本文仅供学习使用,如有侵权请及时联系,博主会第一时间进行处理
信源熵及其性质研究
- 一、实验目的
- 二、实验原理及内容
- 三、实验设备与材料
- 四、实验步骤
- 五、实验程序及运行结果
- 六、实验总结
一、实验目的
1.掌握离散信源熵的含义及其计算方法;
2.理解熵函数的性质及其物理意义;
3.探究熵的对称性、确定性、扩展性、极值性和上凸性。
二、实验原理及内容
离散信源相关的基本概念、原理和计算公式;
产生离散信息的信源称为离散信源。离散信源产生有限种符号。假设X是一个离散随机变量,信源的数学模型统一抽象为:

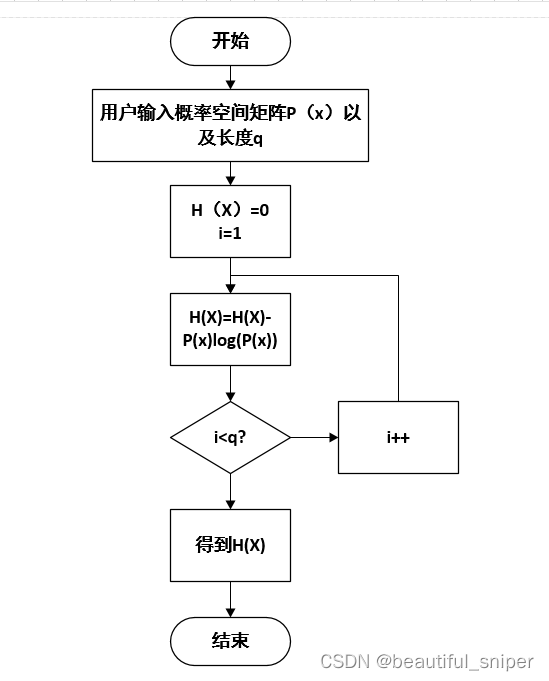
离散信源熵的是从整个信源的统计特性来考虑的。它是从平均意义上来表征信源的总体信息测度的。对于某特定的信源,其信息熵是一个确定的数值。不同的信源因统计特性不同,其熵也不同。离散信源的熵计算公式为:
1.基本要求
对输出两个符号的离散信源的熵进行研究,能够用图形显示出离散信源的熵的曲线,要求横纵坐标表明物理量及其单位等信息。同时根据曲线说明可以体现出的离散信源的相关性质。
2.扩展要求
离散信源的输出符号有限个(可大于2个,可参数设置);可输入各个符号的概率;可判断信源各个符号的概率总和是否为1,从而确定输入符号的概率是否正确;可打印出离散信源的熵值;从熵值探究熵的对称性、确定性、扩展性、极值性。可另加自创。
三、实验设备与材料
计算机和matlab软件
四、实验步骤
1.打开matlab编辑窗口,输入源程序(程序要有注释,且要有合理的结构);
2.保持源文件(文件名一定要和程序的功能相匹配,不可随意保存);
3.单击Debug菜单下的Run,或直接按F5执行;
4.分析运行结果,当不满足设计要求时,调试改进。
五、实验程序及运行结果
基础部分实验程序:
p0=0;%Minimum Probability%
pd=1;%Maximum Probability%
N=100;%100 sampling points%
p=linspace(p0,pd,N);%100 sampling points constitute a linear vector%
pa=[1/2,1/2];%pa is the probability space of discrete memoryless sources%
pb=[1/4,3/4];%pb is the probability space of discrete memoryless sources%
entropya=0;%Initial Entropy of discrete memoryless sources is 0%
entropyb=0;%Initial Entropy of discrete memoryless sources is 0%
for i=1:2%Because there are two messages, the loop is repeated two times.%entropya=entropya+pa(i)*log2(1/pa(i));%information entropy function%entropyb=entropyb+pb(i)*log2(1/pb(i));%information entropy function%
end
disp('Entropy of discrete memory-less sources:');
entropya
disp('Entropy of discrete memory-less sources:');
entropyb
H=-(p).*log2(p)-(1-p).*log2(1-p);% entropy function %
plot(p,H)
title('entropy H(p)=-(p).*log2(p)-(1-p).*log2(1-p)')
xlabel('p');ylabel('H(p) (bit/symbol)')
基础部分运行结果:


扩展部分实验程序:
程序:
i=1:3;
pa=input('Probabilities of entering each symbol:pa=');
p(i)=pa;
if(abs(sum(p(i))-1)>0)disp('The sum of probabilities is not 1');%Determine whether the compliance probability sum is 1elsedisp('The probability sum is 1');%Determine whether the compliance probability sum is 1entropya=0;%Initial Entropy of Source A is 0%I=[];%I is a discrete self-information matrix ofmemory-free sources.%for i=1:3%Because there are three messages, the loop is repeated three times.%entropya=entropya+pa(i)*log2(1/pa(i));%information entropy function%I(i)=log2(1/pa(i));%self-information content%enddisp('self-information content of discrete memoryless sources:');Idisp('entropy of discrete memoryless sources:');entropya
end
结果:

程序:
%symmetry%
pa=[1/2,1/4,1/8,1/8];%pa is the probability space of discrete mnemonic sources%
pb=[1/4,1/2,1/8,1/8];%pb is the probability space of discrete mnemonic sources%
pc=[1/4,1/8,1/2,1/8];%pc is the probability space of discrete mnemonic sources%
entropya=0;%The initial entropy of the discrete mnemonic source is 0%
entropyb=0;%The initial entropy of the discrete mnemonic source is 0%
entropyc=0;%The initial entropy of the discrete mnemonic source is 0%
Ia=[];%Ia is a discrete self-information matrix ofmemory-free sources.%
Ib=[];%Ib is a discrete self-information matrix ofmemory-free sources.%
Ic=[];%Ic is a discrete self-information matrix ofmemory-free sources.%
for i=1:4%Because there are four messages, the loop is repeated four times.%entropya=entropya+pa(i)*log2(1/pa(i));%information entropy function%Ia(i)=log2(1/pa(i));%self-information content%entropyb=entropyb+pb(i)*log2(1/pb(i));%information entropy function%Ib(i)=log2(1/pb(i));%self-information content%entropyc=entropyc+pc(i)*log2(1/pc(i));%information entropy function%Ic(i)=log2(1/pc(i));%self-information content%
end
disp('self-information content of discrete memoryless sources:');
Ia
disp('entropy of discrete memoryless sources:');
entropya
disp('self-information content of discrete memoryless sources:');
Ib
disp('entropy of discrete memoryless sources:');
entropyb
disp('self-information content of discrete memoryless sources:');
Ic
disp('entropy of discrete memoryless sources:');
entropyc
%determinacy%
pa=[1,0];%pa is the probability space of discrete mnemonic sources%
pb=[1,0,0];%pb is the probability space of discrete mnemonic sources%
pc=[1,0,0,0];%pc is the probability space of discrete mnemonic sources%
Ha=pa(1)*log2(1/pa(1))+0;%information entropy function%
disp('entropy of discrete memoryless sources:');
Ha
Hb=pb(1)*log2(1/pb(1))+0+0;%information entropy function%
disp('entropy of discrete memoryless sources:');
Hb
Hc=pc(1)*log2(1/pc(1))+0+0+0;%information entropy function%
disp('entropy of discrete memoryless sources:');
Hc
%extremum property,upper convexity%
p=0.00001:0.001:1;
H=-(p).*log2(p)-(1-p).*log2(1-p);
plot(p,H)
title('entropyH(p)=-(p).*log2(p)-(1-p).*log2(1-p)')
xlabel('p');ylabel('H(p) (bit/symbol)')
结果:


程序:
%expansibility%
pa=[1/4,1/4,1/8,1/8,1/8,1/8];%pa is the probability space of discrete mnemonic sources%
pb=[1/4,1/4,1/8,1/8,1/8,511/4096,1/4096];%pb is the probability space of discrete mnemonic sources%
entropya=0;%The initial entropy of the discrete mnemonic source is 0%
entropyb=0;%The initial entropy of the discrete mnemonic source is 0%
Ia=[];%Ia is a discrete self-information matrix ofmemory-free sources.%
Ib=[];%Ib is a discrete self-information matrix ofmemory-free sources.%
for i=1:6%Because there are six messages, the loop is repeated six times.%entropya=entropya+pa(i)*log2(1/pa(i));%information entropy function%Ia(i)=log2(1/pa(i));%self-information content%
end
disp('self-information content of discrete memoryless sources:');
Ia
disp('entropy of discrete memoryless sources:');
entropya
for i=1:7%Because there are seven messages, the loop is repeated seven times.%entropyb=entropyb+pb(i)*log2(1/pb(i));%information entropy function%Ib(i)=log2(1/pb(i));%self-information content%
end
disp('self-information content of discrete memoryless sources:');
Ib
disp('entropy of discrete memoryless sources:');
entropyb
结果:

六、实验总结
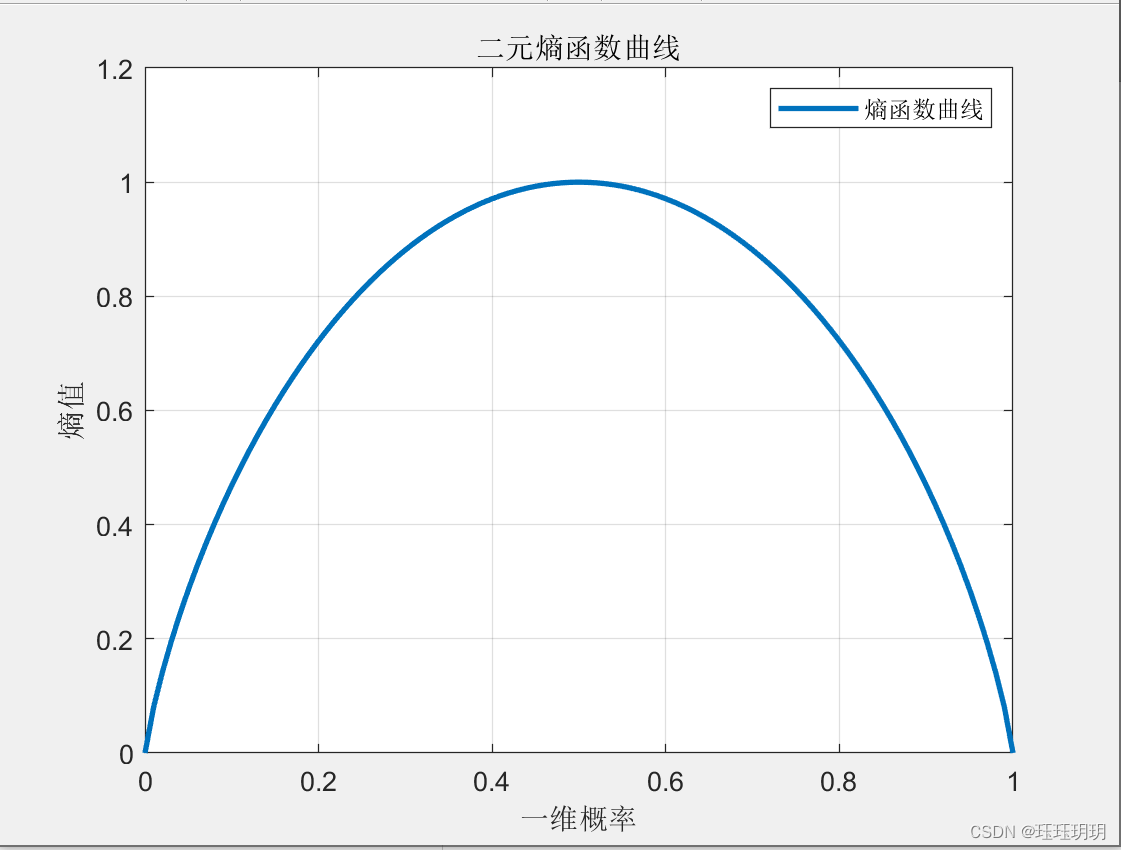
(1)基本部分的实验程序运行的结果中有一个曲线图,该曲线图的横坐标为概率p,纵坐标表示计算后的熵值,单位为(比特/符号)。由于研究的对象为输出两个符号的离散信源的熵,故一个符号对应的概率为p,则另一个符号对应的概率为(1-p)。曲线标题为熵函数的表达式:H(p)=-( p ).*log2( p )-( 1-p ).*log2( 1-p ).
从举的两个例子可以看出:在离散信源情况下,对于具有q个符号的离散信源,只有在q个信源符号等可能出现的情况下,信源熵才能达到最大值。即体现了极值性。由于其函数图像为上凸函数,故体现了上凸性。实验结果与预期效果一致。
(2)扩展部分的实验程序运行的结果中第一部分实现了判断是否符合输入概率和为1。若为1,则可继续求得自信息以及信息熵;否则结束运行。第二部分包括了三个随机变量的总体结构相同的概率空间的自信息以及信源熵,结果信源熵都相同,验证了对称性。第三部分验证了确定性。第四部分得到的曲线可验证极值性和上凸性。第五部分的运行结果验证了扩展性。实验结果与预期效果一致。


![[信息论与编码] 03. 离散信源、信源熵、联合熵、条件熵](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20190605200610931.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3FxXzQxNzg1Mjg4,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)