0X00 版本信息
Golang:1.16.8
Metricbeat:7.14
0X01 Metricbeat介绍
Metricbeat quick start: installation and configuration | Metricbeat Reference [7.14] | Elastic![]() https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/7.14/metricbeat-installation-configuration.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/7.14/metricbeat-installation-configuration.html
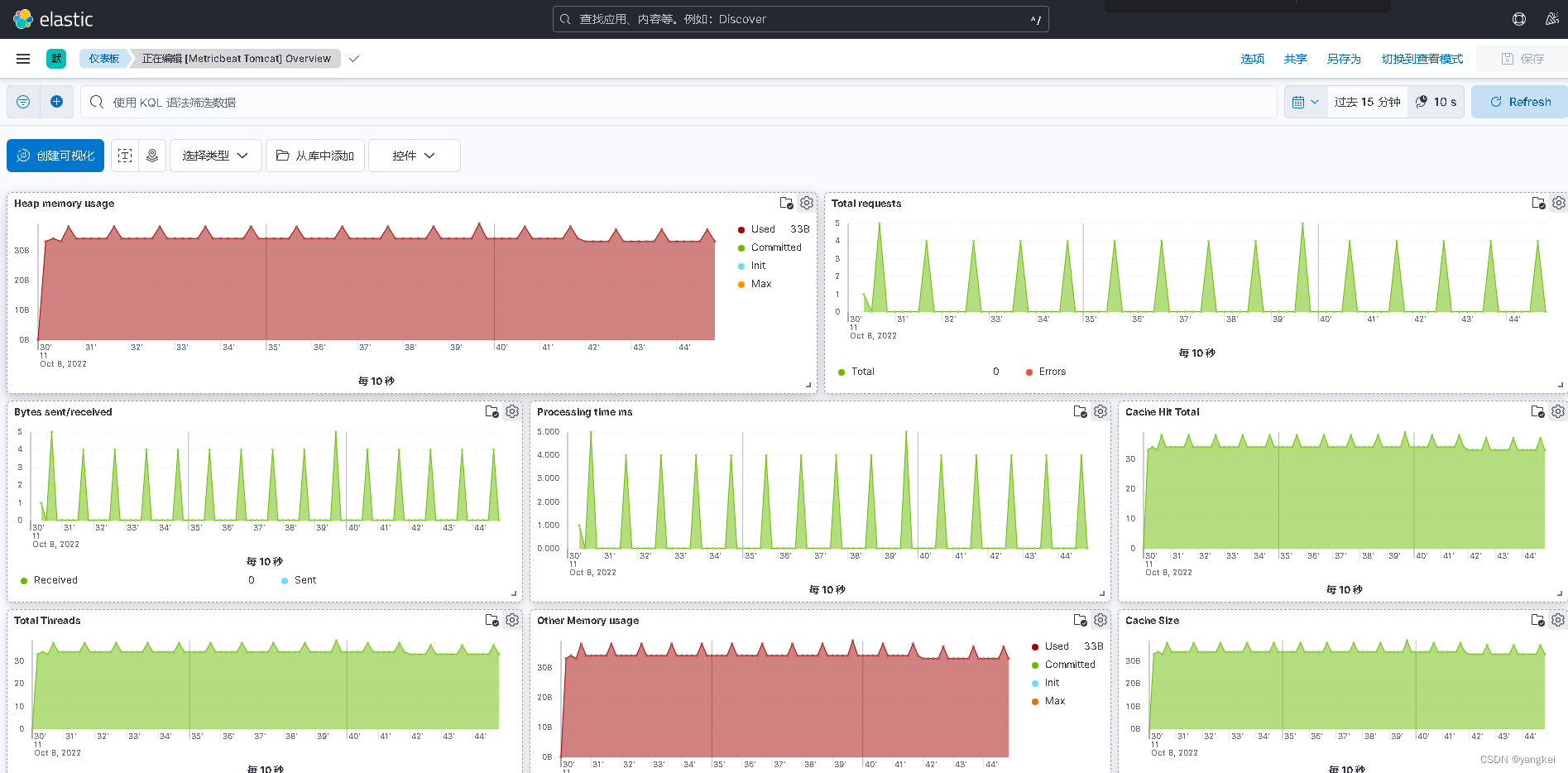
Metricbeat 通过从操作系统和服务收集指标来帮助您监控服务器及其托管的服务。
Metricbeat基于libbeat开发,可以收集你想要的指标并发送到ES,然后在kibana展现。
0X02 Metricbeat监控的模块
| 名称 | 说明 |
| module | metricbeat监听各种指标的模块 |
| metricset | module中能监听到的具体指标数据集,例如system module就会包含cpu disk mem等数据集 |
metricbeat.yml中定义了要监控的性能指标,默认如下:

在modules.d文件夹中,默认只有system.yml是以yml为后缀的文件,其他的文件默认加了disable后缀,不会被识别。
关于module的多层级映射关系如下:
metricbeat.yml指定加载哪些module的yml文件 --> modules.d中定义module的yml配置文件,包括module名称、采集时间间隔、metricsets --> module中定义采集数据的具体数据
0X03 输出
metribeat输出的event:
Event structure | Metricbeat Reference [7.14] | Elastic![]() https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/7.14/metricbeat-event-structure.htmlmetricbeat输出的错误event:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/7.14/metricbeat-event-structure.htmlmetricbeat输出的错误event:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/7.14/error-event-structure.html![]() https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/7.14/error-event-structure.htmlprocesser:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/7.14/error-event-structure.htmlprocesser:
在将事件发送到输出之前,对事件进行进一步处理
Filter and enhance data with processors | Metricbeat Reference [7.14] | Elastic![]() https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/7.14/filtering-and-enhancing-data.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/7.14/filtering-and-enhancing-data.html
0X04 源码分析
【Elastic Stack系列】第四章:源码分析(二) Metricbeat篇 – Twocups版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处:https://twocups.cn/index.php/202 […] https://twocups.cn/index.php/2021/03/15/33/
https://twocups.cn/index.php/2021/03/15/33/
该文章只讲了metricbeat主流程,还有一些细枝末节没有涉及到,我在此处补充一下所看到的细枝末节源码。
1.Runner的实现方式
metricbeat使用Runner的概念来并行运行各个module,在metricbeat.go的Run函数中运行了N个Runner,调用Runner.Start方法:
for _, r := range bt.runners {r.Start()wg.Add(1)thatRunner := rgo func() {defer wg.Done()<-bt.donethatRunner.Stop()}()}Runner interface:
type Runner interface {// fmt.Stringer is required here because when used as a cfgfile.Runner// we need a way to print a threadsafe set of fields since it will likely// be printed from a concurrent goroutine.fmt.Stringer// Start starts the Module. If Start is called more than once, only the// first will start the Module.Start()// Stop stops the Module and waits for module's MetricSets to exit. The// publisher.Client will be closed by Stop. If Stop is called more than// once, only the first stop the Module and wait for it to exit.Stop()
}interface定义了Start()方法和Stop()方法,看一下具体实现:
func (mr *runner) Start() {// 使用sync.once控制被执行函数只能被调用一次mr.startOnce.Do(func() {output := mr.mod.Start(mr.done)mr.wg.Add(1)moduleList.Add(mr.mod.Name())go func() {defer mr.wg.Done()PublishChannels(mr.client, output)}()})
}func (mr *runner) Stop() {mr.stopOnce.Do(func() {close(mr.done)mr.client.Close()mr.wg.Wait()moduleList.Remove(mr.mod.Name())})
}2. moduleList
在Runner Start()和Stop()里面可以看到Runner启停执行的操作,里面有一个moduleList很扎眼,下面来看看moduleList具体是干嘛的,首先看看module的定义(metricbeat/mb/module/runner.go):
var (moduleList *monitoring.UniqueList
)func init() {moduleList = monitoring.NewUniqueList()monitoring.NewFunc(monitoring.GetNamespace("state").GetRegistry(), "module", moduleList.Report, monitoring.Report)
}进一步查看*monitoring.UniqueList(libbeat/monitoring/list.go):
package monitoringimport ("sync"
)// UniqueList is used to collect a list of items (strings) and get the total count and all unique strings.
type UniqueList struct {sync.Mutexlist map[string]int
}// NewUniqueList create a new UniqueList
func NewUniqueList() *UniqueList {return &UniqueList{list: map[string]int{},}
}// Add adds an item to the list and increases the count for it.
func (l *UniqueList) Add(item string) {l.Lock()defer l.Unlock()l.list[item]++
}// Remove removes and item for the list and decreases the count.
func (l *UniqueList) Remove(item string) {l.Lock()defer l.Unlock()l.list[item]--
}// Report can be used as reporting function for monitoring.
// It reports a total count value and a names array with all the items.
func (l *UniqueList) Report(m Mode, V Visitor) {V.OnRegistryStart()defer V.OnRegistryFinished()var items []stringvar count int64l.Lock()defer l.Unlock()for key, val := range l.list {if val > 0 {items = append(items, key)}count += int64(val)}ReportInt(V, "count", count)ReportStringSlice(V, "names", items)
}
可以看到moduleList就是一个UniqueList的实例,该struct包含了一个map[string]int和一个锁,Add就是把map[string]的计数+1,Remove就是把map[string]的计数-1。
3.Runner的动态加载实现:RunnerList(libbeat/cfgfile/list.go)
package cfgfileimport ("sync""github.com/joeshaw/multierror""github.com/mitchellh/hashstructure""github.com/pkg/errors""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/beat""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/common""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/common/reload""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/logp""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/publisher/pipetool"
)// RunnerList implements a reloadable.List of Runners
type RunnerList struct {runners map[uint64]Runnermutex sync.RWMutexfactory RunnerFactorypipeline beat.PipelineConnectorlogger *logp.Logger
}// NewRunnerList builds and returns a RunnerList
func NewRunnerList(name string, factory RunnerFactory, pipeline beat.PipelineConnector) *RunnerList {return &RunnerList{runners: map[uint64]Runner{},factory: factory,pipeline: pipeline,logger: logp.NewLogger(name),}
}// Reload the list of runners to match the given state
func (r *RunnerList) Reload(configs []*reload.ConfigWithMeta) error {r.mutex.Lock()defer r.mutex.Unlock()var errs multierror.ErrorsstartList := map[uint64]*reload.ConfigWithMeta{}stopList := r.copyRunnerList()r.logger.Debugf("Starting reload procedure, current runners: %d", len(stopList))// diff current & desired state, create action listsfor _, config := range configs {hash, err := HashConfig(config.Config)if err != nil {r.logger.Errorf("Unable to hash given config: %s", err)errs = append(errs, errors.Wrap(err, "Unable to hash given config"))continue}if _, ok := r.runners[hash]; ok {delete(stopList, hash)} else {startList[hash] = config}}r.logger.Debugf("Start list: %d, Stop list: %d", len(startList), len(stopList))// Stop removed runnersfor hash, runner := range stopList {r.logger.Debugf("Stopping runner: %s", runner)delete(r.runners, hash)go runner.Stop()moduleStops.Add(1)}// Start new runnersfor hash, config := range startList {runner, err := createRunner(r.factory, r.pipeline, config)if err != nil {if _, ok := err.(*common.ErrInputNotFinished); ok {// error is related to state, we should not log at error levelr.logger.Debugf("Error creating runner from config: %s", err)} else {r.logger.Errorf("Error creating runner from config: %s", err)}errs = append(errs, errors.Wrap(err, "Error creating runner from config"))continue}r.logger.Debugf("Starting runner: %s", runner)r.runners[hash] = runnerrunner.Start()moduleStarts.Add(1)}// NOTE: This metric tracks the number of modules in the list. The true// number of modules in the running state may differ because modules can// stop on their own (i.e. on errors) and also when this stops a module// above it is done asynchronously.moduleRunning.Set(int64(len(r.runners)))return errs.Err()
}// Stop all runners
func (r *RunnerList) Stop() {r.mutex.Lock()defer r.mutex.Unlock()if len(r.runners) == 0 {return}r.logger.Infof("Stopping %v runners ...", len(r.runners))wg := sync.WaitGroup{}for hash, runner := range r.copyRunnerList() {wg.Add(1)delete(r.runners, hash)// Stop modules in parallelgo func(h uint64, run Runner) {defer wg.Done()r.logger.Debugf("Stopping runner: %s", run)run.Stop()r.logger.Debugf("Stopped runner: %s", run)}(hash, runner)}wg.Wait()
}// Has returns true if a runner with the given hash is running
func (r *RunnerList) Has(hash uint64) bool {r.mutex.RLock()defer r.mutex.RUnlock()_, ok := r.runners[hash]return ok
}// HashConfig hashes a given common.Config
func HashConfig(c *common.Config) (uint64, error) {var config map[string]interface{}if err := c.Unpack(&config); err != nil {return 0, err}return hashstructure.Hash(config, nil)
}func (r *RunnerList) copyRunnerList() map[uint64]Runner {list := make(map[uint64]Runner, len(r.runners))for k, v := range r.runners {list[k] = v}return list
}func createRunner(factory RunnerFactory, pipeline beat.PipelineConnector, config *reload.ConfigWithMeta) (Runner, error) {// Pass a copy of the config to the factory, this way if the factory modifies it,// that doesn't affect the hash of the original one.c, _ := common.NewConfigFrom(config.Config)return factory.Create(pipetool.WithDynamicFields(pipeline, config.Meta), c)
}
0X05 创建自己的module
Metricbeat提供了丰富的命令行功能,进入到metricbeat目录下然后执行mage -l,查看支持的命令·列表:

使用mage createMetricset命令可以创建自己的module。
0X06 libbeat流程分析
1.libbeat设计了通用的beat运行方案,beat进程的入口为main.go,例如 libbeat/main.go;metricbeat/main.go:
package mainimport ("os""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/metricbeat/cmd"
)func main() {if err := cmd.RootCmd.Execute(); err != nil {os.Exit(1)}
}2.libbeat定义了所有beat进程的命令行功能,参考libbeat/cmd/root.go:
package cmdimport ("flag""fmt""os""strings""github.com/spf13/cobra""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/beat""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/cfgfile""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/cmd/instance""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/cmd/platformcheck""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/licenser""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/outputs/elasticsearch"
)func init() {// backwards compatibility workaround, convert -flags to --flags:for i, arg := range os.Args[1:] {if strings.HasPrefix(arg, "-") && !strings.HasPrefix(arg, "--") && len(arg) > 2 {os.Args[1+i] = "-" + arg}}
}// BeatsRootCmd handles all application command line interface, parses user
// flags and runs subcommands
type BeatsRootCmd struct {cobra.CommandRunCmd *cobra.CommandSetupCmd *cobra.CommandVersionCmd *cobra.CommandCompletionCmd *cobra.CommandExportCmd *cobra.CommandTestCmd *cobra.CommandKeystoreCmd *cobra.Command
}// GenRootCmdWithSettings returns the root command to use for your beat. It take the
// run command, which will be called if no args are given (for backwards compatibility),
// and beat settings
func GenRootCmdWithSettings(beatCreator beat.Creator, settings instance.Settings) *BeatsRootCmd {// Add global Elasticsearch license endpoint check.// Check we are actually talking with Elasticsearch, to ensure that used features actually exist.elasticsearch.RegisterGlobalCallback(licenser.FetchAndVerify)if err := platformcheck.CheckNativePlatformCompat(); err != nil {fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "Failed to initialize: %v\n", err)os.Exit(1)}if settings.IndexPrefix == "" {settings.IndexPrefix = settings.Name}rootCmd := &BeatsRootCmd{}rootCmd.Use = settings.Name// Due to a dependence upon the beat name, the default config file patherr := cfgfile.ChangeDefaultCfgfileFlag(settings.Name)if err != nil {panic(fmt.Errorf("failed to set default config file path: %v", err))}// must be updated prior to CLI flag handling.rootCmd.RunCmd = genRunCmd(settings, beatCreator)rootCmd.ExportCmd = genExportCmd(settings)rootCmd.TestCmd = genTestCmd(settings, beatCreator)rootCmd.SetupCmd = genSetupCmd(settings, beatCreator)rootCmd.KeystoreCmd = genKeystoreCmd(settings)rootCmd.VersionCmd = GenVersionCmd(settings)rootCmd.CompletionCmd = genCompletionCmd(settings, rootCmd)// Root command is an alias for runrootCmd.Run = rootCmd.RunCmd.Run// Persistent flags, common across all subcommandsrootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("E"))rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("c"))rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("d"))rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("v"))rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("e"))rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("environment"))rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("path.config"))rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("path.data"))rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("path.logs"))rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("path.home"))rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("system.hostfs"))rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("strict.perms"))if f := flag.CommandLine.Lookup("plugin"); f != nil {rootCmd.PersistentFlags().AddGoFlag(f)}// Inherit root flags from run command// TODO deprecate when root command no longer executes run (7.0)rootCmd.Flags().AddFlagSet(rootCmd.RunCmd.Flags())// Register subcommands common to all beatsrootCmd.AddCommand(rootCmd.RunCmd)rootCmd.AddCommand(rootCmd.SetupCmd)rootCmd.AddCommand(rootCmd.VersionCmd)rootCmd.AddCommand(rootCmd.CompletionCmd)rootCmd.AddCommand(rootCmd.ExportCmd)rootCmd.AddCommand(rootCmd.TestCmd)rootCmd.AddCommand(rootCmd.KeystoreCmd)return rootCmd
}
可以看到此处的GenRootCmdWithSettings函数,生成了rooCmd包含的所有的命令,包括RunCmd,SetupCmd等等。咱们主要来看这一行:
rootCmd.RunCmd = genRunCmd(settings, beatCreator)3.该行生成了beat默认运行的cmd,咱们看看genRunCmd具体干了什么:libbeat/cmd/run.go:
package cmdimport ("flag""os""github.com/spf13/cobra""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/beat""github.com/elastic/beats/v7/libbeat/cmd/instance"
)func genRunCmd(settings instance.Settings, beatCreator beat.Creator) *cobra.Command {name := settings.NamerunCmd := cobra.Command{Use: "run",Short: "Run " + name,Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {err := instance.Run(settings, beatCreator)if err != nil {os.Exit(1)}},}// Run subcommand flags, only available to *beat runrunCmd.Flags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("N"))runCmd.Flags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("httpprof"))runCmd.Flags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("cpuprofile"))runCmd.Flags().AddGoFlag(flag.CommandLine.Lookup("memprofile"))if settings.RunFlags != nil {runCmd.Flags().AddFlagSet(settings.RunFlags)}return &runCmd
}
可以看到此处使用cobra.command定义了run命令执行的具体函数,即:

4.咱们接着看instance.Run函数干了啥,libbeat/cmd/instance/beat.go:
func Run(settings Settings, bt beat.Creator) error {err := setUmaskWithSettings(settings)if err != nil && err != errNotImplemented {return errw.Wrap(err, "could not set umask")}name := settings.NameidxPrefix := settings.IndexPrefixversion := settings.VersionelasticLicensed := settings.ElasticLicensedreturn handleError(func() error {defer func() {if r := recover(); r != nil {logp.NewLogger(name).Fatalw("Failed due to panic.","panic", r, zap.Stack("stack"))}}()b, err := NewBeat(name, idxPrefix, version, elasticLicensed)if err != nil {return err}// Add basic inforegistry := monitoring.GetNamespace("info").GetRegistry()monitoring.NewString(registry, "version").Set(b.Info.Version)monitoring.NewString(registry, "beat").Set(b.Info.Beat)monitoring.NewString(registry, "name").Set(b.Info.Name)monitoring.NewString(registry, "hostname").Set(b.Info.Hostname)// Add additional info to state registry. This is also reported to monitoringstateRegistry := monitoring.GetNamespace("state").GetRegistry()serviceRegistry := stateRegistry.NewRegistry("service")monitoring.NewString(serviceRegistry, "version").Set(b.Info.Version)monitoring.NewString(serviceRegistry, "name").Set(b.Info.Beat)beatRegistry := stateRegistry.NewRegistry("beat")monitoring.NewString(beatRegistry, "name").Set(b.Info.Name)monitoring.NewFunc(stateRegistry, "host", host.ReportInfo, monitoring.Report)return b.launch(settings, bt)}())
}这块代码加载了basic info和什么registry,没仔细看,重点在最后一行:
b.launch(settings, bt)那继续看这个launch函数,也在libbeat/cmd/instance/beat.go中:
func (b *Beat) launch(settings Settings, bt beat.Creator) error {defer logp.Sync()defer logp.Info("%s stopped.", b.Info.Beat)err := b.InitWithSettings(settings)if err != nil {return err}defer func() {if err := b.processing.Close(); err != nil {logp.Warn("Failed to close global processing: %v", err)}}()// Windows: Mark service as stopped.// After this is run, a Beat service is considered by the OS to be stopped// and another instance of the process can be started.// This must be the first deferred cleanup task (last to execute).defer svc.NotifyTermination()// Try to acquire exclusive lock on data path to prevent another beat instance// sharing same data path.bl := newLocker(b)err = bl.lock()if err != nil {return err}defer bl.unlock()// Set Beat ID in registry vars, in case it was loaded from meta fileinfoRegistry := monitoring.GetNamespace("info").GetRegistry()monitoring.NewString(infoRegistry, "uuid").Set(b.Info.ID.String())serviceRegistry := monitoring.GetNamespace("state").GetRegistry().GetRegistry("service")monitoring.NewString(serviceRegistry, "id").Set(b.Info.ID.String())svc.BeforeRun()defer svc.Cleanup()// Start the API Server before the Seccomp lock down, we do this so we can create the unix socket// set the appropriate permission on the unix domain file without having to whitelist anything// that would be set at runtime.if b.Config.HTTP.Enabled() {s, err := api.NewWithDefaultRoutes(logp.NewLogger(""), b.Config.HTTP, monitoring.GetNamespace)if err != nil {return errw.Wrap(err, "could not start the HTTP server for the API")}s.Start()defer s.Stop()}if err = seccomp.LoadFilter(b.Config.Seccomp); err != nil {return err}beater, err := b.createBeater(bt)if err != nil {return err}r, err := b.setupMonitoring(settings)if err != nil {return err}if r != nil {defer r.Stop()}if b.Config.MetricLogging == nil || b.Config.MetricLogging.Enabled() {reporter, err := log.MakeReporter(b.Info, b.Config.MetricLogging)if err != nil {return err}defer reporter.Stop()}ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())var stopBeat = func() {b.Instrumentation.Tracer().Close()beater.Stop()}svc.HandleSignals(stopBeat, cancel)err = b.loadDashboards(ctx, false)if err != nil {return err}logp.Info("%s start running.", b.Info.Beat)// Launch config managerb.Manager.Start(beater.Stop)defer b.Manager.Stop()return beater.Run(&b.Beat)
}中间执行了很多了操作,例如给数据加锁,防止其他beat使用等等,最后一块是重点:

在这里启动了beat的config manager,最后调用了beater.Run,这个Run也就是libbeat/beta/beat.go中定义的:
type Beater interface {// The main event loop. This method should block until signalled to stop by an// invocation of the Stop() method.Run(b *Beat) error// Stop is invoked to signal that the Run method should finish its execution.// It will be invoked at most once.Stop()
}至此,从main.go的入口到最后调用实际beat的Run()函数的整个流程就跑通了