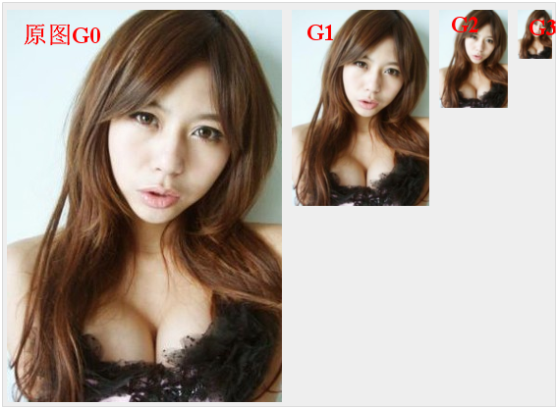
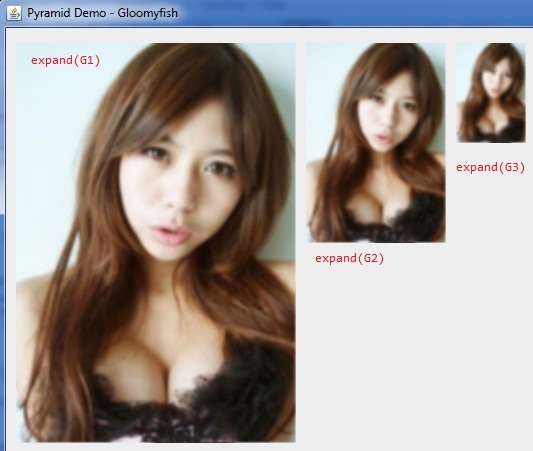
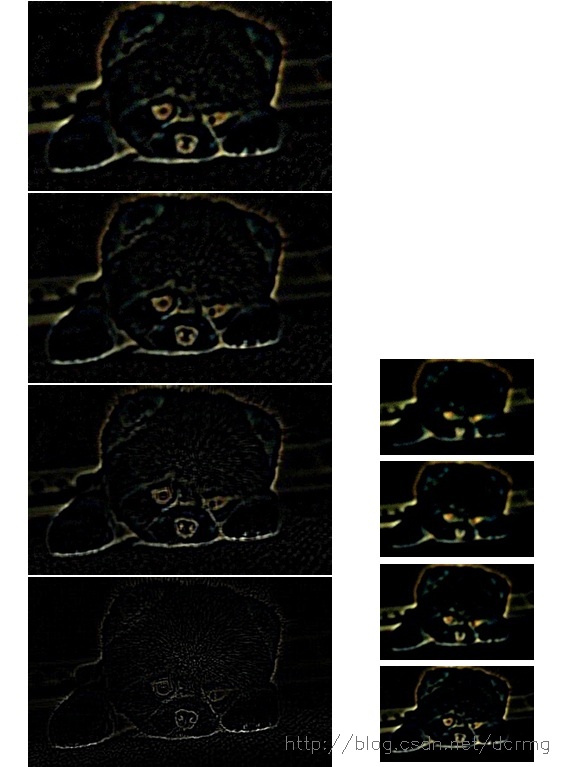
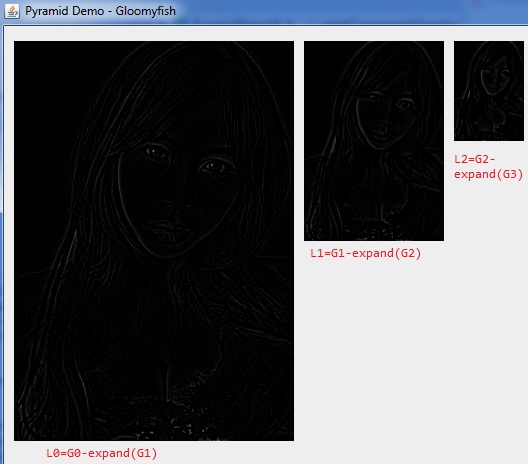
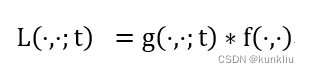一:图像金字塔基本操作
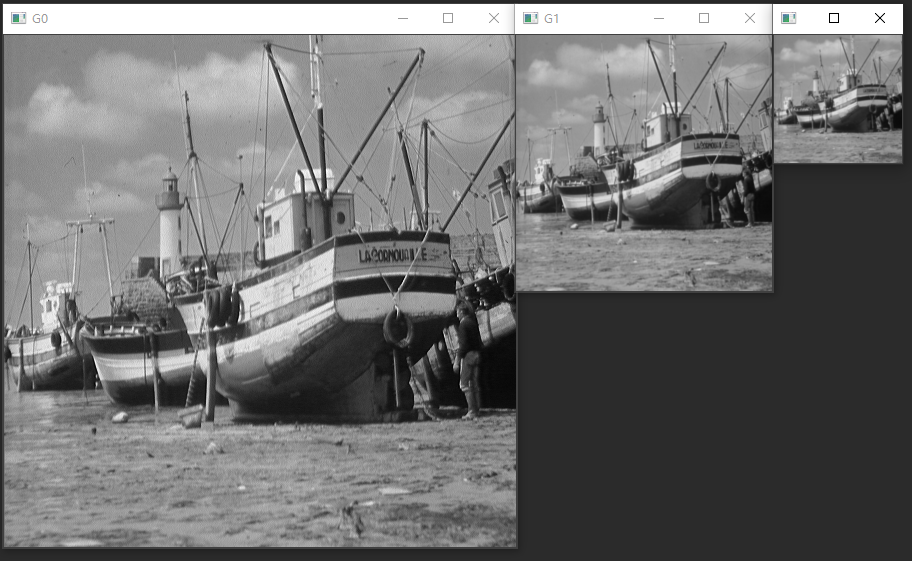
对一张图像不断的模糊之后向下采样,得到不同分辨率的图像,同时每次得到的
新的图像宽与高是原来图像的1/2, 最常见就是基于高斯的模糊之后采样,得到的
一系列图像称为高斯金字塔。
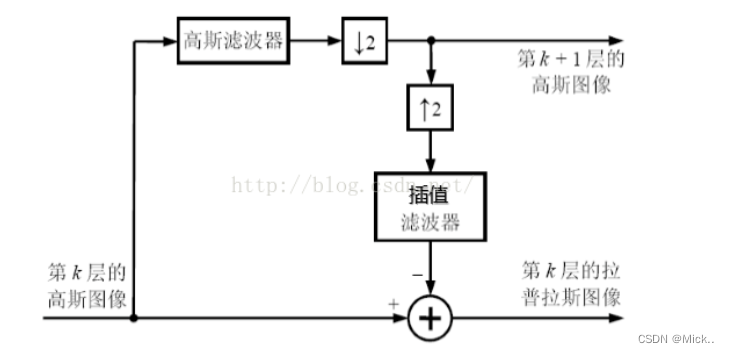
高斯金字塔不同(DoG)又称为拉普拉斯金字塔,其计算公式如下:
L(i) = G(i) – expand(G(i+1))
第i层拉普拉斯金字塔是由第i层高斯金字塔减去第i+1层高斯金字塔expand之后得到。
本文得到的DoG(Difference of Gaussian)结果如下:
二:关键代码解析
金字塔reduce操作实现代码如下:
private BufferedImage pyramidReduce(BufferedImage src) {int width = src.getWidth();int height = src.getHeight();BufferedImage dest = createSubCompatibleDestImage(src, null);int[] inPixels = new int[width*height];int ow = width/2;int oh = height/2;int[] outPixels = new int[ow*oh];getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels );int inRow=0, inCol = 0, index = 0, oudex =0, ta = 0;float[][] keneralData = this.getHVGaussianKeneral();for(int row=0; row<oh; row++) {for(int col=0; col<ow; col++) {inRow = 2* row;inCol = 2* col;if(inRow >= height) {inRow = 0;}if(inCol >= width) {inCol = 0;}float sumRed = 0, sumGreen = 0, sumBlue = 0;for(int subRow = -2; subRow <= 2; subRow++) {int inRowOff = inRow + subRow;if(inRowOff >= height || inRowOff < 0) {inRowOff = 0;}for(int subCol = -2; subCol <= 2; subCol++) {int inColOff = inCol + subCol;if(inColOff >= width || inColOff < 0) {inColOff = 0;}index = inRowOff * width + inColOff;ta = (inPixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff;int red = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;int green = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;int blue = inPixels[index] & 0xff;sumRed += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * red;sumGreen += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * green;sumBlue += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * blue;}}oudex = row * ow + col;outPixels[oudex] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(sumRed) << 16) | (clamp(sumGreen) << 8) | clamp(sumBlue);}}setRGB( dest, 0, 0, ow, oh, outPixels );return dest;}public BufferedImage pyramidExpand(BufferedImage src) {int width = src.getWidth();int height = src.getHeight();int[] inPixels = new int[width*height];getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels );int ow = 2*width;int oh =2*height;int[] outPixels = new int[ow * oh];int index = 0, outdex = 0, ta = 0;float[][] keneralData = this.getHVGaussianKeneral();BufferedImage dest = createTwiceCompatibleDestImage(src, null);for(int row=0; row<oh; row++) {for(int col=0; col<ow; col++) {float sumRed = 0, sumGreen = 0, sumBlue = 0;for(int subRow = -2; subRow <= 2; subRow++) {double srcRow = (row + subRow)/2.0;double j = Math.floor(srcRow);double t = srcRow - j; if(t > 0) {continue;}if(srcRow >= height || srcRow < 0) {srcRow = 0;}for(int subCol = -2; subCol <= 2; subCol++) {double srcColOff = (col + subCol)/2.0;j = Math.floor(srcColOff);t = srcColOff - j;if(t > 0) {continue;}if(srcColOff >= width || srcColOff < 0) {srcColOff = 0;}index = (int)(srcRow * width + srcColOff);ta = (inPixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff;int red = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;int green = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;int blue = inPixels[index] & 0xff;sumRed += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * red;sumGreen += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * green;sumBlue += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * blue;}}outdex = row * ow + col;outPixels[outdex] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(4.0f * sumRed) << 16) | (clamp(4.0f * sumGreen) << 8) | clamp(4.0f * sumBlue);// outPixels[outdex] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(sumRed) << 16) | (clamp(sumGreen) << 8) | clamp(sumBlue);}}setRGB( dest, 0, 0, ow, oh, outPixels );return dest;
}操作不是reduce的可逆操作。
关于什么是卷积,高斯滤波请参见博客上的其它相关文章。
高斯金字塔全部算法源代码如下:
package com.gloomyfish.image.pyramid;import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.awt.image.ColorModel;public class PyramidAlgorithm extends GaussianFilter {private float a;public PyramidAlgorithm() {a = 0.4f;}public void setParameter(float p) {this.a = p;}public BufferedImage[] pyramidDown(BufferedImage src, int level) {BufferedImage[] imagePyramids = new BufferedImage[level + 1];imagePyramids[0] = src;for(int i=1; i<imagePyramids.length; i++) {imagePyramids[i] = pyramidReduce(imagePyramids[i-1]);}return imagePyramids;}public BufferedImage[] pyramidUp(BufferedImage[] srcImage) {BufferedImage[] imagePyramids = new BufferedImage[srcImage.length];for(int i=0; i<srcImage.length; i++) {imagePyramids[i] = pyramidExpand(srcImage[i]);}return imagePyramids;}/**** l1 = g1 - expand(g2)* l2 = g2 - expand(g3)* l0 = g0 - expand(g1)* @param reduceImages* @param expandImages* @return*/public BufferedImage[] getLaplacianPyramid(BufferedImage[] reduceImages) {BufferedImage[] laplaciImages = new BufferedImage[reduceImages.length -1];for(int i=1; i<reduceImages.length; i++) {BufferedImage expandImage = pyramidExpand(reduceImages[i]);laplaciImages[i-1] = createCompatibleDestImage(expandImage, null);int width = reduceImages[i-1].getWidth();int height = reduceImages[i-1].getHeight();int ewidth = expandImage.getWidth();width = (width > ewidth) ? ewidth : width;height = (height > expandImage.getHeight()) ? expandImage.getHeight():height;System.out.println(" width = " + width + " expand width = " + ewidth);int[] reducePixels = new int[width*height];int[] expandPixels = new int[width*height];int[] laPixels = new int[width*height];getRGB( reduceImages[i-1], 0, 0, width, height, reducePixels);getRGB( expandImage, 0, 0, width, height, expandPixels );int index = 0;int er = 0, eg = 0, eb = 0;for(int row=0; row<height; row++) {int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;for(int col=0; col<width; col++) {index = row * width + col;ta = (reducePixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff;tr = (reducePixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;tg = (reducePixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;tb = reducePixels[index] & 0xff;ta = (expandPixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff;er = (expandPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;eg = (expandPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;eb = expandPixels[index] & 0xff;tr = tr - er;tg = tg - eg;tb = tb - eb;laPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(tr) << 16) | (clamp(tg) << 8) | clamp(tb);}}setRGB( laplaciImages[i-1], 0, 0, width, height, laPixels );}return laplaciImages;}private BufferedImage pyramidReduce(BufferedImage src) {int width = src.getWidth();int height = src.getHeight();BufferedImage dest = createSubCompatibleDestImage(src, null);int[] inPixels = new int[width*height];int ow = width/2;int oh = height/2;int[] outPixels = new int[ow*oh];getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels );int inRow=0, inCol = 0, index = 0, oudex =0, ta = 0;float[][] keneralData = this.getHVGaussianKeneral();for(int row=0; row<oh; row++) {for(int col=0; col<ow; col++) {inRow = 2* row;inCol = 2* col;if(inRow >= height) {inRow = 0;}if(inCol >= width) {inCol = 0;}float sumRed = 0, sumGreen = 0, sumBlue = 0;for(int subRow = -2; subRow <= 2; subRow++) {int inRowOff = inRow + subRow;if(inRowOff >= height || inRowOff < 0) {inRowOff = 0;}for(int subCol = -2; subCol <= 2; subCol++) {int inColOff = inCol + subCol;if(inColOff >= width || inColOff < 0) {inColOff = 0;}index = inRowOff * width + inColOff;ta = (inPixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff;int red = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;int green = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;int blue = inPixels[index] & 0xff;sumRed += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * red;sumGreen += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * green;sumBlue += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * blue;}}oudex = row * ow + col;outPixels[oudex] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(sumRed) << 16) | (clamp(sumGreen) << 8) | clamp(sumBlue);}}setRGB( dest, 0, 0, ow, oh, outPixels );return dest;}public BufferedImage createSubCompatibleDestImage(BufferedImage src, ColorModel dstCM) {if ( dstCM == null )dstCM = src.getColorModel();return new BufferedImage(dstCM, dstCM.createCompatibleWritableRaster(src.getWidth()/2, src.getHeight()/2), dstCM.isAlphaPremultiplied(), null);}public BufferedImage createTwiceCompatibleDestImage(BufferedImage src, ColorModel dstCM) {if ( dstCM == null )dstCM = src.getColorModel();return new BufferedImage(dstCM, dstCM.createCompatibleWritableRaster(src.getWidth()*2, src.getHeight()*2), dstCM.isAlphaPremultiplied(), null);}public BufferedImage pyramidExpand(BufferedImage src) {int width = src.getWidth();int height = src.getHeight();int[] inPixels = new int[width*height];getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels );int ow = 2*width;int oh =2*height;int[] outPixels = new int[ow * oh];int index = 0, outdex = 0, ta = 0;float[][] keneralData = this.getHVGaussianKeneral();BufferedImage dest = createTwiceCompatibleDestImage(src, null);for(int row=0; row<oh; row++) {for(int col=0; col<ow; col++) {float sumRed = 0, sumGreen = 0, sumBlue = 0;for(int subRow = -2; subRow <= 2; subRow++) {double srcRow = (row + subRow)/2.0;double j = Math.floor(srcRow);double t = srcRow - j; if(t > 0) {continue;}if(srcRow >= height || srcRow < 0) {srcRow = 0;}for(int subCol = -2; subCol <= 2; subCol++) {double srcColOff = (col + subCol)/2.0;j = Math.floor(srcColOff);t = srcColOff - j;if(t > 0) {continue;}if(srcColOff >= width || srcColOff < 0) {srcColOff = 0;}index = (int)(srcRow * width + srcColOff);ta = (inPixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff;int red = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;int green = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;int blue = inPixels[index] & 0xff;sumRed += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * red;sumGreen += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * green;sumBlue += keneralData[subRow + 2][subCol + 2] * blue;}}outdex = row * ow + col;outPixels[outdex] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(4.0f * sumRed) << 16) | (clamp(4.0f * sumGreen) << 8) | clamp(4.0f * sumBlue);// outPixels[outdex] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(sumRed) << 16) | (clamp(sumGreen) << 8) | clamp(sumBlue);}}setRGB( dest, 0, 0, ow, oh, outPixels );return dest;}}
会有问题,使用时请自己处理吧。
UI实现源代码如下:
package com.gloomyfish.image.pyramid;import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.MediaTracker;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JComponent;
import javax.swing.JFileChooser;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;public class PyramidDemoUI extends JComponent implements ActionListener {/*** */private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;private JButton upButton;private JButton downButton;private BufferedImage[] reduceImages;private BufferedImage[] expandImages;private BufferedImage sourceImage;private Dimension mySize;private MediaTracker tracker;public PyramidDemoUI(File f){initComponents(f);}private void initComponents(File f){// TODO Auto-generated method stubtry { sourceImage = ImageIO.read(f); } catch (IOException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } tracker = new MediaTracker(this); tracker.addImage(sourceImage, 1); // blocked 10 seconds to load the image data try { if (!tracker.waitForID(1, 10000)) { System.out.println("Load error."); System.exit(1); }// end if } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1); }// end catch JPanel btnPanel = new JPanel();btnPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT));upButton = new JButton("Laplacian Pyramid");downButton = new JButton("Pyramid Down");upButton.addActionListener(this);downButton.addActionListener(this);btnPanel.add(upButton);btnPanel.add(downButton);mySize = new Dimension(800, 800); JFrame mainFrame = new JFrame("Pyramid Demo - Gloomyfish");mainFrame.getContentPane().setLayout(new BorderLayout());mainFrame.getContentPane().add(this, BorderLayout.CENTER);mainFrame.getContentPane().add(btnPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);mainFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); mainFrame.pack(); mainFrame.setVisible(true); }@Overridepublic Dimension getPreferredSize() {return mySize;}@Overrideprotected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
// g.drawImage(sourceImage, 10, 10, sourceImage.getWidth(), sourceImage.getHeight(), null);int width = 10;
// if(reduceImages != null) {
// for(int i=1; i<reduceImages.length; i++) {
// width += (10 + reduceImages[i-1].getWidth());
// g.drawImage(reduceImages[i], width, 10, reduceImages[i].getWidth(), reduceImages[i].getHeight(), null);
// }
// }width = 10;if(expandImages != null) {for(int i=0; i<expandImages.length; i++) {g.drawImage(expandImages[i], width, 15, expandImages[i].getWidth(), expandImages[i].getHeight(), null);// g.drawImage(expandImages[i], width, 15 + sourceImage.getHeight(), expandImages[i].getWidth(), expandImages[i].getHeight(), null);width += (10 + expandImages[i].getWidth());}}super.paintComponent(g);}public static void main(String[] args) { JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser(); chooser.showOpenDialog(null); File f = chooser.getSelectedFile(); new PyramidDemoUI(f); }@Overridepublic void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {if(event.getActionCommand().equals("Laplacian Pyramid")) {if(reduceImages != null) {// int size = reduceImages.length;PyramidAlgorithm pyramid = new PyramidAlgorithm();expandImages = pyramid.getLaplacianPyramid(reduceImages);// expandImages = pyramid.pyramidUp(reduceImages);repaint();} else {}} else if(event.getActionCommand().equals("Pyramid Down")) {// a.Smooth the image with Gaussian filter 5×5(1/4-a/2, 1/4, a, 1/4, 1/4-a/2) a = [0.3,0.6]// b.Sub sample the image by half - 选择偶数行与列// c.If reached desired size stop, else send the result to step 1PyramidAlgorithm pyramid = new PyramidAlgorithm();reduceImages = pyramid.pyramidDown(sourceImage, 3);repaint();} else {// do nothing}} }