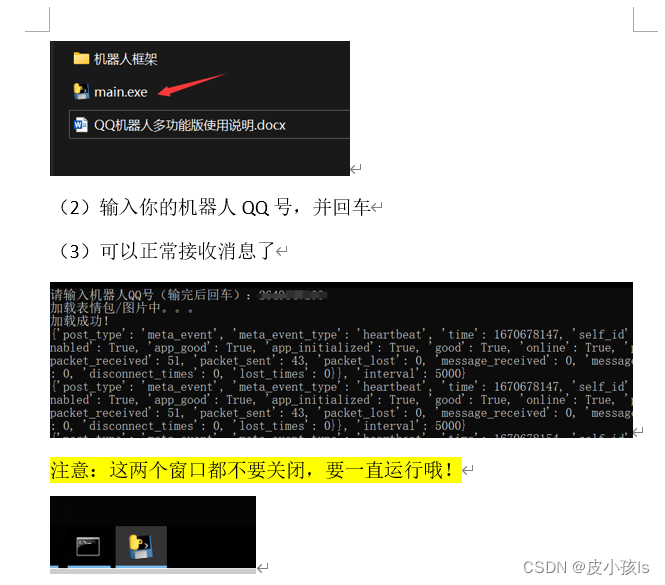
Linux date命令修改时间的问题
- 问题
- 路径
- 找原因
- 解决方法
问题
Android10;高通平台
使用下面date命令修改时间日期,时分秒生效,年月日不生效
=> date -D YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss
路径
\android\external\toybox\toys\posix\date.c
\android\external\toybox\lib\args.c
找原因
首先在命令行键入
=> adb shell date -D 2020-10-01 22:59:00
去代码看一下参数传的有没有什么问题
\android\external\toybox\main.c
// argc:参数的数量 argv: 参数
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{if (!*argv) return 127;if (CFG_TOYBOX) {// Call the multiplexer, adjusting this argv[] to be its' argv[1].// (It will adjust it back before calling toy_exec().)toys.argv = argv-1;toybox_main();}...
}
argc = 4,
argv[0] = date, argv[1] = -D, argv[2] = 2020-10-01, argv[3] = 22:59:00

很明显这里并没有什么问题,我们接着往下看调用toybox_main()
// Multiplexer command, first argument is command to run, rest are args to that.
// If first argument starts with - output list of command install paths.
void toybox_main(void)
{static char *toy_paths[]={"usr/","bin/","sbin/",0};int i, len = 0;if (toys.argv[1]) {toy_exec(toys.argv+1);if (0<readlink(toys.argv[1], libbuf, sizeof(libbuf)))toy_exec_which(toy_find(basename(libbuf)), toys.argv);}...
}
参数传给toys.argv,我们看一下toys.argv里面是怎么存放数据的:
其中toys.argv[0]为空,toys.argv[1] = date, toys.argv[2] = -D, toys.argv[3] = 2020-10-08, toys.argv[4] = 22:59:00
还是没有问题,我们接着往下看
// Lookup internal toybox command to run via argv[0]
void toy_exec(char *argv[])
{toy_exec_which(toy_find(basename(*argv)), argv);
}// Run an internal toybox command.
void toy_exec_which(struct toy_list *which, char *argv[])
{...// Run commandtoy_init(which, argv);if (toys.which) toys.which->toy_main();xexit();
}
void toy_init(struct toy_list *which, char *argv[])
{void *oldwhich = toys.which;...// Continue to portion of init needed by standalone commandstoy_singleinit(which, argv);
}static void toy_singleinit(struct toy_list *which, char *argv[])
{toys.which = which;toys.argv = argv;...if (NEED_OPTIONS && which->options) get_optflags();else {toys.optargs = argv+1;for (toys.optc = 0; toys.optargs[toys.optc]; toys.optc++);}toys.old_umask = umask(0);if (!(which->flags & TOYFLAG_UMASK)) umask(toys.old_umask);toys.signalfd--;toys.toycount = ARRAY_LEN(toy_list);
}
这里走的分支是get_optflags()
get_optflags()是对参数的解析,通过log可以发现get_optflags的for循环只循环了gof.argc=1(-D),gof.argc=3(22:59:00),漏掉了gof.argc=2就是年月日
先看gof.argc=1的循环:
gof.arg是字符型指针,指向toys.argv[1] = -D 的”-”,++后就指向了”D”, 所以传给gotflag()的参数是”D”
// Fill out toys.optflags, toys.optargs, and this[] from toys.argv
void get_optflags(void)
{struct getoptflagstate gof;struct opts *catch;unsigned long long saveflags;char *letters[]={"s",""};// Iterate through command line arguments, skipping argv[0]for (gof.argc=1; toys.argv[gof.argc]; gof.argc++) {gof.arg = toys.argv[gof.argc];catch = NULL;// Parse this argumentif (gof.stopearly>1) goto notflag;gof.nodash_now = 0;// Various things with dashesif (*gof.arg == '-') {// Handle -if (!gof.arg[1]) goto notflag;gof.arg++;if (*gof.arg=='-') {struct longopts *lo;gof.arg++;// Handle --if (!*gof.arg) {gof.stopearly += 2;continue;}// do we match a known --longopt?for (lo = gof.longopts; lo; lo = lo->next) {if (!strncmp(gof.arg, lo->str, lo->len)) {if (!gof.arg[lo->len]) gof.arg = 0;else if (gof.arg[lo->len] == '=' && lo->opt->type)gof.arg += lo->len;else continue;// It's a match.catch = lo->opt;break;}}// Should we handle this --longopt as a non-option argument?if (!lo && gof.noerror) {gof.arg -= 2;goto notflag;}// Long option parsed, handle option.gotflag(&gof, catch);continue;}// Handle things that don't start with a dash.} else {if (gof.nodash && (gof.nodash>1 || gof.argc == 1)) gof.nodash_now = 1;else goto notflag;}// At this point, we have the args part of -args. Loop through// each entry (could be -abc meaning -a -b -c)saveflags = toys.optflags;while (*gof.arg) {// Identify next option char.for (catch = gof.opts; catch; catch = catch->next)if (*gof.arg == catch->c)if (!((catch->flags&4) && gof.arg[1])) break;// Handle option char (advancing past what was used)if (gotflag(&gof, catch) ) {toys.optflags = saveflags;gof.arg = toys.argv[gof.argc];goto notflag;}}continue;// Not a flag, save value in toys.optargs[]
notflag:if (gof.stopearly) gof.stopearly++;toys.optargs[toys.optc++] = toys.argv[gof.argc];}...
}
看下为什么会把年月日跳过,gotflag()中选项(-option)解析, gotflag(&gof, catch);
传入的gof->arg 指向 ”D”, gof->arg有参数++指向” ”
// Use getoptflagstate to parse one command line option from argv
static int gotflag(struct getoptflagstate *gof, struct opts *opt)
{int type;// Set flagstoys.optflags |= opt->dex[1];gof->excludes |= opt->dex[2];if (opt->flags&2) gof->stopearly=2;...// Does this option take an argument?if (!gof->arg) {if (opt->flags & 8) return 0;gof->arg = "";} else gof->arg++; // 指向" "type = opt->type; // type = ":"...return 0;
}
char*arg = ” ”
gof->nodash_now = 0, !arg[0] = 1, opt->flags = 0
进行判断,++argc,argc由1变为2,也是导致年月日被跳过的原因
这时arg指向“2020-10-08”, opt->arg指向“2020-10-08”
解决方法
由于args.c是解析命令行参数的共用文件,没把握最好不要修改,很容易影响到其他命令的解析。我们可以让被跳过的参数2为任意字符,如("+"可为任意字符)
=> date -D + YYYY-MM-DDhh:mm:ss
另外也可以使用
=> date MMDDhhmmYYYY.ss set
来设置时间



![OpenHarmony啃论文俱乐部—盘点开源鸿蒙引用的三方开源软件[1]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9f5bf9c110d2ecfc54abf0b39fe6e243.png)