文章目录
- 虚拟化介绍
- kvm简介
- Qemu-KVM虚拟化
- 部署kvm
- KVM管理界面安装
虚拟化介绍
虚拟化:在一台计算机上虚拟出多个逻辑的计算机,而且每个逻辑计算机
它可以是不同操作系统
虚拟化技术:可以扩大硬件容量,单个cpu模拟出多个cpu并行,
允许一个平台上同时运行多个操作系统,应用程序都可以在相互独立
的空间内运行,而且互不影响。
为什么企业使用虚拟化技术
1、节约成本
2、提高效率,物理机我们一般称为宿主机(Host),宿主机上面的虚拟机称为客户机(Guest)。
那么 Host 是如何将自己的硬件资源虚拟化,并提供给 Guest 使用的呢?
这个主要是通过一个叫做 Hypervisor 的程序实现的。
Hypervisor:一种运行在物理服务器硬件与操作系统之间的中间软件层
可允许多个操作系统和应用来共享硬件资源
根据 Hypervisor 的实现方式和所处的位置,虚拟化又分为两种:
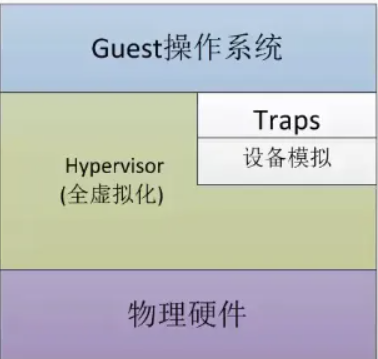
完全虚拟化:直接在物理机上部署虚拟化,且不需要修改操作系统内核
半虚拟化:需要修改操作系统内核,使其支持虚拟化驱动来实现虚拟化技术
全虚拟化
半虚拟化
kvm简介
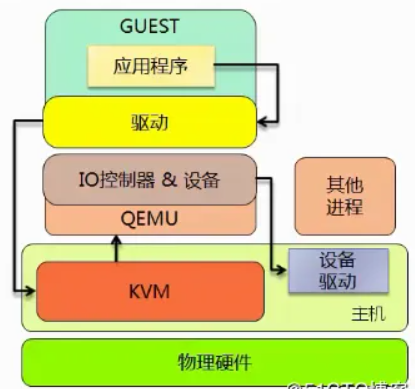
kVM 全称是 Kernel-Based Virtual Machine。也就是说 KVM 是基于 Linux 内核实现的。
KVM有一个内核模块叫 kvm.ko,只用于管理虚拟 CPU 和内存。
那 IO 的虚拟化,比如存储和网络设备则是由 Linux 内核与Qemu来实现。
Qemu-KVM虚拟化
KVM本身不执行任何设备模拟,需要用户空间程序QEMU通过/dev/kvm接口设置一个虚拟客户机的地址空间。
- KVM和Qemu的关系
- Qemu是一个独立的虚拟化解决方案,通过intel-VT 或AMD SVM实现全虚拟化,安装qemu的系统,可以直接模拟出另一个完全不同的系统环境。QEMU本身可以不依赖于KVM,但是如果有KVM的存在并且硬件(处理器)支持比如Intel VT功能,那么QEMU在对处理器虚拟化这一块可以利用KVM提供的功能来提升性能。
- KVM是集成到Linux内核的Hypervisor,是X86架构且硬件支持虚拟化技术(Intel-VT或AMD-V)的Linux的全虚拟化解决方案。它是Linux的一个很小的模块,利用Linux做大量的事,如任务调度、内存管理与硬件设备交互等。准确来说,KVM是Linux kernel的一个模块。
- Qemu的三种运行模式:
- 1.第一种模式是通过kqemu模块实现内核态的加速。
- 2.第二种模式是在用户态直接运行QEMU,由QEMU对目标机的 所有 指令进行翻译后执行,相当于全虚拟化。
- 3.第三种模式则是KVM官方提供的kvm-qemu加速模式。
- qmeu的两种特点:
- 1.QEMU可以在没有主机内核驱动程序的情况下运行。
- 2.它适用于多种操作系统(GNU / Linux,* BSD,Mac OS X,Windows)和体系结构。
- 3.它执行FPU的精确软件仿真。
QEMU的两种操作模式:完整的系统仿真和用户模式仿真。
- QEMU用户模式仿真具有以下功能:
- 1.通用Linux系统调用转换器,包括大部分ioctls。
- 2.使用本机CPU clone的仿真为线程使用Linux调度程序。
- 3.通过将主机信号重新映射到目标信号来实现精确信号处理。
- QEMU全系统仿真具有以下特点:
- 1.QEMU使用完整的软件MMU来实现最大的便携性。
- 2.QEMU可以选择使用内核加速器,如kvm。加速器本地执行大部分客户代码,同时继续模拟机器的其余部分。
- 3.可以仿真各种硬件设备,并且在某些情况下,客户机操作系统可以透明地使用主机设备(例如串行和并行端口,USB,驱动器)。主机设备传递可用于与外部物理外围设备(例如网络摄像头,调制解调器或磁带驱动器)交谈。
- 4.对称多处理(SMP)支持。目前,内核加速器需要使用多个主机CPU进行仿真。
部署kvm
环境说明
| 主机名 | ip | 系统 |
|---|---|---|
| kvm | 192.168.202.138 | centos 8 |
首先先修改机器配置
- 内存尽量给大点,cpu虚拟化功能都勾选,虚拟计数器看情况勾选

//新建分区,将硬盘所有大小都给这个分区
KVM管理界面安装
Kvm的web界面是由webvirtmgr程序提供的
//安装依赖包
[root@centos8 ~]# yum -y install git python2-pip supervisor nginx python2-devel
[root@centos8 ~]# wget http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/os/x86_64/Packages/libxml2-python-2.9.1-6.el7.5.x86_64.rpm
//下载webvirtmgr
[root@centos8 ~]# wget https://download-ib01.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/p/python-websockify-0.6.0-2.el7.noarch.rpm
[root@centos8 ~]# rpm -ivh --nodeps libxml2-python-2.9.1-6.el7.5.x86_64.rpm
warning: libxml2-python-2.9.1-6.el7.5.x86_64.rpm: Header V3 RSA/SHA256 Signature, key ID f4a80eb5: NOKEY
Verifying... ################################# [100%]
Preparing... ################################# [100%]
Updating / installing...1:libxml2-python-2.9.1-6.el7.5 ################################# [100%]//升级pip
[root@centos8 ~]# pip2 install --upgrade pip
WARNING: Running pip install with root privileges is generally not a good idea. Try `pip2 install --user` instead.
Collecting pipDownloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/27/79/8a850fe3496446ff0d584327ae44e7500daf6764ca1a382d2d02789accf7/pip-20.3.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl (1.5MB)100% |████████████████████████████████| 1.5MB 51kB/s
Installing collected packages: pipFound existing installation: pip 9.0.3Uninstalling pip-9.0.3:Successfully uninstalled pip-9.0.3
Successfully installed pip-20.3.4
You are using pip version 20.3.4, however version 22.2.2 is available.
You should consider upgrading via the 'pip install --upgrade pip' command.
[root@centos8 ~]# pip -V
pip 20.3.4 from /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pip (python 2.7)//github拉取webvirtmgr
[root@centos8 ~]# cd /usr/local/src/
[root@centos8 src]# git clone http://github.com/retspen/webvirtmgr.git[root@centos8 src]# cd webvirtmgr/
[root@centos8 webvirtmgr]# ls
conf images networks setup.py
console instance README.rst storages
create interfaces requirements.txt templates
deploy locale secrets Vagrantfile
dev-requirements.txt manage.py serverlog vrtManager
hostdetail MANIFEST.in servers webvirtmgr//安装webvirtmgr
[root@centos8 webvirtmgr]# pip install -r requirements.txt//检查sqlite3是否安装
[root@centos8 webvirtmgr]# python3
Python 3.6.8 (default, Jan 19 2022, 23:28:49)
[GCC 8.5.0 20210514 (Red Hat 8.5.0-7)] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import sqlite3
>>> exit()//初始化账号信息
[root@centos8 webvirtmgr]# python2 manage.py syncdb
WARNING:root:No local_settings file found.
Creating tables ...
Creating table auth_permission
Creating table auth_group_permissions
Creating table auth_group
Creating table auth_user_groups
Creating table auth_user_user_permissions
Creating table auth_user
Creating table django_content_type
Creating table django_session
Creating table django_site
Creating table servers_compute
Creating table instance_instance
Creating table create_flavorYou just installed Django's auth system, which means you don't have any superusers defined.
Would you like to create one now? (yes/no): yes
Username (leave blank to use 'root'): root
Email address: wjh@qq.com
Password:
Password (again):
Superuser created successfully.
Installing custom SQL ...
Installing indexes ...
Installed 6 object(s) from 1 fixture(s)//拷贝web网页到指定目录
[root@centos8 webvirtmgr]# mkdir /var/www/
[root@centos8 webvirtmgr]# cp -r /usr/local/src/webvirtmgr/ /var/www/
[root@centos8 webvirtmgr]# chown -R nginx.nginx /var/www/webvirtmgr///配置密钥认证
由于这里webvirtmgr和kvm服务部署在同一台机器,所以这里是本地信任;如果kvm部署在其他机器上的时候,那么就需要把公钥发送到kvm主机中
[root@centos8 ~]# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:PQ3B2ODEaZM8hFyvvjJzQFGrU9zEoVzze4O/TEZ2pD0 root@centos8
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 3072]----+
| . B*O*. |
| +=XB++ |
| oBo+ . .|
| .o o o o + |
| .o S o + *Eo|
| .o . = o.|
| .. + |
| + .. + . |
| =. o |
+----[SHA256]-----+[root@centos8 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@192.168.137.130/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.137.130 (192.168.137.130)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:u3A9HCdz3qc1ZfyEQNpSYXCaJOq8Gt1t0g7nfv8eh0o.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.137.130's password: Number of key(s) added: 1Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.137.130'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.//配置端口转发
[root@centos8 ~]# ssh 192.168.137.130 -L localhost:8000:localhost:8000//查看端口
[root@centos8 ~]# ss -anlt
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 32 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6080 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:8000 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:6080 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:8000 [::]:* //配置nginx
[root@centos8 ~]# cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf.bak
[root@centos8 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf删除listen [::]:80;行
参数server_name行改成server_name localhost;
删除root /usr/share/nginx/html;行
server {listen 80 ;server_name localhost;在include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;行下添加location / {root html;index index.html index.htm;//配置nginx虚拟机
[root@centos8 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/webvirtmgr.conf
server {listen 80 default_server;server_name $hostname;#access_log /var/log/nginx/webvirtmgr_access_log;location /static/ {root /var/www/webvirtmgr/webvirtmgr;expires max;}location / {proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000;proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-for $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;proxy_set_header Host $host:$server_port;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $remote_addr;proxy_connect_timeout 600;proxy_read_timeout 600;proxy_send_timeout 600;client_max_body_size 1024M;}
}//确保bind绑定本机的8000端口
[root@centos8 ~]# grep "bind" /var/www/webvirtmgr/conf/gunicorn.conf.py
# bind - The socket to bind.
bind = '127.0.0.1:8000'//重启nginx服务,并查看端口
[root@centos8 ~]# systemctl restart nginx.service
[root@centos8 ~]# ss -anlt
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 32 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6080 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:8000 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:6080 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:8000 [::]:* //设置supervisor
[root@centos8 ~]# vim /etc/supervisord.conf
//最后一行添加
[program:webvirtmgr]
command=/usr/bin/python2 /var/www/webvirtmgr/manage.py run_gunicorn -c /var/www/webvirtmgr/conf/gunicorn.conf.py
directory=/var/www/webvirtmgr
autostart=true
autorestart=true
logfile=/var/log/supervisor/webvirtmgr.log
log_stderr=true
user=nginx[program:webvirtmgr-console]
command=/usr/bin/python2 /var/www/webvirtmgr/console/webvirtmgr-console
directory=/var/www/webvirtmgr
autostart=true
autorestart=true
stdout_logfile=/var/log/supervisor/webvirtmgr-console.log
redirect_stderr=true
user=nginx//启动并开机自启
[root@centos8 ~]# systemctl enable --now supervisord.service//配置nginx用户
[root@centos8 ~]# su - nginx -s /bin/bash
[nginx@centos8 ~]$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/var/lib/nginx/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:eQItHVwOqs0LWzkuCpdj+DKNLpHA3izm/6EU8ghS6No nginx@centos8
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 3072]----+
| .o.. |
| . +.+ |
|o . + o . |
|oo + + . |
|=+o.o * S . |
|**++.= o o |
|*=Eoo.o |
|=*oo... |
|o++o.. |
+----[SHA256]-----+[nginx@centos8 ~]$ echo -e "StrictHostKeyChecking=no\nUserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null" > ~/.ssh/config
[nginx@centos8 ~]$ cat .ssh/config
StrictHostKeyChecking=no
UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null
[nginx@centos8 ~]$ chmod 600 .ssh/config
[nginx@centos8 ~]$ ssh-copy-id root@192.168.137.130
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.137.130' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@192.168.137.130's password: Number of key(s) added: 1Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.137.130'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.[nginx@centos8 ~]$ exit
logout[root@centos8 ~]# vim /etc/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/50-libvirt-remote-access.pkla
[Remote libvirt SSH access]
Identity=unix-user:root
Action=org.libvirt.unix.manage
ResultAny=yes
ResultInactive=yes
ResultActive=yes[root@centos8 ~]# systemctl restart nginx.service
[root@centos8 ~]# systemctl restart libvirtdchannel 1012: open failed: connect failed: Device or resource busy
channel 1013: open failed: connect failed: Device or resource busy发现问题所在,我53端口一直没起来
web界面,nginx也报错502,原来是selinux permissive模式不行,必须disabled永久关闭
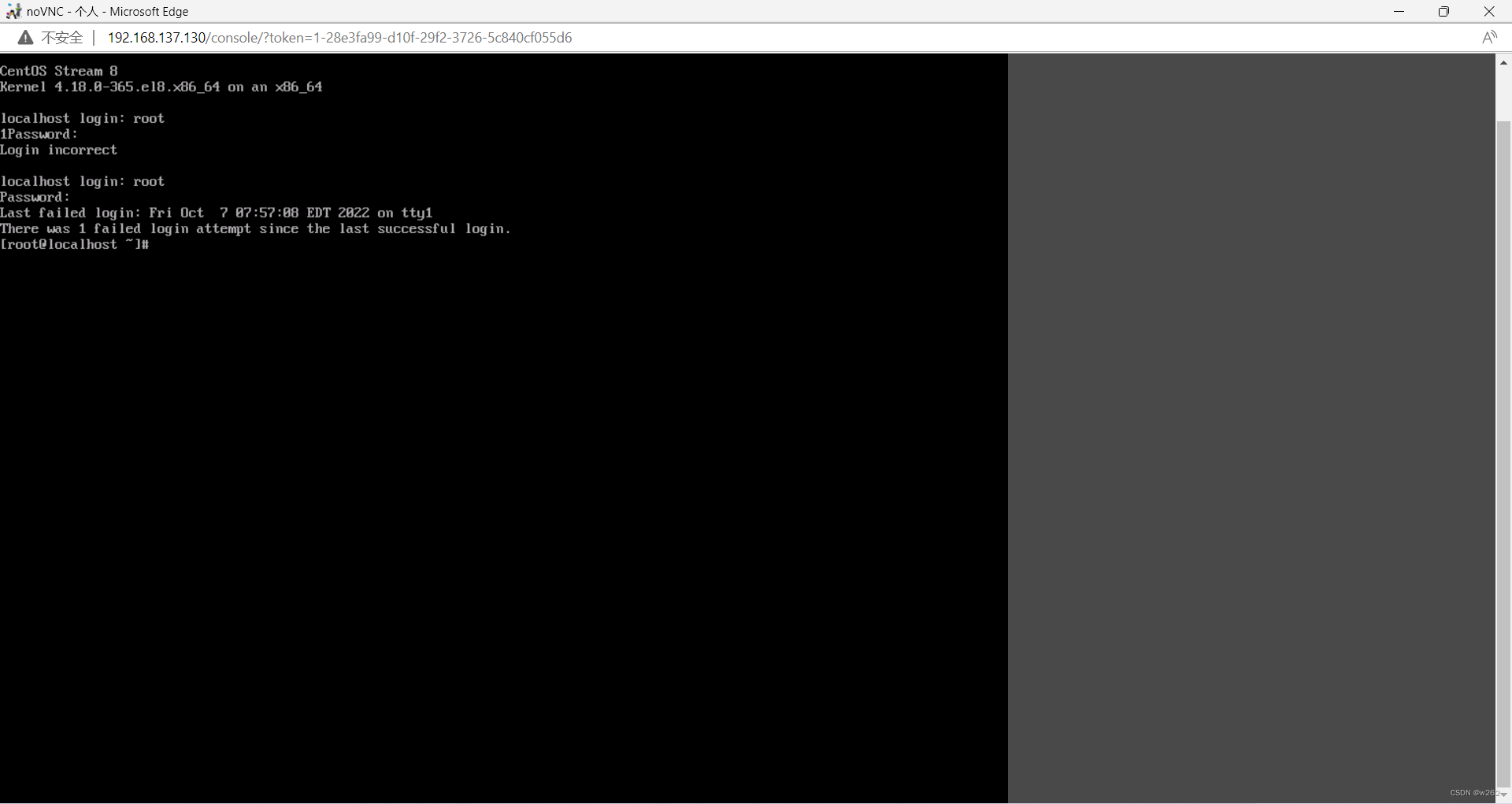
重开rebootweb界面登录

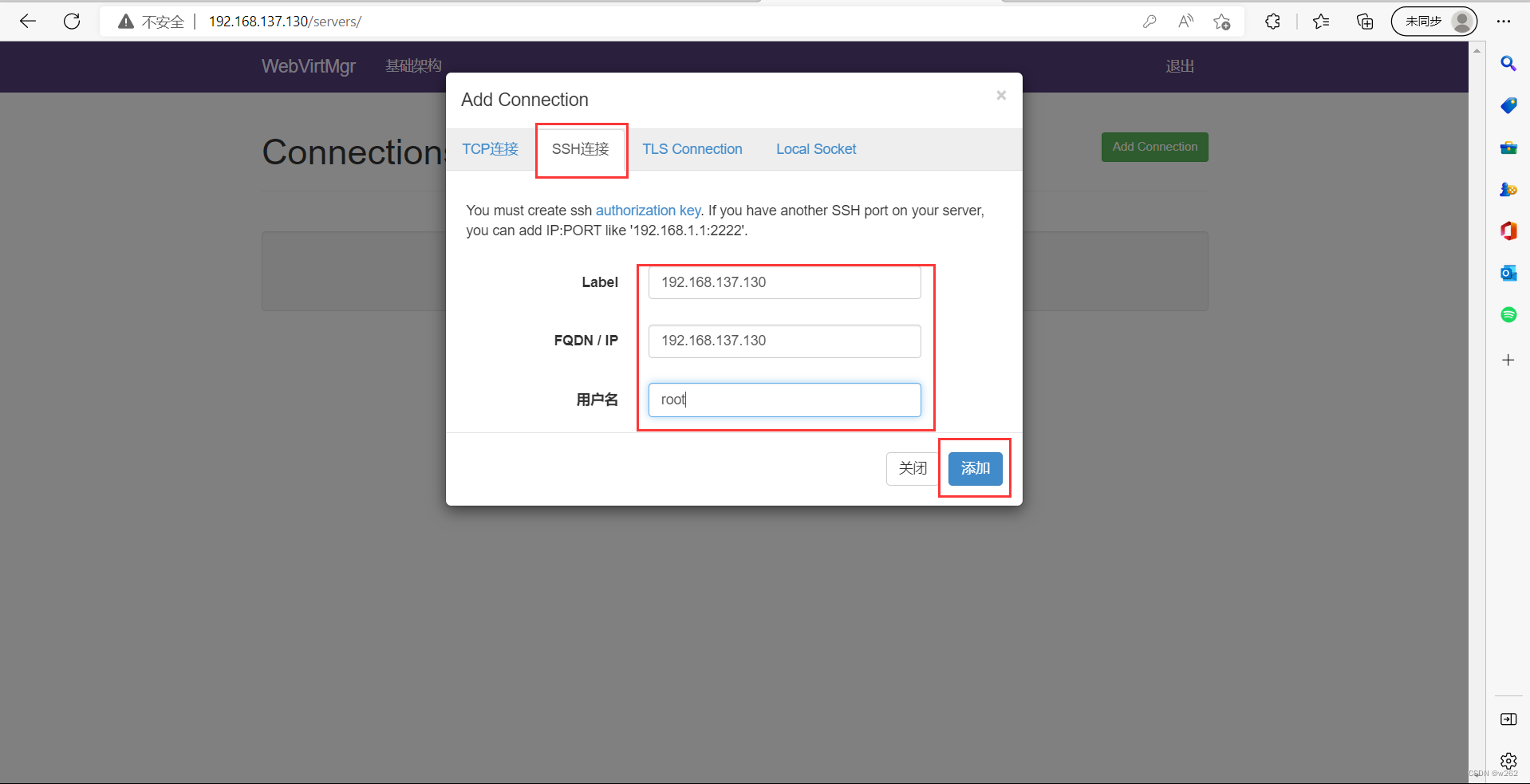
新建连接
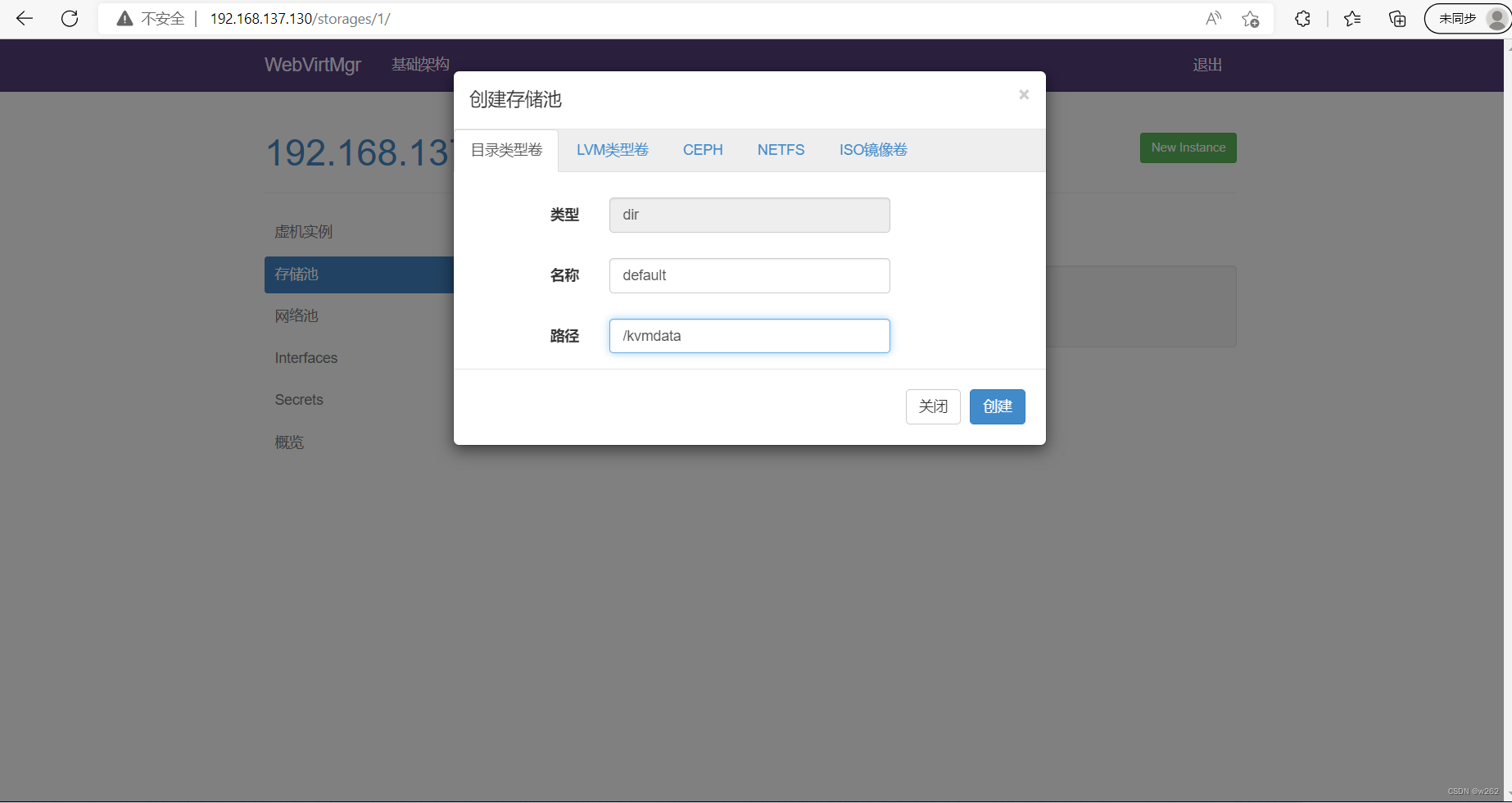
 新建存储池
新建存储池
 通过工具上传镜像
通过工具上传镜像
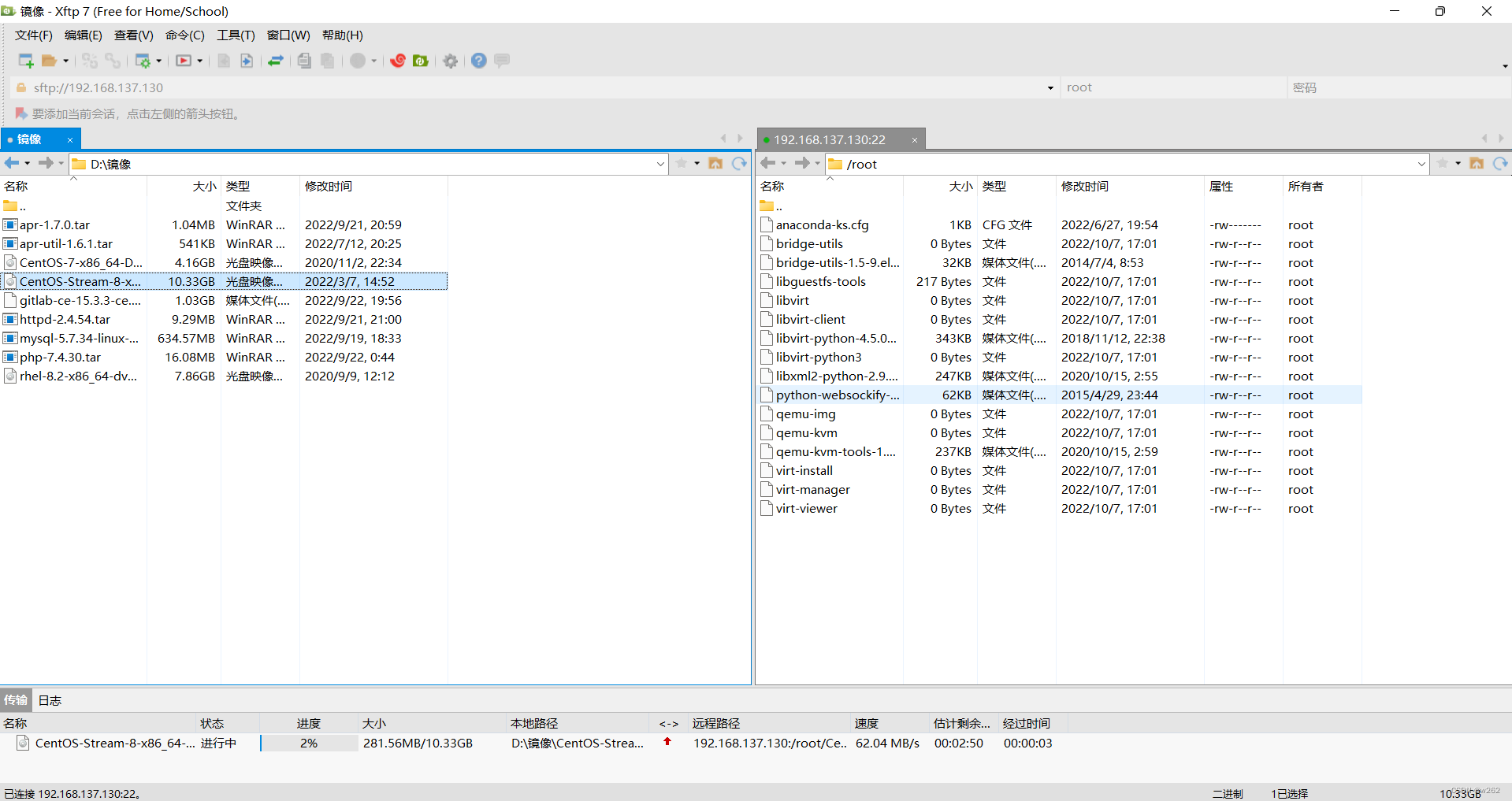 //新建镜像
//新建镜像
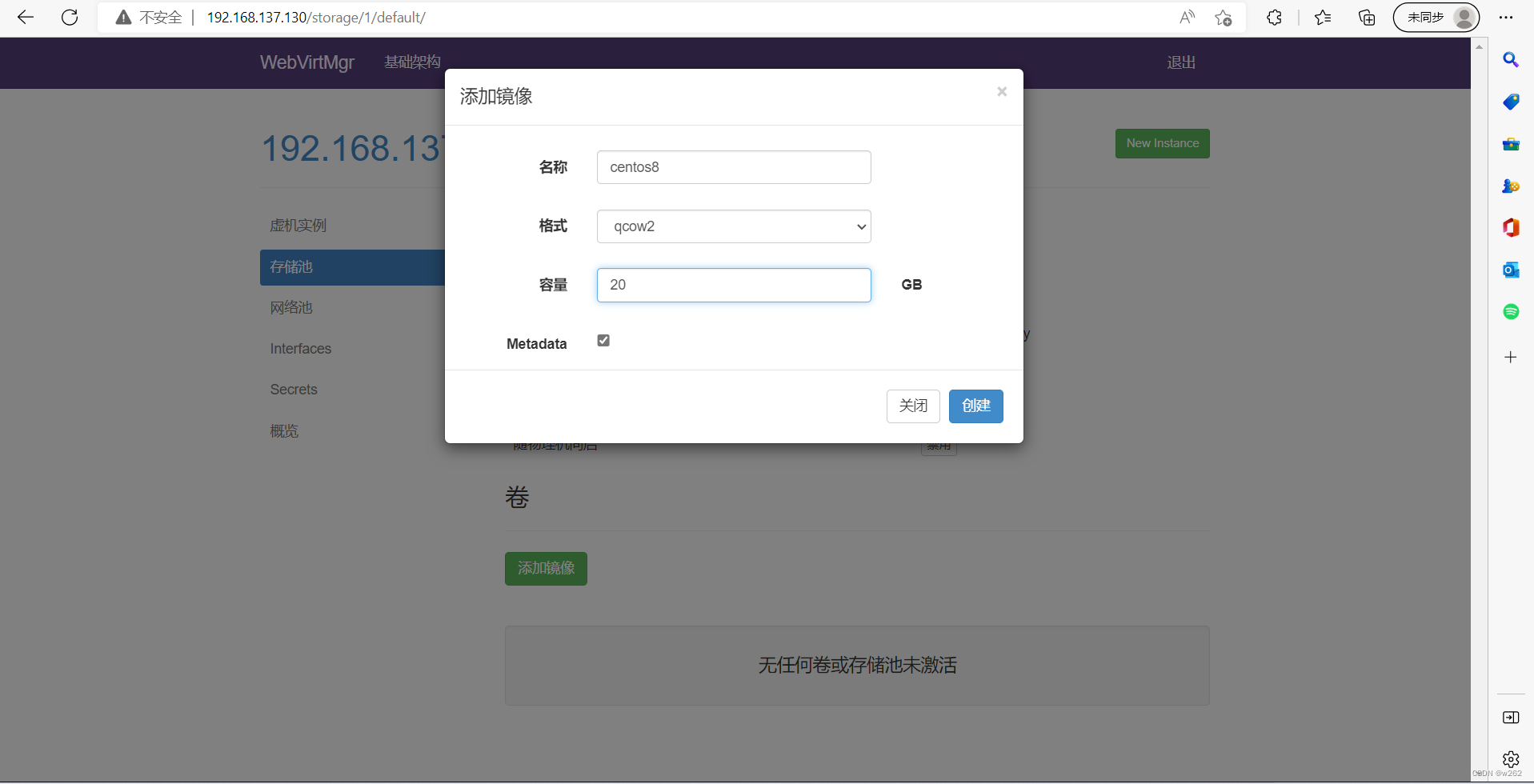
网络池,新建网络
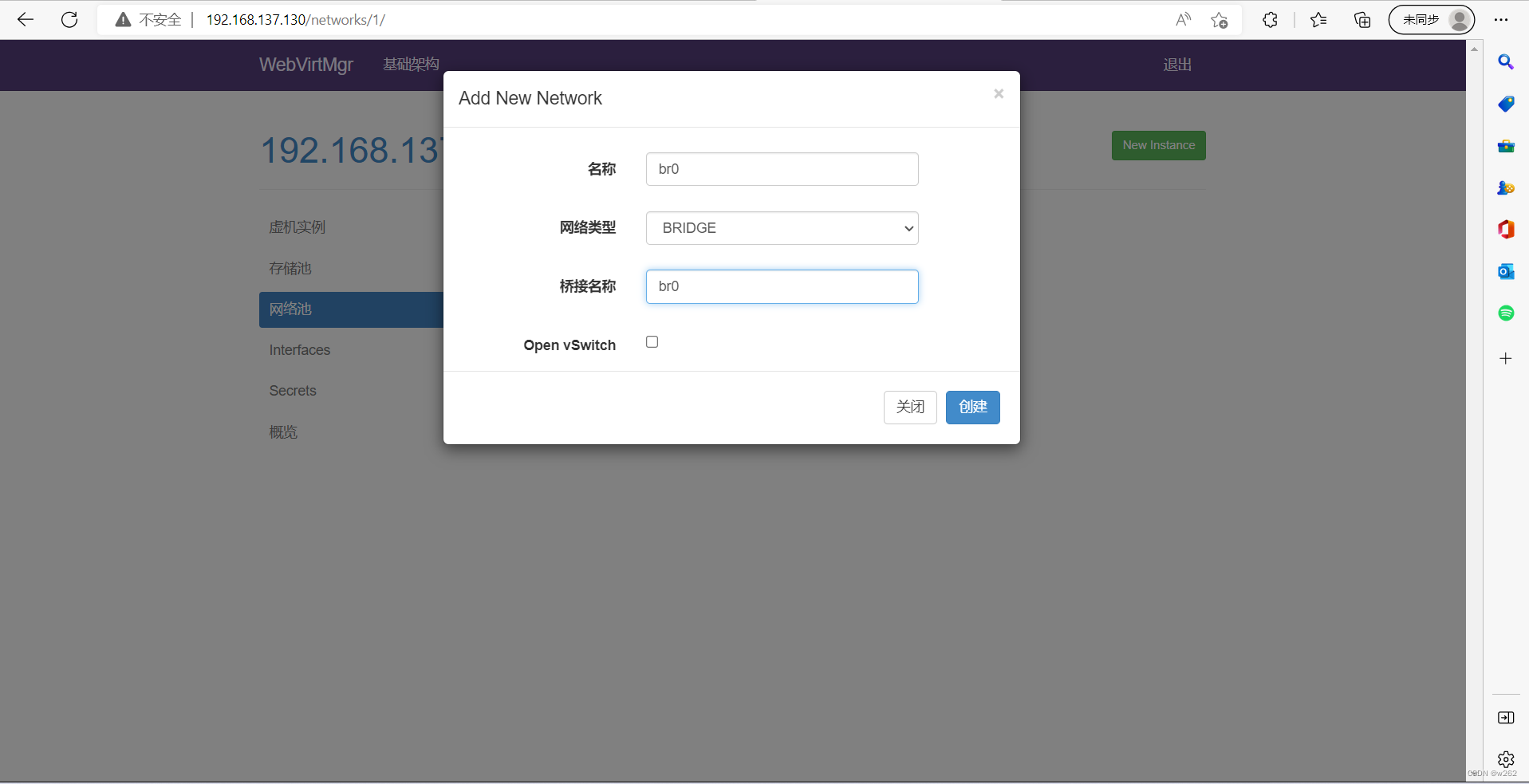
自定义创建虚拟机
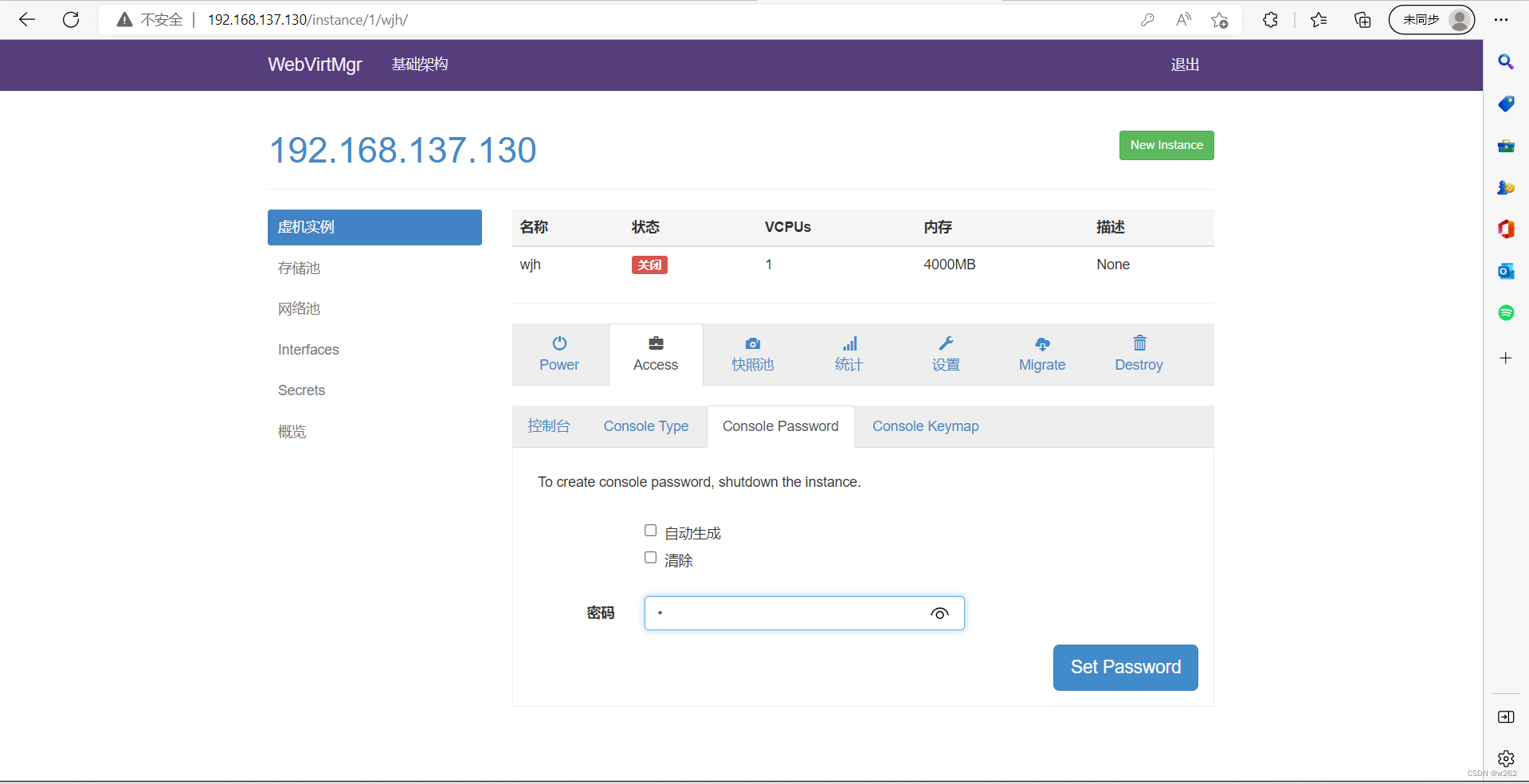
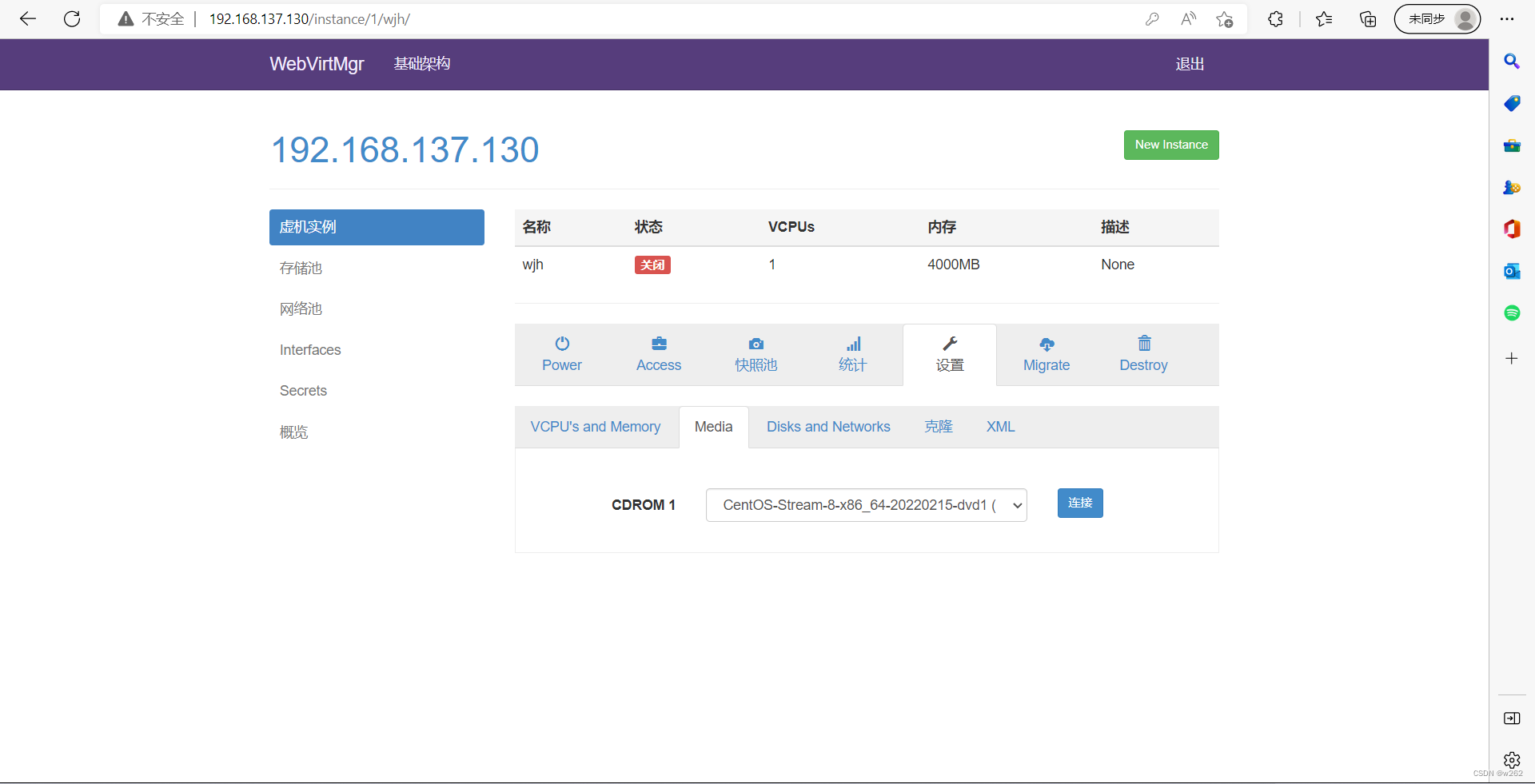
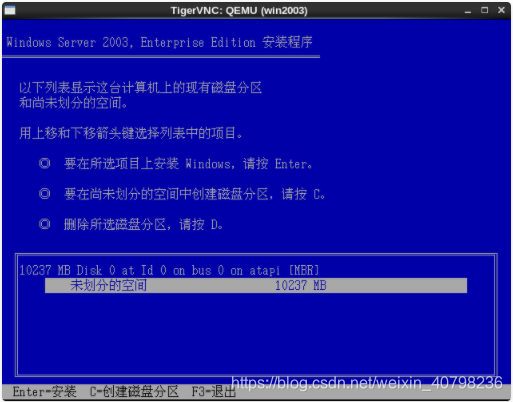
开始安装
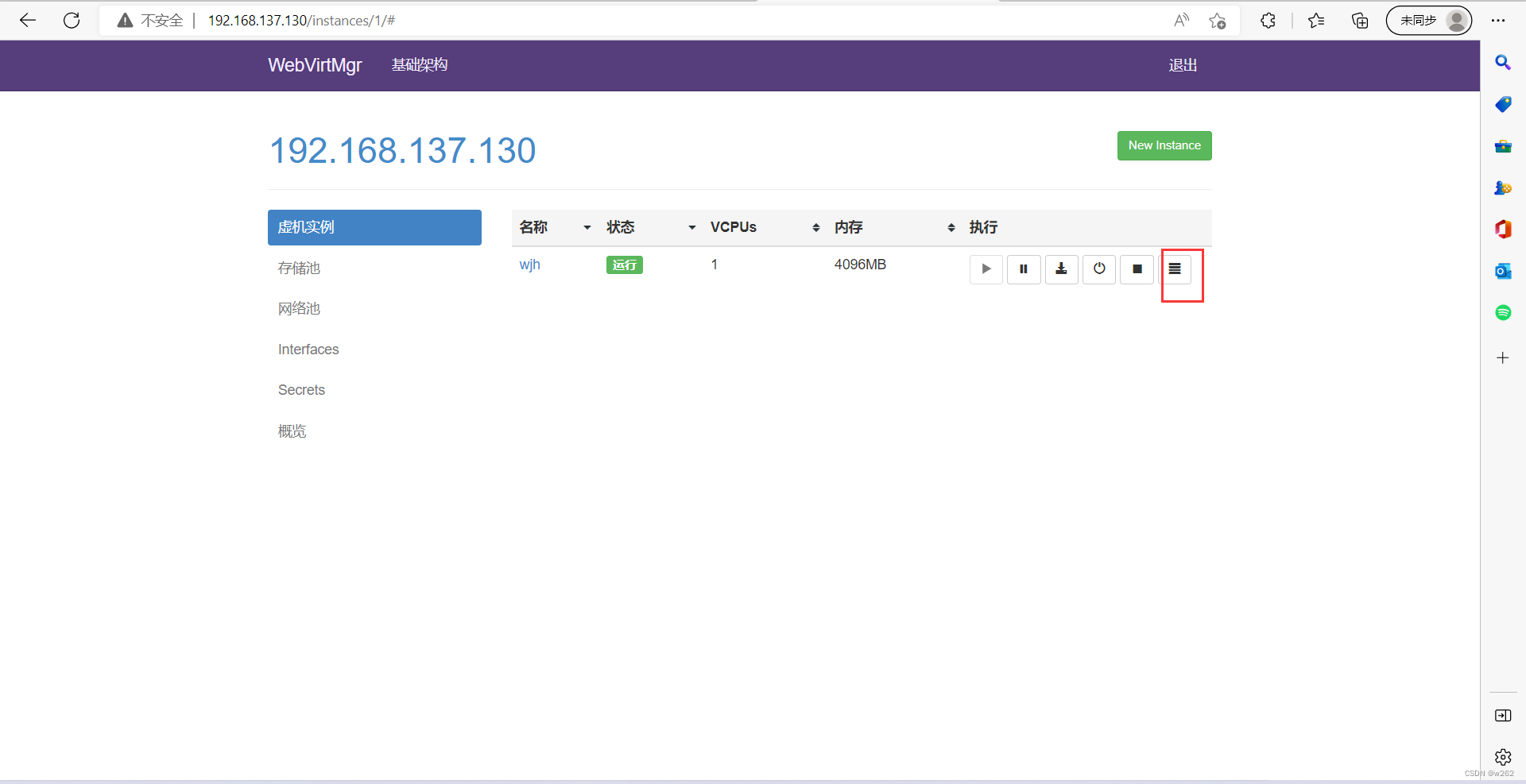
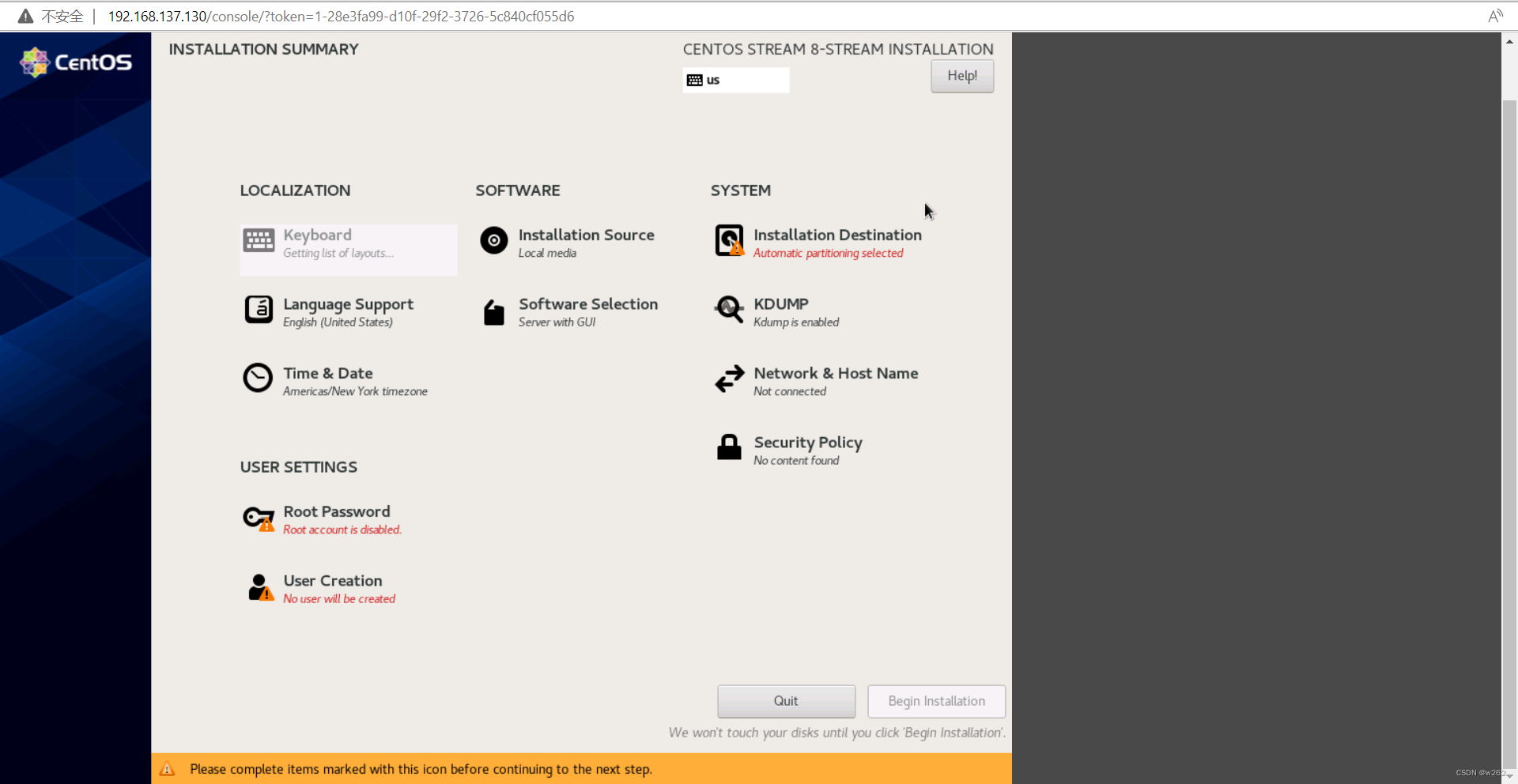
安装完成