基本概念
这里介绍一种用于n维图像数据的边界优化和区域分割的分割技术。该分割算法来自论文:Interactive Graph Cuts for Optimal Boundary & Region Segmentation of Objects in N-D Images。该方法通过交互式的或自动的定位一个或多个代表“物体”的点以及一个或多个代表“背景”的点来进行初始化—这些点被称作种子(Seed并被用于分割的硬约束(hard constraints)。另外的软约束(soft constraints)反映了边界和/或区域信息。基本原理如下图:
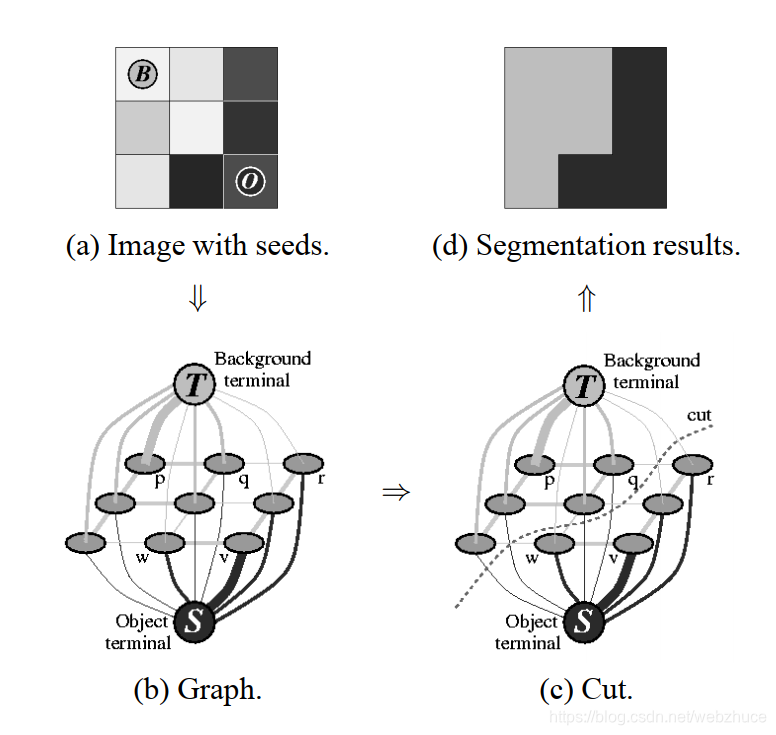
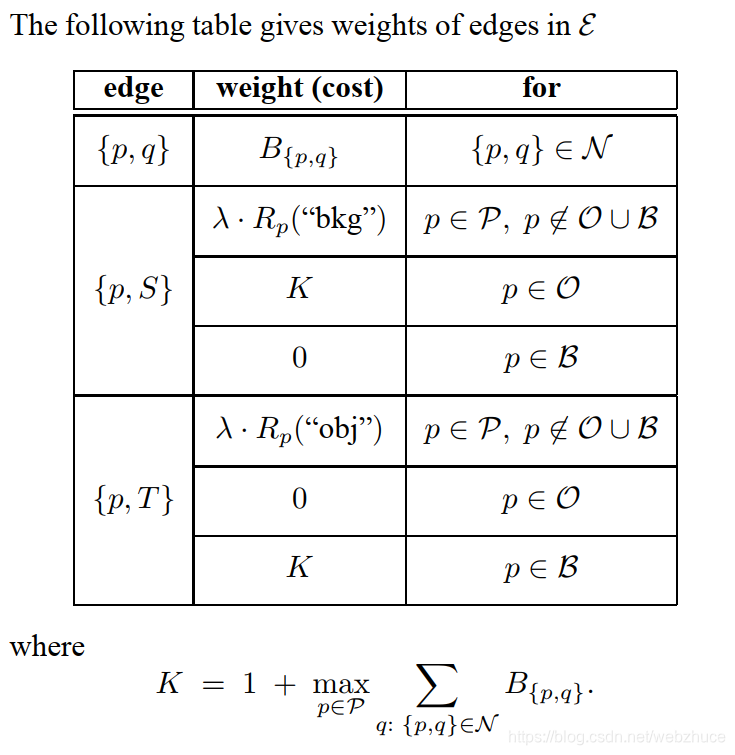
图弧的权重计算如下。
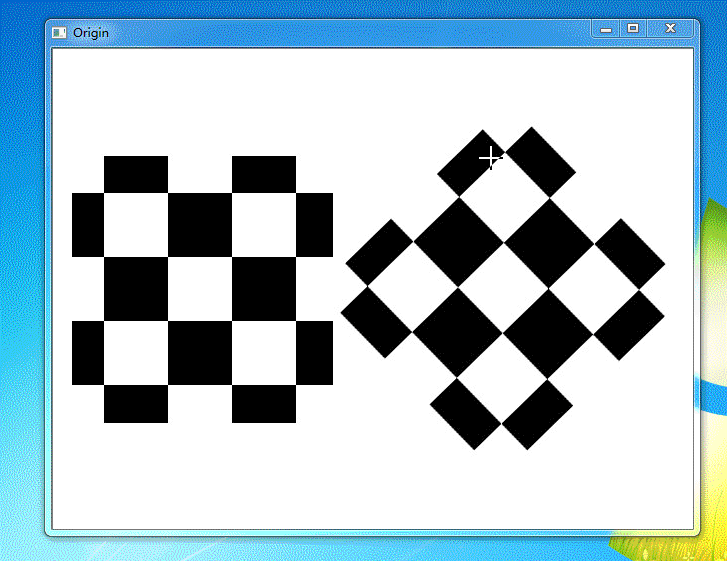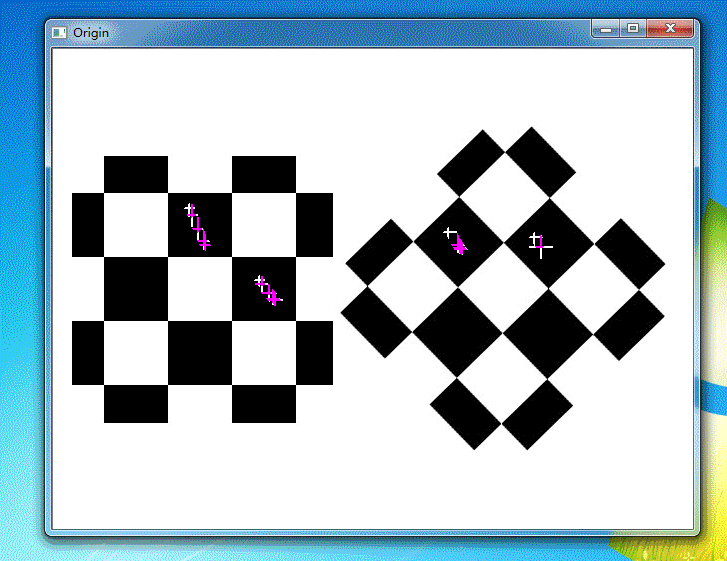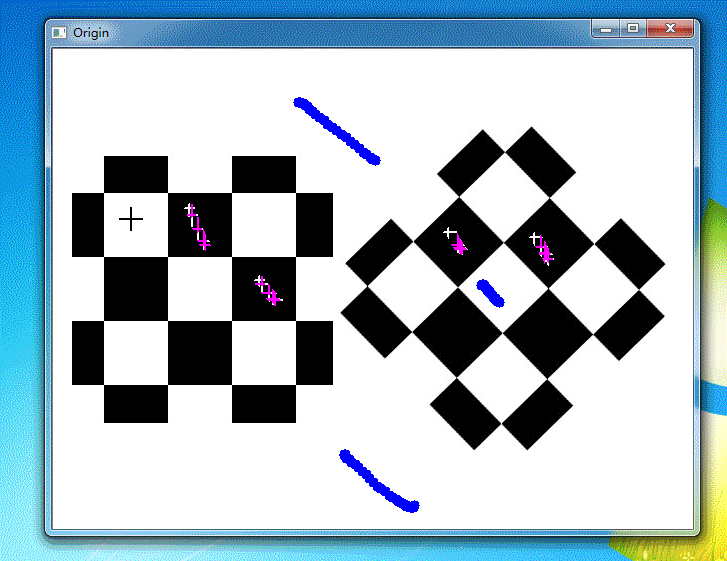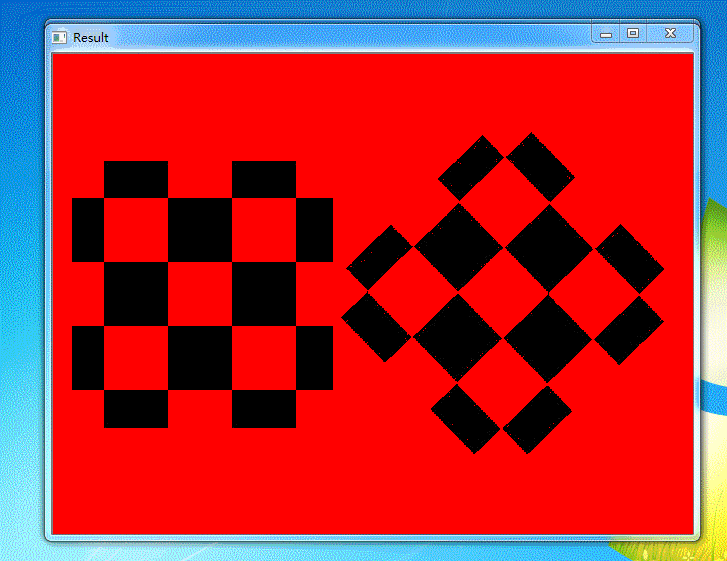
示例演示
我们利用OpenCV的GCGraph(实现最大流最小割)实现了Graph Cut算法。下面是核心算法的代码,完整的工程代码链接。
cv::Mat GraphCut::runInitially(const std::vector<cv::Point> &objectseeds, const std::vector<cv::Point> &backgroundseeds)
{Mat image; // copy of image_ for computingif (image_.channels() == 3){cvtColor(image_, image, cv::COLOR_RGB2GRAY);}else{image_.copyTo(image);}//update mask and compute intensity distributionsuchar objecthist[256] = { 0 };int objectcount = 0;uchar backgroundhist[256] = { 0 };int backgroundcount = 0;uchar pixel = 0;for (auto &p : objectseeds){pixel = image.at<uchar>(p);++objecthist[pixel];++objectcount;mask_.at<uchar>(p) = OBJECT;}for (auto &p : backgroundseeds){pixel = image.at<uchar>(p);++backgroundhist[pixel];++backgroundcount;mask_.at<uchar>(p) = BACKGROUND;}//compute weight and create graphint vtxCount = image.cols * image.rows,edgeCount = 2 * (4 * image.cols * image.rows - 3 * (image.cols + image.rows) + 2);graph_.create(vtxCount, edgeCount);std::vector<cv::Point> neighbors;neighbors.push_back({ -1, 0 }); //leftneighbors.push_back({ 1, 0 }); //rightneighbors.push_back({ 0, -1 }); //upneighbors.push_back({ 0, 1 }); //downneighbors.push_back({ -1, -1 }); //left-upneighbors.push_back({ -1, 1 }); //left-downneighbors.push_back({ 1, -1 }); //right-upneighbors.push_back({ 1, 1 }); //right-downPoint p, neighborp;//compute neighbor weights(B{p,q}) and Kstd::vector<std::vector<double>> neighborweights;neighborweights.reserve(vtxCount);double maxsum = 0.0, sum = 0.0, weight = 0;uchar neighborpixel = 0;for (p.y = 0; p.y < image.rows; p.y++){for (p.x = 0; p.x < image.cols; p.x++){pixel = image.at<uchar>(p);std::vector<double> weights;sum = 0.0;for (auto &offset : neighbors){neighborp.x = p.x + offset.x;neighborp.y = p.y + offset.y;if (neighborp.x < 0 || neighborp.x >= image.cols ||neighborp.y < 0 || neighborp.y >= image.rows){weights.push_back(0.0);continue;}neighborpixel = image.at<uchar>(neighborp);weight = -1.0 * std::pow((pixel - neighborpixel), 2) / (2.0 * std::pow(sigma_, 2));weight = exp(weight) / std::sqrt(std::pow(offset.x, 2) + std::pow(offset.y, 2));weights.push_back(weight);sum += weight; }neighborweights.push_back(weights);if (maxsum < sum)maxsum = sum;}}double k = 1 + maxsum;neighbors.clear();neighbors.push_back({ -1, 0 }); //left//neighbors.push_back({ 1, 0 }); //rightneighbors.push_back({ 0, -1 }); //up//neighbors.push_back({ 0, 1 }); //downneighbors.push_back({ -1, -1 }); //left-up//neighbors.push_back({ -1, 1 }); //left-downneighbors.push_back({ 1, -1 }); //right-up//neighbors.push_back({ 1, 1 }); //right-downfor (p.y= 0; p.y < image.rows; p.y++){for (p.x = 0; p.x < image.cols; p.x++){// add nodeint vtxIdx = graph_.addVtx();pixel = image.at<uchar>(p);// set t-weightsdouble fromSource, toSink;if (mask_.at<uchar>(p) == NO_INDICATING){//Pr(0, 1)fromSource = -log(std::max((int)backgroundhist[pixel], 1) / (double)backgroundcount) * lambda_;toSink = -log(std::max((int)objecthist[pixel], 1) / (double)objectcount) * lambda_;//std::cout << fromSource << " " << toSink << std::endl;}else if (mask_.at<uchar>(p) == BACKGROUND){fromSource = 0;toSink = k;}else // OBJECT{fromSource = k;toSink = 0;}graph_.addTermWeights(vtxIdx, fromSource, toSink);// set n-weightsfor (int i = 0;i < neighbors.size(); i++){auto &offset = neighbors[i];neighborp.x = p.x + offset.x;neighborp.y = p.y + offset.y;if (neighborp.x < 0 || neighborp.x >= image.cols ||neighborp.y < 0 || neighborp.y >= image.rows)continue;weight = neighborweights[p.x + p.y * image.cols][i * 2];graph_.addEdges(vtxIdx, vtxIdx + offset.x + offset.y * image.cols, weight, weight);} }}//resultMat result;image_.copyTo(result);graph_.maxFlow();for (p.y = 0; p.y < result.rows; p.y++){for (p.x = 0; p.x < result.cols; p.x++){if (!graph_.inSourceSegment(p.y * image.cols + p.x /*vertex index*/)){if(result.channels() == 1)result.at<uchar>(p) = 0;else{result.at<cv::Vec3b>(p)[0] = 0;result.at<cv::Vec3b>(p)[1] = 0;result.at<cv::Vec3b>(p)[2] = 255;}} }}return result;
}
运行结果
参考资料
- 图像处理、分析与机器视觉[M]