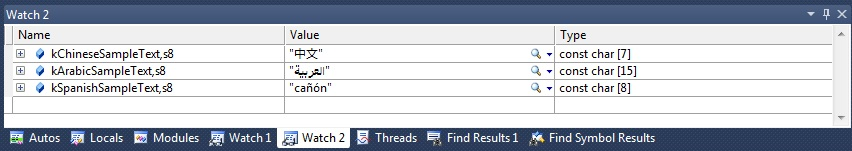
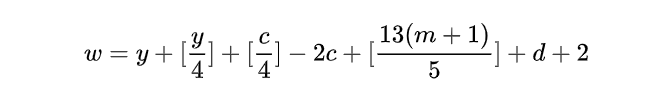56帧时

63帧时
/**
比平均背景法性能更加良好的方法,codeBook模型实现背景减除
核心代码详细解析和实现 by zcube
*/
/************************************************************************/
/* A few more thoughts on codebook models
In general, the codebook method works quite well across a wide number of conditions,
and it is relatively quick to train and to run. It doesn’t deal well with varying patterns of
light — such as morning, noon, and evening sunshine — or with someone turning lights
on or off indoors. This type of global variability can be taken into account by using
several different codebook models, one for each condition, and then allowing the condition
to control which model is active. */
/************************************************************************/#include "stdafx.h"
#include <cv.h>
#include <highgui.h>
#include <cxcore.h>#define CHANNELS 3
// 设置处理的图像通道数,要求小于等于图像本身的通道数///
// 下面为码本码元的数据结构
// 处理图像时每个像素对应一个码本,每个码本中可有若干个码元
// 当涉及一个新领域,通常会遇到一些奇怪的名词,不要被这些名词吓坏,其实思路都是简单的
typedef struct ce {uchar learnHigh[CHANNELS]; // High side threshold for learning// 此码元各通道的阀值上限(学习界限)uchar learnLow[CHANNELS]; // Low side threshold for learning// 此码元各通道的阀值下限// 学习过程中如果一个新像素各通道值x[i],均有 learnLow[i]<=x[i]<=learnHigh[i],则该像素可合并于此码元uchar max[CHANNELS]; // High side of box boundary// 属于此码元的像素中各通道的最大值uchar min[CHANNELS]; // Low side of box boundary// 属于此码元的像素中各通道的最小值int t_last_update; // This is book keeping to allow us to kill stale entries// 此码元最后一次更新的时间,每一帧为一个单位时间,用于计算staleint stale; // max negative run (biggest period of inactivity)// 此码元最长不更新时间,用于删除规定时间不更新的码元,精简码本
} code_element; // 码元的数据结构typedef struct code_book {code_element **cb;// 码元的二维指针,理解为指向码元指针数组的指针,使得添加码元时不需要来回复制码元,只需要简单的指针赋值即可int numEntries;// 此码本中码元的数目int t; // count every access// 此码本现在的时间,一帧为一个时间单位
} codeBook; // 码本的数据结构///
// int updateCodeBook(uchar *p, codeBook &c, unsigned cbBounds)
// Updates the codebook entry with a new data point
//
// p Pointer to a YUV pixel
// c Codebook for this pixel
// cbBounds Learning bounds for codebook (Rule of thumb: 10)
// numChannels Number of color channels we're learning
//
// NOTES:
// cvBounds must be of size cvBounds[numChannels]
//
// RETURN
// codebook index
int cvupdateCodeBook(uchar *p, codeBook &c, unsigned *cbBounds, int numChannels)
{if(c.numEntries == 0) c.t = 0;// 码本中码元为零时初始化时间为0c.t += 1; // Record learning event// 每调用一次加一,即每一帧图像加一//SET HIGH AND LOW BOUNDSint n;unsigned int high[3],low[3];for (n=0; n<numChannels; n++){high[n] = *(p+n) + *(cbBounds+n);// *(p+n) 和 p[n] 结果等价,经试验*(p+n) 速度更快if(high[n] > 255) high[n] = 255;low[n] = *(p+n)-*(cbBounds+n);if(low[n] < 0) low[n] = 0;// 用p 所指像素通道数据,加减cbBonds中数值,作为此像素阀值的上下限}//SEE IF THIS FITS AN EXISTING CODEWORDint matchChannel; int i;for (i=0; i<c.numEntries; i++){// 遍历此码本每个码元,测试p像素是否满足其中之一matchChannel = 0;for (n=0; n<numChannels; n++)//遍历每个通道{if((c.cb[i]->learnLow[n] <= *(p+n)) && (*(p+n) <= c.cb[i]->learnHigh[n])) //Found an entry for this channel// 如果p 像素通道数据在该码元阀值上下限之间{ matchChannel++;}}if (matchChannel == numChannels) // If an entry was found over all channels// 如果p 像素各通道都满足上面条件{c.cb[i]->t_last_update = c.t;// 更新该码元时间为当前时间// adjust this codeword for the first channelfor (n=0; n<numChannels; n++)//调整该码元各通道最大最小值{if (c.cb[i]->max[n] < *(p+n))c.cb[i]->max[n] = *(p+n);else if (c.cb[i]->min[n] > *(p+n))c.cb[i]->min[n] = *(p+n);}break;}}// ENTER A NEW CODE WORD IF NEEDEDif(i == c.numEntries) // No existing code word found, make a new one// p 像素不满足此码本中任何一个码元,下面创建一个新码元{code_element **foo = new code_element* [c.numEntries+1];// 申请c.numEntries+1 个指向码元的指针for(int ii=0; ii<c.numEntries; ii++)// 将前c.numEntries 个指针指向已存在的每个码元foo[ii] = c.cb[ii];foo[c.numEntries] = new code_element;// 申请一个新的码元if(c.numEntries) delete [] c.cb;// 删除c.cb 指针数组c.cb = foo;// 把foo 头指针赋给c.cbfor(n=0; n<numChannels; n++)// 更新新码元各通道数据{c.cb[c.numEntries]->learnHigh[n] = high[n];c.cb[c.numEntries]->learnLow[n] = low[n];c.cb[c.numEntries]->max[n] = *(p+n);c.cb[c.numEntries]->min[n] = *(p+n);}c.cb[c.numEntries]->t_last_update = c.t;c.cb[c.numEntries]->stale = 0;c.numEntries += 1;}// OVERHEAD TO TRACK POTENTIAL STALE ENTRIESfor(int s=0; s<c.numEntries; s++){// This garbage is to track which codebook entries are going staleint negRun = c.t - c.cb[s]->t_last_update;// 计算该码元的不更新时间if(c.cb[s]->stale < negRun) c.cb[s]->stale = negRun;}// SLOWLY ADJUST LEARNING BOUNDSfor(n=0; n<numChannels; n++)// 如果像素通道数据在高低阀值范围内,但在码元阀值之外,则缓慢调整此码元学习界限{if(c.cb[i]->learnHigh[n] < high[n]) c.cb[i]->learnHigh[n] += 1;if(c.cb[i]->learnLow[n] > low[n]) c.cb[i]->learnLow[n] -= 1;}return(i);
}///
// uchar cvbackgroundDiff(uchar *p, codeBook &c, int minMod, int maxMod)
// Given a pixel and a code book, determine if the pixel is covered by the codebook
//
// p pixel pointer (YUV interleaved)
// c codebook reference
// numChannels Number of channels we are testing
// maxMod Add this (possibly negative) number onto max level when code_element determining if new pixel is foreground
// minMod Subract this (possible negative) number from min level code_element when determining if pixel is foreground
//
// NOTES:
// minMod and maxMod must have length numChannels, e.g. 3 channels => minMod[3], maxMod[3].
//
// Return
// 0 => background, 255 => foreground
uchar cvbackgroundDiff(uchar *p, codeBook &c, int numChannels, int *minMod, int *maxMod)
{// 下面步骤和背景学习中查找码元如出一辙int matchChannel;//SEE IF THIS FITS AN EXISTING CODEWORDint i;for (i=0; i<c.numEntries; i++){matchChannel = 0;for (int n=0; n<numChannels; n++){if ((c.cb[i]->min[n] - minMod[n] <= *(p+n)) && (*(p+n) <= c.cb[i]->max[n] + maxMod[n]))matchChannel++; //Found an entry for this channelelsebreak;}if (matchChannel == numChannels)break; //Found an entry that matched all channels}if(i == c.numEntries) // p像素各通道值满足码本中其中一个码元,则返回白色return(255);return(0);
}//UTILITES/
/
//int clearStaleEntries(codeBook &c)
// After you've learned for some period of time, periodically call this to clear out stale codebook entries
//
//c Codebook to clean up
//
// Return
// number of entries cleared
int cvclearStaleEntries(codeBook &c)
{int staleThresh = c.t >> 1; // 设定刷新时间int *keep = new int [c.numEntries]; // 申请一个标记数组int keepCnt = 0; // 记录不删除码元数目//SEE WHICH CODEBOOK ENTRIES ARE TOO STALEfor (int i=0; i<c.numEntries; i++)// 遍历码本中每个码元{if (c.cb[i]->stale > staleThresh) // 如码元中的不更新时间大于设定的刷新时间,则标记为删除keep[i] = 0; //Mark for destructionelse{keep[i] = 1; //Mark to keepkeepCnt += 1;}}// KEEP ONLY THE GOODc.t = 0; //Full reset on stale tracking// 码本时间清零code_element **foo = new code_element* [keepCnt];// 申请大小为keepCnt 的码元指针数组int k=0;for(int ii=0; ii<c.numEntries; ii++){if(keep[ii]){foo[k] = c.cb[ii];foo[k]->stale = 0; //We have to refresh these entries for next clearStalefoo[k]->t_last_update = 0;k++;}}//CLEAN UPdelete [] keep;delete [] c.cb;c.cb = foo;// 把foo 头指针地址赋给c.cb int numCleared = c.numEntries - keepCnt;// 被清理的码元个数c.numEntries = keepCnt;// 剩余的码元地址return(numCleared);
}int main()
{///// 需要使用的变量CvCapture* capture;IplImage* rawImage;IplImage* yuvImage;IplImage* ImaskCodeBook;codeBook* cB;unsigned cbBounds[CHANNELS];uchar* pColor; //YUV pointerint imageLen;int nChannels = CHANNELS;int minMod[CHANNELS];int maxMod[CHANNELS];//// 初始化各变量cvNamedWindow("Raw");cvNamedWindow("CodeBook");capture = cvCreateFileCapture("tree.avi");if (!capture){printf("Couldn't open the capture!");return -1;}rawImage = cvQueryFrame(capture);yuvImage = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(rawImage), 8, 3); // 给yuvImage 分配一个和rawImage 尺寸相同,8位3通道图像ImaskCodeBook = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(rawImage), IPL_DEPTH_8U, 1);// 为ImaskCodeBook 分配一个和rawImage 尺寸相同,8位单通道图像cvSet(ImaskCodeBook, cvScalar(255));// 设置单通道数组所有元素为255,即初始化为白色图像imageLen = rawImage->width * rawImage->height;cB = new codeBook[imageLen];// 得到与图像像素数目长度一样的一组码本,以便对每个像素进行处理for (int i=0; i<imageLen; i++)// 初始化每个码元数目为0cB[i].numEntries = 0;for (int i=0; i<nChannels; i++){cbBounds[i] = 10; // 用于确定码元各通道的阀值minMod[i] = 20; // 用于背景差分函数中maxMod[i] = 20; // 调整其值以达到最好的分割}//// 开始处理视频每一帧图像for (int i=0;;i++){cvCvtColor(rawImage, yuvImage, CV_BGR2YCrCb);// 色彩空间转换,将rawImage 转换到YUV色彩空间,输出到yuvImage// 即使不转换效果依然很好// yuvImage = cvCloneImage(rawImage);if (i <= 30)// 30帧内进行背景学习{pColor = (uchar *)(yuvImage->imageData);// 指向yuvImage 图像的通道数据for (int c=0; c<imageLen; c++){cvupdateCodeBook(pColor, cB[c], cbBounds, nChannels);// 对每个像素,调用此函数,捕捉背景中相关变化图像pColor += 3;// 3 通道图像, 指向下一个像素通道数据}if (i == 30)// 到30 帧时调用下面函数,删除码本中陈旧的码元{for (int c=0; c<imageLen; c++)cvclearStaleEntries(cB[c]);}}else{uchar maskPixelCodeBook;pColor = (uchar *)((yuvImage)->imageData); //3 channel yuv imageuchar *pMask = (uchar *)((ImaskCodeBook)->imageData); //1 channel image// 指向ImaskCodeBook 通道数据序列的首元素for(int c=0; c<imageLen; c++){maskPixelCodeBook = cvbackgroundDiff(pColor, cB[c], nChannels, minMod, maxMod);// 我看到这儿时豁然开朗,开始理解了codeBook 呵呵*pMask++ = maskPixelCodeBook;pColor += 3;// pColor 指向的是3通道图像}}if (!(rawImage = cvQueryFrame(capture)))break;cvShowImage("Raw", rawImage);cvShowImage("CodeBook", ImaskCodeBook);if (cvWaitKey(30) == 27)break;if (i == 56 || i == 63)cvWaitKey();} cvReleaseCapture(&capture);if (yuvImage)cvReleaseImage(&yuvImage);if(ImaskCodeBook) cvReleaseImage(&ImaskCodeBook);cvDestroyAllWindows();delete [] cB;return 0;
}