C语言链表
- 链表的概念及结构
- 概念
- 结构
- 链表的分类
- 单链表的实现(无头)
- 双向链表的实现
- 总结:链表和顺序表的区别
链表的概念及结构
概念
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的 。
结构
- 代码
struct Slist
{int* a;struct Slist* next;
};
-
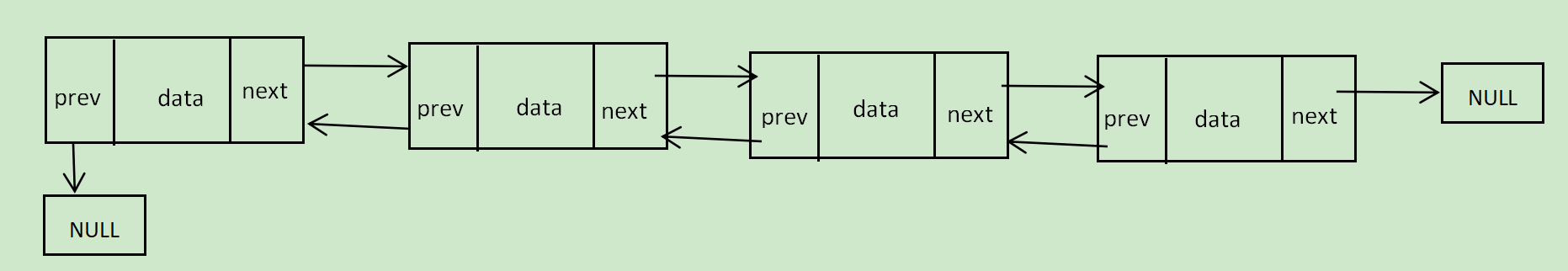
逻辑结构:

-
物理结构:

-
注意:
- 从上图可以看出,链式结构在逻辑上是连续的,但是在物理上是不一定是连续的。
- 这些结点一般是从堆上申请出来的。
- 从堆上申请的空间,是按照一定的策划来分配的,两次申请的空间可能连续,大概率是不连续的。
链表的分类
-
实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构:
1. 单向或者双向
①单向
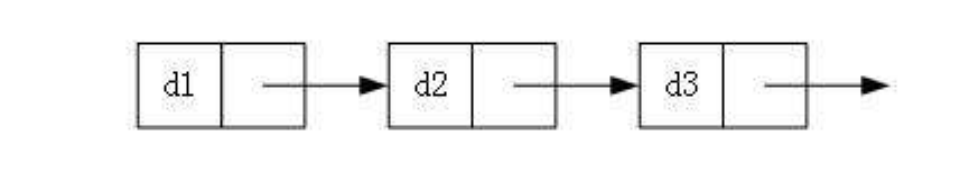
②双向
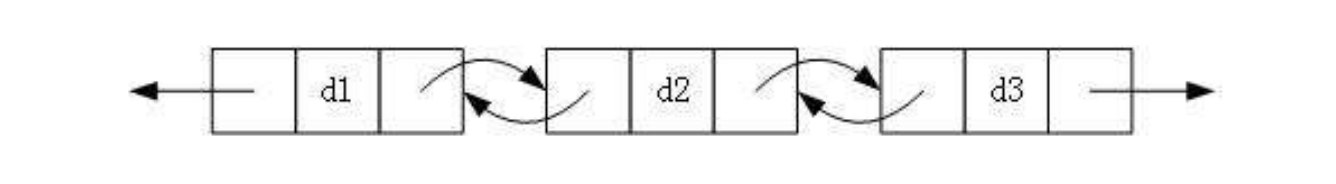 2.带头或者不带头
2.带头或者不带头
①带头
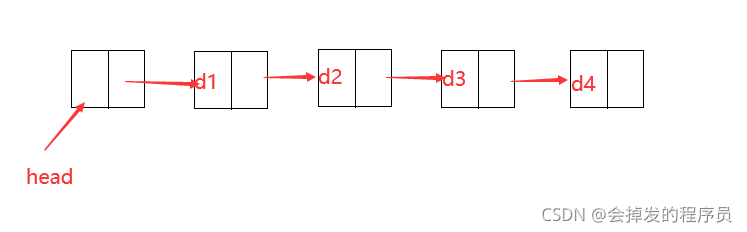
②不带头
 3.循环或者非循环
3.循环或者非循环
①循环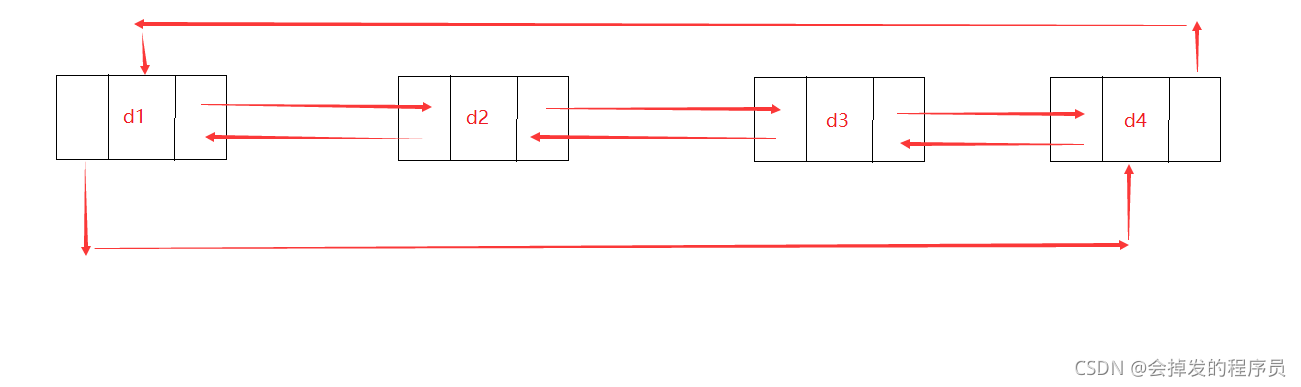
②非循环
-
虽然有这么多种结构的链表,但是我们实际中最常用的只有两种结构:
1. 无头单向非循环链表 2.带头双向循环链表
2.带头双向循环链表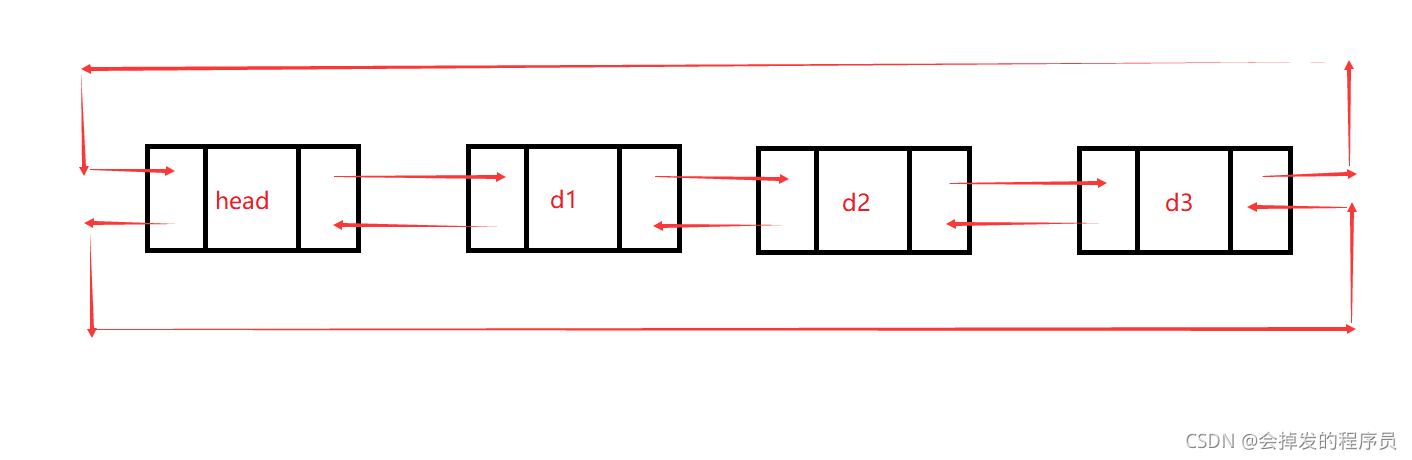
1. 无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多。
2. 带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,实现反而简单了,后面我们代码实现了就知道了。
单链表的实现(无头)
- 单链表结构
typedef int SLTDateType;typedef struct SListNode
{SLTDateType data;struct SListNode* next;
}SListNode;
- 单链表需要的功能
// 动态申请一个节点
SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDateType x);
// 单链表打印
void SListPrint(SListNode* plist);
// 单链表尾插
void SListPushBack(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x);
// 单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x);
// 单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SListNode** pplist);
// 单链表头删
void SListPopFront(SListNode** pplist);
// 单链表查找
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* plist, SLTDateType x);
// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
// 分析思考为什么不在pos位置之前插入?
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLTDateType x);
// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
// 分析思考为什么不删除pos位置?
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos);
// 单链表的销毁
void SListDestory(SListNode** pplist);
- 功能实现
SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDateType x)
{SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));if (newnode == NULL){exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;return newnode;
}void SListPrint(SListNode* plist)
{if (plist == NULL){printf("NULL\n");return;}else{while (plist){printf("%d->", plist->data);plist = plist->next;}printf("NULL\n");}
}void SListPushBack(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x)
{SListNode* tail = *pplist;SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = NULL;if (tail == NULL){*pplist = newnode;}else{while (tail->next){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}void SListPushFront(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x)
{SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = *pplist;*pplist = newnode;
}void SListPopBack(SListNode** pplist)
{assert(*pplist);SListNode* tail = *pplist;SListNode* Pretail = NULL;if (tail->next == NULL){*pplist = NULL;return;}else{while (tail->next){Pretail = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tail = NULL;Pretail->next = NULL;}
}void SListPopFront(SListNode** pplist)
{assert(*pplist);SListNode* front = *pplist;*pplist = front->next;free(front);front = NULL;
}SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* plist, SLTDateType x)
{assert(plist);SListNode* pos = plist;while (pos && pos->data != x){pos = pos->next;}return pos;
}void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
{assert(pos);SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos)
{assert(pos);assert(pos->next);SListNode* node = pos->next;pos->next = node->next;free(node);
}void SListDestory(SListNode** pplist)
{SListNode* node = *pplist;SListNode* PreNode = NULL;while (node){PreNode = node->next;free(node);node = PreNode;}
}双向链表的实现
- 双向链表的结构
typedef int LTDateType;typedef struct ListNode
{LTDateType data;struct ListNode* next;struct ListNode* prev;
}LTNode;- 双向链表的功能
//创建链表返回头结点
LTNode* ListInit();
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(LTNode* phead);
// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(LTNode* phead);// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDateType x);
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead);
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDateType x);
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(LTNode* phead);
// 双向链表查找
LTNode* ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDateType x);
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDateType x);
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(LTNode* pos);
- 功能实现
LTNode* ListInit()
{//哨兵位头结点LTNode* phead = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if (phead == NULL){printf("开辟空间失败!!!\n");exit(-1);}phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead;
}void ListDestory(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead;LTNode* p = NULL;LTNode* tail = phead->prev;while (cur != tail){p = cur;cur = cur->next;free(p);}free(tail);
}void ListPrint(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);LTNode* front = phead->next;while (front != phead){printf("%d ", front->data);front = front->next;}printf("\n");
}void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDateType x)
{assert(phead);LTNode* tail = phead->prev;LTNode* newnode = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if (newnode == NULL){printf("开辟空间失败!!\n");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;tail->next = newnode;newnode->prev = tail;newnode->next = phead;phead->prev = newnode;
}void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead != phead->next);LTNode* tail = phead->prev;LTNode* TailFront = tail->prev;TailFront->next = phead;phead->prev = TailFront;free(tail);
}void ListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDateType x)
{assert(phead);LTNode* next = phead->next;LTNode* newnode = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if (newnode == NULL){printf("开辟空间失败!!\n");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;phead->next = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;newnode->next = next;next->prev = newnode;
}void ListPopFront(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead != phead->next);LTNode* head = phead->next;//头结点phead->next = head->next;head->next->prev = phead;free(head);
}LTNode* ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDateType x)
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}void ListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDateType x)
{assert(pos);LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;LTNode* newnode = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if (newnode == NULL){printf("开辟空间失败!!\n");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;posPrev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = posPrev;newnode->next = pos;pos->prev = newnode;
}void ListErase(LTNode* pos)
{assert(pos);LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;LTNode* posNext = pos->next;posPrev->next = posNext;posNext->prev = posPrev;free(pos);
}
总结:链表和顺序表的区别
| 不同点 | 顺序表 | 链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 存储空间上 | 物理上一定连续 | 逻辑上连续,物理上不一定连续 |
| 随机访问 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 任意位置上插入或者删除元素 | 可能需要移动元素,效率低下 | 只需修改指针指向 |
| 插入 | 动态顺序表,空间不够时需要扩容 | 没有容量的概念 |
| 应用场景 | 元素高效存储+频繁访问 | 任意位置插入和删除频繁 |