熟悉 Android 开发的小伙伴都知道,不能再非主线程中修改 UI 控件,而且当时老师告诉我们就是在非主线程的代码修改 UI 控件可以用 Handler。以至于后来我也都是这么做的,最近有人问我这个自定义的 Handler 为啥下面都是黄色的,是不是他写的不对。于是点进去看了下源码,发现原来我用了这么多年的构造早就是被废弃了的,而我还在坚持。
This Handler class should be static or leaks might occur (anonymous android.os.Handler)
@SuppressLint("HandlerLeak")
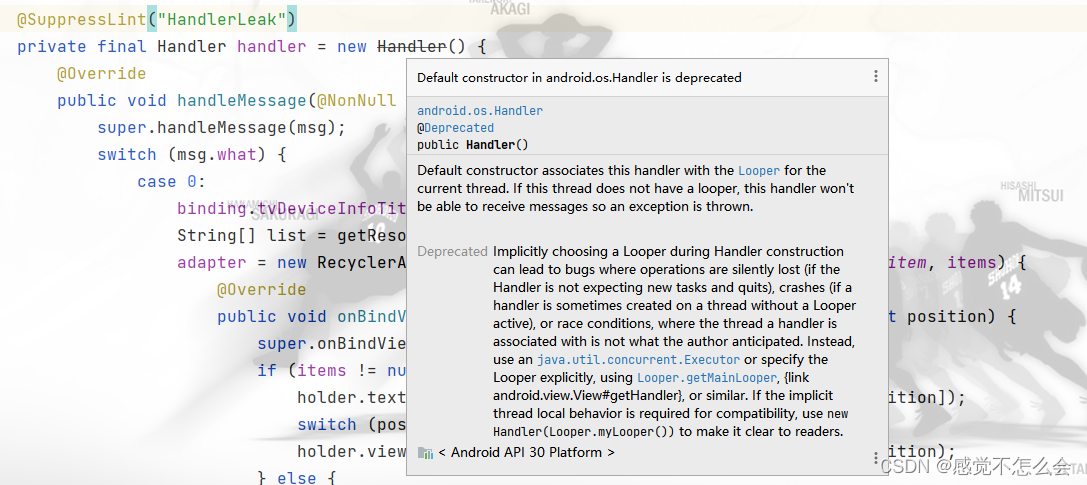
查看源码发现只是构造函数被废弃了
给出的解释如下
Default constructor associates this handler with the Looper for the current thread. If this thread does not have a looper, this handler won't be able to receive messages so an exception is thrown.
Deprecated
Implicitly choosing a Looper during Handler construction can lead to bugs where operations are silently lost (if the Handler is not expecting new tasks and quits), crashes (if a handler is sometimes created on a thread without a Looper active), or race conditions, where the thread a handler is associated with is not what the author anticipated. Instead, use an java.util.concurrent.Executor or specify the Looper explicitly, using Looper.getMainLooper, {link android.view.View#getHandler}, or similar. If the implicit thread local behavior is required for compatibility, use new Handler(Looper.myLooper()) to make it clear to readers.译文:
默认构造函数将此处理程序与当前线程的循环器关联。如果这个线程没有循环程序,这个处理程序将无法接收消息,因此会抛出一个异常。
弃用
隐式地选择一个电影在处理程序建设会导致错误操作在哪里默默地丢失(如果处理程序不期望新任务和退出),崩溃(如果一个处理程序有时没有电影活动)上创建一个线程,或者竞态条件,相关的线程处理程序并不是作者的预期。相反,使用java.util.concurrent. execute
刚好借此机会,简单了解一下 Handler 的机制。(以下内容部分来源于菜鸟教程)
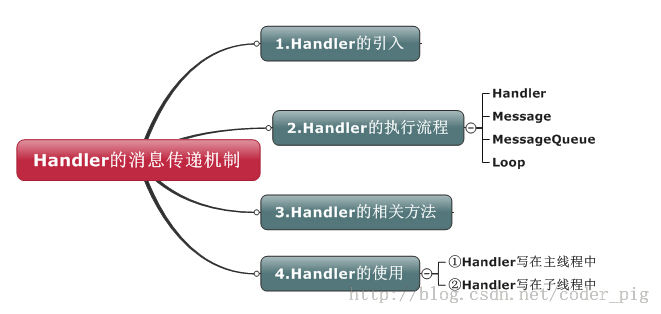
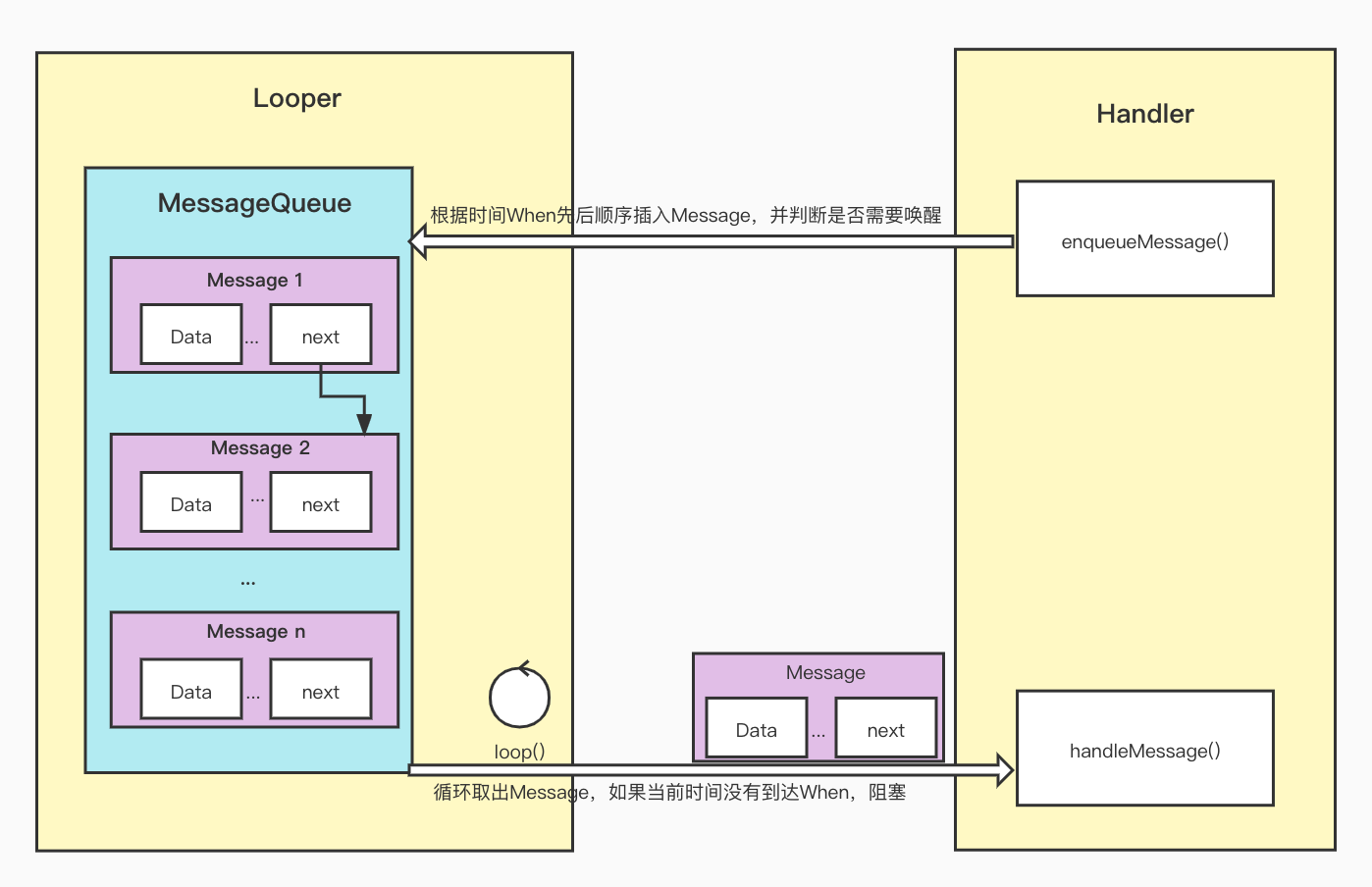
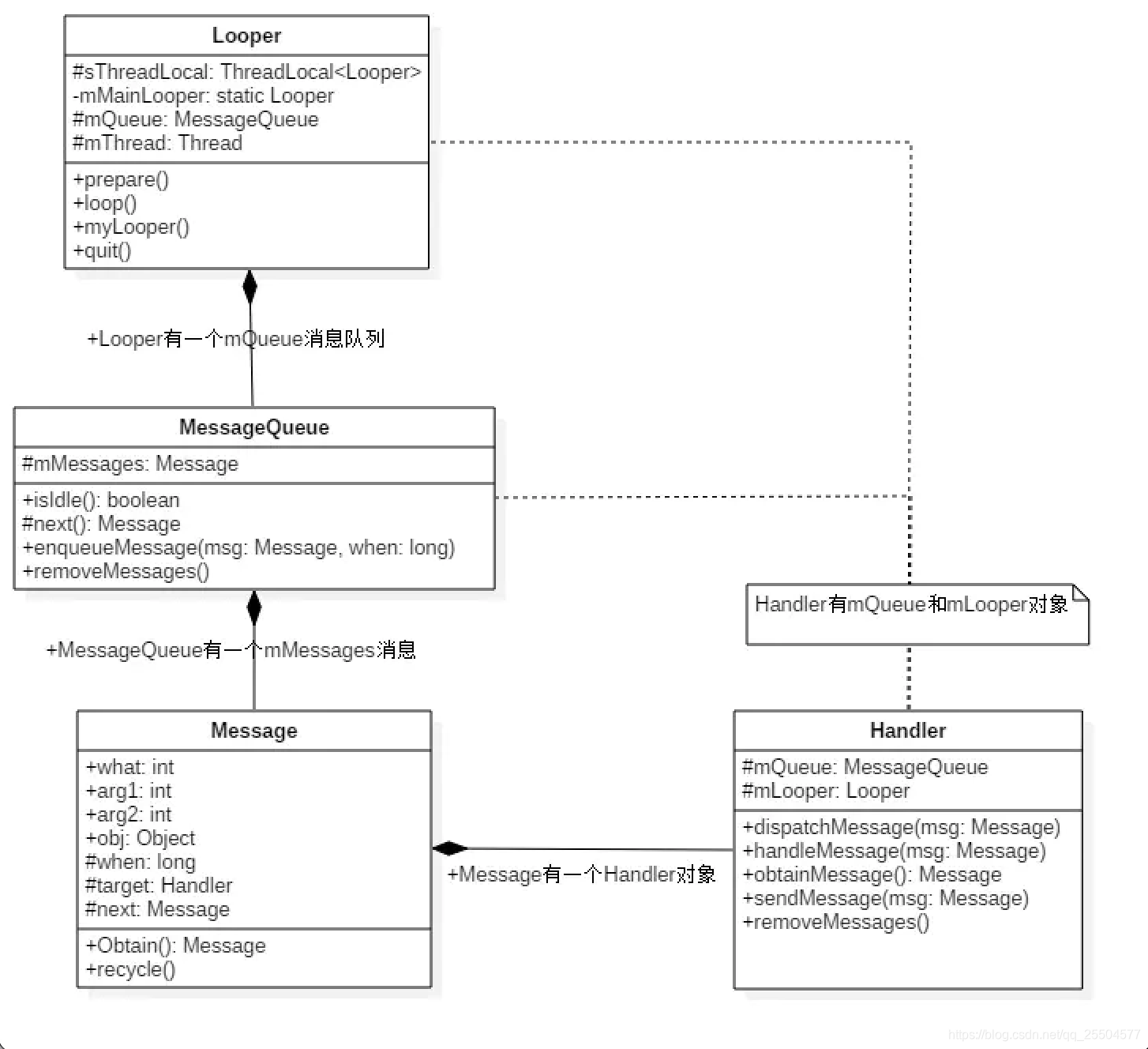
- UI线程:就是我们的主线程,系统在创建UI线程的时候会初始化一个Looper对象,同时也会创建一个与其关联的MessageQueue;
- Handler:作用就是发送与处理信息,如果希望Handler正常工作,在当前线程中要有一个Looper对象
- Message:Handler接收与处理的消息对象
- MessageQueue:消息队列,先进先出管理Message,在初始化Looper对象时会创建一个与之关联的MessageQueue;
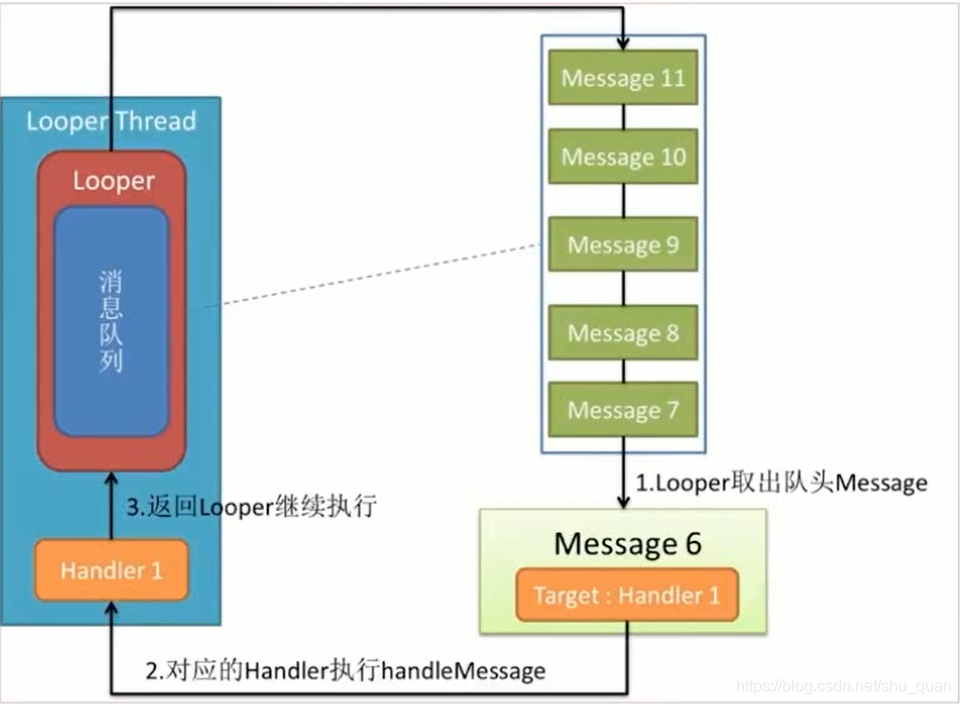
- Looper:每个线程只能够有一个Looper,管理MessageQueue,不断地从中取出Message分发给对应的Handler处理!
流程图如下
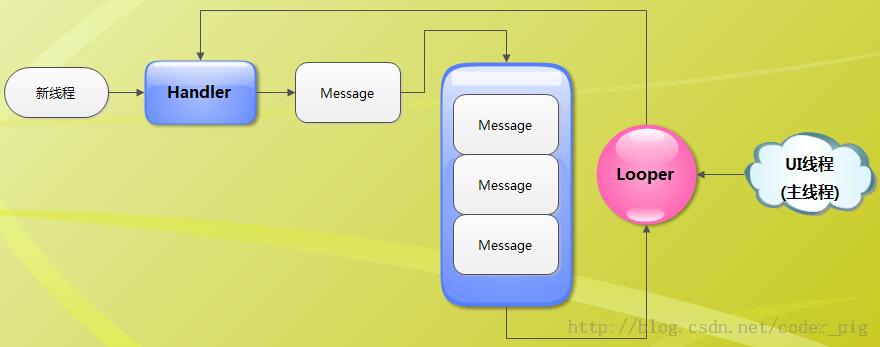
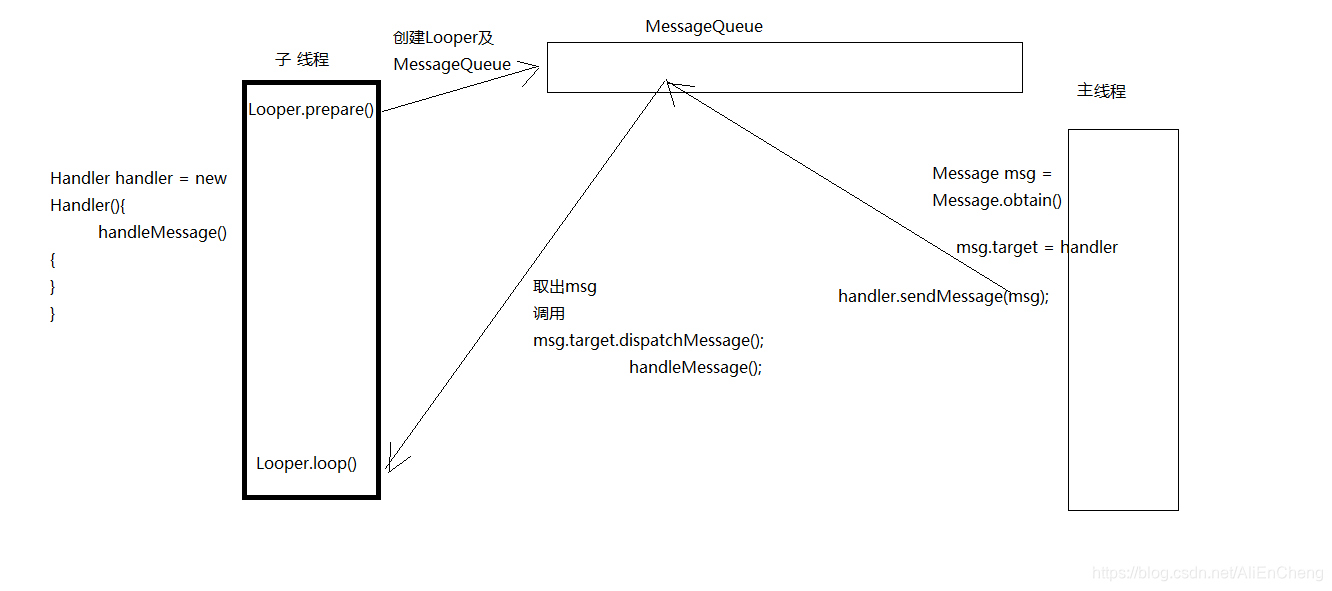
也就是说当我们需要在子线程的执行后修改 UI 控件时,可以新建一个 Handler 对象,通过 Handler 的方法发送消息,在新建的 Handler 对象中执行修改 UI 的结果。
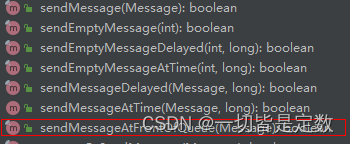
Handler 的相关方法
- void handleMessage(Message msg):处理消息的方法,通常是用于被重写!
- sendEmptyMessage(int what):发送空消息
- sendEmptyMessageDelayed(int what,long delayMillis):指定延时多少毫秒后发送空信息
- sendMessage(Message msg):立即发送信息
- sendMessageDelayed(Message msg):指定延时多少毫秒后发送信息
- final boolean hasMessage(int what):检查消息队列中是否包含what属性为指定值的消息 如果是参数为(int what,Object object):除了判断what属性,还需要判断Object属性是否为指定对象的消息
我们先来简单的看一下源码部分。
Looper
Looper 比较重要的两个方法是 prepare( ) 和 loop( )
构造方法如下:
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);mThread = Thread.currentThread();}
在创建时会新建一个 MessageQueue,然后通过 prepare 方法创建 Looper,结果通过 ThreadLocal 保存,这个我在源码里没找到这个类的注释,但根据下面可以看到。
// sThreadLocal.get() will return null unless you've called prepare().
译文:除非你调用了prepare(),否则sThreadLocal.get()将返回null。
// sThreadLocal.get() will return null unless you've called prepare().@UnsupportedAppUsagestatic final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>();/** Initialize the current thread as a looper.* This gives you a chance to create handlers that then reference* this looper, before actually starting the loop. Be sure to call* {@link #loop()} after calling this method, and end it by calling* {@link #quit()}.*/public static void prepare() {prepare(true);}private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");}sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));}/*** Initialize the current thread as a looper, marking it as an* application's main looper. See also: {@link #prepare()}** @deprecated The main looper for your application is created by the Android environment,* so you should never need to call this function yourself.*/@Deprecatedpublic static void prepareMainLooper() {prepare(false);synchronized (Looper.class) {if (sMainLooper != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared.");}sMainLooper = myLooper();}}prepareMainLooper 方法的注释则是更加直白,我们不需要创建,主程序会自动创建的。
接下来的 loop 方法就比较重要了,当我们在子线程中使用 Handler 则必须手动调用 Looper.prepare() 和 Looper.loop()。我们可以看到这段代码获取到 MessageQueue 后开启消息循环,不断从 MessageQueue 中取消息,无则阻塞,等待消息。有则调用 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg) 处理消息。因此,Looper 只负责开启消息循环接收消息并处理消息。处理完消息后会调用 msg.recycleUnchecked() 来回收消息。
/*** Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call* {@link #quit()} to end the loop.*/public static void loop() {final Looper me = myLooper();if (me == null) {throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");}if (me.mInLoop) {Slog.w(TAG, "Loop again would have the queued messages be executed"+ " before this one completed.");}me.mInLoop = true;final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.Binder.clearCallingIdentity();final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();// Allow overriding a threshold with a system prop. e.g.// adb shell 'setprop log.looper.1000.main.slow 1 && stop && start'final int thresholdOverride =SystemProperties.getInt("log.looper."+ Process.myUid() + "."+ Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ".slow", 0);boolean slowDeliveryDetected = false;for (;;) {Message msg = queue.next(); // might blockif (msg == null) {// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.return;}// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the loggerfinal Printer logging = me.mLogging;if (logging != null) {logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);}// Make sure the observer won't change while processing a transaction.final Observer observer = sObserver;final long traceTag = me.mTraceTag;long slowDispatchThresholdMs = me.mSlowDispatchThresholdMs;long slowDeliveryThresholdMs = me.mSlowDeliveryThresholdMs;if (thresholdOverride > 0) {slowDispatchThresholdMs = thresholdOverride;slowDeliveryThresholdMs = thresholdOverride;}final boolean logSlowDelivery = (slowDeliveryThresholdMs > 0) && (msg.when > 0);final boolean logSlowDispatch = (slowDispatchThresholdMs > 0);final boolean needStartTime = logSlowDelivery || logSlowDispatch;final boolean needEndTime = logSlowDispatch;if (traceTag != 0 && Trace.isTagEnabled(traceTag)) {Trace.traceBegin(traceTag, msg.target.getTraceName(msg));}final long dispatchStart = needStartTime ? SystemClock.uptimeMillis() : 0;final long dispatchEnd;Object token = null;if (observer != null) {token = observer.messageDispatchStarting();}long origWorkSource = ThreadLocalWorkSource.setUid(msg.workSourceUid);try {msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);if (observer != null) {observer.messageDispatched(token, msg);}dispatchEnd = needEndTime ? SystemClock.uptimeMillis() : 0;} catch (Exception exception) {if (observer != null) {observer.dispatchingThrewException(token, msg, exception);}throw exception;} finally {ThreadLocalWorkSource.restore(origWorkSource);if (traceTag != 0) {Trace.traceEnd(traceTag);}}if (logSlowDelivery) {if (slowDeliveryDetected) {if ((dispatchStart - msg.when) <= 10) {Slog.w(TAG, "Drained");slowDeliveryDetected = false;}} else {if (showSlowLog(slowDeliveryThresholdMs, msg.when, dispatchStart, "delivery",msg)) {// Once we write a slow delivery log, suppress until the queue drains.slowDeliveryDetected = true;}}}if (logSlowDispatch) {showSlowLog(slowDispatchThresholdMs, dispatchStart, dispatchEnd, "dispatch", msg);}if (logging != null) {logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);}// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();if (ident != newIdent) {Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);}msg.recycleUnchecked();}}
Looper 提供的退出的方法则为
/*** Quits the looper.* <p>* Causes the {@link #loop} method to terminate without processing any* more messages in the message queue.* </p><p>* Any attempt to post messages to the queue after the looper is asked to quit will fail.* For example, the {@link Handler#sendMessage(Message)} method will return false.* </p><p class="note">* Using this method may be unsafe because some messages may not be delivered* before the looper terminates. Consider using {@link #quitSafely} instead to ensure* that all pending work is completed in an orderly manner.* </p>** @see #quitSafely*/public void quit() {mQueue.quit(false);}/*** Quits the looper safely.* <p>* Causes the {@link #loop} method to terminate as soon as all remaining messages* in the message queue that are already due to be delivered have been handled.* However pending delayed messages with due times in the future will not be* delivered before the loop terminates.* </p><p>* Any attempt to post messages to the queue after the looper is asked to quit will fail.* For example, the {@link Handler#sendMessage(Message)} method will return false.* </p>*/public void quitSafely() {mQueue.quit(true);}Message
- 使用 what 来区分消息
- 使用 arg1、arg2、obj、data 来传递数据
- 参数 target,它决定了 Message 所关联的 Handler
MessageQueue
- enqueueMessage 方法往消息列表中插入一条数据,
- next 方法从消息队列中取出一条消息并将其从消息队列中移除
- quit 方法退出消息列表,通过参数 safe 决定是否直接退出
Handler
构造函数大家可以查看源码,这里就不一一列举了,只提一下我原来一直用的被废弃的方法,而且我相信有很多人还在这样用~
Java 构造函数,也叫构造方法,是 Java中一种特殊的函数。与函数名相同,无返回值。
作用:一般用来初始化成员属性和成员方法的,即 new 对象产生后,就调用了对象的属性和方法。
因此感觉这部分不太重要,只要写的东西能实现所需功能就行了吧(出问题再改(手动狗头))。我看到网上好多人都这么写了。
private final Handler handler = new Handler(new Handler.Callback() {@Overridepublic boolean handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {return false;}});
最后,简单了解了下 Handler 机制可以加深记忆和更深的使用。因此,这次就不写实例了~~~
感谢 菜鸟教程 。
如有侵权问题,请联系我。