前半部分文章摘自:http://blog.csdn.net/a1043498776/article/details/72681890
Kudu的背景
Hadoop中有很多组件,为了实现复杂的功能通常都是使用混合架构,
- Hbase:实现快速插入和修改,对大量的小规模查询也很迅速
- HDFS/Parquet + Impala/Hive:对超大的数据集进行查询分析,对于这类场景, Parquet这种列式存储文件格式具有极大的优势。
- HDFS/Parquet + Hbase:这种混合架构需要每隔一段时间将数据从hbase导出成Parquet文件,然后用impala来实现复杂的查询分析
以上的架构没办法把复杂的实时查询集成在Hbase上
Kudu的设计
- Kudu是对HDFS和HBase功能上的补充,能提供快速的分析和实时计算能力,并且充分利用CPU和I/O资源,支持数据原地修改,支持简单的、可扩展
的数据模型。 - Kudu的定位是提供”fast analytics on fast data”,kudu期望自己既能够满足分析的需求(快速的数据scan),也能够满足查询的需求(快速的随机访问)。它定位OLAP和少量的OLTP工作流,如果有大量的random accesses,官方建议还是使用HBase最为合适
Kudu的结构
其实跟Hbase是有点像的
Kudu的使用
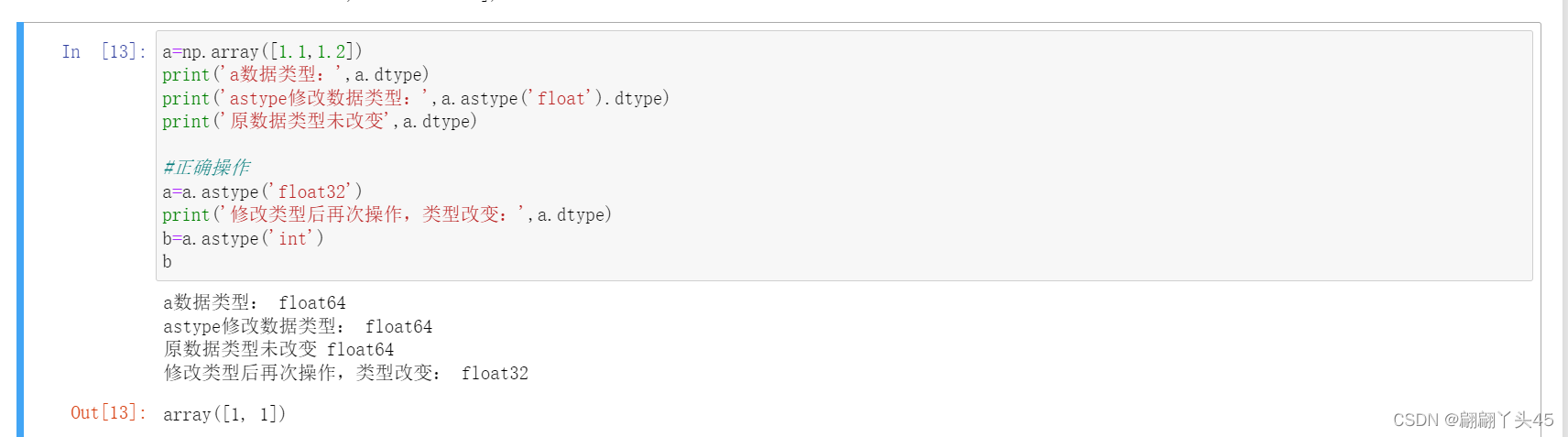
1:支持主键(类似 关系型数据库)
2:支持事务操作,可对数据增删改查数据
3:支持各种数据类型
4:支持 alter table。可删除列(非主键)
5:支持 INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, UPSERT
6:支持Hash,Range分区
进入Impala-shell -i node1ip
具体的CURD语法可以查询官方文档,我就不一一列了
http://kudu.apache.org/docs/kudu_impala_integration.html
建表
Create table kudu_table (Id string,Namestring,Age int,
Primary key(id,name)
)partition by hash partitions 16
Stored as kudu;
插入数据
Insert into kudu_table
Select * from impala_table;
注意
以上的sql语句都是在impala里面执行的。Kudu和hbase一样都是nosql查询的,Kudu本身只提供api。impala集成了kudu。
Kudu Api
奉上我的Git地址:
https://github.com/LinMingQiang/spark-util/tree/spark-kudu
Scala Api
pom.xml
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
Spark Kudu Api
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
Kudu与Spark集成
Kudu从1.0.0版开始,通过Data Source API与Spark集成。使用--packages选项包括kudu-spark依赖关系:
如果使用Spark与Scala 2.10,请使用kudu-spark_2.10工件
spark-shell --packages org.apache.kudu:kudu-spark_2.10:1.1.0如果在Scala 2.11中使用Spark 2,请使用kudu-spark2_2.11工件
spark-shell --packages org.apache.kudu:kudu-spark2_2.11:1.1.0然后导入kudu-spark并创建一个数据框:
import org.apache.kudu.spark.kudu._
import org.apache.kudu.client._
import collection.JavaConverters._
// Read a table from Kudu
val df = sqlContext.read.options(Map("kudu.master" -> "kudu.master:7051","kudu.table" -> "kudu_table")).kudu
// Query using the Spark API...
df.select("id").filter("id" >= 5).show()
// ...or register a temporary table and use SQL
df.registerTempTable("kudu_table")
val filteredDF = sqlContext.sql("select id from kudu_table where id >= 5").show()
// Use KuduContext to create, delete, or write to Kudu tables
val kuduContext = new KuduContext("kudu.master:7051", sqlContext.sparkContext)
// Create a new Kudu table from a dataframe schema
// NB: No rows from the dataframe are inserted into the table
kuduContext.createTable("test_table", df.schema, Seq("key"),new CreateTableOptions().setNumReplicas(1).addHashPartitions(List("key").asJava, 3))
// Insert data
kuduContext.insertRows(df, "test_table")
// Delete data
kuduContext.deleteRows(filteredDF, "test_table")
// Upsert data
kuduContext.upsertRows(df, "test_table")
// Update data
val alteredDF = df.select("id", $"count" + 1)
kuduContext.updateRows(filteredRows, "test_table"
// Data can also be inserted into the Kudu table using the data source, though the methods on KuduContext are preferred
// NB: The default is to upsert rows; to perform standard inserts instead, set operation = insert in the options map
// NB: Only mode Append is supported
df.write.options(Map("kudu.master"-> "kudu.master:7051", "kudu.table"-> "test_table")).mode("append").kudu
// Check for the existence of a Kudu table
kuduContext.tableExists("another_table")
// Delete a Kudu table
kuduContext.deleteTable("unwanted_table")Spark集成已知问题和限制
-
注册为临时表时,必须为具有大写字母或非ASCII字符的名称的Kudu表分配备用名称。
-
具有包含大写字母或非ASCII字符的列名称的Kudu表可能不与SparkSQL一起使用。为解决这个问题可能Columns会被重命名。
-
<>并且OR谓词不被推送到Kudu,而是将被Spark任务解析。只有LIKE具有后缀通配符的谓词被推送到Kudo,这意味着LIKE "FOO%"被Kudo解析,但LIKE "FOO%BAR"不是可解析的通配符。 -
Kudo不支持SparkSQL支持的所有类型,如
Date,Decimal和复杂类型。 -
Kudu表只能在SparkSQL中注册为临时表。可能不会使用HiveContext查询Kudu表。
Kudu Python客户端
Kudu Python客户端为C ++客户端API提供了一个Python友好的界面。下面的示例演示了部分Python客户端的使用。
import kudu
from kudu.client import Partitioning
from datetime import datetime
# Connect to Kudu master server
client = kudu.connect(host='kudu.master', port=7051)
# Define a schema for a new table
builder = kudu.schema_builder()
builder.add_column('key').type(kudu.int64).nullable(False).primary_key()
builder.add_column('ts_val', type_=kudu.unixtime_micros, nullable=False, compression='lz4')
schema = builder.build()
# Define partitioning schema
partitioning = Partitioning().add_hash_partitions(column_names=['key'], num_buckets=3)
# Create new table
client.create_table('python-example', schema, partitioning)
# Open a table
table = client.table('python-example')
# Create a new session so that we can apply write operations
session = client.new_session()
# Insert a row
op = table.new_insert({'key': 1, 'ts_val': datetime.utcnow()})
session.apply(op)
# Upsert a row - upsert操作该操作的实现原理是通过判断插入的记录里是否存在主键冲突来决定是插入还是更新,当出现主键冲突时则进行更新操作
op = table.new_upsert({'key': 2, 'ts_val': "2016-01-01T00:00:00.000000"})
session.apply(op)
# Updating a row
op = table.new_update({'key': 1, 'ts_val': ("2017-01-01", "%Y-%m-%d")})
session.apply(op)
# Delete a row
op = table.new_delete({'key': 2})
session.apply(op)
# Flush write operations, if failures occur, capture print them.
try:session.flush()
except kudu.KuduBadStatus as e:print(session.get_pending_errors())
# Create a scanner and add a predicate
scanner = table.scanner()
scanner.add_predicate(table['ts_val'] == datetime(2017, 1, 1))
# Open Scanner and read all tuples
# Note: This doesn't scale for large scans
result = scanner.open().read_all_tuples()与MapReduce,YARN和其他框架集成
Kudu旨在与Hadoop生态系统中的MapReduce,YARN,Spark和其他框架集成。见 RowCounter.java 和 ImportCsv.java 的例子,你可以模拟在你自己的集成。请继续关注未来使用YARN和Spark的更多示例。
小结
- Kudu简单来说就是加强版的Hbase,除了像hbase一样可以高效的单条数据查询,他的表结构是类型关系型数据库的。集合impala可以达到复杂sql的实时查询。适合做OLAP(官方也是这么定位的)
- Kudu本质上是将性能的优化,寄托在以列式存储为核心的基础上,希望通过提高存储效率,加快字段投影过滤效率,降低查询时CPU开销等来提升性能。而其他绝大多数设计,都是为了解决在列式存储的基础上支持随机读写这样一个目的而存在的。比如类Sql的元数据结构,是提高列式存储效率的一个辅助手段,唯一主键的设定也是配合列式存储引入的定制策略,至于其他如Delta存储,compaction策略等都是在这个设定下为了支持随机读写,降低latency不确定性等引入的一些Tradeoff方案。
官方测试结果上,如果是存粹的随机读写,或者单行的检索请求这类场景,由于这些Tradeoff的存在,HBASE的性能吞吐率是要优于Kudu不少的(2倍到4倍),kudu的优势还是在支持类SQL检索这样经常需要进行投影操作的批量顺序检索分析场合。目前kudu还处在Incubator阶段,并且还没有成熟的线上应用(小米走在了前面,做了一些业务应用的尝试),在数据安全,备份,系统健壮性等方面也还要打个问号,所以是否使用kudu,什么场合,什么时间点使用,是个需要好好考量的问题 ;)








![[高通SDM450][Android9.0]adb无法进行remount的解决方案](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8cd70d682083497fa1a65107184fa104.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBATXIuIEhlYmlu,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16#pic_center)