1.异常测试
package com.testngdemo;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class test {
@Test(expectedExceptions = ArithmeticException.class )
public void divisionWithException() {
int i = 1 / 0;
System.out.println("After division the value of i is :"+ i);
}
}
testng.xml配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="Suite1">
<test name="test1">
<classes>
<class name="com.testngdemo.test"/>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
运行结果:

2.忽略测试
package com.testngdemo;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class test {
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("这是第一个测试用例");
}
@Test(enabled = false )
public void test2(){
System.out.println("这是第二个测试用例");
}
}
testng.xml配置和异常测试一样;
运行结果:

3.超时测试
package com.testngdemo;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class test {
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("这是第一个测试用例");
}
@Test(timeOut = 2000 )
public void test2()throws Exception{
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("这是第二个测试用例");
}
}
testng.xml配置和异常测试一样;
运行结果:

4.优先级测试
使用@Test的priority属性可支持设置用例的优先级。如果不带这个属性,默认priority是等于0,而且priority值越小,优先级越高;
package com.testngdemo;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class test {
public class TestNG_Demo2 {
@Test(priority = 2)
public void test1(){
System.out.println("test1");
}
@Test(priority = 4)
public void test2(){
System.out.println("test2");
}
@Test(priority = 1)
public void test3(){
System.out.println("test3");
}
@Test
public void test4(){
System.out.println("test4");
}
}
}
testng.xml配置和异常测试一样;
运行结果:

5.分组测试
package com.testngdemo;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class test {
public class TestNG_Demo2 {
@Test(groups = {"Fucntion","API"})
public void test01(){
System.out.println("API Testing and Function testing");
}
@Test(groups = {"API"})
public void test02(){
System.out.println("API Testing");
}
@Test(groups = {"Fucntion"})
public void test03(){
System.out.println("Function testing");
}
@Test
public void test04(){
System.out.println("not in API and Function testing");
}
}
}
通过testng.xml配置只测试包含API的分组:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="Suite1">
<test name="test1">
<groups>
<run>
<include name="API "/>
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="com.testngdemo.test"/>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
运行结果如下:

通过testng.xml配置只测试API和Fucntion的分组:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="Suite1">
<test name="test1">
<groups>
<run>
<include name="API "/>
<include name="Fucntion "/>
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="com.testngdemo.test"/>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
运行结果如下:

通过testng.xml配置测试不含API和Fucntion的分组:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="Suite1">
<test name="test1">
<groups>
<run>
<exclude name="API"/>
<exclude name="Fucntion"/>
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="com.testngdemo.test"/>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
运行结果:

通过testng.xml配置通过自定义分组管理API和Fucntion的分组:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="Suite1">
<test name="test1">
<groups>
<define name="all">
<include name="API"/>
<include name="Fucntion"/>
</define>
<run>
<include name="all"/>
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="com.testngdemo.test"/>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
运行结果:

6.依赖测试
硬依赖:所有的依赖方法必须成功执行,才会执行接下来的方法,如果其中有一个依赖的方法失败了,那么接下来的方法是不会被执行,会默认标记跳过(skip)。
package com.testngdemo;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class test {
public class TestNG_Demo2 {
@Test(dependsOnMethods = "tomcatServiceIsDown")
public void restartTomcatService(){
System.out.println("Restart the tomcat server when it is down!");
}
@Test
public void tomcatServiceIsDown(){
System.out.println("tomcat service is down!");
}
}
}
软依赖:不管依赖的方法是否成功执行,接下来的方法都可以运行。软依赖的实现是在@Test中添加属性alwaysRun=true来实现。
package com.testngdemo;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class test {
public class TestNG_Demo2 {
@Test(groups = {"tomcat"})
public void restartTomcatService(){
System.out.println("Restart the tomcat server when it is down!");
}
@Test(groups = {"tomcat"})
public void tomcatServiceIsDown(){
System.out.println("tomcat service is down!");
Assert.assertTrue(10==11);
}
@Test(dependsOnGroups = {"tomcat"}, alwaysRun = true)
public void startAppServer(){
System.out.println("Start App service");
}
}
}
通过testng.xml配置依赖暂忽略;
7.附@Test注解相关属性
| 编号 | 属性名称 | 属性作用 | 备注 |
| 1 | alwaysRun | 如果设置为true,则此测试方法将始终运行,即使它取决于失败的方法。 |
|
| 2 | dataProvider | 该测试方法的数据提供者的名称。 |
|
| 3 | dataProviderClass | 在哪里寻找数据提供者的类。 |
|
| 4 | dependsOnGroups | 此方法所依赖的组列表。 |
|
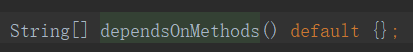
| 5 | dependsOnMethods | 此方法所依赖的方法列表。 |
|
| 6 | description | 此方法的说明。 |
|
| 7 | enabled | 是否启用了此类/方法上的方法。 |
|
| 8 | expectedExceptions | 预期测试方法将引发的异常列表。 |
|
| 9 | expectedExceptionsMessageRegExp | 如果指定了ExpectedExceptions,则其消息必须与在此属性中指定的正则表达式匹配。 |
|
| 10 | groups | 此类/方法所属的组的列表。 |
|
| 11 | ignoreMissingDependencies | 如果设置为true,则即使缺少或排除了它依赖的方法,该测试也将运行。 |
|
| 12 | invocationCount | 应该调用此方法的次数。 |
|
| 13 | invocationTimeOut | 此测试方法的调用总数应采用的最大毫秒数。 |
|
| 14 | parameters | 不推荐使用 | 建议使用Use @Parameters |
| 15 | priority | 调度优先级。 |
|
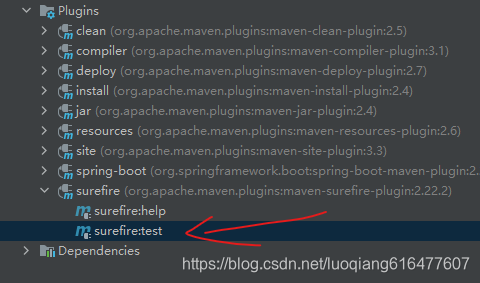
| 16 | retryAnalyzer | 如果应重试测试,应调用该类的名称以进行测试。 |
|
| 17 | sequential | 不推荐使用 | 建议使用单线程 |
| 18 | singleThreaded | 如果设置为true,则即使当前正在使用parallel =“ true”运行测试,也保证该测试类上的所有方法都可以在同一线程中运行。 |
|
| 19 | skipFailedInvocations | 如果将true和invocationCount指定为为1,则失败后的所有调用都将被标记为SKIP而不是FAIL。 |
|
| 20 | successPercentage | 此方法预期成功的百分比。 |
|
| 21 | suiteName | 该测试类应放入的套件名称。 |
|
| 22 | testName | 应该放置该测试类的测试的名称 |
|
| 23 | threadPoolSize | 此方法的线程池的大小。 |
|
| 24 | timeOut | 此测试应花费的最大毫秒数。 |
|