文章目录
- Time 2021-12-26——Hireek
- 什么是线程
- 线程的等待和通知
- 等待线程终止的join方法
- 让线程睡眠的sleep方法
- 让出CPU执行权的yield方法
- 线程中断
- demo
- 线程上下文切换
- 线程死锁
- 什么是死锁
- 如何避免死锁
- 用户线程与守护线程
- ThreadLocal
- introduction,下文只阐述重要的set方法。
- Entry(ThreadLocal->弱应用)
- public void set(T value)
- private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value, int staleSlot)
- 内存溢出问题
- ThreadLocal不支持继承性
- 先看一下demo测试
- lnheritableThreadLocal
Time 2021-12-26——Hireek
什么是线程
引用自深入理解JVM第三版,
线程是比进程更轻量级的调度执行单位,线程的引入,可以把一个进程的资源分配和 执行调度分开,各个线程既可以共享进程资源(内存地址、文件I/O等),又可以独立调度。目前线程是Java里面进行处理器资源调度的最基本单位,不过如果日后Loom项目能成功为Java引入纤程 (Fiber)的话,可能就会改变这一点。
线程的等待和通知
之后整理synchronized再进行补充,暂不展开。
等待线程终止的join方法
等待该线程死亡(执行完毕),阻塞当前线程。
// eg: a.join();/*** Waits for this thread to die.** <p> An invocation of this method behaves in exactly the same* way as the invocation** <blockquote>* {@linkplain #join(long) join}{@code (0)}* </blockquote>** @throws InterruptedException* if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The* <i>interrupted status</i> of the current thread is* cleared when this exception is thrown.*/public final void join() throws InterruptedException {join(0); // a.join(),阻塞当前线程(正在运行的线程),等待a线程死亡。}/*** Waits at most {@code millis} milliseconds for this thread to* die. A timeout of {@code 0} means to wait forever.** <p> This implementation uses a loop of {@code this.wait} calls* conditioned on {@code this.isAlive}. As a thread terminates the* {@code this.notifyAll} method is invoked. It is recommended that* applications not use {@code wait}, {@code notify}, or* {@code notifyAll} on {@code Thread} instances.** @param millis* the time to wait in milliseconds** @throws IllegalArgumentException* if the value of {@code millis} is negative** @throws InterruptedException* if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The* <i>interrupted status</i> of the current thread is* cleared when this exception is thrown.*/public final synchronized void join(long millis) // synchronizedthrows InterruptedException {long base = System.currentTimeMillis();long now = 0;if (millis < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");}if (millis == 0) {while (isAlive()) { // 循环判断a线程是否存活,防止虚假唤醒(别的地方调用了notify/notifyAll)。wait(0); // 获取监视器锁等待}} else {while (isAlive()) {long delay = millis - now;if (delay <= 0) {break;}wait(delay);now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;}}}
跟thread.cpp源码。
// a线程退出时,会调用exit方法,执行ensure_join方法。
// For any new cleanup additions, please check to see if they need to be applied to
// cleanup_failed_attach_current_thread as well.
void JavaThread::exit(bool destroy_vm, ExitType exit_type) {//...// Notify waiters on thread object. This has to be done after exit() is called// on the thread (if the thread is the last thread in a daemon ThreadGroup the// group should have the destroyed bit set before waiters are notified).ensure_join(this);//...
}
static void ensure_join(JavaThread* thread) {// We do not need to grab the Threads_lock, since we are operating on ourself.Handle threadObj(thread, thread->threadObj());assert(threadObj.not_null(), "java thread object must exist");ObjectLocker lock(threadObj, thread);// Ignore pending exception (ThreadDeath), since we are exiting anywaythread->clear_pending_exception();// Thread is exiting. So set thread_status field in java.lang.Thread class to TERMINATED.java_lang_Thread::set_thread_status(threadObj(), java_lang_Thread::TERMINATED);// Clear the native thread instance - this makes isAlive return false and allows the join()// to complete once we've done the notify_all belowjava_lang_Thread::set_thread(threadObj(), NULL);lock.notify_all(thread); // 唤醒阻塞的线程。// Ignore pending exception (ThreadDeath), since we are exiting anywaythread->clear_pending_exception();
}
让线程睡眠的sleep方法
/*** Causes the currently executing thread to sleep (temporarily cease* execution) for the specified number of milliseconds, subject to* the precision and accuracy of system timers and schedulers. The thread* does not lose ownership of any monitors. 让线程暂时休眠,不会失去任何监视器的所有权。** @param millis* the length of time to sleep in milliseconds** @throws IllegalArgumentException* if the value of {@code millis} is negative** @throws InterruptedException* if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The* <i>interrupted status</i> of the current thread is* cleared when this exception is thrown. 如果被中断,则清除中断标志,并抛出中断异常。对应下文hotspot源码*/
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
对应hotspot JNI源码
// jvm.cpp
JVM_ENTRY(void, JVM_Sleep(JNIEnv* env, jclass threadClass, jlong millis))JVMWrapper("JVM_Sleep");if (millis < 0) {THROW_MSG(vmSymbols::java_lang_IllegalArgumentException(), "timeout value is negative");}if (Thread::is_interrupted (THREAD, true) && !HAS_PENDING_EXCEPTION) {THROW_MSG(vmSymbols::java_lang_InterruptedException(), "sleep interrupted");}// Save current thread state and restore it at the end of this block.// And set new thread state to SLEEPING.JavaThreadSleepState jtss(thread);HOTSPOT_THREAD_SLEEP_BEGIN(millis);EventThreadSleep event;if (millis == 0) {os::naked_yield();} else {ThreadState old_state = thread->osthread()->get_state();thread->osthread()->set_state(SLEEPING);if (os::sleep(thread, millis, true) == OS_INTRPT) {// An asynchronous exception (e.g., ThreadDeathException) could have been thrown on// us while we were sleeping. We do not overwrite those.if (!HAS_PENDING_EXCEPTION) {if (event.should_commit()) {post_thread_sleep_event(&event, millis);}HOTSPOT_THREAD_SLEEP_END(1);// TODO-FIXME: THROW_MSG returns which means we will not call set_state()// to properly restore the thread state. That's likely wrong.THROW_MSG(vmSymbols::java_lang_InterruptedException(), "sleep interrupted");}}thread->osthread()->set_state(old_state);}if (event.should_commit()) {post_thread_sleep_event(&event, millis);}HOTSPOT_THREAD_SLEEP_END(0);
JVM_END// ————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————// os_posix.cppint os::sleep(Thread* thread, jlong millis, bool interruptible) {assert(thread == Thread::current(), "thread consistency check");ParkEvent * const slp = thread->_SleepEvent ;slp->reset() ;OrderAccess::fence() ;if (interruptible) {jlong prevtime = javaTimeNanos();for (;;) {// 循环check中断标志if (os::is_interrupted(thread, true)) {return OS_INTRPT;}jlong newtime = javaTimeNanos();if (newtime - prevtime < 0) {// time moving backwards, should only happen if no monotonic clock// not a guarantee() because JVM should not abort on kernel/glibc bugsassert(!os::supports_monotonic_clock(), "unexpected time moving backwards detected in os::sleep(interruptible)");} else {millis -= (newtime - prevtime) / NANOSECS_PER_MILLISEC;}if (millis <= 0) {return OS_OK;}prevtime = newtime;{assert(thread->is_Java_thread(), "sanity check");JavaThread *jt = (JavaThread *) thread;ThreadBlockInVM tbivm(jt);OSThreadWaitState osts(jt->osthread(), false /* not Object.wait() */);jt->set_suspend_equivalent();// cleared by handle_special_suspend_equivalent_condition() or// java_suspend_self() via check_and_wait_while_suspended()slp->park(millis);// were we externally suspended while we were waiting?jt->check_and_wait_while_suspended();}}} else {OSThreadWaitState osts(thread->osthread(), false /* not Object.wait() */);jlong prevtime = javaTimeNanos();for (;;) {// It'd be nice to avoid the back-to-back javaTimeNanos() calls on// the 1st iteration ...jlong newtime = javaTimeNanos();if (newtime - prevtime < 0) {// time moving backwards, should only happen if no monotonic clock// not a guarantee() because JVM should not abort on kernel/glibc bugsassert(!os::supports_monotonic_clock(), "unexpected time moving backwards detected on os::sleep(!interruptible)");} else {millis -= (newtime - prevtime) / NANOSECS_PER_MILLISEC;}if (millis <= 0) break ;prevtime = newtime;slp->park(millis);}return OS_OK ;}
}
让出CPU执行权的yield方法
yield,屈服,放弃
/*** A hint to the scheduler that the current thread is willing to yield* its current use of a processor. The scheduler is free to ignore this* hint.** <p> Yield is a heuristic attempt to improve relative progression* between threads that would otherwise over-utilise a CPU. Its use* should be combined with detailed profiling and benchmarking to* ensure that it actually has the desired effect.** <p> It is rarely appropriate to use this method. It may be useful* for debugging or testing purposes, where it may help to reproduce* bugs due to race conditions. It may also be useful when designing* concurrency control constructs such as the ones in the* {@link java.util.concurrent.locks} package.*/
public static native void yield(); // 放弃当前对cpu的占用。使用场景很少。
// use
if (Thread.activeCount() > 1) {Thread.yield();
}
cpp代码
JVM_ENTRY(void, JVM_Yield(JNIEnv *env, jclass threadClass))JVMWrapper("JVM_Yield");
if (os::dont_yield()) return;
HOTSPOT_THREAD_YIELD();
os::naked_yield();
JVM_END
// linux
void os::naked_yield() {sched_yield(); // 放弃CPU使用权,加入到同等优先级队列的末尾
}
线程中断
线程中断是一种线程间的协作模式。
demo
package test;import java.util.Arrays;/*** 描述** @author Hireek* @date 2021/12/26 14:50*/
public class InterruptDemo extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(e.getStackTrace()));System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {System.out.println("被中断");}}}public static void main(String[] args) {InterruptDemo thread = new InterruptDemo();thread.start();thread.interrupt();}
}
/* 运行输出
[java.lang.Thread.sleep(Native Method), test.InterruptDemo.run(InterruptDemo.java:18)]
false
被中断
[java.lang.Thread.sleep(Native Method), test.InterruptDemo.run(InterruptDemo.java:18)]
false
被中断
*/
先来查看Thread类的三个有关中断的方法。
/*** Interrupts this thread.** <p> Unless the current thread is interrupting itself, which is* always permitted, the {@link #checkAccess() checkAccess} method* of this thread is invoked, which may cause a {@link* SecurityException} to be thrown.** <p> If this thread is blocked in an invocation of the {@link* Object#wait() wait()}, {@link Object#wait(long) wait(long)}, or {@link* Object#wait(long, int) wait(long, int)} methods of the {@link Object}* class, or of the {@link #join()}, {@link #join(long)}, {@link* #join(long, int)}, {@link #sleep(long)}, or {@link #sleep(long, int)},* methods of this class, then its interrupt status will be cleared and it* will receive an {@link InterruptedException}.** <p> If this thread is blocked in an I/O operation upon an {@link* java.nio.channels.InterruptibleChannel InterruptibleChannel}* then the channel will be closed, the thread's interrupt* status will be set, and the thread will receive a {@link* java.nio.channels.ClosedByInterruptException}.** <p> If this thread is blocked in a {@link java.nio.channels.Selector}* then the thread's interrupt status will be set and it will return* immediately from the selection operation, possibly with a non-zero* value, just as if the selector's {@link* java.nio.channels.Selector#wakeup wakeup} method were invoked.** <p> If none of the previous conditions hold then this thread's interrupt* status will be set. </p>** <p> Interrupting a thread that is not alive need not have any effect.** @throws SecurityException* if the current thread cannot modify this thread** @revised 6.0* @spec JSR-51*/
/*
translation
中断此线程。
除非当前线程正在中断自己,这总是被允许的,否则调用此线程的checkAccess方法,这可能会导致抛出SecurityException 。
如果此线程在调用Object类的wait() 、 wait(long)或wait(long, int)方法或join() 、 join(long) 、 join(long, int)被阻塞、 sleep(long)或sleep(long, int) ,此类的方法,则其中断状态将被清除并收到InterruptedException 。
如果此线程在InterruptibleChannel的 I/O 操作中被阻塞,则通道将关闭,线程的中断状态将被设置,线程将收到java.nio.channels.ClosedByInterruptException 。
如果该线程在java.nio.channels.Selector被阻塞,则该线程的中断状态将被设置,并且它将立即从选择操作中返回,可能具有非零值,就像调用了选择器的wakeup方法一样。
如果前面的条件都不成立,则将设置此线程的中断状态。
中断一个不活跃的线程不需要有任何影响。
抛出:
SecurityException – 如果当前线程不能修改这个线程
*/
public void interrupt() {if (this != Thread.currentThread())checkAccess();// 用于第二第三种情况的处理(如果此线程在InterruptibleChannel的 I/O 操作中被阻塞,如果该线程在java.nio.channels.Selector被阻塞)。synchronized (blockerLock) {Interruptible b = blocker;if (b != null) {interrupt0(); // Just to set the interrupt flagb.interrupt(this);return;}}interrupt0();
}/*** Tests whether the current thread has been interrupted. The* <i>interrupted status</i> of the thread is cleared by this method. In* other words, if this method were to be called twice in succession, the* second call would return false (unless the current thread were* interrupted again, after the first call had cleared its interrupted* status and before the second call had examined it).** <p>A thread interruption ignored because a thread was not alive* at the time of the interrupt will be reflected by this method* returning false.** @return <code>true</code> if the current thread has been interrupted;* <code>false</code> otherwise.* @see #isInterrupted()* @revised 6.0*/
public static boolean interrupted() {return currentThread().isInterrupted(true); // 注意是静态方法,作用在当前线程。返回中断中断状态,并清除。
}/*** Tests whether this thread has been interrupted. The <i>interrupted* status</i> of the thread is unaffected by this method.** <p>A thread interruption ignored because a thread was not alive* at the time of the interrupt will be reflected by this method* returning false.** @return <code>true</code> if this thread has been interrupted;* <code>false</code> otherwise.* @see #interrupted()* @revised 6.0*/
public boolean isInterrupted() {return isInterrupted(false); // 返回中断状态。
}/*** Tests if some Thread has been interrupted. The interrupted state* is reset or not based on the value of ClearInterrupted that is* passed.*/
private native boolean isInterrupted(boolean ClearInterrupted);
再看看cpp代码
void os::interrupt(Thread* thread) {debug_only(Thread::check_for_dangling_thread_pointer(thread);)OSThread* osthread = thread->osthread();if (!osthread->interrupted()) {osthread->set_interrupted(true); // 设置中断标记-> true// More than one thread can get here with the same value of osthread,// resulting in multiple notifications. We do, however, want the store// to interrupted() to be visible to other threads before we execute unpark().OrderAccess::fence();ParkEvent * const slp = thread->_SleepEvent ;if (slp != NULL) slp->unpark() ;}// For JSR166. Unpark even if interrupt status already was setif (thread->is_Java_thread())((JavaThread*)thread)->parker()->unpark();ParkEvent * ev = thread->_ParkEvent ;if (ev != NULL) ev->unpark() ;
}
所以对于Thread.interrupt来说,它最重要的事情其实是调用3个unpark()方法对象唤醒线程,而我们老生常谈的修改打断标记,反倒是没那么重要。是否响应该标记、是在jvm层上响应还是在java层上响应等等逻辑,都取决于实际需要。
线程上下文切换
这得从线程的实现和调度谈起。
线程调度是指系统为线程分配处理器使用权的过程。java采用抢占式调度。
1:1的内核线程模型是如今Java虚拟机线程实现的主流选择,但是这种映射到操作系统上的线程天然的缺陷是切换、调度成本高昂,系统能容纳的线程数量也很有限。现实的需求在迫使Java去研究新的解决方案。—>有栈协程,新的并发编程模型。
这里一般指的是内核线程的切换。
// 线程A -> 系统中断 -> 线程B
处理器要去执行线程A的程序代码时,并不是仅有代码程序就能跑得起来,程序是数据与代码的组合体,代码执行时还必须要有上下文数据的支撑。而这里说的“上下文”,以程序员的角度来看,是方法调用过程中的各种局部的变量与资源;以线程的角度来看,是方法的调用栈中存储的各类信息;而以操作系统和硬件的角度来看,则是存储在内存、缓存和寄存器中的一个个具体数值。物理硬件的各种存储设备和寄存器是被操作系统内所有线程共享的资源,当中断发生,从线程A切换到线程B去执行之前,操作系统首先要把线程A的上下文数据妥善保管好,然后把寄存器、内存分页等恢复到线程B挂起时候的状态,这样线程B被重新激活后才能仿佛从来没有被挂起过。这种保护和恢复现场的工作,免不了涉及一系列数据在各种寄存器、缓存中的来回拷贝,当然不可能是一种轻量级的操作。
线程死锁
具体demo就不展示了。
什么是死锁
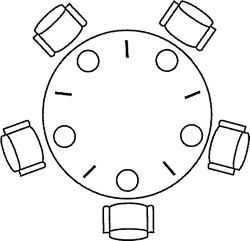
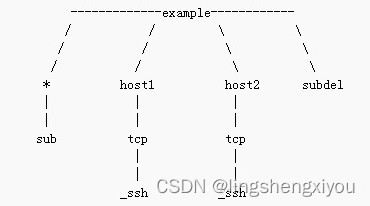
死锁是指两个或两个以上的线程在执行过程中,因争夺资源而造成的互相等待的现象,在无外力作用的情况下,这些线程会一直相互等待而无法继续运行下去。如图,

必须具备以下四个条件
- 互斥条件:指线程对己经获取到的资源进行排它性使用,即该资源同时只由一个线程占用。如果此时还有其他线程请求获取该资源,则请求者只能等待,直至占有资源的线程释放该资源。
- 请求并持有条件:指一个线程己经持有了至少一个资源,但又提出了新的资源请求,而新资源己被其他线程占有,所以当前线程会被阻塞,但阻塞的同时并不释放自己已经获取的资源。
- 不可剥夺条件:指线程获取到的资源在自己使用完之前不能被其他线程抢占,只有在自己使用完毕后才由自己释放该资源。
- 环路等待条件:指在发生死锁时,必然存在一个线程→资源的环形链,即线程集合{TO,TLT2,…,Tn}中的TO正在等待一个Tl占用的资源,Tl正在等待T2占用的资源,…Tn正在等待己被TO占用的资源。
如何避免死锁
要想避免死锁,只需要破坏掉至少一个构造死锁的必要条件即可,但是学过操作系统的读者应该都知道,目前只有请求并持有和环路等待条件是可以被破坏的。造成死锁的原因其实和申请资源的顺序有很大关系,使用资源申请的有序性原则就可以避免死锁(破坏资源的求并持有和环路等待条件)。
p s: 当cpu较高时,可以使用jstack命令排查死锁。
用户线程与守护线程
/*** Marks this thread as either a {@linkplain #isDaemon daemon} thread* or a user thread. The Java Virtual Machine exits when the only* threads running are all daemon threads. ** <p> This method must be invoked before the thread is started. 必须在start之前调用** @param on* if {@code true}, marks this thread as a daemon thread** @throws IllegalThreadStateException* if this thread is {@linkplain #isAlive alive}** @throws SecurityException* if {@link #checkAccess} determines that the current* thread cannot modify this thread*/
public final void setDaemon(boolean on) {checkAccess();if (isAlive()) {throw new IllegalThreadStateException();}daemon = on;
}/*** Tests if this thread is a daemon thread.** @return <code>true</code> if this thread is a daemon thread;* <code>false</code> otherwise.* @see #setDaemon(boolean)*/
public final boolean isDaemon() {return daemon;
}
ThreadLocal
introduction,下文只阐述重要的set方法。
/*** 提供线程的局部变量,每个线程独立初始化的变量副本。* This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from* their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its* {@code get} or {@code set} method) has its own, independently initialized* copy of the variable. {@code ThreadLocal} instances are typically private* static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g.,* a user ID or Transaction ID).** <p>For example, the class below generates unique identifiers local to each* thread.* A thread's id is assigned the first time it invokes {@code ThreadId.get()}* and remains unchanged on subsequent calls.* <pre>* import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;** public class ThreadId {* // Atomic integer containing the next thread ID to be assigned* private static final AtomicInteger nextId = new AtomicInteger(0);** // Thread local variable containing each thread's ID* private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadId =* new ThreadLocal<Integer>() {* @Override protected Integer initialValue() {* return nextId.getAndIncrement();* }* };** // Returns the current thread's unique ID, assigning it if necessary* public static int get() {* return threadId.get();* }* }* </pre>* <p>Each thread holds an implicit reference to its copy of a thread-local* variable as long as the thread is alive and the {@code ThreadLocal}* instance is accessible; after a thread goes away, all of its copies of* thread-local instances are subject to garbage collection (unless other* references to these copies exist).** @author Josh Bloch and Doug Lea* @since 1.2*/
Entry(ThreadLocal->弱应用)
/*** The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using* its main ref field as the key (which is always a* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */Object value;Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {super(k);value = v;}
}
// extend WeakReference,key即为ThreadLocal对象,是弱引用(每次gc都会回收)。value还是强引用。
public void set(T value)
/*** Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}* method to set the values of thread-locals.** @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of* this thread-local.*/
public void set(T value) {Thread t = Thread.currentThread();ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); // 获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMapif (map != null)map.set(this, value); // 有,则setelsecreateMap(t, value); // 无
}/**
* Set the value associated with key.
*
* @param key the thread local object
* @param value the value to be set
*/
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at// least as common to use set() to create new entries as// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast// path would fail more often than not.Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);// 向后遍历,查询重复key或key为null的情况。for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == key) {e.value = value; // replacereturn;}if (k == null) {replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); return;}}tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);int sz = ++size;if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)rehash();
}
private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value, int staleSlot)
1.清理key为null的数据 2. 覆盖旧数据
/*** Replace a stale entry encountered during a set operation* with an entry for the specified key. The value passed in* the value parameter is stored in the entry, whether or not* an entry already exists for the specified key.** As a side effect, this method expunges all stale entries in the* "run" containing the stale entry. (A run is a sequence of entries* between two null slots.)** @param key the key* @param value the value to be associated with key* @param staleSlot index of the first stale entry encountered while* searching for key.*/
private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value,int staleSlot) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;Entry e;// Back up to check for prior stale entry in current run.// We clean out whole runs at a time to avoid continual// incremental rehashing due to garbage collector freeing// up refs in bunches (i.e., whenever the collector runs).int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;// 向前遍历,查询key为null的情况。确定扫描范围for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = prevIndex(i, len))if (e.get() == null)slotToExpunge = i;// Find either the key or trailing null slot of run, whichever// occurs first// 向后遍历,查询key相同的可覆盖数据,for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = nextIndex(i, len)) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();// If we find key, then we need to swap it// with the stale entry to maintain hash table order.// The newly stale slot, or any other stale slot// encountered above it, can then be sent to expungeStaleEnwtry// to remove or rehash all of the other entries in run.if (k == key) { // swap it with the stale entry e.value = value;tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];tab[staleSlot] = e;// Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it existsif (slotToExpunge == staleSlot)slotToExpunge = i;cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len); // 扫描过时数据,Heuristically scan some cells looking for stale entriesreturn;}// If we didn't find stale entry on backward scan, the// first stale entry seen while scanning for key is the// first still present in the run.if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)slotToExpunge = i;}// If key not found, put new entry in stale slottab[staleSlot].value = null;tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);// If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge them,删除。if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
}
内存溢出问题
线程如果一直不死亡,又没有触发到清理方法,本地变量的值为强引用,还是可能会造成内存泄漏。使用remove()方法来避免。
ThreadLocal不支持继承性
先看一下demo测试
/*** 继承性测试** @author Hireek* @date 2021/12/27 07:09*/
public class TestThreadLocal {// 创建线程变量public static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); // apublic static void main(String[] args) {// 父线程中设置线程变量threadLocal.set("hello world");// 启动子线程Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {// 子线程输出线程变量的值System.out.println("thread:" + threadLocal.get());});thread.start();System.out.println("main:" + threadLocal.get());}
}
/* run resultmain:hello worldthread:null*/
可以发现,同一个 ThreadLocal变量在父线程中被设置值后,在子线程中是获取不到的。那么有没有办法让子线程能访问到父线程中的值? 答案是有。
lnheritableThreadLocal
将上面代码a处改成,就可以解决了。
public static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
// run result
// thread:hello world
// main:hello world
看下源码一探究竟
public class InheritableThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {/*** Computes the child's initial value for this inheritable thread-local* variable as a function of the parent's value at the time the child* thread is created. This method is called from within the parent* thread before the child is started.* <p>* This method merely returns its input argument, and should be overridden* if a different behavior is desired.** @param parentValue the parent thread's value* @return the child thread's initial value*/protected T childValue(T parentValue) {return parentValue;}/*** Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal.** @param t the current thread*/ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {return t.inheritableThreadLocals;}/*** Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal.** @param t the current thread* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the table.*/void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {t.inheritableThreadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);}
}
// 初始化线程时,如果parent线程的inheritableThreadLocals不为null, 会初始化局部变量inheritableThreadLocals。
private Thread(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,boolean inheritThreadLocals) {// ...setPriority(priority);if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)this.inheritableThreadLocals =ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);// ...
}
部分内容参考了大佬博客,链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tera/p/14020276.html