目录
一:静态存储和动态存储
二:存储类别
三:malloc函数
四: free函数
五:内存初始化函数memset
六:calloc函数
七:realloc函数
八:线性表
九:链式存储结构
十:线性表的基本操作
十一:链表的创建和链接
十二:链表的遍历
十三:链表的插入
十四:链表的删除
十五:链表实际应用
一:静态存储和动态存储
变量从变量值存在的时间(即生存期)角度分:静态存储方式和动态存储方式
静态:在编译时确定了固定的内存地址与内存大小,如:函数里的static局部变量、全局变量等
动态:由程序控制,运行时主动性的向系统申请所需大小的内存段,并且每次分配到的内存地址不固定
在动态存储区存放一下数据:
1、函数形式参数
2、自动变量(未加static声明)
3、函数调用时的现场保护和返回地址
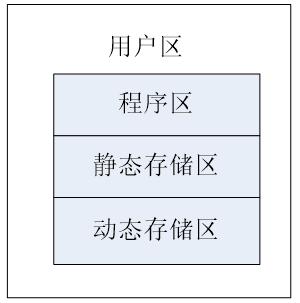
二:存储类别

三:malloc函数
malloc函数 如下

malloc函数示例

四: free函数
free函数 如下

free函数示例

五:内存初始化函数memset
memset函数 如下

memset函数示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main( )
{ char buffer[] = "This is a test of the memset function"; printf( "Before: %s\n", buffer ); memset( buffer, 0, 4 ); printf( "After: %s\n", buffer ); return 0;
}
六:calloc函数
calloc函数 如下

calloc函数示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void main() {float *calloc1;int i;calloc1 = (float *) calloc(3, sizeof(float));if(calloc1!=NULL) {for(i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++)printf("\ncalloc1[%d]holds%05.5f", i,calloc1[i]);free(calloc1);}else { printf("Not enough memory \n"); }
}七:realloc函数
realloc函数 如下

realloc函数示例
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){int *ptr , i;ptr = (int *)calloc(5, sizeof(int));if(ptr ==NULL) return 1;*ptr = 1;*(ptr+1) = 2;ptr[2] = 4;ptr[3] = 8;ptr[4] = 16;ptr = (int *)realloc(ptr,7*sizeof(int));if(ptr == NULL) return 1;ptr[5] = 32; ptr[6] = 64;for(i = 0;i < 7;i++){printf(“ptr[%d]:%d\n", i, ptr[i]);}realloc(ptr,0); /* free(ptr);*/return 0;
}
八:线性表
线性表 如下

顺序存储结构以及特点

九:链式存储结构
链式存储结构 如下

单链表 如下

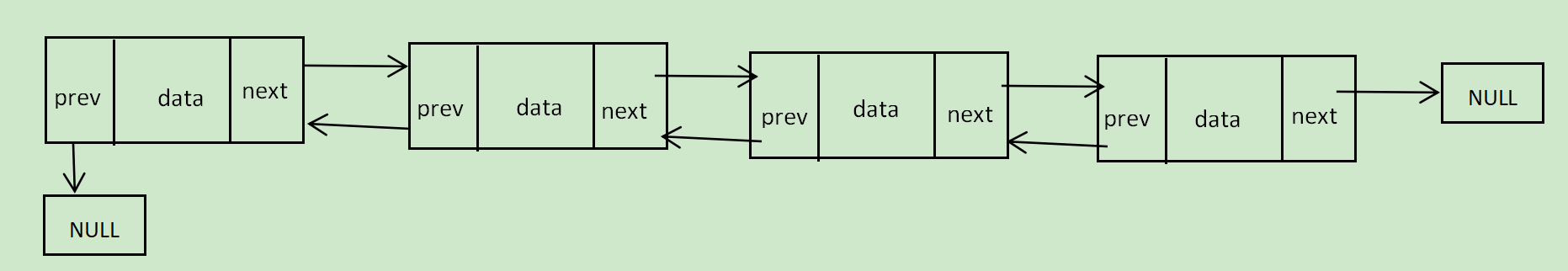
单链表状态图 如下

单链表节点数据结构定义 如下

单链表初始化 如下

循环单链表状态图 如下

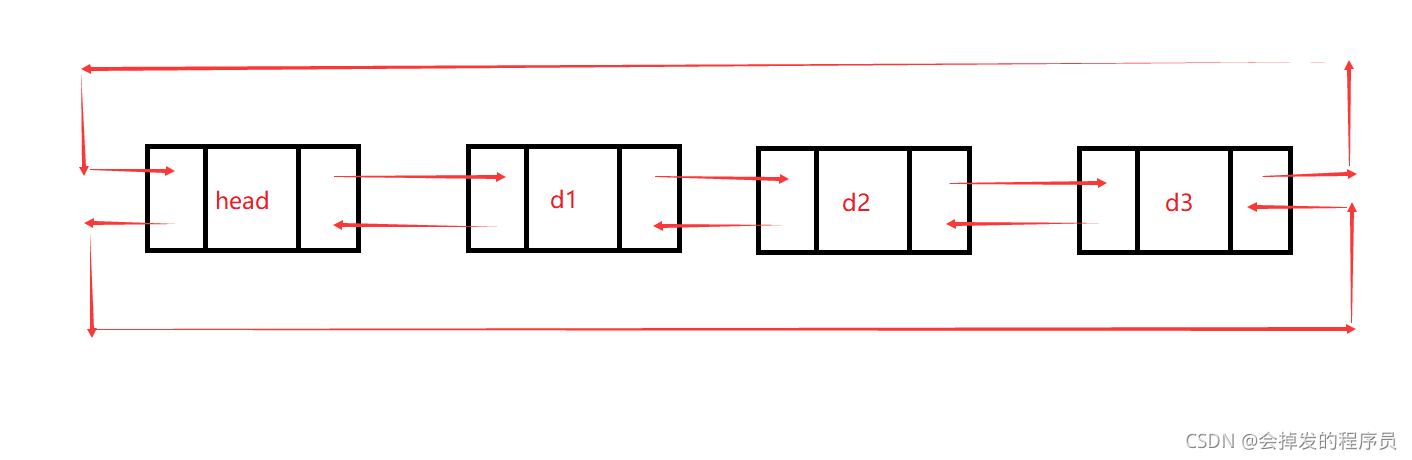
双向链表状态图 如下

双向循环链表状态图 如下

十:线性表的基本操作
初始化
插入
删除
遍历(即访问每一个元素,如打印所有信息)
查找
排序
十一:链表的创建和链接
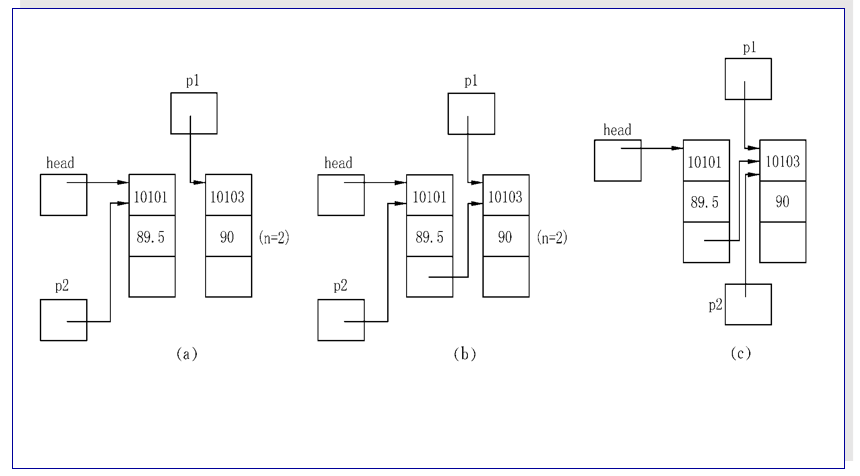


十二:链表的遍历
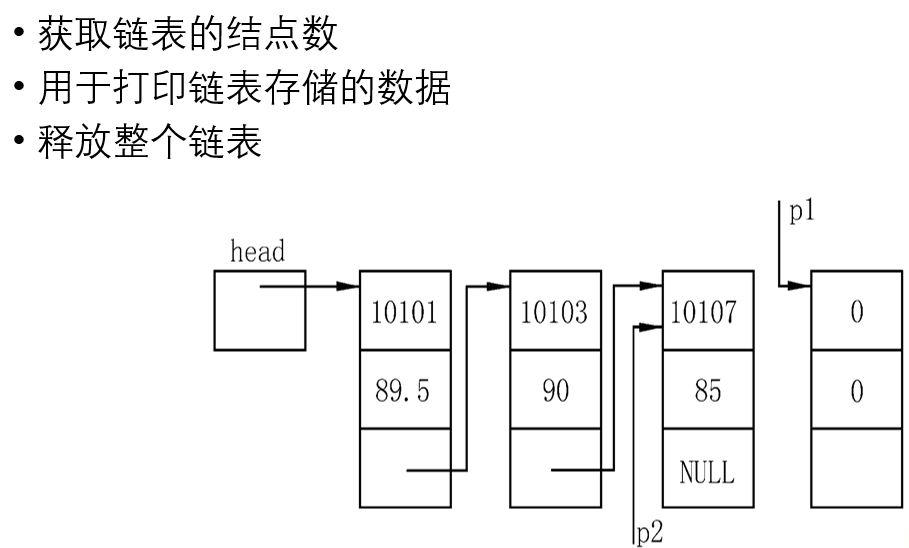
十三:链表的插入
1.插入链表头和链表尾

2.插入中间的位置

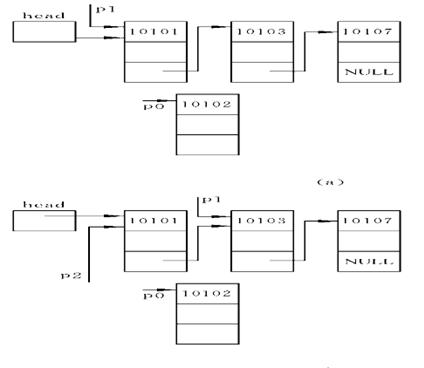
十四:链表的删除

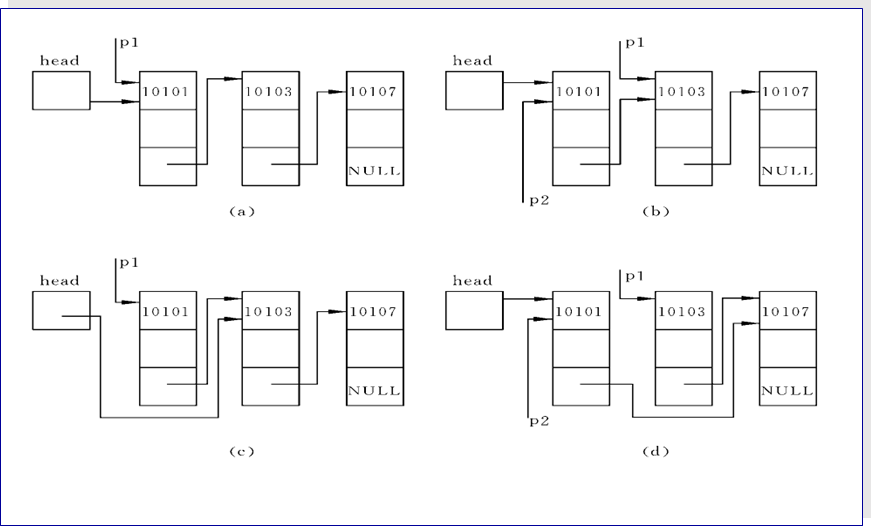
十五:链表实际应用
普通链表设计

通用链表设计

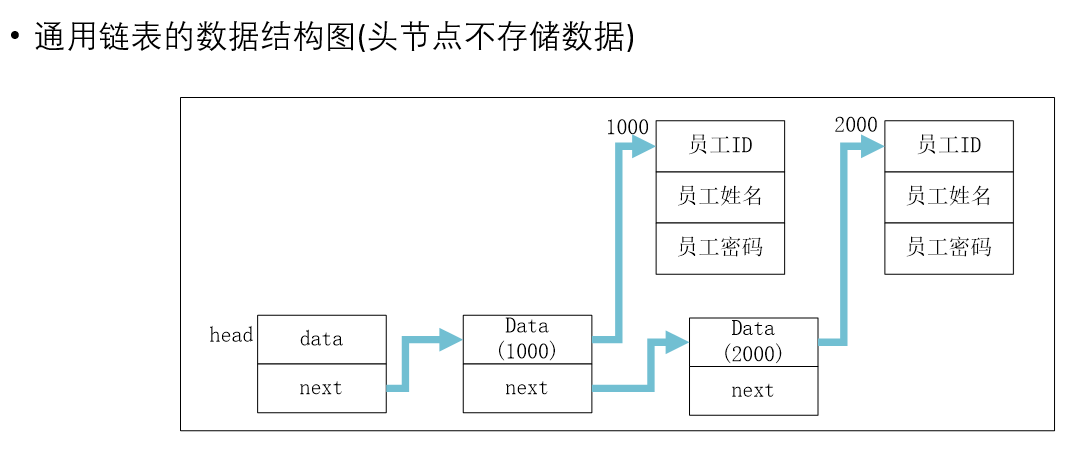
通用链表基本操作
初始化链表void *List_Init(void *data)
添加链表节点void List_Add(struct list *head,void *data)
获取链表节点个数int List_Count(struct list *head)
获取链表某个节点(返回链表节点的data)void *List_GetNode(struct list *head,int Index)
Index---链表节点编号,head---链表头节点
删除链表的某个节点int List_Del(struct list *head,int Index)
释放链表void List_Free(struct list *head)
通用链表初始化
void *List_Init(void *data)
{struct list * head;head = (struct list *)malloc(sizeof(struct list));head->data=data;head->next=NULL;return head;
}
通用链表添加节点到尾部
void List_Add(struct list *head,void *data)
{struct list *pNode,p1=head;pNode=(struct list *)malloc(sizeof(struct list ));while(p1->next != NULL ){ p1=p1->next; } //遍历链表,找到最末尾的节点p1->next=pNode;pNode->data=data;pNode->next=NULL;
}
通用链表获取链表节点个数
int LIST_Count(struct list * head)
{struct list * p1;int nCount = 0;p1=head->next;while(p1 != NULL){nCount++;p1=p1->next;}return nCount;
}
通用链表释放链表
void *List_Free(struct list *head)
{struct list *ptr=head;while(ptr!=NULL){ptr=ptr->next;free(head->data);//先释放数据存储的内存空间free(head);//再释放链表节点的内存空间head=ptr;}return head;
}
通用链表示例
void test()
{struct list *head;struct staff *people1,*people2;//初始化链表head=List_Init(NULL);//头节点不存储数据,参数为NULLpeople1=(struct staff *)malloc(sizeof(struct staff));people2=(struct staff *)malloc(sizeof(struct staff));people1->iStaffID=1001;strcpy(people1->acName,"张三");strcpy(people1->acPasswd,"123456");people2->iStaffID=1002;strcpy(people2->acName,"李四");strcpy(people2->acPasswd,"123456");//添加链表节点List_Add(head,people1);List_Add(head,people2);//员工信息打印函数Staff_Print(head);
}//员工信息打印函数
void Staff_Print(struct list *head)
{struct list *p1=head->next;struct staff *people1;while(p1 != NULL){ people1=p2->data;printf("%5d%10s%10s\n",people1->iStaffID,people1->acName,people1->acPasswd);p1=p1->next;}
}