一,什么是handler
handler是消息机制的一个上层接口 更新UI的操作 耗时完毕后发送消息给主线程更新UI
耗时操作只能在子线程中执行,Android是线程不安全的你不能在子线程中更新UI 所以Android引入了handler机制
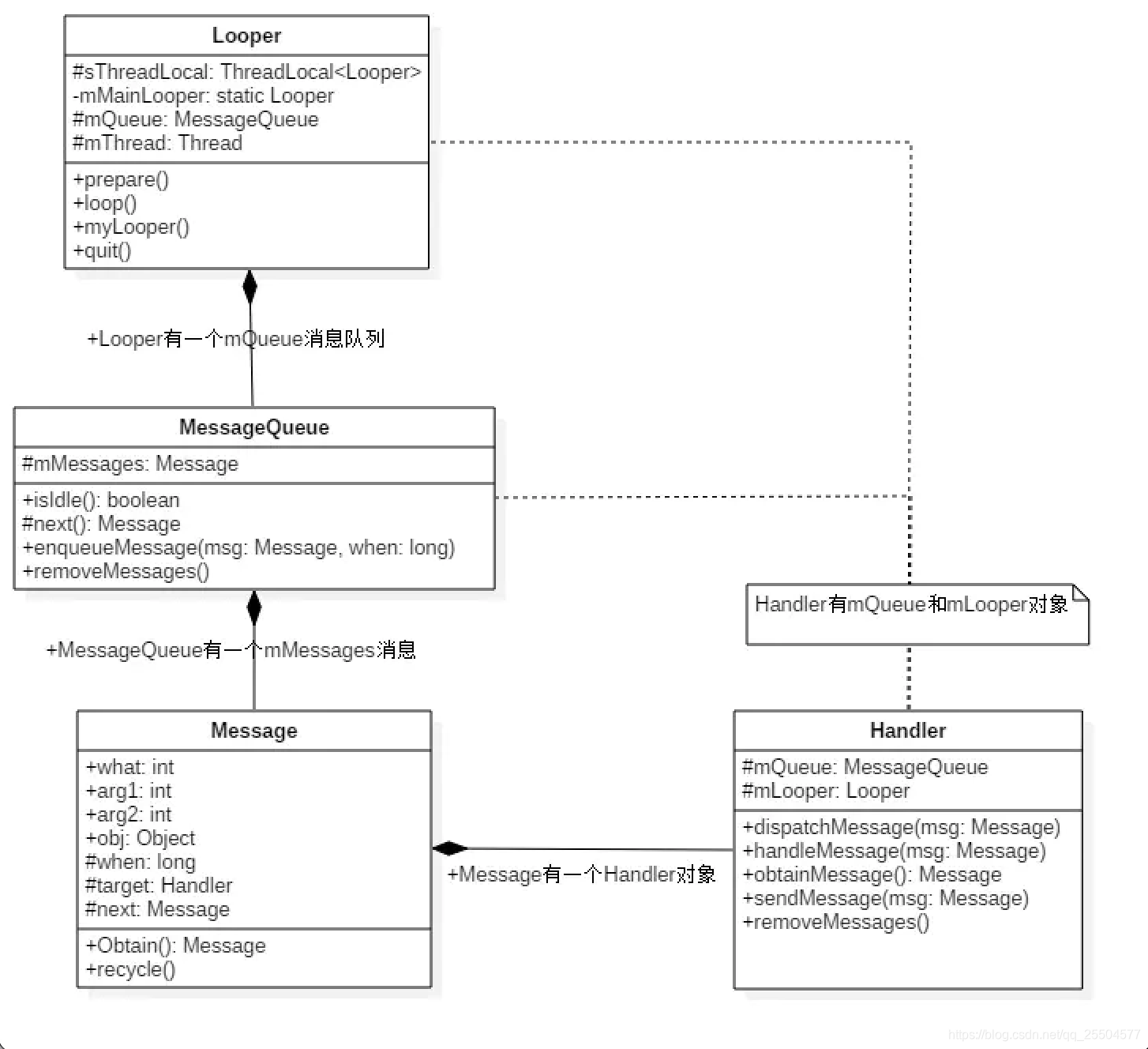
handler通过发送和处理message和Runnable对象来关联相对应线程的MssagerQueue(消息队列)
1.可以让对应的message(message是放置信息,可以传递一些参数)和runnable(Runnable则是直接给出处理的方法)在未来的某个时间进行相应处理
2.让自己想要处理的耗时操作放在子线程,让更新UI操作放在主线程
3.队列就是依次执行,Handler会处理完一个消息或者执行完某个处理在进行下一步,这样不会出现多个线程同时要求进行UI处理而引发的混乱现象
二,handler的使用方法
1.post(runnable) Runnable则是直接给出处理的方法)在未来的某个时间进行相应处理源码底层还是调用了sendmassage(massage)方法
2.sendmassage(massage) 放置信息,可以传递一些参数 ,可以定时处理更新UI
三,handler机制的原理
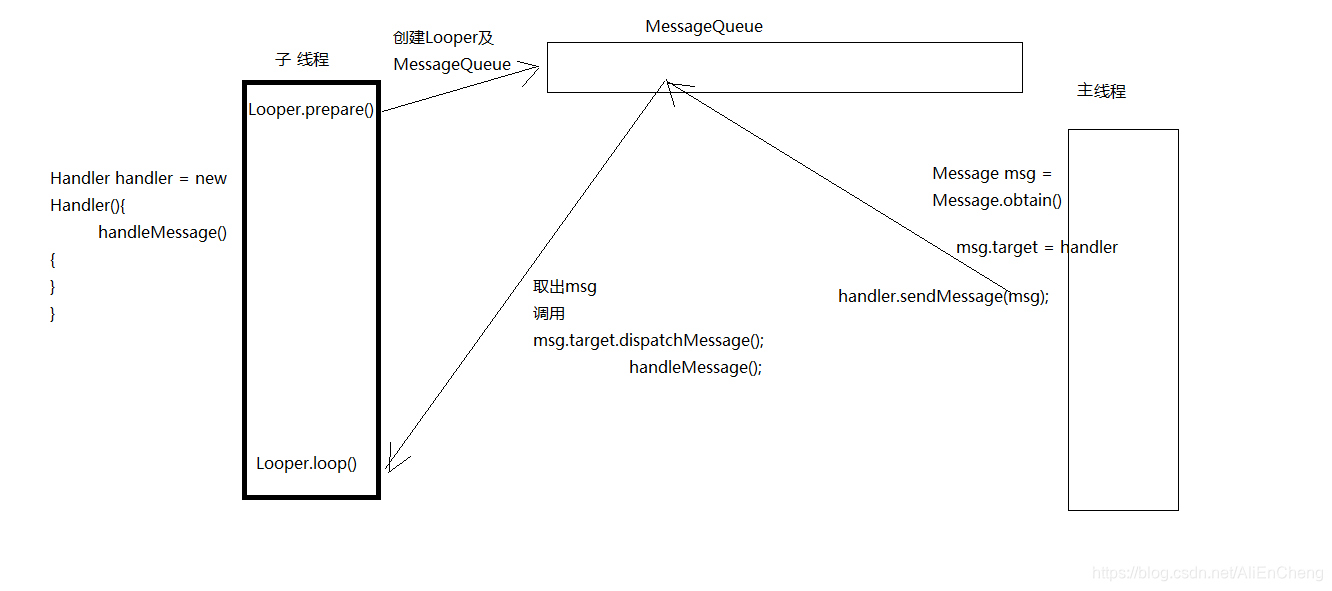
首先我们先看图
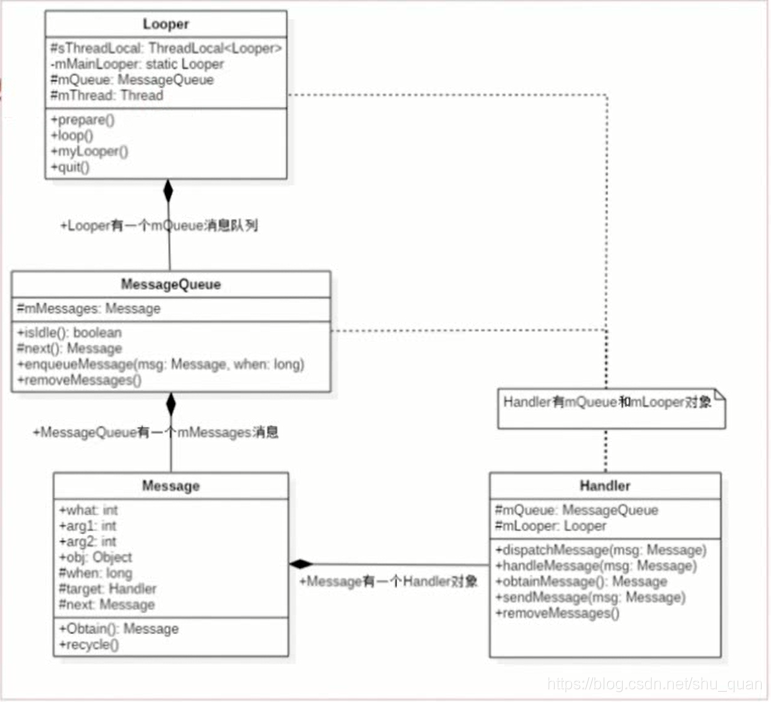
looper
每一个线程所独有的,通过loop()方法读取MessageQueue当中的消息 读到消息后,把消息发送给Handler来进行处理
messageQueue
消息队列(先进先出的方式来管理的message),在创建looper的时候就创建了MESSagerQueue,已经关联到了一起
mssage
消息对象
handler
作用1.可以发送消息
作用2.处理消息(处理looper发送过来的消息)
1.1获取looper (mLooper = Looper.myLooper()),通过looper 获取massageQueue( mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;)
/*** Use the {@link Looper} for the current thread with the specified callback interface* and set whether the handler should be asynchronous.** Handlers are synchronous by default unless this constructor is used to make* one that is strictly asynchronous.** Asynchronous messages represent interrupts or events that do not require global ordering* with respect to synchronous messages. Asynchronous messages are not subject to* the synchronization barriers introduced by {@link MessageQueue#enqueueSyncBarrier(long)}.** @param callback The callback interface in which to handle messages, or null.* @param async If true, the handler calls {@link Message#setAsynchronous(boolean)} for* each {@link Message} that is sent to it or {@link Runnable} that is posted to it.** @hide*/public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) {final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass();if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) &&(klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) {Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " +klass.getCanonicalName());}}mLooper = Looper.myLooper();if (mLooper == null) {throw new RuntimeException("Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");}mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;mCallback = callback;mAsynchronous = async;}
1.2 looper是怎么获取的呢?
// sThreadLocal.get() will return null unless you've called prepare().static final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>(); /*** Return the Looper object associated with the current thread. Returns* null if the calling thread is not associated with a Looper.*/public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() {return sThreadLocal.get();}sThreadLocal.get()作用:通过不同的线程访问同一个ThreadLocal ,不管是get方法还是set方法对所做的读写操作仅限于各自线程内部,这就是为什么handler里边通过ThreadLocal 来保存looper 这样他就可以使每一个线程有单独唯一的looper
1.3 looper作用
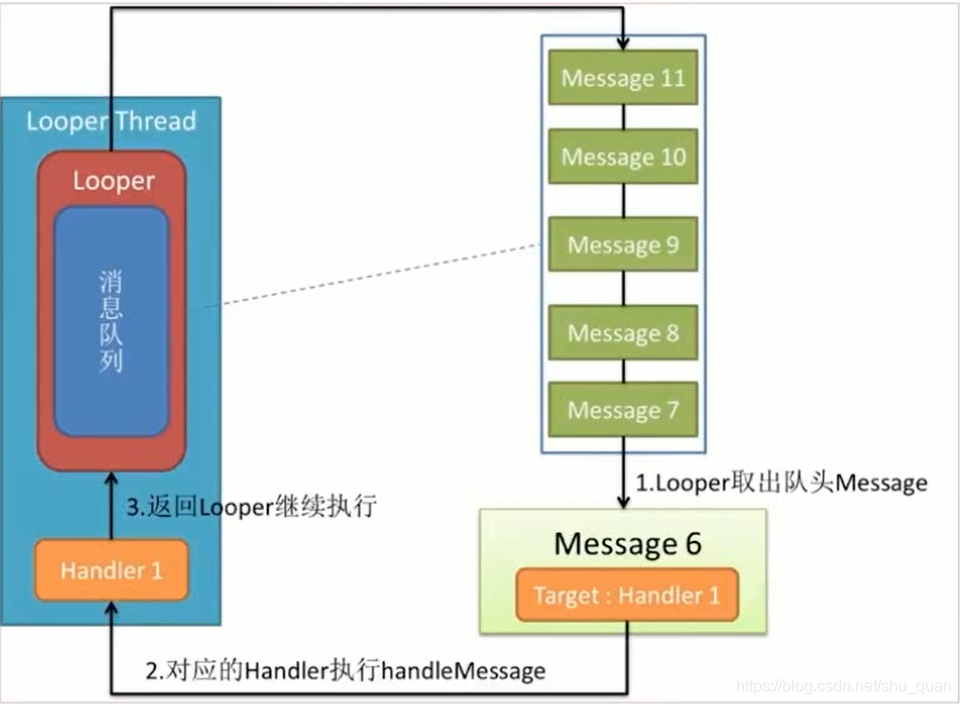
/*** Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call* {@link #quit()} to end the loop.*/public static void loop() {final Looper me = myLooper();if (me == null) {throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");}final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.Binder.clearCallingIdentity();final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();for (;;) {Message msg = queue.next(); // might blockif (msg == null) {// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.return;}// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the loggerfinal Printer logging = me.mLogging;if (logging != null) {logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);}final long slowDispatchThresholdMs = me.mSlowDispatchThresholdMs;final long traceTag = me.mTraceTag;if (traceTag != 0 && Trace.isTagEnabled(traceTag)) {Trace.traceBegin(traceTag, msg.target.getTraceName(msg));}final long start = (slowDispatchThresholdMs == 0) ? 0 : SystemClock.uptimeMillis();final long end;try {msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);end = (slowDispatchThresholdMs == 0) ? 0 : SystemClock.uptimeMillis();} finally {if (traceTag != 0) {Trace.traceEnd(traceTag);}}if (slowDispatchThresholdMs > 0) {final long time = end - start;if (time > slowDispatchThresholdMs) {Slog.w(TAG, "Dispatch took " + time + "ms on "+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", h=" +msg.target + " cb=" + msg.callback + " msg=" + msg.what);}}if (logging != null) {logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);}// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();if (ident != newIdent) {Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);}msg.recycleUnchecked();}}源码中loopr 就是创建了一个FOR的死循环,然后从消息队列中逐个的去获取消息,最后处理消息的过程
总结:looper 是通过prepare 来创建LOOPER 把他保存在ThreadLocal中 然后通过lopper.loop()开启循环来进行消息的分发
/** Initialize the current thread as a looper.* This gives you a chance to create handlers that then reference* this looper, before actually starting the loop. Be sure to call* {@link #loop()} after calling this method, and end it by calling* {@link #quit()}.*/public static void prepare() {prepare(true);}private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");}sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));}源码中调用 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); target就是一个handler 是中转器 (/*package*/ Handler target;)
handler总结: 通过handler将消息传递给了消息队列(massageQueue) 而消息队列又将消息分发给了handler 来处理,这就是handler的2个作用,一个是接收,发送消息,一个是处理消息
四,handler引起的内存泄露及解决办法
handler发送的消息在当前handler的消息队列中,如果此时activity finish掉了,那么消息队列的消息依旧会由handler进行处理,若此时handler声明为内部类(非静态内部类),我们知道内部类天然持有外部类的实例引用,这样在GC垃圾回收机制进行回收时发现这个Activity居然还有其他引用存在,因而就不会去回收这个Activity,进而导致activity泄露。
解决方案:
1.把handler设置成静态内部类,因为静态内部类不持有外部类的引用,所以使用静态的handler不会导致activity的泄露
2.onDestroy生命周期中调用 handler.removeCallbacks();,进行释放
3.handler内部类持有外部activity的弱引用