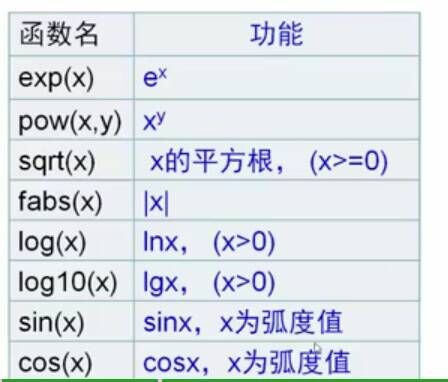
ls() 列出scapy中实现的所有网络协议
| >>> ls() ARP : ARP ASN1_Packet : None BOOTP : BOOTP CookedLinux : cooked linux DHCP : DHCP options DHCP6 : DHCPv6 Generic Message) DHCP6OptAuth : DHCP6 Option - Authentication DHCP6OptBCMCSDomains : DHCP6 Option - BCMCS Domain Name List DHCP6OptBCMCSServers : DHCP6 Option - BCMCS Addresses List DHCP6OptClientFQDN : DHCP6 Option - Client FQDN DHCP6OptClientId : DHCP6 Client Identifier Option DHCP6OptDNSDomains : DHCP6 Option - Domain Search List option DHCP6OptDNSServers : DHCP6 Option - DNS Recursive Name Server DHCP6OptElapsedTime : DHCP6 Elapsed Time Option DHCP6OptGeoConf : DHCP6OptIAAddress : DHCP6 IA Address Option (IA_TA or IA_NA suboption) DHCP6OptIAPrefix : DHCP6 Option - IA_PD Prefix option DHCP6OptIA_NA : DHCP6 Identity Association for Non-temporary Addresses Option DHCP6OptIA_PD : DHCP6 Option - Identity Association for Prefix Delegation DHCP6OptIA_TA : DHCP6 Identity Association for Temporary Addresses Option DHCP6OptIfaceId : DHCP6 Interface-Id Option DHCP6OptInfoRefreshTime : DHCP6 Option - Information Refresh Time DHCP6OptNISDomain : DHCP6 Option - NIS Domain Name DHCP6OptNISPDomain : DHCP6 Option - NIS+ Domain Name DHCP6OptNISPServers : DHCP6 Option - NIS+ Servers DHCP6OptNISServers : DHCP6 Option - NIS Servers DHCP6OptOptReq : DHCP6 Option Request Option DHCP6OptPref : DHCP6 Preference Option DHCP6OptRapidCommit : DHCP6 Rapid Commit Option DHCP6OptReconfAccept : DHCP6 Reconfigure Accept Option DHCP6OptReconfMsg : DHCP6 Reconfigure Message Option DHCP6OptRelayAgentERO : DHCP6 Option - RelayRequest Option DHCP6OptRelayMsg : DHCP6 Relay Message Option DHCP6OptRemoteID : DHCP6 Option - Relay Agent Remote-ID DHCP6OptSIPDomains : DHCP6 Option - SIP Servers Domain Name List DHCP6OptSIPServers : DHCP6 Option - SIP Servers IPv6 Address List DHCP6OptSNTPServers : DHCP6 option - SNTP Servers DHCP6OptServerId : DHCP6 Server Identifier Option …… |
lsc() 列出所有scapy中的命令或方法
| >>> lsc() arpcachepoison : Poison target's cache with (your MAC,victim's IP) couple arping : Send ARP who-has requests to determine which hosts are up bind_layers : Bind 2 layers on some specific fields' values corrupt_bits : Flip a given percentage or number of bits from a string corrupt_bytes : Corrupt a given percentage or number of bytes from a string defrag : defrag(plist) -> ([not fragmented], [defragmented], defragment : defrag(plist) -> plist defragmented as much as possible dyndns_add : Send a DNS add message to a nameserver for "name" to have a new "rdata" dyndns_del : Send a DNS delete message to a nameserver for "name" etherleak : Exploit Etherleak flaw fragment : Fragment a big IP datagram fuzz : Transform a layer into a fuzzy layer by replacing some default values by random objects getmacbyip : Return MAC address corresponding to a given IP address hexdiff : Show differences between 2 binary strings hexdump : -- hexedit : -- is_promisc : Try to guess if target is in Promisc mode. The target is provided by its ip. linehexdump : -- ls : List available layers, or infos on a given layer promiscping : Send ARP who-has requests to determine which hosts are in promiscuous mode rdpcap : Read a pcap file and return a packet list …… |
ls(pkt) 列出报文的所有字段的值
| >>> ls(a[0]) dst : DestMACField = 'a0:1d:48:b3:80:83' (None) src : SourceMACField = '00:0c:29:ac:89:2f' (None) type : XShortEnumField = 2048 (0) -- version : BitField = 4L (4) ihl : BitField = 5L (None) tos : XByteField = 16 (0) len : ShortField = 92 (None) id : ShortField = 4551 (1) flags : FlagsField = 2L (0) frag : BitField = 0L (0) ttl : ByteField = 64 (64) proto : ByteEnumField = 6 (0) chksum : XShortField = 1811 (None) src : Emph = '172.31.100.222' (None) dst : Emph = '172.31.100.149' ('127.0.0.1') options : PacketListField = [] ([]) -- sport : ShortEnumField = 22 (20) dport : ShortEnumField = 57386 (80) seq : IntField = 3315415675L (0) ack : IntField = 323931312 (0) dataofs : BitField = 5L (None) reserved : BitField = 0L (0) flags : FlagsField = 24L (2) window : ShortField = 242 (8192) chksum : XShortField = 8705 (None) urgptr : ShortField = 0 (0) options : TCPOptionsField = [] ({}) -- load : StrField = '\x95\xf6\x96q\xe1u\x1ee\x90\xf2\xa6\x97&\x1a\xc3\x96M\xb9[FhAA\x14U\xf6\xa9z\xc3H\xa7o\xd8\x8a\x1e\x07\xb8\xab\xe8\xc7\xce\x94\r\xca*c\xe0\xf9xu\x1f2' ('') |
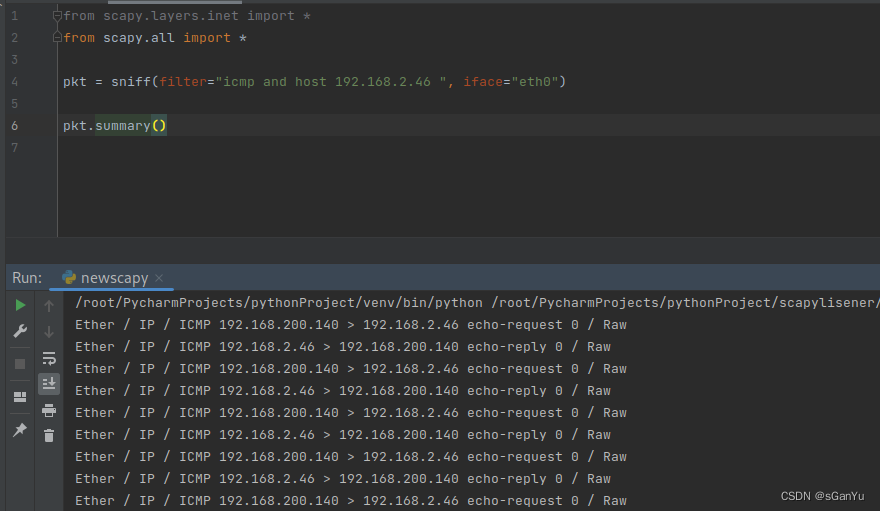
pkt.summary() 显示一个一行的报文摘要
| >>> a[0].summary() 'Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:ssh > 172.31.100.149:57386 PA / Raw' |
pkt.show() 按照层次显示报文内容
| >>> a[0].show() ###[ Ethernet ]### dst= a0:1d:48:b3:80:83 src= 00:0c:29:ac:89:2f type= 0x800 ###[ IP ]### version= 4L ihl= 5L tos= 0x10 len= 92 id= 4551 flags= DF frag= 0L ttl= 64 proto= tcp chksum= 0x713 src= 172.31.100.222 dst= 172.31.100.149 \options\ ###[ TCP ]### sport= ssh dport= 57386 seq= 3315415675L ack= 323931312 dataofs= 5L reserved= 0L flags= PA window= 242 chksum= 0x2201 urgptr= 0 options= [] ###[ Raw ]### load= '\x95\xf6\x96q\xe1u\x1ee\x90\xf2\xa6\x97&\x1a\xc3\x96M\xb9[FhAA\x14U\xf6\xa9z\xc3H\xa7o\xd8\x8a\x1e\x07\xb8\xab\xe8\xc7\xce\x94\r\xca*c\xe0\xf9xu\x1f2' |
pkt.show2() 与show方法类似,但是针对组装好的报文(例如报文的校验和已经计算完毕)
| >>> a.show2() ###[ IP ]### version= 4L ihl= 5L tos= 0x0 len= 20 id= 1 flags= frag= 0L ttl= 64 proto= hopopt chksum= 0x1d0a src= 111.111.111.111 dst= 127.0.0.1 \options\ |
构造多层数据报文
| >>> a = Ether()/IP()/TCP() >>> a <Ether type=0x800 |<IP frag=0 proto=tcp |<TCP |>>> |
组装报文
| >>> a = Ether()/IP()/TCP() >>> a <Ether type=0x800 |<IP frag=0 proto=tcp |<TCP |>>> >>> str(a) '\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x08\x00E\x00\x00(\x00\x01\x00\x00@\x06|\xcd\x7f\x00\x00\x01\x7f\x00\x00\x01\x00\x14\x00P\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00P\x02 \x00\x91|\x00\x00' |
| >>> a = IP() >>> a <IP |> >>> a.src = "111.111.111.111" >>> a <IP src=111.111.111.111 |> >>> ls(a) version : BitField = 4 (4) ihl : BitField = None (None) tos : XByteField = 0 (0) len : ShortField = None (None) id : ShortField = 1 (1) flags : FlagsField = 0 (0) frag : BitField = 0 (0) ttl : ByteField = 64 (64) proto : ByteEnumField = 0 (0) chksum : XShortField = None (None) src : Emph = '111.111.111.111' (None) dst : Emph = '127.0.0.1' ('127.0.0.1') options : PacketListField = [] ([]) >>> IP(str(a)) <IP version=4L ihl=5L tos=0x0 len=20 id=1 flags= frag=0L ttl=64 proto=hopopt chksum=0x1d0a src=111.111.111.111 dst=127.0.0.1 |> |
查看报文中某层协议的内容
| >>> a = Ether()/IP()/TCP() >>> a[IP] <IP frag=0 proto=tcp |<TCP |>> |
查看报文的16进制编码:
| >>> a=Ether()/IP(dst="www.slashdot.org")/TCP()/"GET /index.html HTTP/1.0 \n\n" >>> hexdump(a) 0000 5C DD 70 91 CA A0 00 0C 29 AC 89 2F 08 00 45 00 \.p.....)../..E. 0010 00 43 00 01 00 00 40 06 DC 63 AC 1F 64 DE D8 22 .C....@..c..d.." 0020 B5 30 00 14 00 50 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 50 02 .0...P........P. 0030 20 00 1F 61 00 00 47 45 54 20 2F 69 6E 64 65 78 ..a..GET /index 0040 2E 68 74 6D 6C 20 48 54 54 50 2F 31 2E 30 20 0A .html HTTP/1.0 . 0050 0A |
使用rdpcap读取.cap包
| >>> a = rdpcap("/root/server.cap") >>> a <server.cap: TCP:941 UDP:396 ICMP:8 Other:67> >>> a[TCP] <TCP from server.cap: TCP:941 UDP:0 ICMP:0 Other:0> >>> ctr = 0 >>> for tcppacket in a[TCP]: >>> if tcppacket[IP].src == "172.31.100.222": >>> ctr+=1 >>> ctr 19 |
pkt.command() 显示构建pkt的scapy命令
| >>> a <IP src=111.111.111.111 |> >>> a.command() "IP(src='111.111.111.111')" |
通过指定子网掩码的方式,可以一次指定多个IP
| >>> a = IP(dst="172.31.100.0/24")/ICMP() >>> send(a) WARNING: Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast. .....WARNING: Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast. .WARNING: more Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast. .WARNING: Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast. .WARNING: Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast. .WARNING: more Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast. .WARNING: Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast. .WARNING: Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast. .WARNING: more Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast. .WARNING: Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast. .WARNING: Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast. |
| >>> a = IP(dst="172.31.100.0/24")/ICMP() >>> [p for p in a] [<IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.0 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.1 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.2 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.3 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.4 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.5 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.6 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.7 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.8 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.9 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.10 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.11 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=172.31.100.12 |<ICMP |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=icmp dst=…… |
也可以通过指定多个IP,多个端口来构建数据包
例如下面的例子一共可以构建4(4src IPs) X 6(6 sports) X 2(2 dports) = 48个报文
| >>> a = IP(src="172.31.100.0/30")/TCP(sport=[(50000,50005)],dport=[80,443]) >>> [p for p in a] [<IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.0 |<TCP sport=50000 dport=http |>>, <p src=172.31.100.0 |<TCP sport=50000 dport=https |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp<TCP sport=50001 dport=http |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.0 |<Trt=https |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.0 |<TCP sport=50002 dporag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.0 |<TCP sport=50002 dport=https |>>, <IP fra72.31.100.0 |<TCP sport=50003 dport=http |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172ort=50003 dport=https |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.0 |<TCP spo |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.0 |<TCP sport=50004 dport=https oto=tcp src=172.31.100.0 |<TCP sport=50005 dport=http |>>, <IP frag=0 prot0.0 |<TCP sport=50005 dport=https |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.10000 dport=http |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.1 |<TCP sport=50000IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.1 |<TCP sport=50001 dport=http |>>, <IPsrc=172.31.100.1 |<TCP sport=50001 dport=https |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp sCP sport=50002 dport=http |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.1 |<TCP=https |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.1 |<TCP sport=50003 dport==0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.1 |<TCP sport=50003 dport=https |>>, <IP frag=.31.100.1 |<TCP sport=50004 dport=http |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.3t=50004 dport=https |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.1 |<TCP sport>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp src=172.31.100.1 |<TCP sport=50005 dport=https |>o=tcp src=172.31.100.2 |<TCP sport=50000 dport=http |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=2 |<TCP sport=50000 dport=https |>>, <IP frag=0 proto=tcp sr…… |
TCP leveltraceroute
| >>> traceroute("139.219.196.95") Begin emission: ********Finished to send 30 packets. ********* Received 17 packets, got 17 answers, remaining 13 packets 139.219.196.95:tcp80 1 172.31.100.1 11 2 172.31.99.1 11 3 172.30.1.17 11 4 172.30.1.5 11 5 106.120.78.189 11 7 59.43.77.1 11 11 42.159.128.81 11 12 42.159.128.81 11 22 139.219.196.95 SA 23 139.219.196.95 SA 24 139.219.196.95 SA 25 139.219.196.95 SA 26 139.219.196.95 SA 27 139.219.196.95 SA 28 139.219.196.95 SA 29 139.219.196.95 SA 30 139.219.196.95 SA (<Traceroute: TCP:9 UDP:0 ICMP:8 Other:0>, <Unanswered: TCP:13 UDP:0 ICMP:0 Other:0>) |
conversations()方法可以绘制出网络会话的情况(需要安装对应插件,Kali默认已安装)
>>>a = sniff()
>>>a.conversations()

summary()方法打印所有报文的summary
| >>> a = sniff() >>> a <Sniffed: TCP:16 UDP:0 ICMP:0 Other:0> >>> a.summary() Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:ssh > 172.31.100.149:57386 PA / Raw Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59163 RA Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59163 RA Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59163 RA Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59164 RA Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59164 RA Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59164 RA Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59165 RA …… |
nsummary()方法与summary()类似,只不过多打印出报文序号
| 0000 >>> a.nsummary() 0000 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:ssh > 172.31.100.149:57386 PA / Raw 0001 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59163 RA 0002 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59163 RA 0003 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59163 RA 0004 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59164 RA 0005 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59164 RA 0006 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59164 RA 0007 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59165 RA 0008 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59165 RA 0009 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59165 RA …… |
hexdump()打印出所有报文的16进制编码
| >>> a.hexdump() 0000 00:54:41.301614 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:ssh > 172.31.100.149:57386 PA / Raw 0000 A0 1D 48 B3 80 83 00 0C 29 AC 89 2F 08 00 45 10 ..H.....)../..E. 0010 00 5C 1A 4A 40 00 40 06 FE 8F AC 1F 64 DE AC 1F .\.J@.@.....d... 0020 64 95 00 16 E0 2A C5 AC BD CB 13 4F 85 64 50 18 d....*.....O.dP. 0030 00 F2 22 01 00 00 2A 54 2E E1 3B 1D F4 C3 19 24 .."...*T..;....$ 0040 6D 33 CF 2C 7A EA 8C 0F A6 E7 6C 97 71 34 2B CB m3.,z.....l.q4+. 0050 36 87 64 FC 40 C6 3C AC 89 16 7C BA 25 FA BC 15 6.d.@.<...|.%... 0060 C4 6E 1D 7A 62 EE A2 F4 D7 96 .n.zb..... 0001 00:54:53.204504 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59163 RA 0000 A0 1D 48 B3 80 83 00 0C 29 AC 89 2F 08 00 45 00 ..H.....)../..E. 0010 00 28 74 25 40 00 40 06 A4 F8 AC 1F 64 DE AC 1F .(t%@.@.....d... 0020 64 95 00 50 E7 1B 00 00 00 00 DB A5 F5 AE 50 14 d..P..........P. 0030 00 00 D5 5D 00 00 ...].. 0002 00:54:53.718446 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149:59163 RA 0000 A0 1D 48 B3 80 83 00 0C 29 AC 89 2F 08 00 45 00 ..H.....)../..E. 0010 00 28 74 68 40 00 40 06 A4 B5 AC 1F 64 DE AC 1F .(th@.@.....d... 0020 64 95 00 50 E7 1B 00 00 00 00 DB A5 F5 AE 50 14 d..P..........P. 0030 00 00 D5 5D 00 00 ...].. 0003 00:54:54.220690 Ether / IP / TCP 172.31.100.222:http > 172.31.100.149: …… |
filter()用一个lambda表达式对报文进行过滤(不会对原报文集合进行修改)
| >>> a = sniff() >>> a <Sniffed: TCP:147 UDP:219 ICMP:9 Other:47> >>> b = a[IP].filter(lambda x:x[IP].src=="172.31.100.149") >>> b <filtered IP from Sniffed: TCP:72 UDP:2 ICMP:5 Other:0> >>> c = a[TCP].filter(lambda x:x[TCP].dport==80) >>> c <filtered TCP from Sniffed: TCP:17 UDP:0 ICMP:0 Other:0> |