Linux可执行文件制作
背景
测试过程中,需要针对不同的Linux系统、核心服务版本进行验证,各种环境依赖的python版本以及已安装的库存在较大差异,考虑到实际测试需求以及出差现场使用的要求,需要将测试脚本打包为可执行文件,可以最大程度上减少依赖,保障测试程序的可用性和易用性。本文介绍一种利用python的pyinstaller库,将程序打包为可执行文件的方式,脱离自动化工程或复杂的环境配置。后半部分针对一些固有化的实现进行介绍,希望对大家有所帮助。
环境配置
当前使用的编程语言为python3,建议在测试服务器上安装python3,将能够更好地进行兼容。
Python3环境安装问题
可参考https://wiki.hikvision.com.cn/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=49800240
Pyinstaller安装及使用
安装
(1)方式一:直接用pip安装
pip install pyinstaller
(2)方式二:源码安装
下载pyinstaller安装包后执行以下命令手动安装:
tar -zxvf PyInstaller-3.6.tar.gz
cd PyInstaller-3.6/
python3 setup.py build
python3 setup.py install
如果输入 pyinstaller 命令可以直接使用,那就可以了。
- 问题1:输入pyinstaller命令提示 command not found
解决方式:复制pyinstaller到/usr/bin/下
cd /usr/local/python3/bin/
cp pyinstaller /usr/bin/.
- 问题2:python setup.py build报错
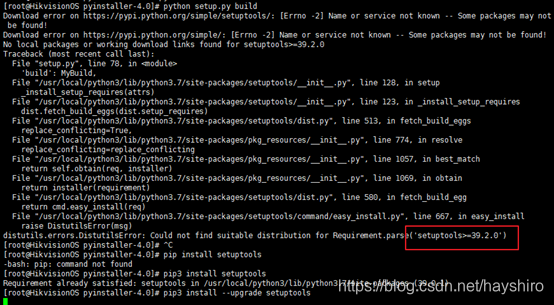
- 解决:需要升级setuotool的版本
wget https://pypi.python.org/packages/41/80/268fda78a53c2629128f8174d2952c7f902c93ebaa2062b64f27aa101b07/setuptools-38.2.3.zip#md5=0ae64455d276ff864b40aca9c06ea7c1
unzip setuptools-38.2.3.zip
cd setuptools-38.2.3
python setup.py install
- 问题3:包依赖关系处理
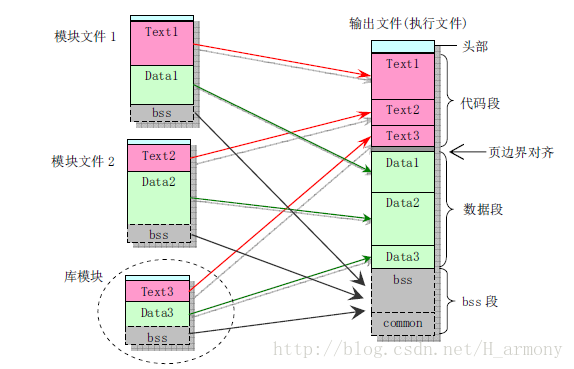
在linux下安装rpm包的时候发现,安装一个服务需要安装很多rpm包,比如安装apache,最少需要安装3-4个包,当然主包只有一个,其中还有好多依赖关系,甚至会出现循环依赖的“死锁”。为了避免包之间的依赖关系问题,可以采取同时安装所有有关rpm包的方式:
rpm -ivh xx1.rpm xx2.rpm xx3.rpm
使用
Pyinstaller使用方法:
rpm -ivh xx1.rpm xx2.rpm xx3.rpm
- 打包成功后有缺失包
安装时,wheel库通过python setup.py build & python setup.py install 安装失败。需要先将wheel文件下载到本地,然后pip install ...wheel。
资源链接:各种python wheel文件
- 包缺失
问题:python用pyinstaller打包时,打包的py文件中有import paramiko,打好包后的文件执行时提示,No module named paramiko。

解决:添加一个-p的参数。如:
pyinstaller -F xx.py -p paramiko
- Hidden-import
常用关键字及代码
(1)日志输出
当前可执行文件执行,会在控制台输出必要的结果,但对于问题的排查或记录来说还是比较麻烦,为生成便于问题定位及结果记录的日志文件,使用python中的logging模块。
logging模块主要提供了一些函数和类来支持灵活地输出日志,实现日志系统相应的功能,可以使用到应用程序和库里。主要提供了类Logger、Handler、Filter和Formatter。
日志总共定义的级别:
CRITICAL 50
ERROR 40
WARNING 30
INFO 20
DEBUG 10
NOTSET 0
使用举例:
# 以INFO级别输出一条日志。
logging.info(msg, *args, **kwargs)
#以level级别输出一条日志。
logging.log(level, msg, *args, **kwargs)
# 设置那一级别的日志不再输出。
logging.disable(lvl)
(2)解密
def _decode_password(self, encode_password):
"""
对加密的密码进行处理, jar包实现
:return: str
"""
java_path = 'jdk1.8.0_161/bin/java'
subprocess.getoutput('chmod 777 %s' % java_path)
cmd = java_path + ' -jar decode.jar'
decode_result = subprocess.Popen(cmd, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, stdin=subprocess.PIPE, shell=True)
decode_result.stdin.write(encode_password.encode('gbk') + b'\r\n')
out, err = decode_result.communicate()
try:
file_context = out + err
file_context = file_context.decode('utf8')
decode_password = str(file_context.split("密码:")[1])
decode_password = decode_password.rstrip('\r\n')
decode_password = decode_password.rstrip('\n')
logging.info("the password decoded:%s" % decode_password)
result = decode_password
except Exception as e:
logging.info("the password decoded failed")
logging.debug(e)
result = False
return result
(3)配置获取(以redis配置获取为例)
def get_conf_redis(self):
"""获取redis配置信息"""
conf_content = subprocess.getoutput("cat %s/../components/redislinux64.1/conf/config.properties\n" % self.path)
redis_conf = {}
for conf in conf_content.splitlines():
# centerdb数据库
if conf.find('cache.1.@ip=') >= 0:
redis_conf['redis_ip'] = conf.split('ip=')[-1]
elif conf.find('cache.1.port=') >= 0:
redis_conf['redis_port'] = conf.split('port=')[-1]
elif conf.find('cache.1.password=') >= 0:
cas_password = conf.split('password=')[-1]
redis_conf['redis_password'] = self._decode_password(cas_password)
return redis_conf
(4)在linux上远程其他服务器(以读取文件为例)
def ssh_machine_file_path(self, machine):
"""ssh连接,获取文件路径"""
# 实例化SSHClient
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
# 自动添加策略,保存服务器的主机名和密钥信息,如果不添加,那么不再本地know_hosts文件中记录的主机将无法连接
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
# 连接SSH服务端,以用户名和密码进行认证
ssh.connect(hostname=machine[0], port=machine[1], username=machine[2], password=machine[3])
# 执行
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('find %s/components/*/conf -type f -name "config.properties"' % self.path)
# 打印执行结果
result = stdout.read().decode('utf-8')
result = result.split('\n')
for i in result[::-1]:
if 'fail' in i or i == '':
print(i)
result.remove(i)
result.append('%s/opsMgrAgent/conf/config.properties' % self.path)
print(result)
ssh.close()
return result
(5)配置文件处理
def set_section_variables(self, section, dict_value, ini_name='use_dict_ip'):"""写入section的值 :param section: str:param dict_value: dict:param ini_name:"""if ini_name == 'use_dict_ip':try:ini_name = dict_value['bic_ip']except KeyError as e:raise Exception('dic_has_no_key:%s' % e)#config_path = os.path.join(self.service_path, 'variables.ini')config = configparser.ConfigParser()config.read(self.config_path, encoding='utf-8')if not config.has_section(section):config.add_section(section)for key, value in dict_value.items():config.set(section, key, value)config.write(open(self.config_path, "w", encoding='utf-8'))def del_section_variables(self, section):config = configparser.ConfigParser()config.read(self.config_path, encoding='utf-8')if config.has_section(section):config.remove_section(section)config.write(open(self.config_path, "w", encoding='utf-8'))
环境分享
pyinstaller –F xx.py