1、环境
anaconda环境安装配置
2、工具
安装labelme工具
3、安装软件
3.1、打开anaconda控制台

3.2、创建虚拟环境
conda create -n labelme python=3.7
3.3、激活环境
conda activate labelme
3.4、下载labelme
pip install labelme
3.5、输入labelme打开软件
以后打开跳过3.2和3.4打开即可
labelme
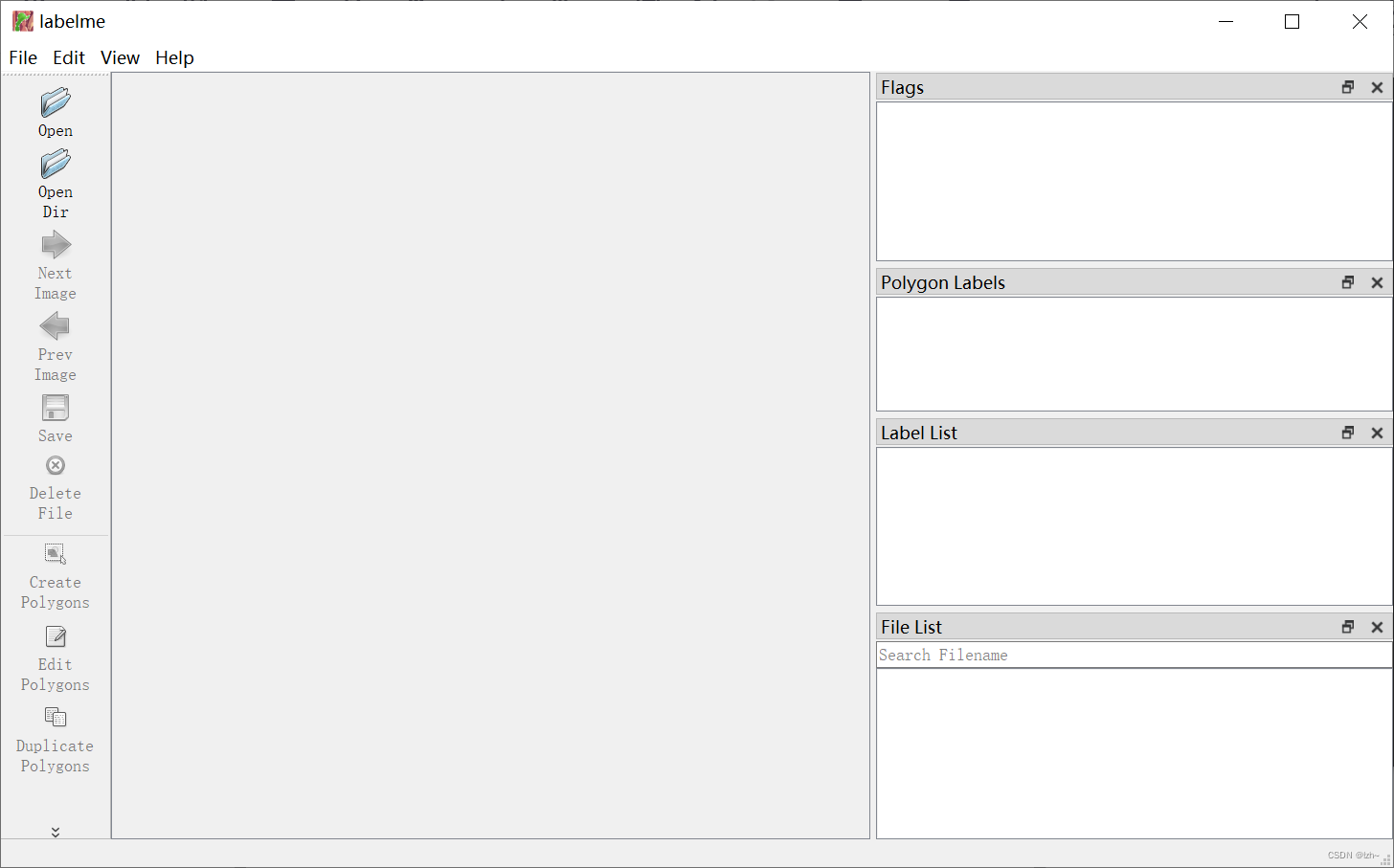
4、制作labelme数据集
4.1、打开文件夹
存有多张图片的文件夹
图片为统一格式(比如都为.png或者.jpg)
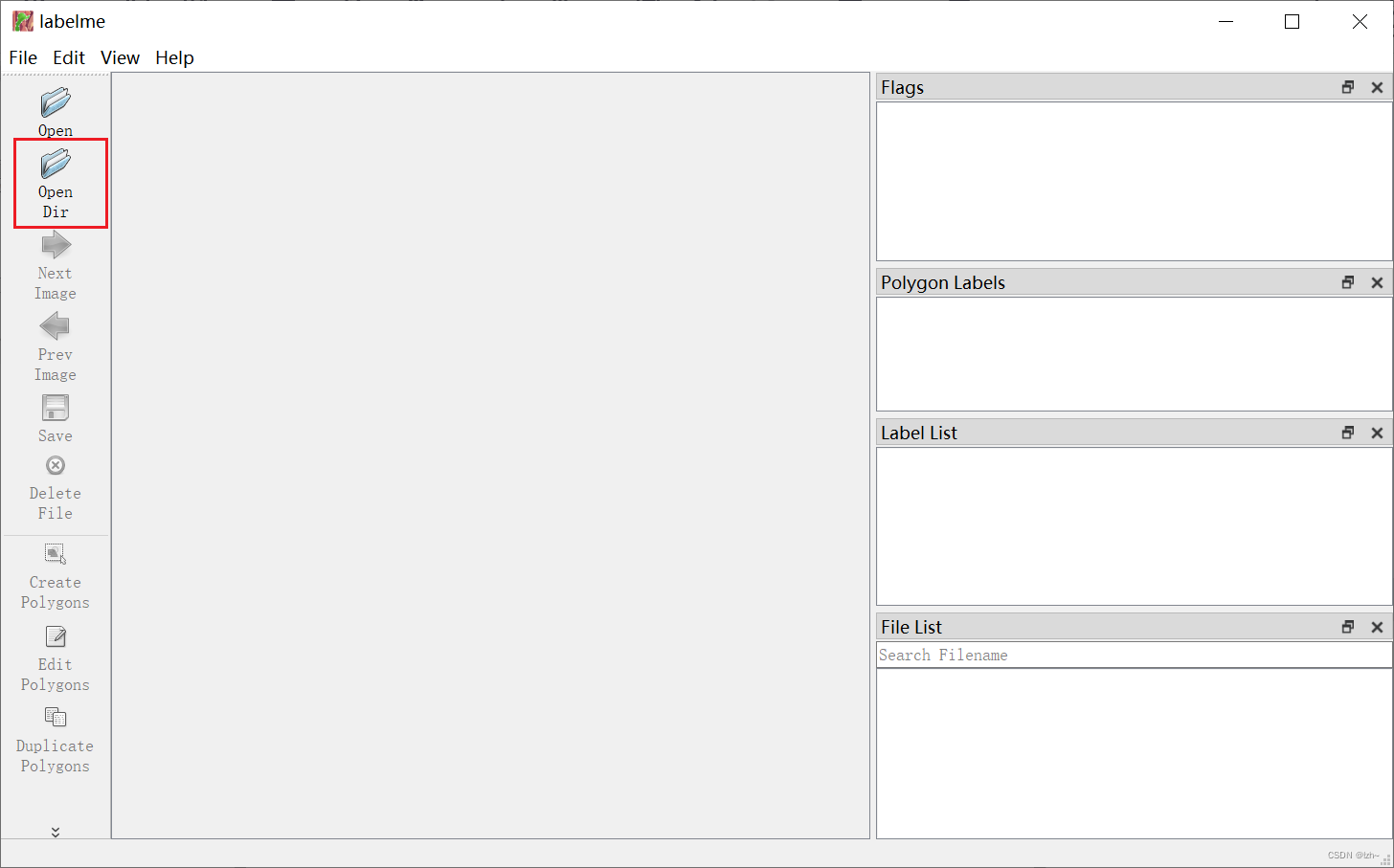
4.2、创建矩形框
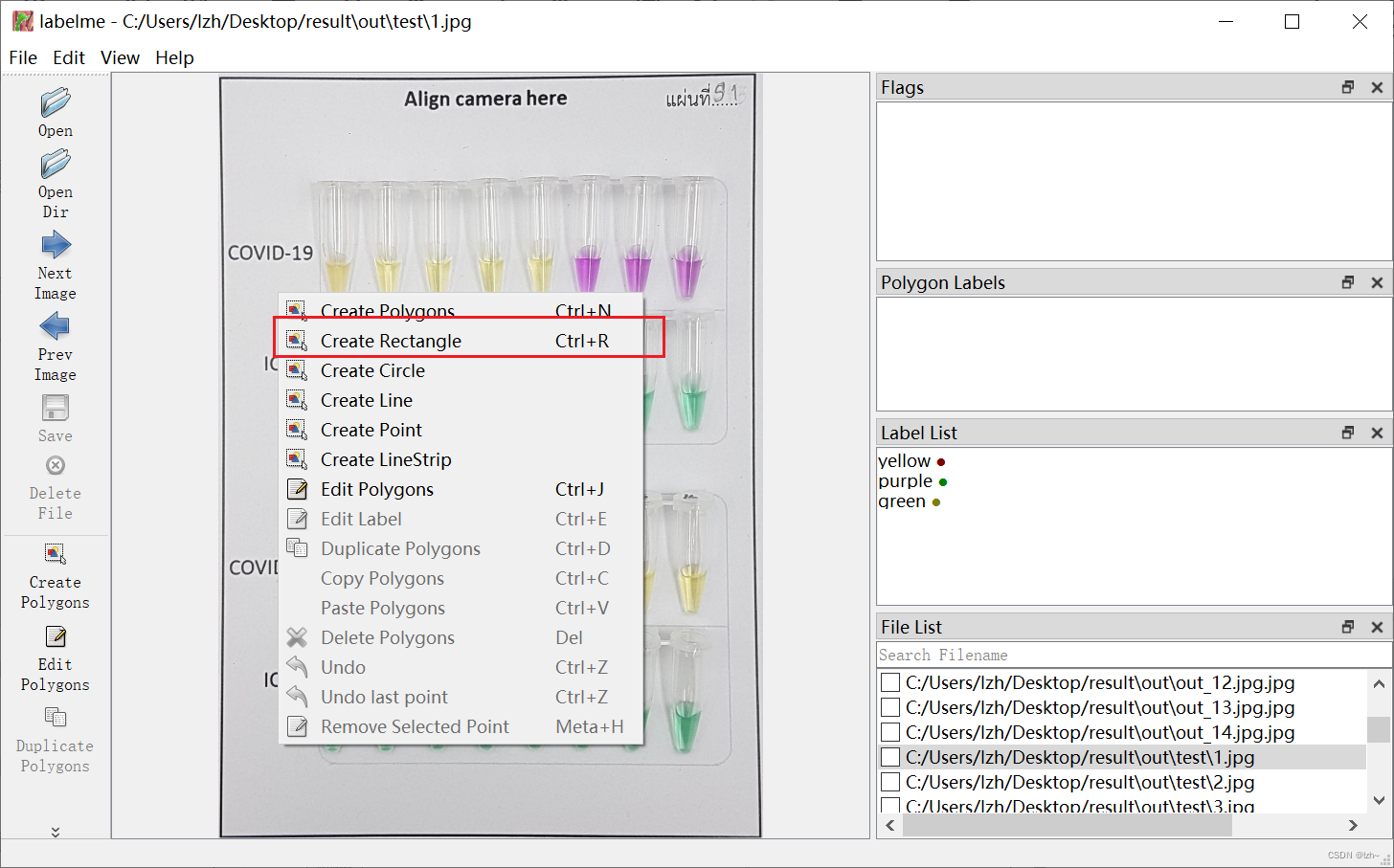
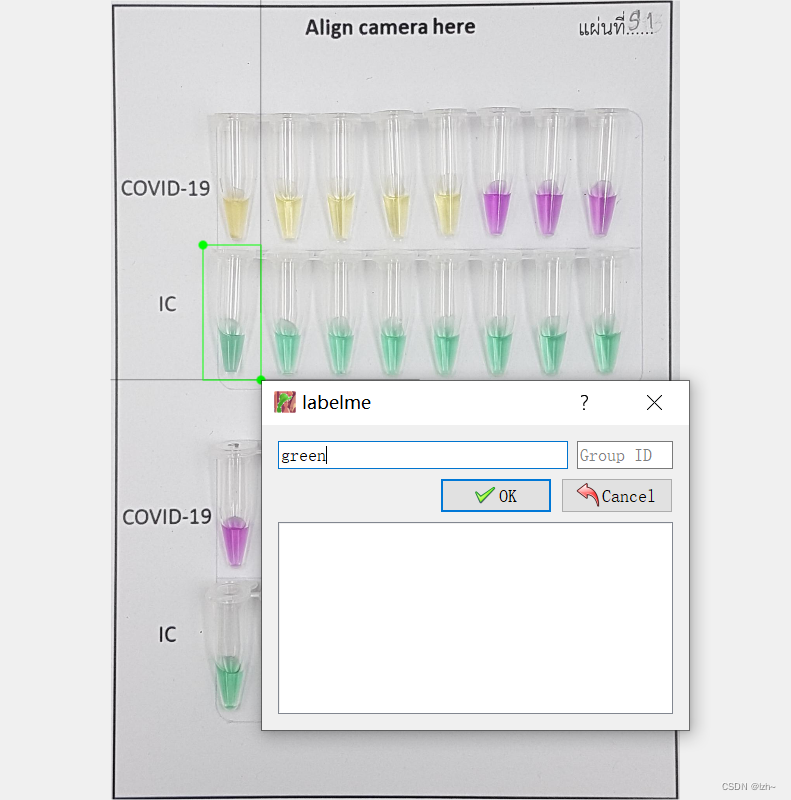
4.3、label名称
为框选住的类别起一个名字
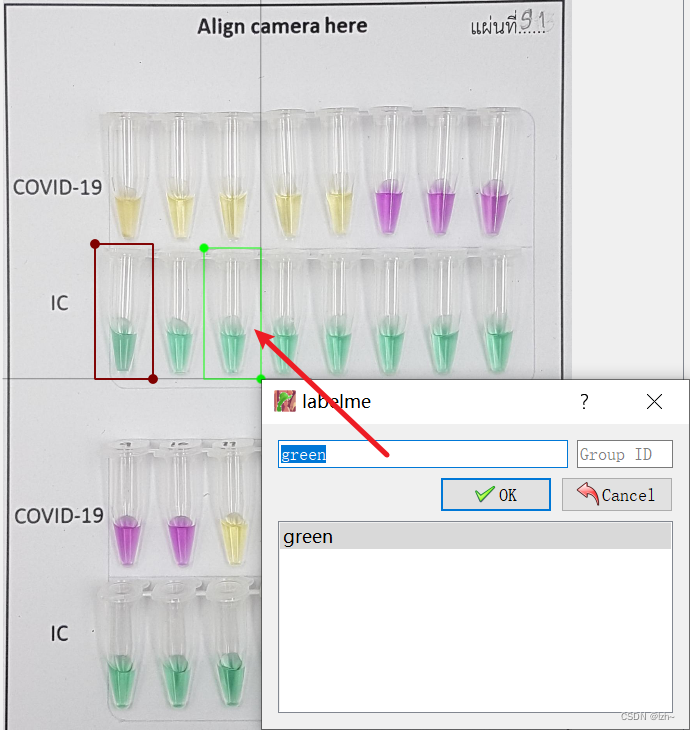
再次框选的时候会保存已经存在的label
4.4、保存
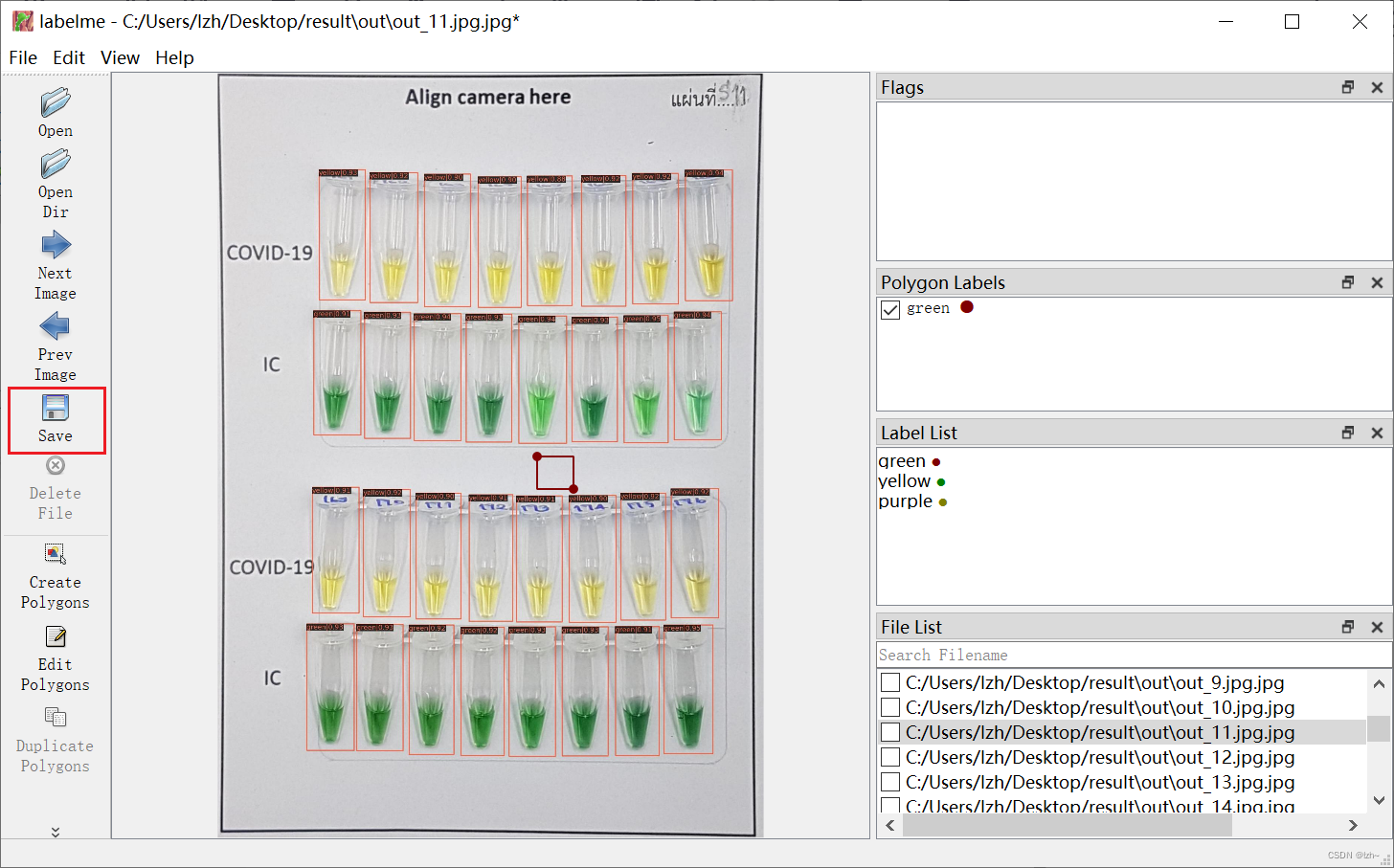
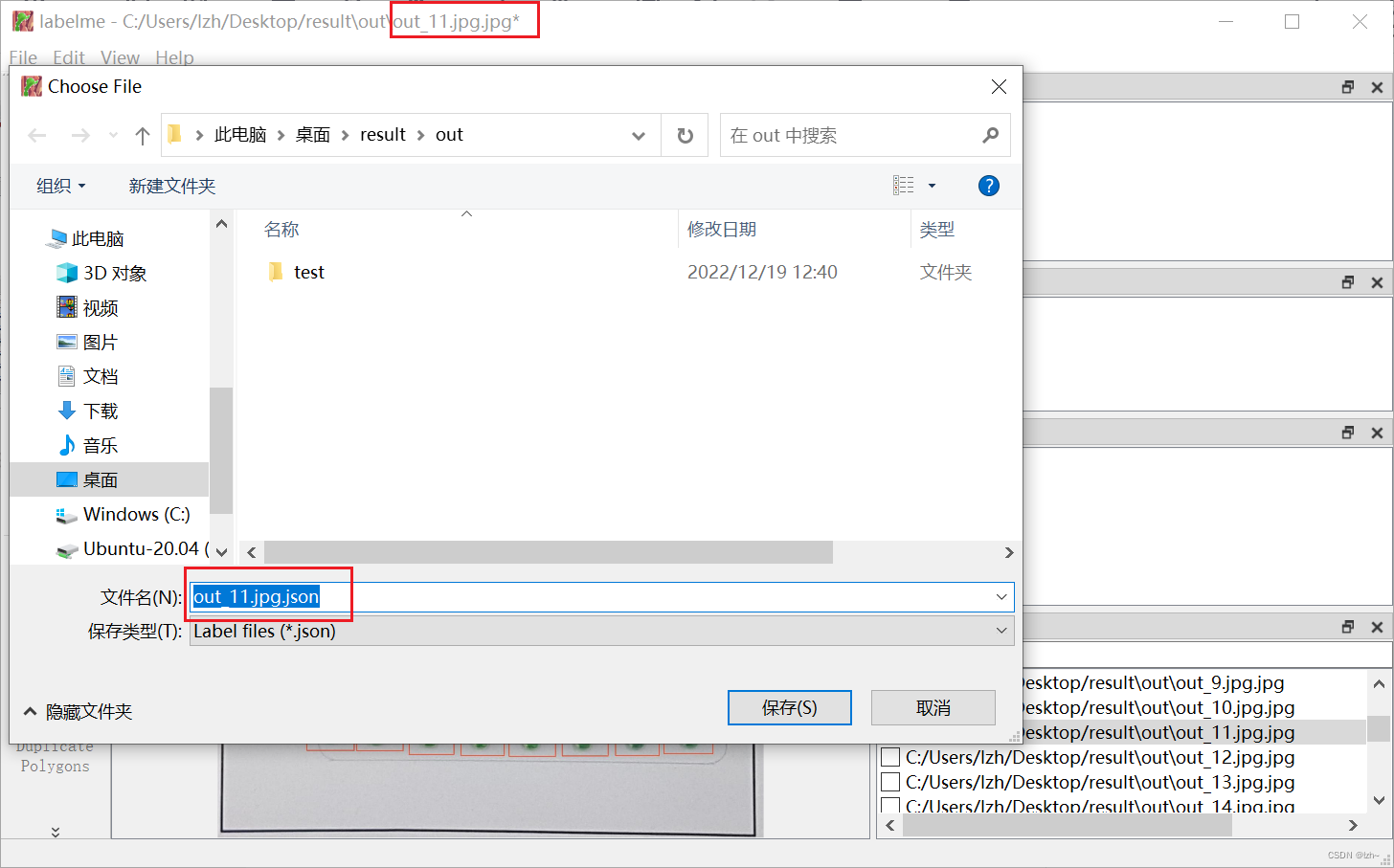
保存名字和图片在同一个路径,同样的名字
4.5、结果
点击下一个继续标注label
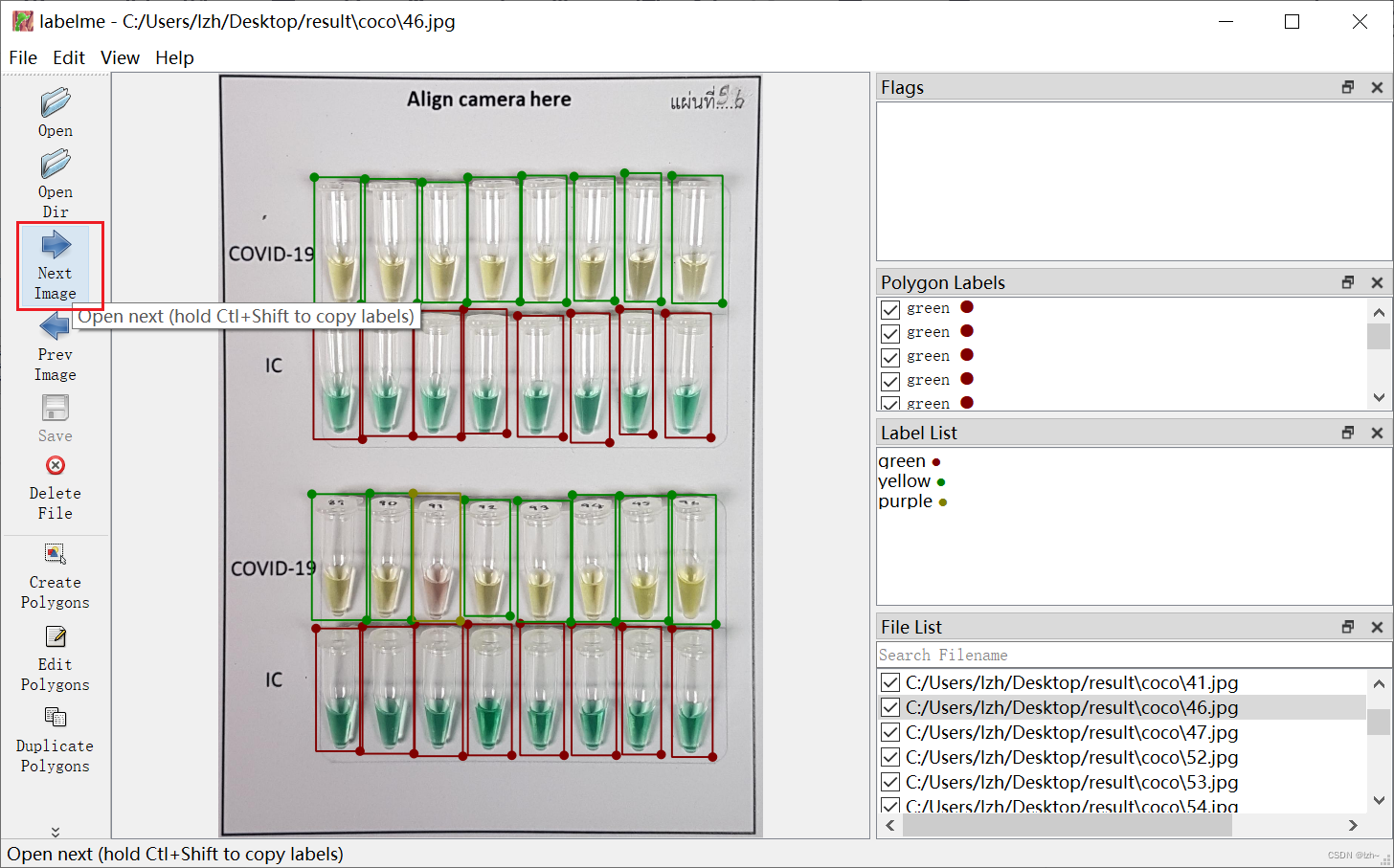
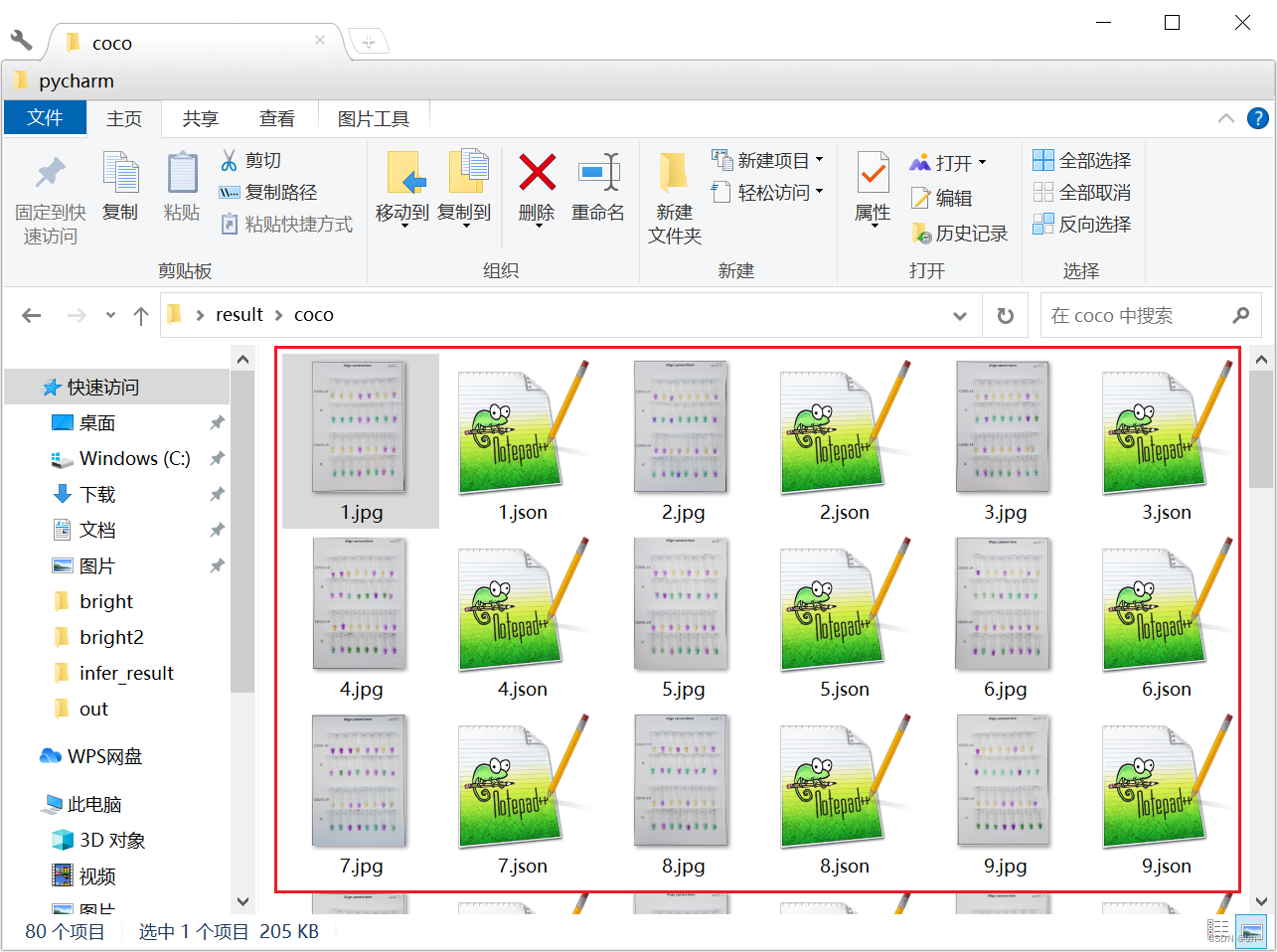
把需要的图片全部做标签保存
5、转换coco数据
5.1、创建目录
- dataset中放第4步制作好的数据集
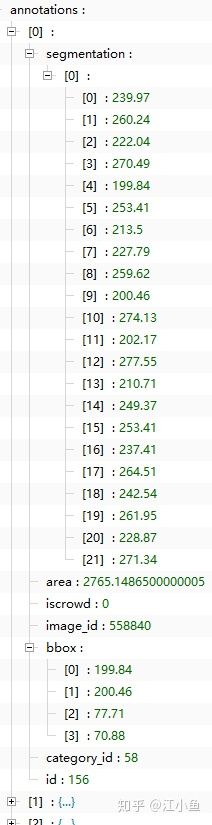
├─data-labelme │ ├─coco │ │ ├─annotations │ │ ├─train2017 │ │ └─val2017 │ ├─dataset ├─json2coco.py
5.2、运行文件
-
然后执行
json2coco.py文件
将代码中标有修改的注释下面代码进行替换import os import json import numpy as np import glob import shutil import cv2 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitnp.random.seed(41)# 修改1->改成自己的类别 classname_to_id = {"green": 0, "purple": 1,"yellow": 2 }class Lableme2CoCo:def __init__(self):self.images = []self.annotations = []self.categories = []self.img_id = 0self.ann_id = 0def save_coco_json(self, instance, save_path):json.dump(instance, open(save_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8'), ensure_ascii=False, indent=1) # indent=2 更加美观显示# 由json文件构建COCOdef to_coco(self, json_path_list):self._init_categories()for json_path in json_path_list:obj = self.read_jsonfile(json_path)self.images.append(self._image(obj, json_path))shapes = obj['shapes']for shape in shapes:annotation = self._annotation(shape)self.annotations.append(annotation)self.ann_id += 1self.img_id += 1instance = {}instance['info'] = 'spytensor created'instance['license'] = ['license']instance['images'] = self.imagesinstance['annotations'] = self.annotationsinstance['categories'] = self.categoriesreturn instance# 构建类别def _init_categories(self):for k, v in classname_to_id.items():category = {}category['id'] = vcategory['name'] = kself.categories.append(category)# 构建COCO的image字段def _image(self, obj, path):image = {}from labelme import utilsimg_x = utils.img_b64_to_arr(obj['imageData'])h, w = img_x.shape[:-1]image['height'] = himage['width'] = wimage['id'] = self.img_idimage['file_name'] = os.path.basename(path).replace(".json", ".jpg")return image# 构建COCO的annotation字段def _annotation(self, shape):# print('shape', shape)label = shape['label']points = shape['points']annotation = {}annotation['id'] = self.ann_idannotation['image_id'] = self.img_idannotation['category_id'] = int(classname_to_id[label])annotation['segmentation'] = [np.asarray(points).flatten().tolist()]annotation['bbox'] = self._get_box(points)annotation['iscrowd'] = 0annotation['area'] = 1.0return annotation# 读取json文件,返回一个json对象def read_jsonfile(self, path):with open(path, "r", encoding='utf-8') as f:return json.load(f)# COCO的格式: [x1,y1,w,h] 对应COCO的bbox格式def _get_box(self, points):min_x = min_y = np.infmax_x = max_y = 0for x, y in points:min_x = min(min_x, x)min_y = min(min_y, y)max_x = max(max_x, x)max_y = max(max_y, y)return [min_x, min_y, max_x - min_x, max_y - min_y]# 训练过程中,如果遇到Index put requires the source and destination dtypes match, got Long for the destination and Int for the source # 参考:https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/issues/6706if __name__ == '__main__':labelme_path = "./data-labelme/dataset"saved_coco_path = "./data-labelme/"print('reading...')# 创建文件if not os.path.exists("%scoco/annotations/" % saved_coco_path):os.makedirs("%scoco/annotations/" % saved_coco_path)if not os.path.exists("%scoco/train2017/" % saved_coco_path):os.makedirs("%scoco/train2017" % saved_coco_path)if not os.path.exists("%scoco/val2017/" % saved_coco_path):os.makedirs("%scoco/val2017" % saved_coco_path)# 获取images目录下所有的joson文件列表print(labelme_path + "/*.json")json_list_path = glob.glob(labelme_path + "/*.json")print('json_list_path: ', len(json_list_path))# 修改2训练集和测试集的比例# 数据划分,这里没有区分val2017和tran2017目录,所有图片都放在images目录下train_path, val_path = train_test_split(json_list_path, test_size=0.1, train_size=0.9)print("train_n:", len(train_path), 'val_n:', len(val_path))# 把训练集转化为COCO的json格式l2c_train = Lableme2CoCo()train_instance = l2c_train.to_coco(train_path)l2c_train.save_coco_json(train_instance, '%scoco/annotations/instances_train2017.json' % saved_coco_path)for file in train_path:# 修改3 换成自己图片的后缀名img_name = file.replace('json', 'jpg')temp_img = cv2.imread(img_name)try:cv2.imwrite("{}coco/train2017/{}".format(saved_coco_path, img_name.split('\\')[-1]), temp_img)except Exception as e:print(e)print('Wrong Image:', img_name )continueprint(img_name + '-->', img_name)for file in val_path:# 修改4 换成自己图片的后缀名img_name = file.replace('json', 'jpg')temp_img = cv2.imread(img_name)try:cv2.imwrite("{}coco/val2017/{}".format(saved_coco_path, img_name.split('\\')[-1]), temp_img)except Exception as e:print(e)print('Wrong Image:', img_name)continueprint(img_name + '-->', img_name)# 把验证集转化为COCO的json格式l2c_val = Lableme2CoCo()val_instance = l2c_val.to_coco(val_path)l2c_val.save_coco_json(val_instance, '%scoco/annotations/instances_val2017.json' % saved_coco_path)
5.3、运行结果
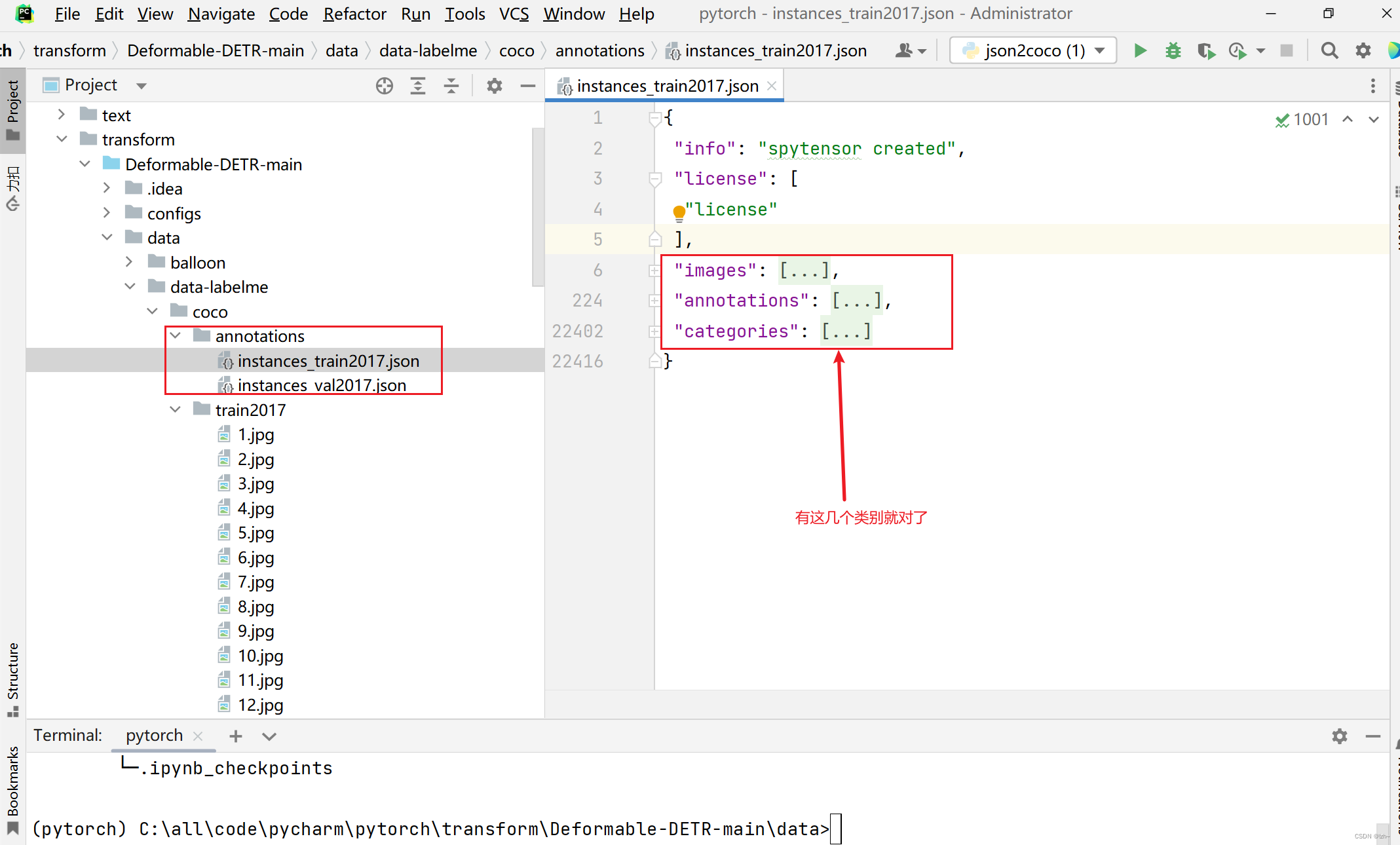
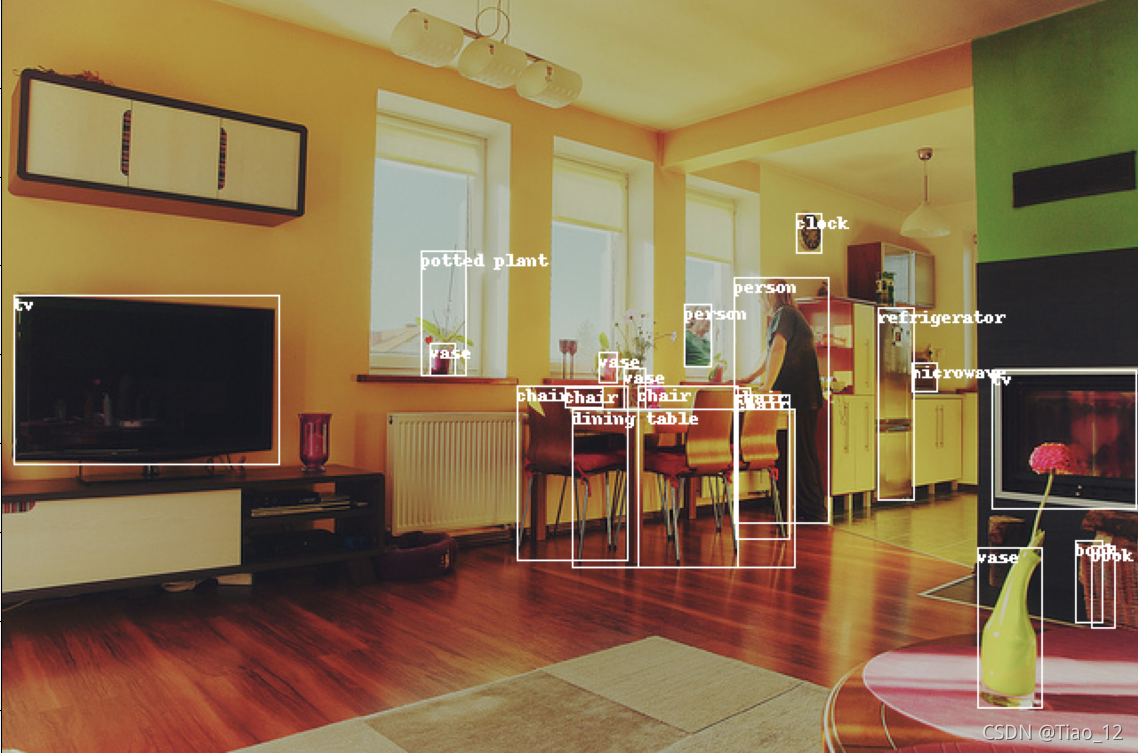
制作数据集完毕,可以进行自己项目的训练了