目录
1.if执行脚本示例
2.源码分析
2.1 compile执行过程
2.1.1 CodeGenerator
2.1.2 ExpressionParser
2.1.3 if脚本ASM反编译结果
2.2 compiledExpression.execute执行过程
3.总结概述
由于Aviator支持的脚本语法较多,下面通过项目中使用较多的if语句来对aviator执行过程进行一次源码剖析,以便更清楚的了解aviator具体的解析执行过程,并加深技术储备,方便后续aviator源码相关问题的快速深入分析,同时希望达到“窥一斑而知全貌”的效果;
1.if执行脚本示例
Map<String, Object> env = new HashMap<>();
env.put("a", 2);
env.put("b", 3);
env.put("c", 4);
Object result = AviatorEvaluator.execute("if(a > 1) { return b+2; } else { return c; }", env);通过执行上述的if脚本,着重分析aviator框架内部的解析逻辑,比如通过asm字节码技术动态生成class、LambdaFunctionBootstrap构造和设计理念以及LambdaFunction函数的构造和设计理念等;
2.源码分析
跟踪AviatorEvaluator.execute方法,内部实现如下:
/*** Execute a text expression with environment** @param cacheKey unique key for caching* @param expression text expression* @param env Binding variable environment* @param cached Whether to cache the compiled result,make true to cache it.*/public Object execute(final String cacheKey, final String expression,final Map<String, Object> env, final boolean cached) {Expression compiledExpression = compile(cacheKey, expression, cached);if (compiledExpression != null) {return compiledExpression.execute(env);} else {throw new ExpressionNotFoundException("Null compiled expression for " + expression);}}其中主要包含2个部分:
1)compile方法通过asm技术生成ClassExpression的子类:这里将整个表达式脚本编译为ClassExpression子类;
2)执行compiledExpression.execute方法:将外部传入的变量集env实参带入方法中进行执行,返回脚本执行结果;
下面对这2个部分分别进行分析:
2.1 compile执行过程
compile方法体中使用了LRU或HashMap对编译后的字节码进行缓存,编译的字节码是通过方法innerCompile来获取的:
private Expression compile(final String cacheKey, final String expression,final String sourceFile, final boolean cached) {if (expression == null || expression.trim().length() == 0) {throw new CompileExpressionErrorException("Blank expression");}if (cacheKey == null || cacheKey.trim().length() == 0) {throw new CompileExpressionErrorException("Blank cacheKey");}if (cached) {FutureTask<Expression> existedTask = null;if (this.expressionLRUCache != null) {boolean runTask = false;synchronized (this.expressionLRUCache) {existedTask = this.expressionLRUCache.get(cacheKey);if (existedTask == null) {existedTask = newCompileTask(expression, sourceFile, cached);runTask = true;this.expressionLRUCache.put(cacheKey, existedTask);}}if (runTask) {existedTask.run();}} else {FutureTask<Expression> task = this.expressionCache.get(cacheKey);if (task != null) {return getCompiledExpression(expression, task);}task = newCompileTask(expression, sourceFile, cached);existedTask = this.expressionCache.putIfAbsent(cacheKey, task);if (existedTask == null) {existedTask = task;existedTask.run();}}return getCompiledExpression(cacheKey, existedTask);} else {return innerCompile(expression, sourceFile, cached);}}innerCompile方法实现如下:
private Expression innerCompile(final String expression, final String sourceFile,final boolean cached) {ExpressionLexer lexer = new ExpressionLexer(this, expression);CodeGenerator codeGenerator = newCodeGenerator(sourceFile, cached);ExpressionParser parser = new ExpressionParser(this, lexer, codeGenerator);Expression exp = parser.parse();if (getOptionValue(Options.TRACE_EVAL).bool) {((BaseExpression) exp).setExpression(expression);}return exp;}这里说明几个主要用到的类:
ExpressionLexer:表达式词法分析器,用来对aviator脚本进行词法解析,如将脚本解析为变量、数字、字符串、注释等,并构造Token流进行后续处理;
CodeGenerator:字节码生成器,用于动态生成自定义的字节码;
ExpressionParser:表达式解析器,用于将脚本编译为表达式对象(ClassExpression),支持对多种aviator支持的脚本进行解析,具体解析过程是将ExpressionLexer构造的Token流通过字节码生成器编译为表达式对象ClassExpression
2.1.1 CodeGenerator
这里用到的CodeGenerator主要包括:

CodeGenerator:定义了字节码生成的顶层接口
ASMCodeGenerator:默认的ASM字节码生成器,对CodeGenerator声明的操作进行ASM具体实现
OptimizeCodeGenerator:为加快执行效率而生的字节码生成器(默认的字节码生成器),可以执行一些前置的计算逻辑,然后再委托ASMCodeGenerator进行字节码生成
2.1.2 ExpressionParser
ExpressionParser完成对多种aviator支持的脚本的解析工作,比如if,for,let等脚本特性,解析逻辑是依赖parse方法完成的,如下:
public Expression parse(final boolean reportErrorIfNotEOF) {StatementType statementType = statements();if (this.lookhead != null && reportErrorIfNotEOF) {if (statementType == StatementType.Ternary) {reportSyntaxError("unexpect token '" + currentTokenLexeme()+ "', maybe forget to insert ';' to complete last expression ");} else {reportSyntaxError("unexpect token '" + currentTokenLexeme() + "'");}}return getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().getResult(true);}这里主要分为2个部分:
1)调用statements完成脚本解析工作,产出Token流(以默认的OptimizeCodeGenerator进行分析)
2)调用OptimizeCodeGenerator的getResult方法完成ASM字节码生成,并根据字节码构造完成ClassExpression实例对象
2.1.1.1 statements方法
statements中主要的解析过程如下:
private StatementType statements() {if (this.lookhead == null) {return StatementType.Empty;}StatementType stmtType = statement();ensureDepthState();while (expectChar(';') || stmtType == StatementType.Other || stmtType == StatementType.Return) {ensureNoStatementAfterReturn(stmtType);if (this.lookhead != null && this.lookhead != Variable.END && !expectChar('}')) {getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onTernaryEnd(this.lookhead);}if (expectChar(';')) {move(true);}if (this.lookhead == null) {break;}StatementType nextStmtType = statement();if (nextStmtType == StatementType.Empty) {break;}stmtType = nextStmtType;ensureDepthState();}ensureNoStatementAfterReturn(stmtType);// If the last statement is ternary,it must be ended with END TOKEN such as null token, '}',// 'end' keyword, or ';'// Otherwise report syntax error.if (stmtType == StatementType.Ternary) {if (lookhead != null && !expectChar(';') && !expectChar('}') && lookhead != Variable.END) {this.back();reportSyntaxError("unexpect token '" + currentTokenLexeme()+ "', maybe forget to insert ';' to complete last expression ");}}return stmtType;}具体的解析过程是在statement方法中,如下:
private StatementType statement() {if (this.lookhead == Variable.IF) {ensureFeatureEnabled(Feature.If);if (ifStatement(false, false)) {return StatementType.Return;} else {return StatementType.Other;}} else if (this.lookhead == Variable.FOR) {ensureFeatureEnabled(Feature.ForLoop);forStatement();return StatementType.Other;} else if (this.lookhead == Variable.RETURN) {ensureFeatureEnabled(Feature.Return);returnStatement();return StatementType.Return;} else if (this.lookhead == Variable.BREAK) {breakStatement();return StatementType.Return;} else if (this.lookhead == Variable.CONTINUE) {continueStatement();return StatementType.Return;} else if (this.lookhead == Variable.LET) {ensureFeatureEnabled(Feature.Let);letStatement();return StatementType.Other;} else if (this.lookhead == Variable.WHILE) {ensureFeatureEnabled(Feature.WhileLoop);whileStatement();return StatementType.Other;} else if (this.lookhead == Variable.FN) {ensureFeatureEnabled(Feature.Fn);fnStatement();return StatementType.Other;} else if (this.lookhead == Variable.TRY) {ensureFeatureEnabled(Feature.ExceptionHandle);tryStatement();return StatementType.Other;} else if (this.lookhead == Variable.THROW) {ensureFeatureEnabled(Feature.ExceptionHandle);throwStatement();return StatementType.Other;} else if (expectChar('{')) {ensureFeatureEnabled(Feature.LexicalScope);if (scopeStatement()) {return StatementType.Return;} else {return StatementType.Other;}} else if (this.lookhead == Variable.USE) {ensureFeatureEnabled(Feature.Use);useStatement();return StatementType.Other;} else {if (ternary()) {return StatementType.Ternary;} else {return StatementType.Empty;}}}这里可以看到:aviator支持的多种脚本特性,比如if、for、let、return等语法都是在这里解析完成的;
以if语法举例说明,继续跟踪ifStatement方法,如下:
/*** <pre>* if(test) {* ...if-body...* }else {* ...else-body...* }* ...statements...* </pre>** ===>** <pre>* __if_callcc(test ? (lambda() -> ...if-body... end)() : (lambda() -> ...else-body... end)(),* lambda()- >* ...statements...* end);* </pre>*/private boolean ifStatement(final boolean isWhile, final boolean isElsif) {if (!isWhile) {move(true);}boolean ifBodyHasReturn = false;boolean elseBodyHasReturn = false;boolean newLexicalScope = this.scope.newLexicalScope;this.scope.newLexicalScope = true;// prepare to call __if_callcc(result, statements)getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onMethodName(Constants.IfReturnFn);{if (!ternary()) {reportSyntaxError("missing test statement for if");}getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onTernaryBoolean(this.lookhead);if (expectChar('{')) {move(true);this.scope.enterBrace();getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onLambdaDefineStart(getPrevToken().withMeta(Constants.SCOPE_META, this.scope.newLexicalScope));getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onLambdaBodyStart(this.lookhead);ifBodyHasReturn = statements() == StatementType.Return;getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onLambdaBodyEnd(this.lookhead);getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onMethodName(anonymousMethodName());getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onMethodInvoke(this.lookhead);getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onTernaryLeft(this.lookhead);} else {reportSyntaxError("expect '{' for " + getLoopKeyword(isWhile) + " statement");}if (!expectChar('}')) {reportSyntaxError("missing '}' to close " + getLoopKeyword(isWhile) + " body");}this.scope.leaveBrace();move(true);elseBodyHasReturn = elseStatement(isWhile, ifBodyHasReturn);getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onMethodParameter(this.lookhead);}{//if (isWhile || isElsif) {// Load ReducerEmptyVal directly.getCodeGenerator().onConstant(Constants.ReducerEmptyVal);} else {if (expectChar(';')) {// the statement is ended.getCodeGenerator().onConstant(Constants.ReducerEmptyVal);} else {// create a lambda function wraps statements after if statement (statements)getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onLambdaDefineStart(getPrevToken().withMeta(Constants.SCOPE_META, this.scope.newLexicalScope) //.withMeta(Constants.INHERIT_ENV_META, true));getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onLambdaBodyStart(this.lookhead);if (statements() == StatementType.Empty) {getCodeGenerator().onConstant(Constants.ReducerEmptyVal);} else {if (ifBodyHasReturn && elseBodyHasReturn && !isElsif) {reportSyntaxError("unreachable code");}}getCodeGeneratorWithTimes().onLambdaBodyEnd(this.lookhead);}}getCodeGenerator().onMethodParameter(this.lookhead);// call __if_callcc(result, statements)getCodeGenerator().onMethodInvoke(this.lookhead);this.scope.newLexicalScope = newLexicalScope;}return ifBodyHasReturn && elseBodyHasReturn;}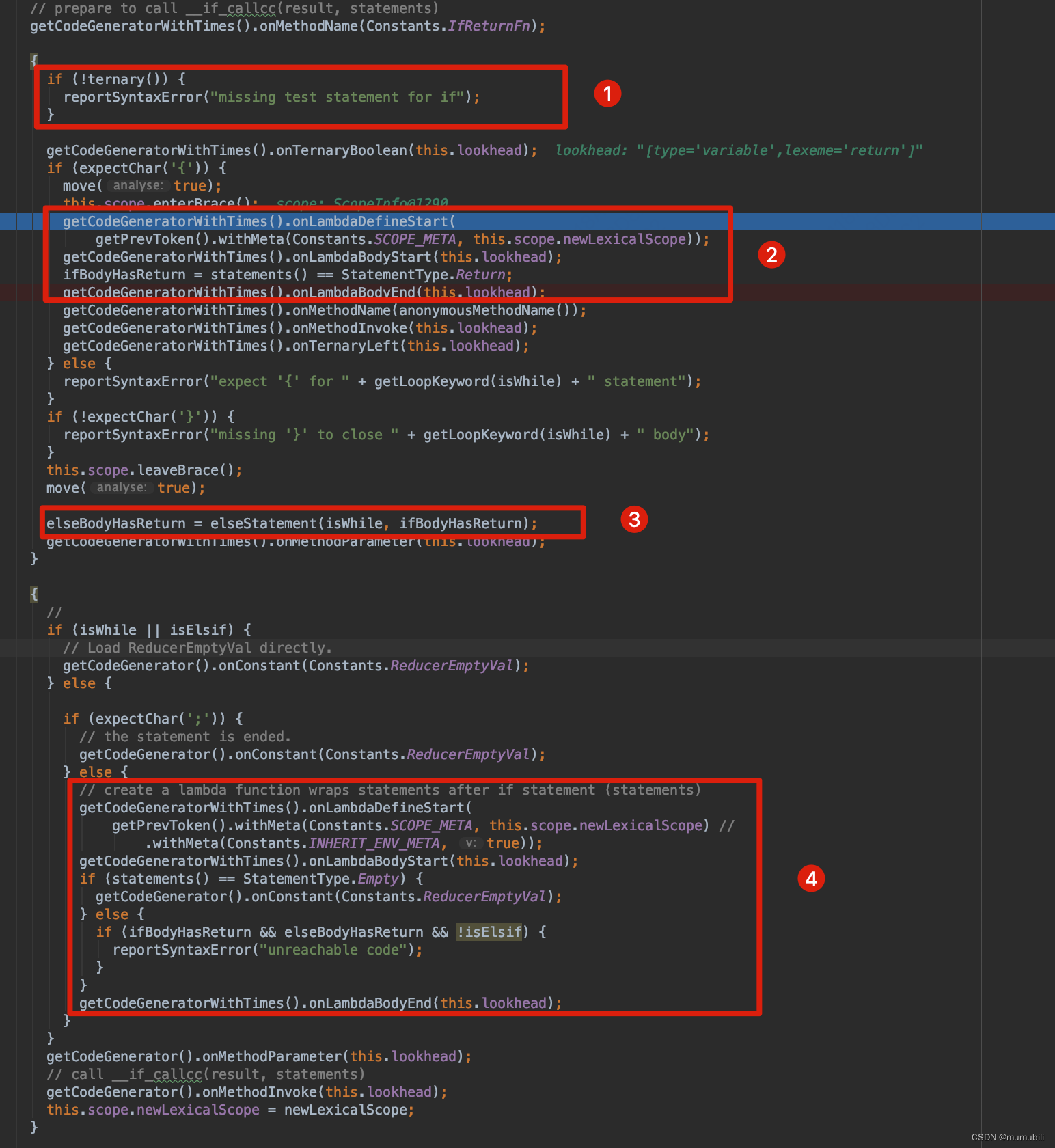
if语法的解析过程主要分为以下几个部分:
1)通过ternary方法完成对if条件语句的解析(解析结果放入OptimizeCodeGenerator的Token流中,后续统一生成字节码)
2)if的方法体(ifBody)抽象为一个lambda表达式,并通过委托给lambdaGenerator进行解析,后面着重分析该解析过程;
3)对elseBody进行解析:这里实际的解析过程和ifBody的解析过程类似,也是委托给新构建的lambdaGenerator进行解析;
private boolean elseStatement(final boolean isWhile, final boolean ifBodyHasReturn) {if (isWhile) {// Call __reducer_break(nil)final CodeGenerator cg = getCodeGeneratorWithTimes();cg.onMethodName(Constants.ReducerBreakFn);cg.onConstant(Variable.NIL);cg.onMethodParameter(this.lookhead);cg.onMethodInvoke(this.lookhead);cg.onTernaryRight(this.lookhead);return false;}if (expectChar(';')) {return withoutElse();}boolean hasReturn = false;boolean hasElsif = this.lookhead == Variable.ELSIF;boolean hasElse = this.lookhead == Variable.ELSE;if (this.lookhead != null && (hasElse || hasElsif || ifBodyHasReturn)) {if (hasElse) {move(true);if (expectChar('{')) {this.scope.enterBrace();move(true);hasReturn = elseBody(false);if (expectChar('}')) {this.scope.leaveBrace();move(true);} else {reportSyntaxError("missing '}' to close 'else' body");}} else {reportSyntaxError("expect '{' for else statement");}} else if (hasElsif) {hasReturn = ifStatement(false, true);getCodeGenerator().onTernaryRight(this.lookhead);} else if (ifBodyHasReturn) {hasReturn = elseBody(true);} else {return withoutElse();}return hasReturn;} else {// Missing else statement, always nil.return withoutElse();}}4)这里对if语句后面的整个脚本抽象为一个lambda表达式,也是通过委托给lambdaGenerator进行解析;
如上的解析过程也可以借助方法注释进行较好的理解:

2.1.1.1.1 lambdaGenerator解析过程分析
对2.1.1.1 节的注释2的代码进一步分析:
1)lambda脚本解析前置环节
onLambdaDefineStart方法构造lambdaGenerator;
onLambdaBodyStart方法将ExpressionParser的codeGenerator替换为新构造的lambdaGenerator,同时维护好lambdaGenerator的父parentCodeGenerator=OptimizeCodeGenerator,lamdba解析完成后再替换回parentCodeGenerator,也即OptimizeCodeGenerator,也及整个脚本的ASM操作是通过OptimizeCodeGenerator和lambdaGenerator(如果包含lambda语法)交替完成的


2)lambda脚本解析完成后
lambda脚本解析完成后,这里会调用getLmabdaBootstrap构造LambdaFunctionBootstrap实例对象,并将LambdaFunctionBootstrap缓存到OptimizeCodeGenerator的
Map<String, LambdaFunctionBootstrap> lambdaBootstraps成员变量中;
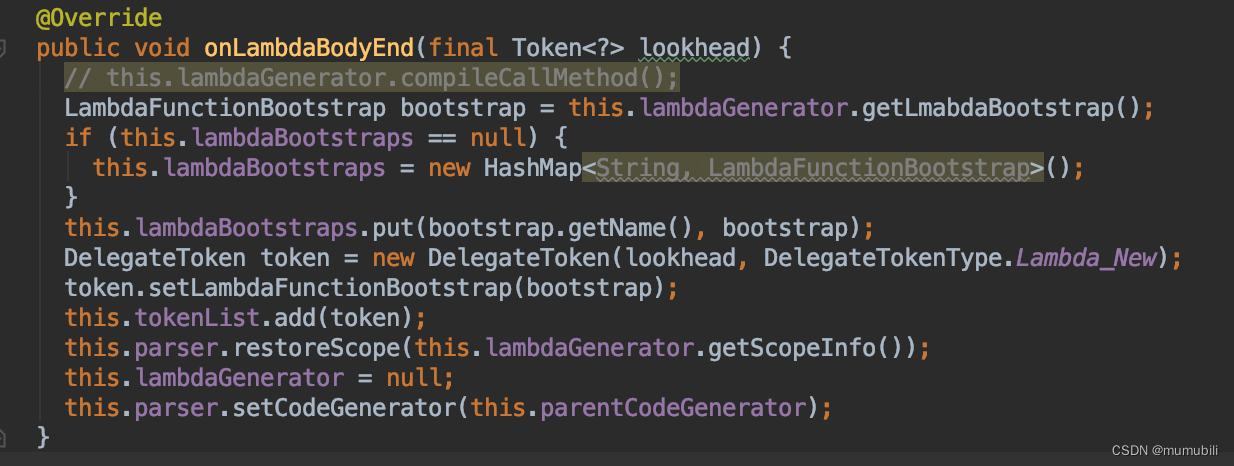
进一步展开getLmabdaBootstrap函数:

可以看到这里也是通过getResult方法通过ASM字节码技术动态构造Expression子类实例(具体分析过程见2.1.1.2),构造的结果放到了LambdaFunctionBootstrap实例对象中,也即lambda表达式的解析结果即为LambdaFunctionBootstrap;
2.1.1.2 OptimizeCodeGenerator.getResult()过程分析
aviator脚本解析完成之后,解析结果Token流会存放到OptimizeCodeGenerator的成员变量List<Token<?>> tokenList中,getResult方法就是根据tokenList生成字节码的过程;
getResult方法具体实现如下:
@Overridepublic Expression getResult(final boolean unboxObject) {// execute literal expressionwhile (execute() > 0) {;}Map<String, VariableMeta/* metadata */> variables = new LinkedHashMap<String, VariableMeta>();Map<String, Integer/* counter */> methods = new HashMap<String, Integer>();Set<Token<?>> constants = new HashSet<>();for (Token<?> token : this.tokenList) {if (ExpressionParser.isConstant(token, this.instance)) {constants.add(token);}switch (token.getType()) {case Variable:if (SymbolTable.isReservedKeyword((Variable) token)) {continue;}String varName = token.getLexeme();VariableMeta meta = variables.get(varName);if (meta == null) {meta = new VariableMeta((CompileTypes) token.getMeta(Constants.TYPE_META), varName,token.getMeta(Constants.INIT_META, false), token.getStartIndex());variables.put(varName, meta);} else {meta.add(token);}break;case Delegate:DelegateToken delegateToken = (DelegateToken) token;if (delegateToken.getDelegateTokenType() == DelegateTokenType.Method_Name) {Token<?> realToken = delegateToken.getToken();if (realToken == null) {continue;}if (realToken.getType() == TokenType.Variable) {String methodName = token.getLexeme();if (!methods.containsKey(methodName)) {methods.put(methodName, 1);} else {methods.put(methodName, methods.get(methodName) + 1);}}} else if (delegateToken.getDelegateTokenType() == DelegateTokenType.Array) {Token<?> realToken = delegateToken.getToken();if (realToken.getType() == TokenType.Variable) {varName = token.getLexeme();VariableMeta varMeta = variables.get(varName);if (varMeta == null) {varMeta =new VariableMeta((CompileTypes) realToken.getMeta(Constants.TYPE_META), varName,realToken.getMeta(Constants.INIT_META, false), realToken.getStartIndex());variables.put(varName, varMeta);} else {varMeta.add(realToken);}}}break;}}Expression exp = null;// Last token is a literal token,then return a LiteralExpressionif (this.tokenList.size() <= 1) {if (this.tokenList.isEmpty()) {exp = new LiteralExpression(this.instance, null, new ArrayList<>(variables.values()));} else {final Token<?> lastToken = this.tokenList.get(0);if (ExpressionParser.isLiteralToken(lastToken, this.instance)) {exp = new LiteralExpression(this.instance,getAviatorObjectFromToken(lastToken).getValue(getCompileEnv()),new ArrayList<>(variables.values()));}}}if (exp == null) {// call asm to generate byte codescallASM(variables, methods, constants);// get result from asmexp = this.codeGen.getResult(unboxObject);}if (exp instanceof BaseExpression) {((BaseExpression) exp).setCompileEnv(getCompileEnv());((BaseExpression) exp).setSourceFile(this.sourceFile);}return exp;}这里主要包含以下几部分:
1)可以前置执行的逻辑提前执行,比如文本表达式(1+2)等,先行计算出执行结果,优化执行效率;
2)初始化常量集、变量集、aviator函数实例集合,为后续ASM生成类成员变量和类构造函数使用;
3)调用callASM方法生成字节码,根据不同的token类型进行不同的asm操作;
private void callASM(final Map<String, VariableMeta/* metadata */> variables,final Map<String, Integer/* counter */> methods, final Set<Token<?>> constants) {this.codeGen.initConstants(constants);this.codeGen.initVariables(variables);this.codeGen.initMethods(methods);this.codeGen.setLambdaBootstraps(this.lambdaBootstraps);this.codeGen.start();for (int i = 0; i < this.tokenList.size(); i++) {Token<?> token = this.tokenList.get(i);switch (token.getType()) {case Operator:OperatorToken op = (OperatorToken) token;switch (op.getOperatorType()) {case ADD:this.codeGen.onAdd(token);break;case SUB:this.codeGen.onSub(token);break;case MULT:this.codeGen.onMult(token);break;case Exponent:this.codeGen.onExponent(token);break;case DIV:this.codeGen.onDiv(token);break;case MOD:this.codeGen.onMod(token);break;case EQ:this.codeGen.onEq(token);break;case NEQ:this.codeGen.onNeq(token);break;case LT:this.codeGen.onLt(token);break;case LE:this.codeGen.onLe(token);break;case GT:this.codeGen.onGt(token);break;case GE:this.codeGen.onGe(token);break;case NOT:this.codeGen.onNot(token);break;case NEG:this.codeGen.onNeg(token);break;case AND:this.codeGen.onAndRight(token);break;case OR:this.codeGen.onJoinRight(token);break;case FUNC:this.codeGen.onMethodInvoke(token);break;case INDEX:this.codeGen.onArrayIndexEnd(token);break;case MATCH:this.codeGen.onMatch(token);break;case TERNARY:this.codeGen.onTernaryRight(token);break;case BIT_AND:this.codeGen.onBitAnd(token);break;case BIT_OR:this.codeGen.onBitOr(token);break;case BIT_XOR:this.codeGen.onBitXor(token);break;case BIT_NOT:this.codeGen.onBitNot(token);break;case SHIFT_LEFT:this.codeGen.onShiftLeft(token);break;case SHIFT_RIGHT:this.codeGen.onShiftRight(token);break;case DEFINE:this.codeGen.onAssignment(token.withMeta(Constants.DEFINE_META, true));break;case ASSIGNMENT:this.codeGen.onAssignment(token);break;case U_SHIFT_RIGHT:this.codeGen.onUnsignedShiftRight(token);break;}break;case Delegate:DelegateToken delegateToken = (DelegateToken) token;final Token<?> realToken = delegateToken.getToken();switch (delegateToken.getDelegateTokenType()) {case And_Left:this.codeGen.onAndLeft(realToken);break;case Join_Left:this.codeGen.onJoinLeft(realToken);break;case Array:this.codeGen.onArray(realToken);break;case Index_Start:this.codeGen.onArrayIndexStart(realToken);break;case Ternary_Boolean:this.codeGen.onTernaryBoolean(realToken);break;case Ternary_Left:this.codeGen.onTernaryLeft(realToken);break;case Method_Name:this.codeGen.onMethodName(realToken);break;case Method_Param:this.codeGen.onMethodParameter(realToken);break;case Lambda_New:this.codeGen.genNewLambdaCode(delegateToken.getLambdaFunctionBootstrap());break;case Ternay_End:this.codeGen.onTernaryEnd(realToken);break;}break;default:this.codeGen.onConstant(token);break;}}}4)调用getResult方法根据生成的字节码构造Expression子类实例(ClassExpression)
@Overridepublic Expression getResult(final boolean unboxObject) {end(unboxObject);byte[] bytes = this.classWriter.toByteArray();try {Class<?> defineClass =ClassDefiner.defineClass(this.className, Expression.class, bytes, this.classLoader);Constructor<?> constructor =defineClass.getConstructor(AviatorEvaluatorInstance.class, List.class, SymbolTable.class);BaseExpression exp = (BaseExpression) constructor.newInstance(this.instance,new ArrayList<VariableMeta>(this.variables.values()), this.symbolTable);exp.setLambdaBootstraps(this.lambdaBootstraps);exp.setFuncsArgs(this.funcsArgs);exp.setSourceFile(this.sourceFile);return exp;} catch (ExpressionRuntimeException e) {throw e;} catch (Throwable e) {if (e.getCause() instanceof ExpressionRuntimeException) {throw (ExpressionRuntimeException) e.getCause();}throw new CompileExpressionErrorException("define class error", e);}}2.1.3 if脚本ASM反编译结果
if脚本的asm的解析过程已分析完成,结合上面的if具体脚本示例和源码中asm字节码生成过程,可以得到上述的if脚本示例动态生成的类如下:
1)ifBody生成的lassLambda_1684208818128_57)
public super class Script_11313134242424_59 extends ClassExpression {private final AviatorObject f0=null;private final AviatorJavaType f1=null;private final AviatorFunction f2=null;public void <init> (final AviatorEvaluatorInstance instance, final List<VariableMeta> vars,final SymbolTable symbolTable){super(instance,vars,symbolTable);f0=AviatorLong.valueOf(2);f1=new AviatorJavaType("b", symbolTable);f2=instance.getFunction("__reducer_return",symbolTable);}public final Object execute0(Env env){return RuntimeUtils.assertNotNull(f2.call(env,f1.add(f0, env))).deref(env);}
}2)elseBody生成的classambda_1684208818128_58)
public super class Script_11313134242424_60 extends ClassExpression {private final AviatorJavaType f0=null;private final AviatorFunction f1=null;public void <init> (final AviatorEvaluatorInstance instance, final List<VariableMeta> vars,final SymbolTable symbolTable){super(instance,vars,symbolTable);f0=new AviatorJavaType("c", symbolTable);f1=instance.getFunction("__reducer_return",symbolTable);}public final Object execute0(Env env){return RuntimeUtils.assertNotNull(f1.call(env,f0)).deref(env);}
}
3)if语句后面的语句生成的classambda_1684208818128_59)
public super class Script_11313134242424_61 extends ClassExpression {private final AviatorJavaType f0=null;public void <init> (final AviatorEvaluatorInstance instance, final List<VariableMeta> vars,final SymbolTable symbolTable){super(instance,vars,symbolTable);f0=new AviatorJavaType("_reducer_empty", symbolTable);}public final Object execute0(Env env){return f0.deref(env); // return null;}
}4)整个if脚本生成的class
public super class Script_11313134242424_58 extends ClassExpression {private final AviatorObject f0=null;private final AviatorJavaType f1=null;private final AviatorFunction f2=null;public void <init> (final AviatorEvaluatorInstance instance, final List<VariableMeta> vars,final SymbolTable symbolTable){super(instance,vars,symbolTable);f0=AviatorLong.valueOf(1);f1=new AviatorJavaType("a", symbolTable);f2=AviatorEvaluatorInstance.getFunction("__if_callcc",symbolTable);}public final Object execute0(Env env){RuntimeUtils.assertNotNull(f2.call(env, if(f1.compare(f0, env).booleanValue(env)){RuntimeUtils.assertNotNull(RuntimeUtils.getFunction(this.newLambda(env, "Lambda_1684208818128_57"), env).call(env));}else{RuntimeUtils.assertNotNull(RuntimeUtils.getFunction(this.newLambda(env, "Lambda_1684208818128_58"), env).call(env));},this.newLambda(env, "Lambda_1684208818128_59"))).getValue(env);}
}2.2 compiledExpression.execute执行过程
上述根据if脚本通过asm字节码最终生成ClassExpression类后,下面即传出变量集env实参进行执行,execute方法如下:
@Overridepublic Object execute(Map<String, Object> map) {if (map == null) {map = Collections.emptyMap();}Env env = genTopEnv(map);EnvProcessor envProcessor = this.instance.getEnvProcessor();if (envProcessor != null) {envProcessor.beforeExecute(env, this);}try {return executeDirectly(env);} finally {if (envProcessor != null) {envProcessor.afterExecute(env, this);}}}这里包含了EnvProcessor前置拦截和后置拦截器,下面主要分析下executeDirectly方法具体执行过程:
@Overridepublic Object executeDirectly(final Map<String, Object> env) {try {Object result = execute0((Env) env);if (RuntimeUtils.isTracedEval(env)) {RuntimeUtils.printlnTrace(env, "Result : " + result);}return result;} catch (ExpressionRuntimeException e) {throw e;} catch (Throwable t) {throw Reflector.sneakyThrow(t);}}ClassExpression的方法executeDirectly中又调用了execute0进行执行,产出结果,这里的execute0即为上面asm字节码生成部分通过asm生成的成员方法,
针对上述的if脚本示例,生成的ClassExpression子类和实现的execute0方法如下:
public super class Script_11313134242424_58 extends ClassExpression {private final AviatorObject f0=null;private final AviatorJavaType f1=null;private final AviatorFunction f2=null;public void <init> (final AviatorEvaluatorInstance instance, final List<VariableMeta> vars,final SymbolTable symbolTable){super(instance,vars,symbolTable);f0=AviatorLong.valueOf(1);f1=new AviatorJavaType("a", symbolTable);f2=AviatorEvaluatorInstance.getFunction("__if_callcc",symbolTable);}public final Object execute0(Env env){RuntimeUtils.assertNotNull(f2.call(env, if(f1.compare(f0, env).booleanValue(env)){RuntimeUtils.assertNotNull(RuntimeUtils.getFunction(this.newLambda(env, "Lambda_1684208818128_57"), env).call(env));}else{RuntimeUtils.assertNotNull(RuntimeUtils.getFunction(this.newLambda(env, "Lambda_1684208818128_58"), env).call(env));},this.newLambda(env, "Lambda_1684208818128_59"))).getValue(env);}
}这样,execute0通过传入env实参,执行的方法体即完整实现了if示例脚本的内容,最终产出if脚本计算结果;
其中在执行到某个具体if分支时,会调用newLambda函数:
public LambdaFunction newLambda(final Env env, final String name) {LambdaFunctionBootstrap bootstrap = this.lambdaBootstraps.get(name);if (bootstrap == null) {throw new ExpressionNotFoundException("Lambda " + name + " not found");}return bootstrap.newInstance(env);}newLambda函数中会调用缓存的lambdaBootstraps,获取对应的LambdaFunctionBootstrap,然后通过newInstance方法创建对应的LambdaFunction,如下:
/*** Create a lambda function.** @param env* @return*/public LambdaFunction newInstance(final Env env) {Reference<LambdaFunction> ref = null;if (this.inheritEnv && (ref = this.fnLocal.get()) != null) {LambdaFunction fn = ref.get();if (fn != null) {fn.setContext(env);return fn;} else {this.fnLocal.remove();}}LambdaFunction fn = new LambdaFunction(this.name, this.params, this.expression, env);fn.setInheritEnv(this.inheritEnv);if (this.inheritEnv) {this.fnLocal.set(new SoftReference<>(fn));}return fn;}后面继续调用LambdaFunction的call函数:
@Overridepublic AviatorObject call(final Map<String, Object> env) {try {if (this.isVariadic && !this.installed) {return variadicCall(env, true);}return AviatorRuntimeJavaType.valueOf(this.expression.executeDirectly(newEnv(env)));} finally {if (this.inheritEnv) {this.context = null;}}}call方法体中,又进一步调用了lambda脚本通过asm生成的expression,进而执行了对应分支的逻辑,至此,最终产出计算结果;
3.总结概述
1)LambdaFunctionBootstrap代表的含义
LambdaFunctionBootstrap是对if语法中ifBody,elseBody,elsifBody以及if语句之后的语句构造的模型(也包括其他的while、for、lambda语法等),是对lambda类型脚本通过asm字节码技术编译后的抽象,包含了lambda类型脚本编译后的Expression
2)LRU缓存中缓存的内容
LRU缓存的key为执行脚本本身,String类型
LRU缓存的value为Expression对象,对于ClassExpression子类对象,内部包含了解析的多个LambdaFunctionBootstrap实例,对于上述if脚本示例,即包含3个LambdaFunctionBootstrap实例

3)LambdaFunction代表的含义
在if脚本示例编译后的ClassExpression子类实例中,方法execute0中调用了newLambda方法,在传入参数env后的执行过程中,通过这里的newLambda会创建LambdaFunction对象,LambdaFunction是对lambda类型脚本在执行过程中的抽象,包含了lambda类型脚本编译后的Expression;
在LambdaFunctionBootstrap中实现了对于LambdaFunction(非线程安全)的ThreadLocal线程本地缓存,提交执行效率;
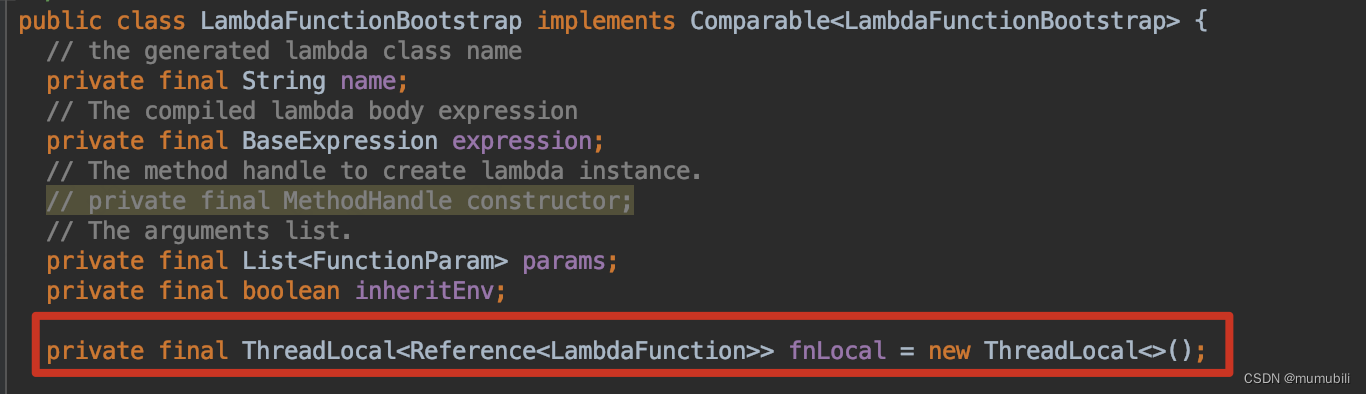
附,LambdaFunction函数作为线程本地缓存,aviator低版本(version<5.3.3)存在内存泄漏问题(JVM内存分析:Aviator低版本内存泄漏问题分析),需要升级到最新的aviator高版本