app性能测试:(三)流量监控
下面对流量监控进行分析:
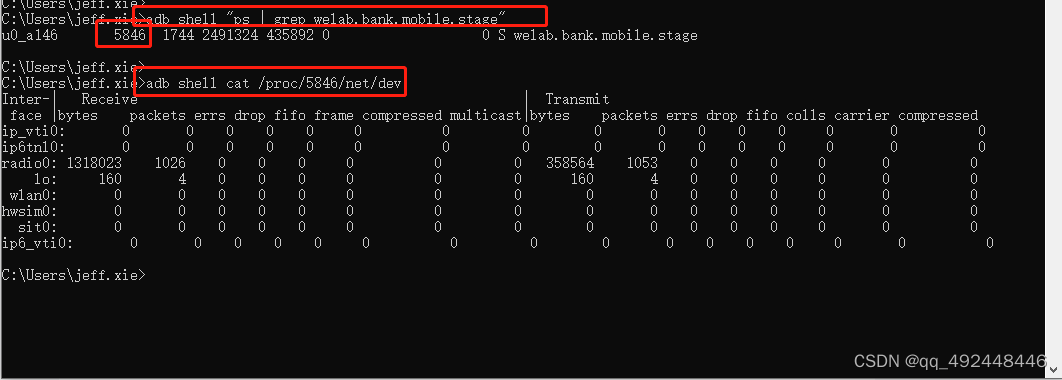
- 获取进程ID指令
adb shell “ps | grep 包名” - 获取进程ID流量
- adb shell cat /proc/pid/net/dev
pid换成第一步获取到的进程ID

receive是指当前进程接收的数据,transmit是指当前进程发出请求的数据,流量是这两者之和
结果里面的wlan0代表wifi 上传下载量标识! 上传下载量单位是字节可以/1024换算成KB
这里可以看到下载的字节数 、数据包 和 发送的字节数 、数据包
rmnet_data0:代表移动网络
wlan0这些值初始化0 打开手机飞行模式再关掉就清0了
监控代码:
#/usr/bin/python
#encoding:utf-8
import csv
import os
import string
import time#控制类
class Controller(object):def __init__(self, count):#定义测试的次数self.counter = count#定义收集数据的数组self.alldata = [("timestamp", "traffic")]#单次测试过程def testprocess(self):#执行获取进程的命令result = os.popen("adb shell \"ps | grep com.zahd.agriculturaltraceability.debug\"")print()#获取进程IDpid = result.readlines()[0].split(" ")[3]#获取进程ID使用的流量traffic = os.popen("adb shell cat /proc/"+pid+"/net/dev")for line in traffic:if "wlan0" in line:#将所有空格换成#line = "#".join(line.split())#按#号拆分,获取收到和发出的流量receive = line.split("#")[1]transmit = line.split("#")[9]elif "rmnet_data0" in line:# 将所有空格换成#line = "#".join(line.split())# 按#号拆分,获取收到和发出的流量receive2 = line.split("#")[1]transmit2 = line.split("#")[9]#计算所有流量的之和alltraffic = int(receive) + int(transmit) + int(receive2) + int(transmit2)#按KB计算流量值alltraffic = alltraffic/1024#获取当前时间currenttime = self.getCurrentTime()#将获取到的数据存到数组中self.alldata.append((currenttime, alltraffic))#多次测试过程控制def run(self):while self.counter >0:self.testprocess()self.counter = self.counter - 1#每5秒钟采集一次数据time.sleep(5)#获取当前的时间戳def getCurrentTime(self):currentTime = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())return currentTime#数据的存储def SaveDataToCSV(self):csvfile = open('traffic.csv', 'w')writer = csv.writer(csvfile)writer.writerows(self.alldata)csvfile.close()if __name__ == "__main__":controller = Controller(5)controller.run()controller.SaveDataToCSV()