思路 |
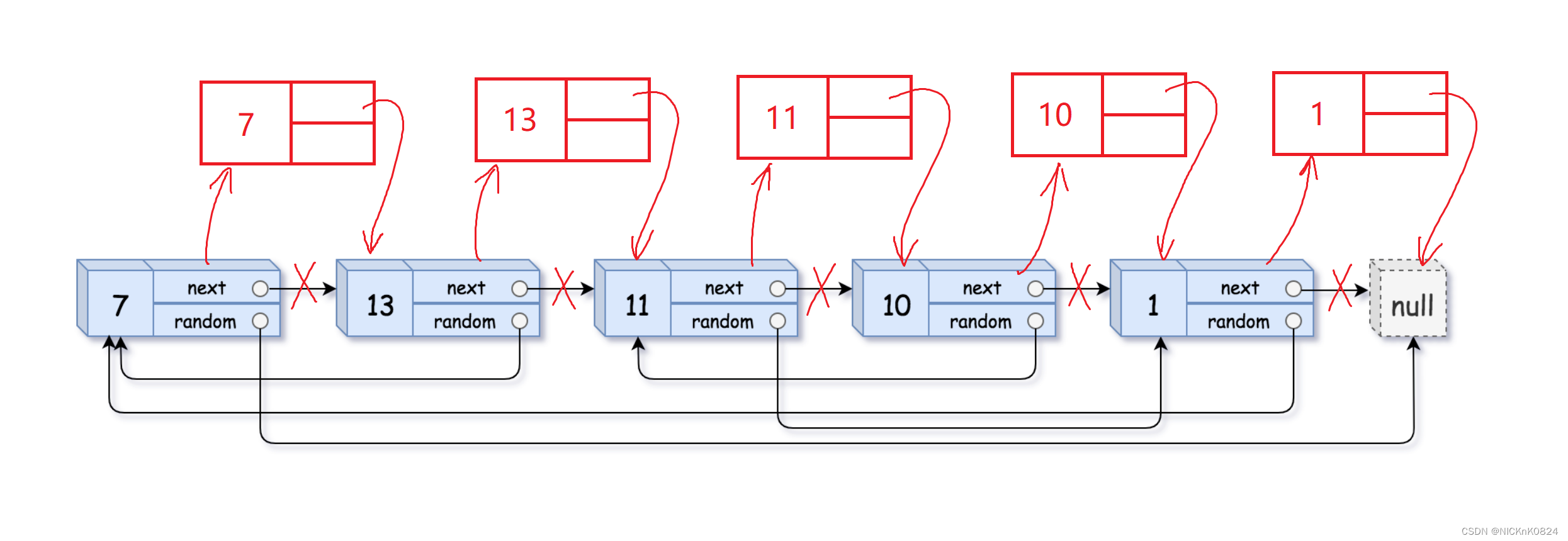
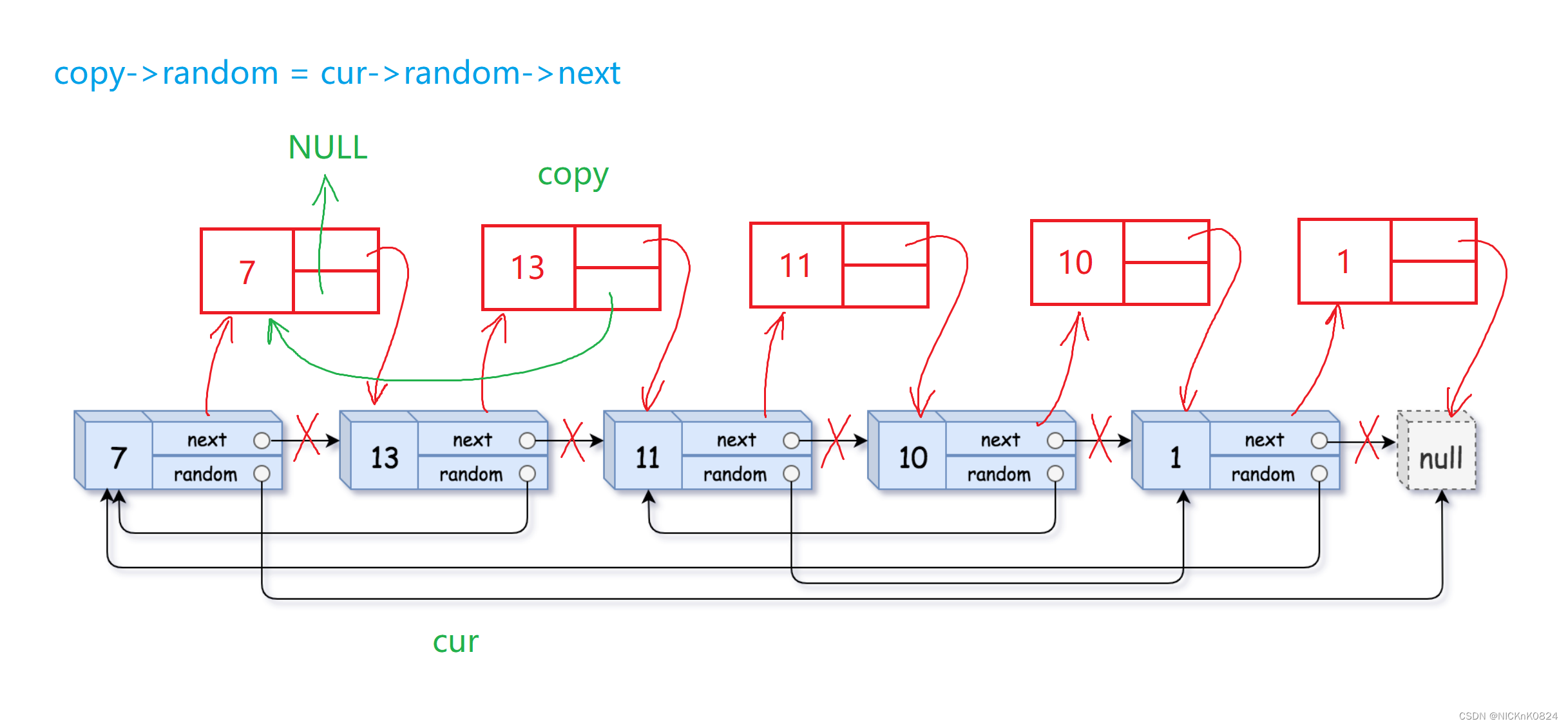
① 复制结点,链接到原链表中
② 更新copy结点的random
③ 将copy结点解下,链接成新的链表
创建一个新的带头结点的链表将所有的copy结点尾插在新头结点后
④ 还原原链表
11.2. | 题解代码 |
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {struct Node* cur=head;struct Node* next=NULL;struct Node* copy=NULL;//1.复制节点,链接到原链表中while(cur){next=cur->next;copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));copy->val=cur->val;cur->next=copy;copy->next=next;cur=next;}//2.更新copy节点的randomcur=head;while(cur){copy=cur->next;if(cur->random==NULL){copy->random=NULL;}else{copy->random=cur->random->next;}cur=cur->next->next;}//3.将copy节点解下,重新链接成新链表,将原链表还原struct Node* copyHead=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));copyHead->next=NULL;struct Node* copyTail=copyHead;cur=head;while(cur){copy=cur->next;next=copy->next;copyTail->next=copy;copyTail=copyTail->next;cur->next=next;cur=cur->next;}struct Node* newHead=copyHead->next;free(copyHead);copyHead=NULL;return newHead;
}