根据百度百科的解释,PCIE(peripheral component interconnect express)是一种高速串行计算机扩展总线标准,它原来的名称为“3GIO”,是由英特尔在2001年提出的,旨在替代旧的PCI,PCI-X和AGP总线标准。PCIe属于高速串行点对点双通道高带宽传输,所连接的设备分配独享通道带宽,不共享总线带宽,主要支持主动电源管理,错误报告,端对端的可靠性传输,热插拔以及服务质量(QOS)等功能。PCIe闪存卡的供应商包括:INTEL、IBM、LSI、OCZ、三星(计划中)、SanDisk、STEC、SuperTalent和东芝(计划中)等,而针对海量的数据增长使得用户对规模更大、可扩展性更强的系统所应用,PCIe 3.0技术的加入最新的LSI MegaRAID控制器及HBA产品的出色性能,就可以实现更大的系统设计灵活性。
PCIE的连接架构:
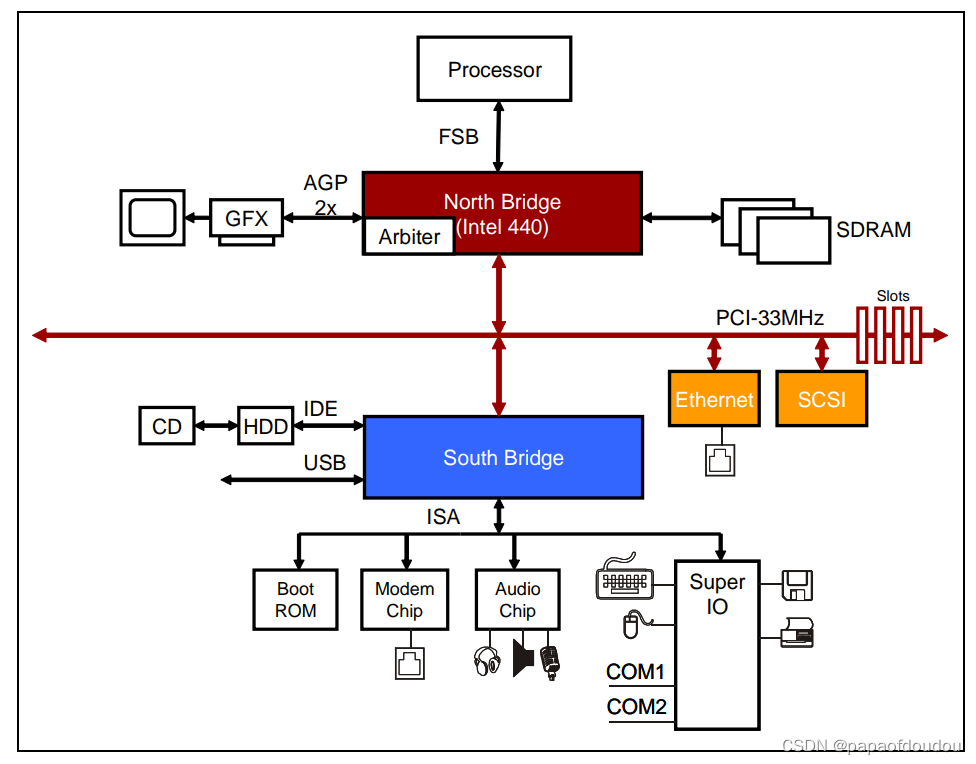
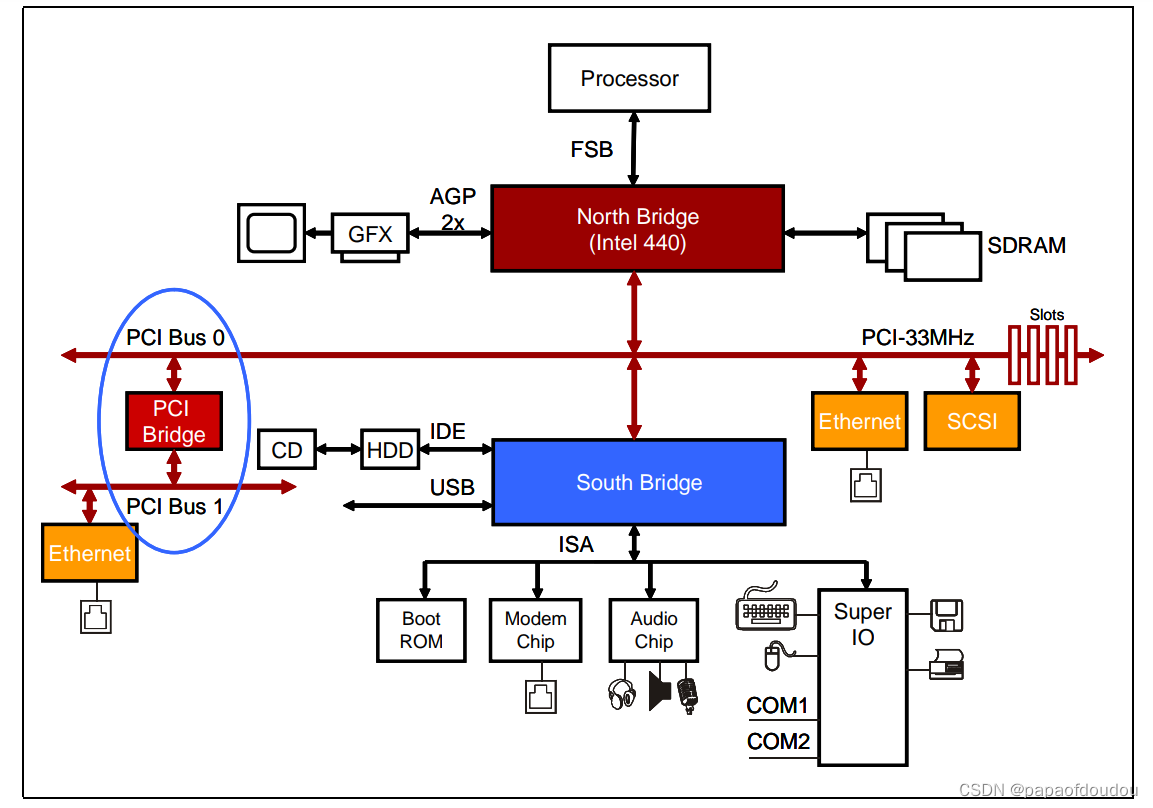
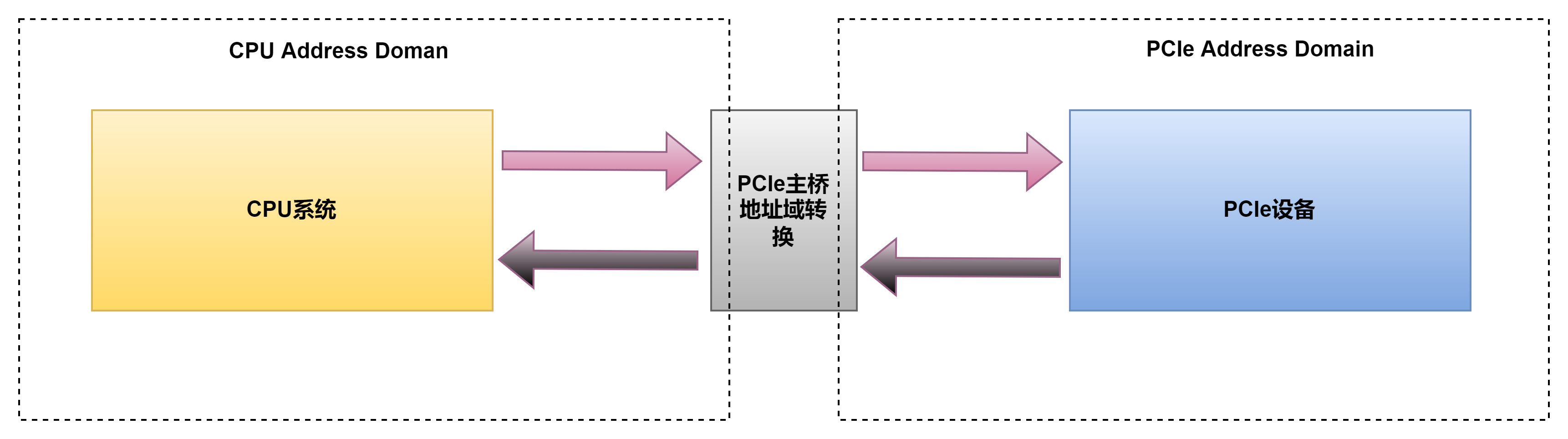
PCI设备有独立的地址空间,也就是PCI总线地址空间,该空间与存储器地址空间通过HOST主桥隔离,两侧实现存储互访,需要经过PCIe桥的翻译:
HOST主桥是一颗很特别的桥片,它可以和CPU集成在一起,也可以集成在北桥芯片中,没有太大区别。HOST主桥和内存在一个级别上,所以可以通过主桥很方便的访问主主存。一个系统可以有多个HOST主桥,每个主桥管理一个PCIe总线数,并有自己的地址空间domain.有几个主桥,就有几个PCIe总线域名,普通PC一般只有1个Host Bridge.
PCIE 接口速度计算方式
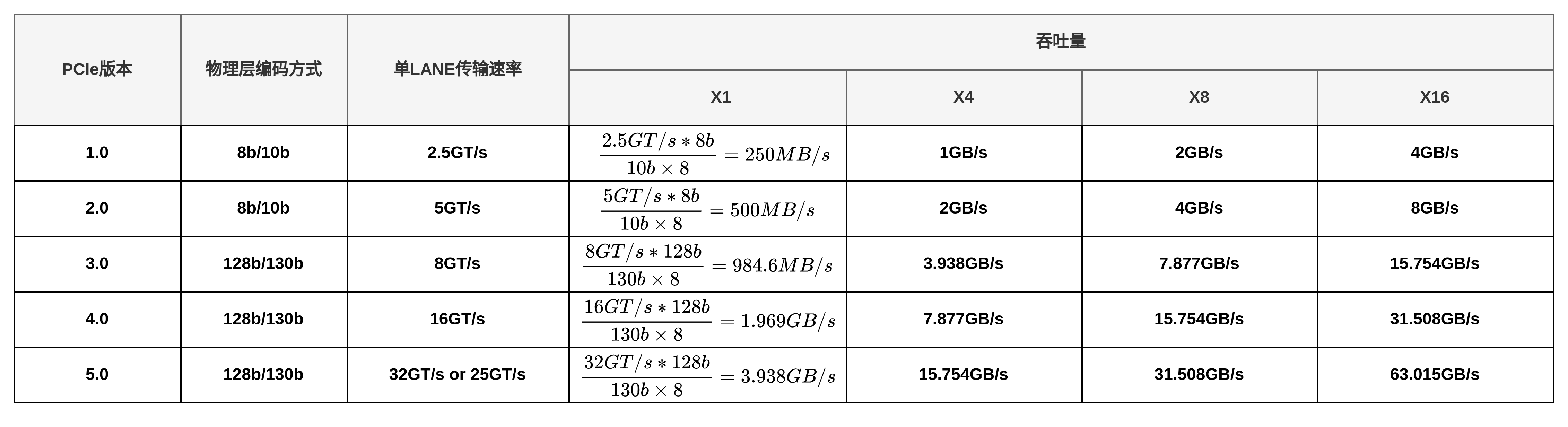
速率为每秒传输量GT/s,而不是每秒位数Gbps,因为传输量包括不提供额外吞吐量的开销位; 比如 PCIe 1.x和PCIe 2.x使用8b / 10b编码方案,导致占用了20% (= 2/10)的原始信道带宽。
GT/s —— Giga transation per second (千兆传输/秒),即每一秒内传输的次数。重点在于描述物理层通信协议的速率属性,可以不和链路宽度等关联。
Gbps —— Giga Bits Per Second (千兆位/秒)。GT/s 与Gbps 之间不存在成比例的换算关系。
实际有效载荷的吞吐量计算公式为:

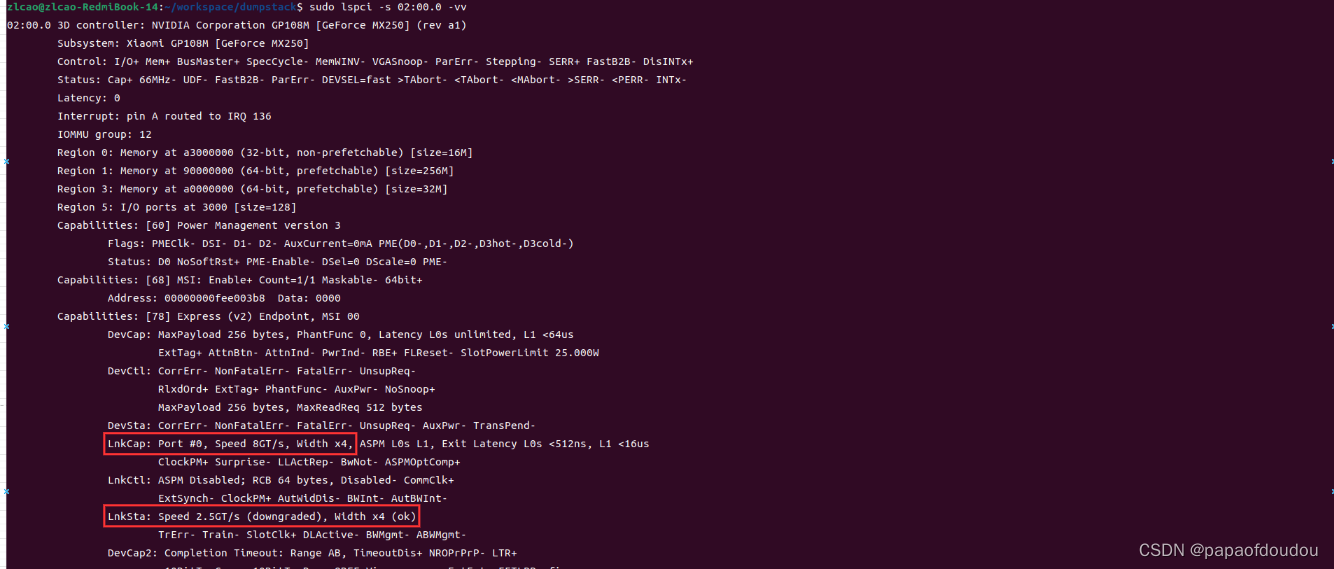
以我的MX250独立显卡为例,标称是PCIE GEN3 8GT/S,但是实际速率只有2.5GT/s
PCIE主桥位置
PCIE主桥继承在北桥芯片中,当前最新的INTEL芯片已经将北桥和CPU集成的到一起,所以PCIE主桥自然也集成到了CPU芯片中。通常我们看到的PCIE插槽都非常大,很难想象能集成到一颗芯片中,但是实际上,接口和控制器是两码事,以GPU为例,由于AI的驱动,GPU产品常常供不应求,尽管地位显赫,但是在计算机架构中GPU始终处于CPU从属的位置,工作在“喂模式”,即使对于集成显卡,虽然物理上与CPU在一起,但是其身份仍然是设备身份,INTEL的集成显卡GPU,它在PCI总线上的BDF地址总是:00:2.0, 也就是0号总线上的2号设备,如下图:
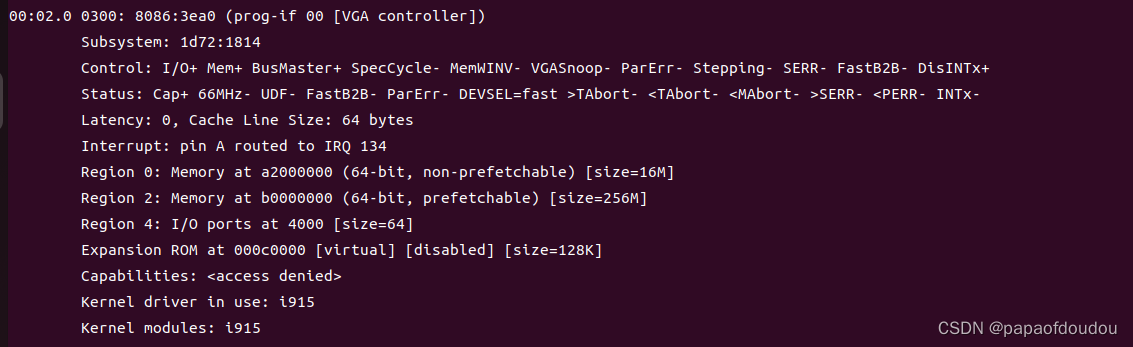
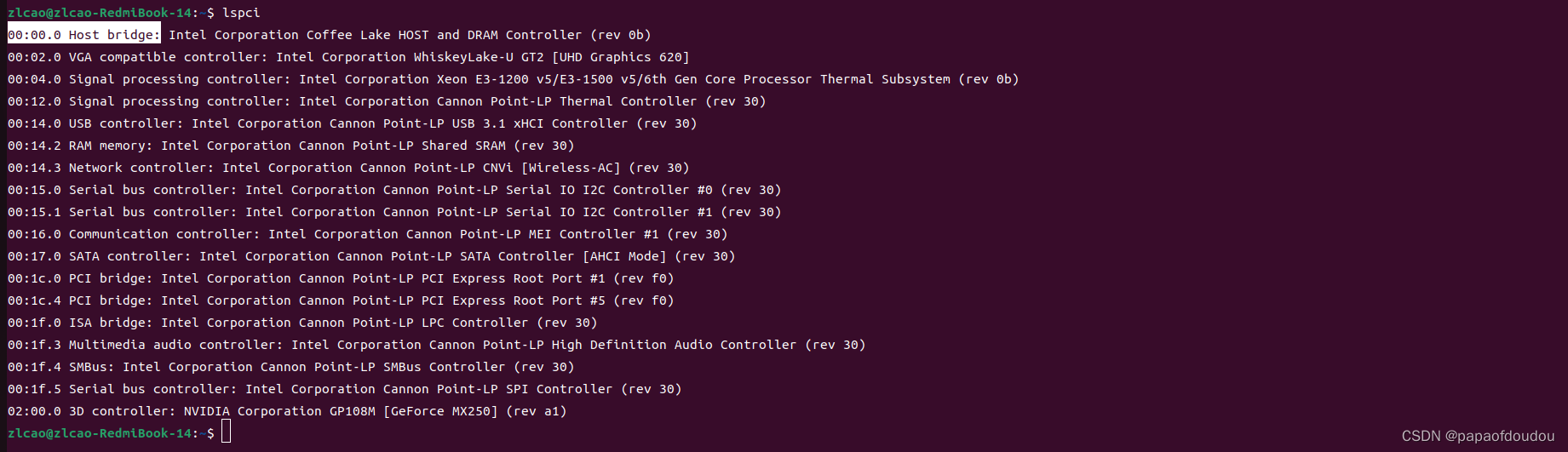
查看系统中的PCIE设备:
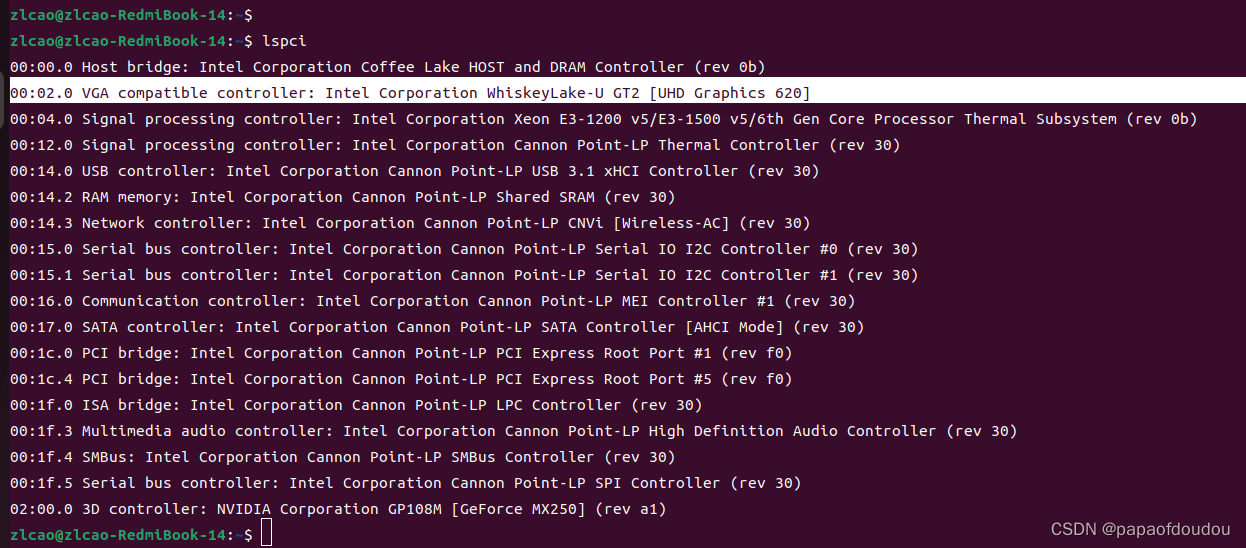
执行命令lspci命令,查看系统中的PCIE设备信息
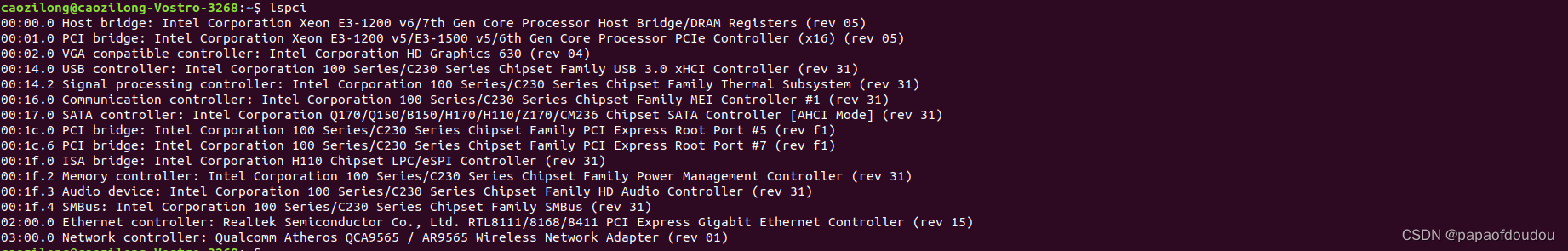
可以看到,系统中有PCIE USB EHCI控制器,以及PCIE网卡,现在我们进一步用命令分析他们。命令格式是: sudo lspci -vvv -s #bdf,其中bdf是BUS,DEVICE,FUNCTION 的缩写,要了解它需要具备一些PCIE的基础知识,简单来说,挂载在PCIE总线上的PCIE设备尽管拓扑结构非常复杂,但是可以唯一的通过bus:device.function去定位,BUS很好理解,它代表的设备挂载的那条PCIE 总线ID,而一条BUS上可以挂载多个设备,通过device区分,对于每个device来说,可以具备多个function,默认的function 0都支持,可以类比一个USB设备可以支持多个配置,而默认的端点0的配置都是支持的。
话说回来,我们可以通过上述命令来针对某个设备DUMP更多的信息出来。
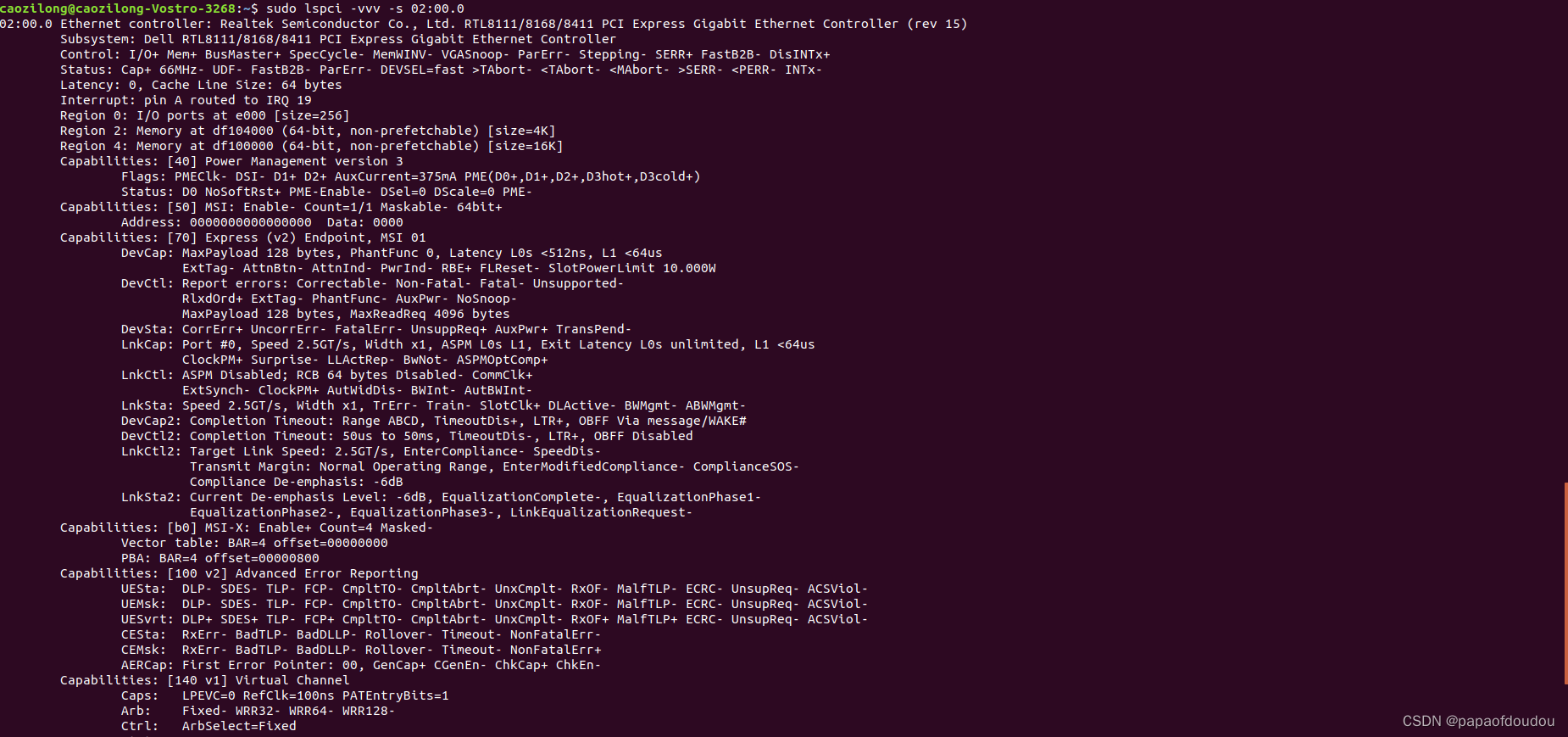
根据LSPCI的输出可以知道,网卡的BDF为02:00.0,我们通过截图中的命令,分析得到网卡设备的中断号为19,支持三个地址空间REGION,HOST端(CPU端)可以通过主机的MMAP函数将REGION中的存储区域映射到系统中进行访问,这样可以直接操纵版卡上的存储资源。另外根据输出信息,网卡支持MSI-X中断,MSI/MSI-X是基于消息传递的中断机制,MSI-X中断允许网卡固件向BAR空间的一片RINGBUF写入16个字节的数据,触发MSI中断,通知HOST端进行响应,是一种设备端和主机端高效的通知机制。
pci_dev的类型
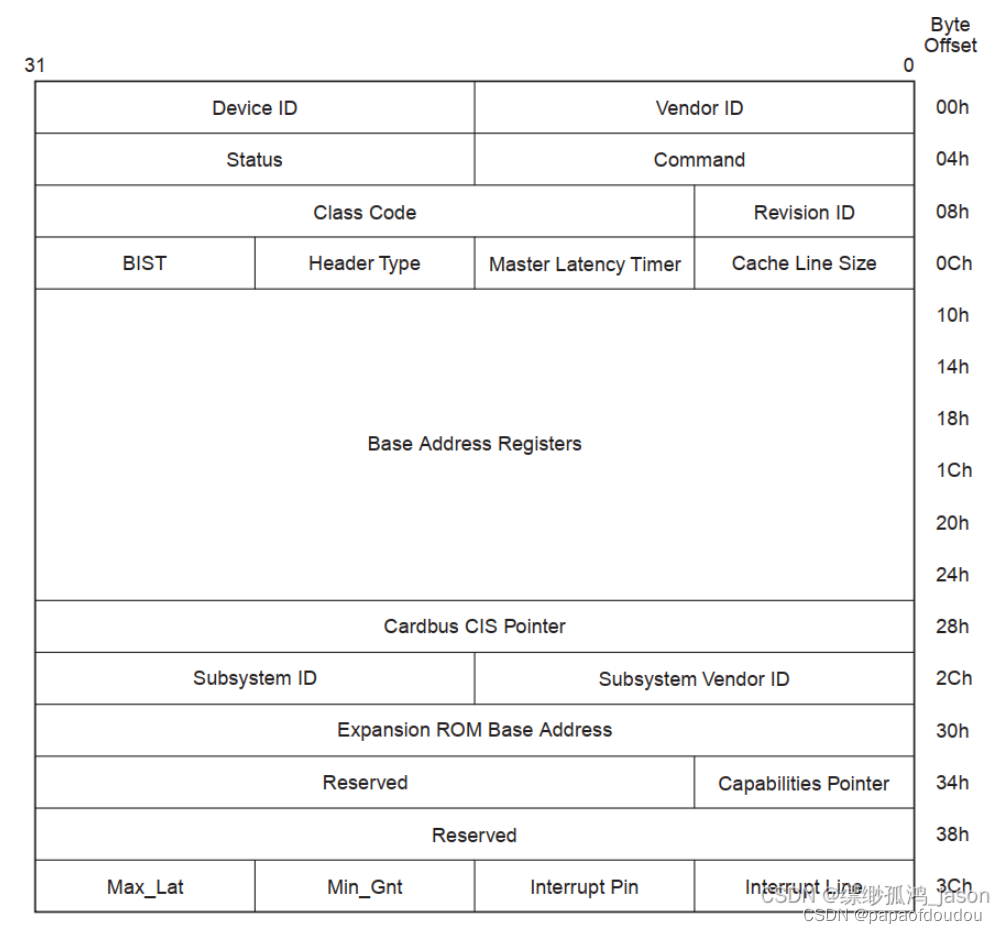
PCI设备类型由PCI设备配置空间的头部定义,目前有三种设备类型,分别是普通设别,BRIDGE设备,和cardbus设备,其中“0型”(type 0)头部用于一般的PCI设备,“1型”头部用于各种PCI-PCI桥, “2型”头部是用于PCI-CardBus桥的,CardBus是笔记本电脑中使用的总线,我们不关心。

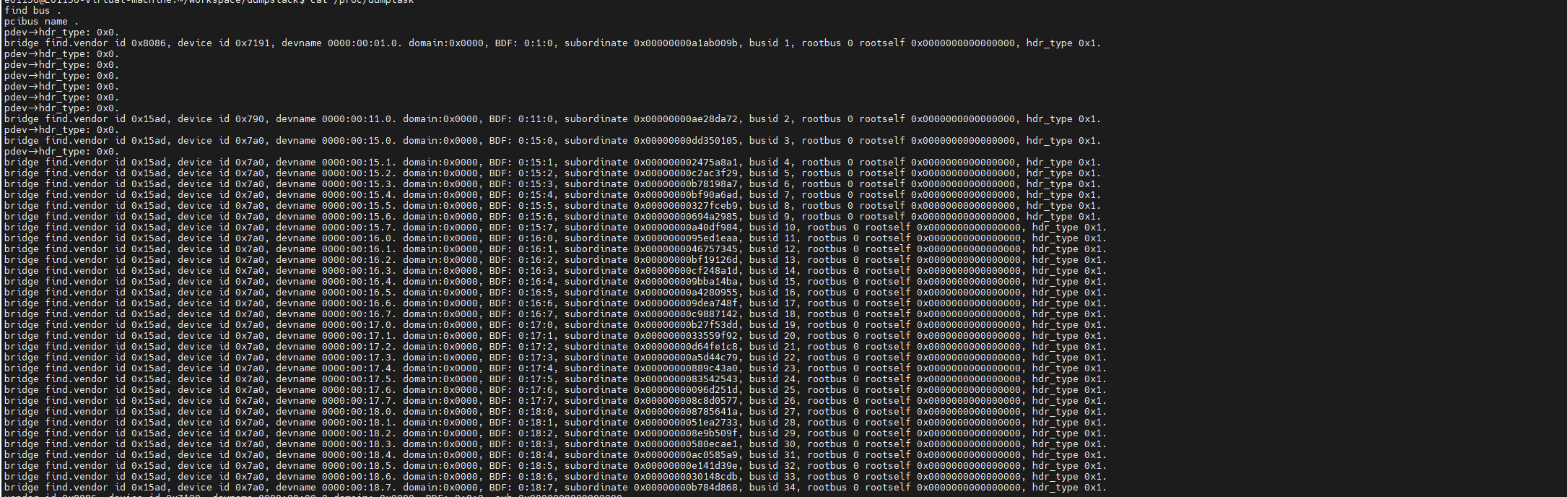
PCI EHCI Controller
在看一下PCIE USB控制器,它的BDF为00:14.0
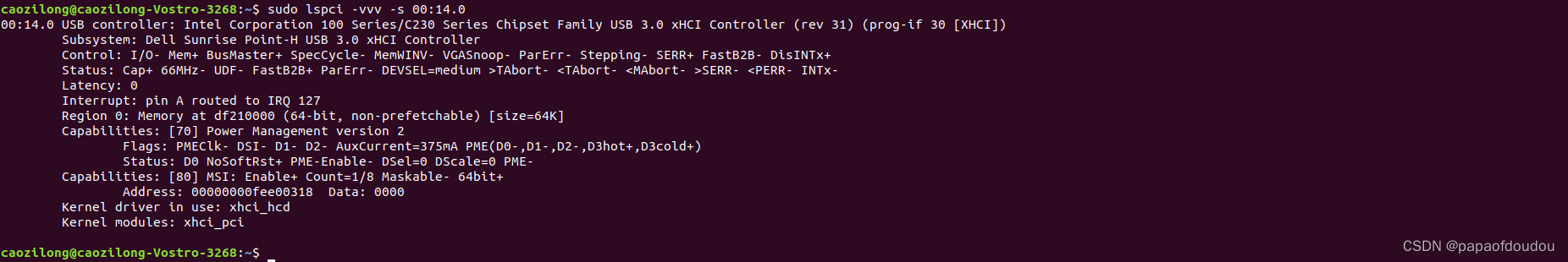
USB控制器支持1个REGION,大小64K(很可能是EHCI寄存器空间,有待证实),中断号为127,同样支持MSI/MSI-X中断机制。
基本可以确定PCI USB Controller的EHCI寄存器空间既是对PCI USB Controller BAR0的映射。 如下图所示:
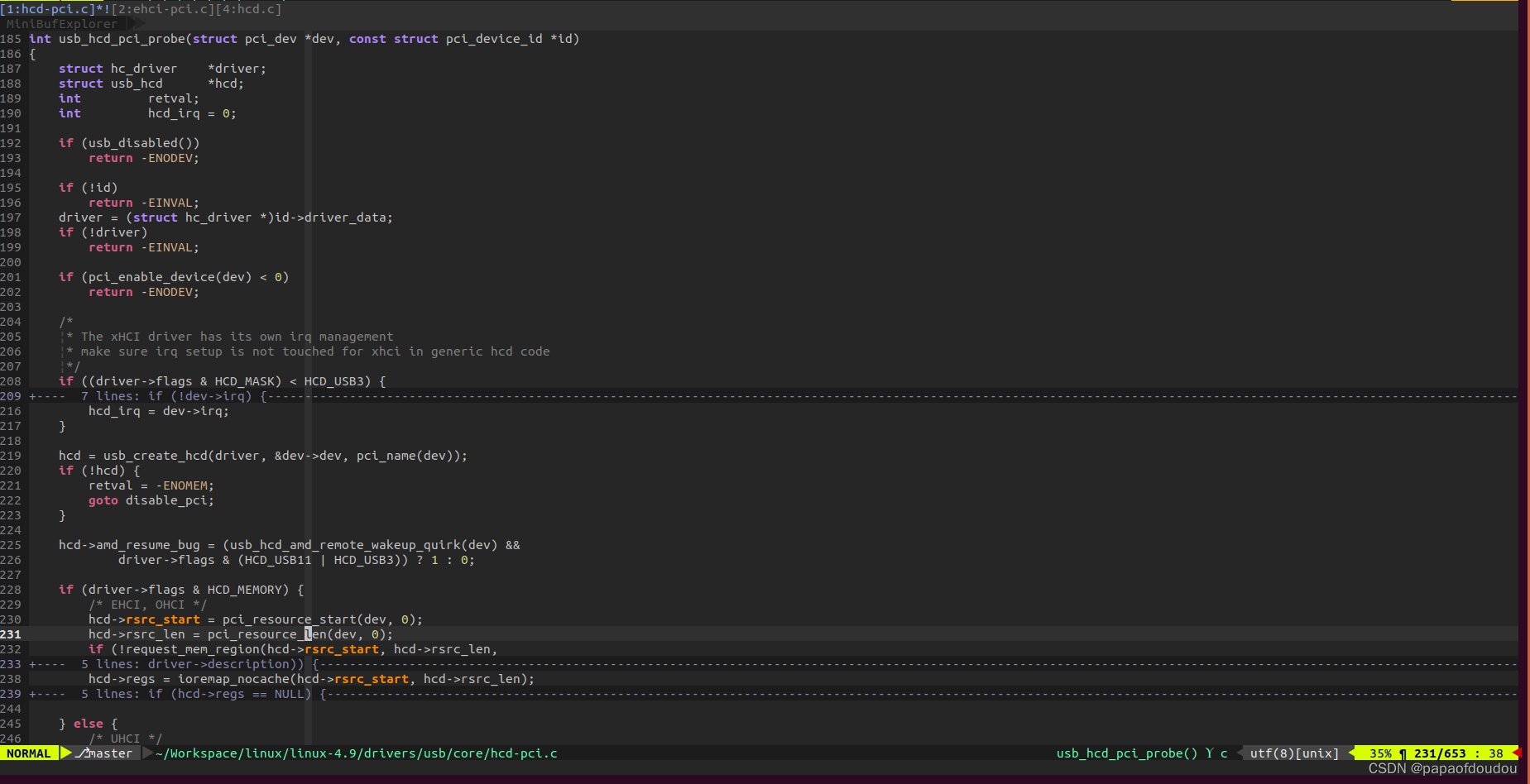
dmesg print
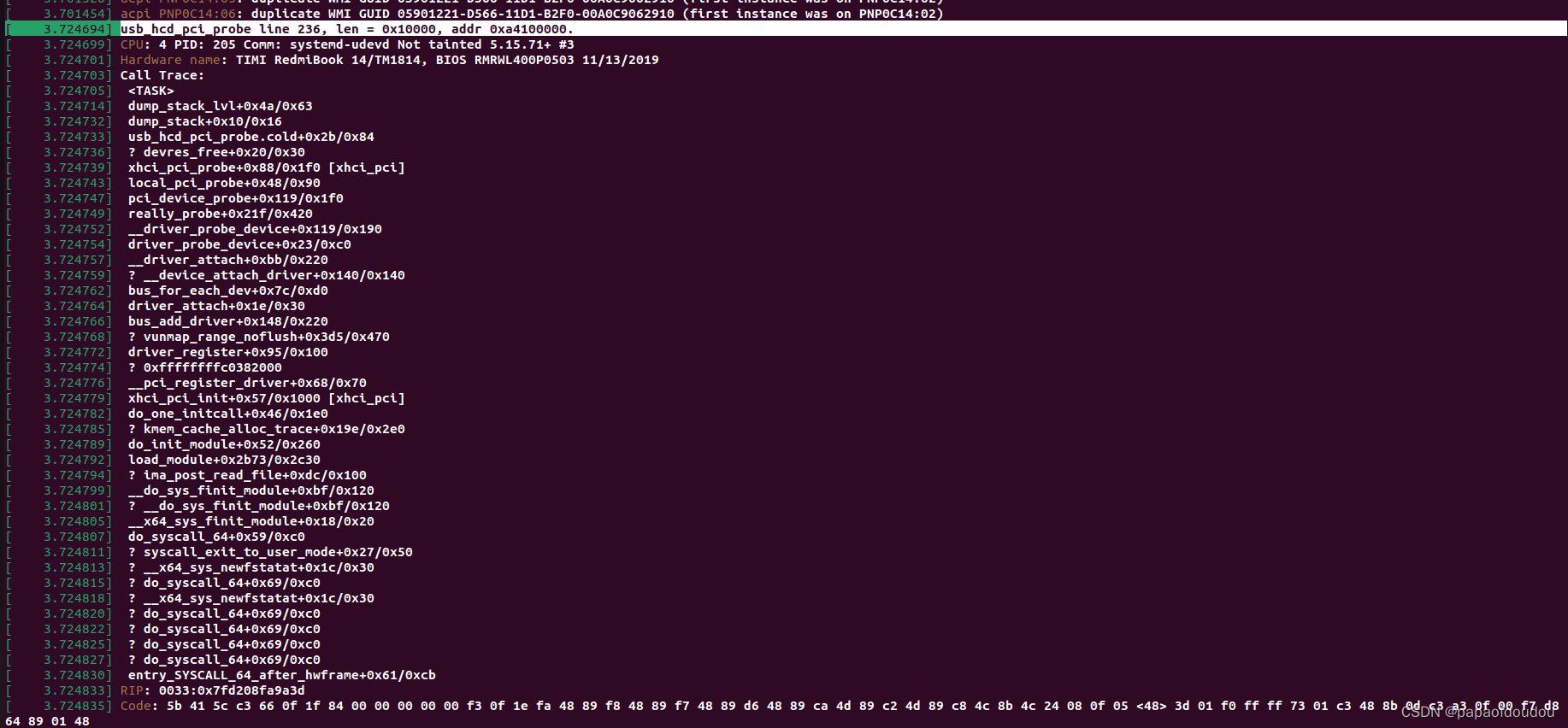
you can see the EHCI length 64k is exactly identical with the output,and so does the base address 0xa4100000,.
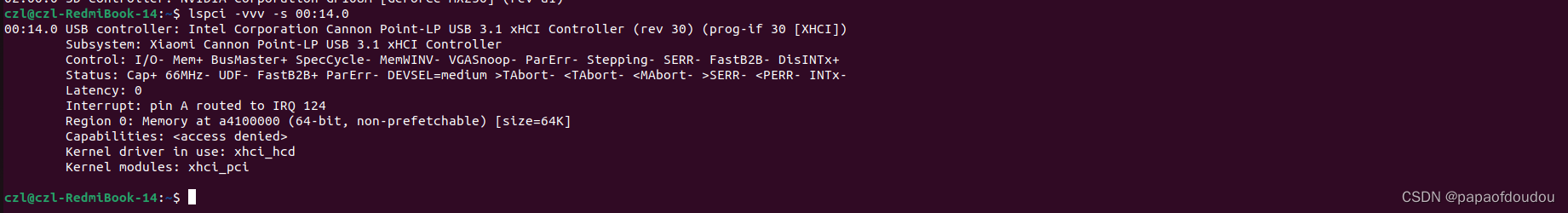
modify the code and print the iomapped EHCI registers. according the iommap funcdtion.
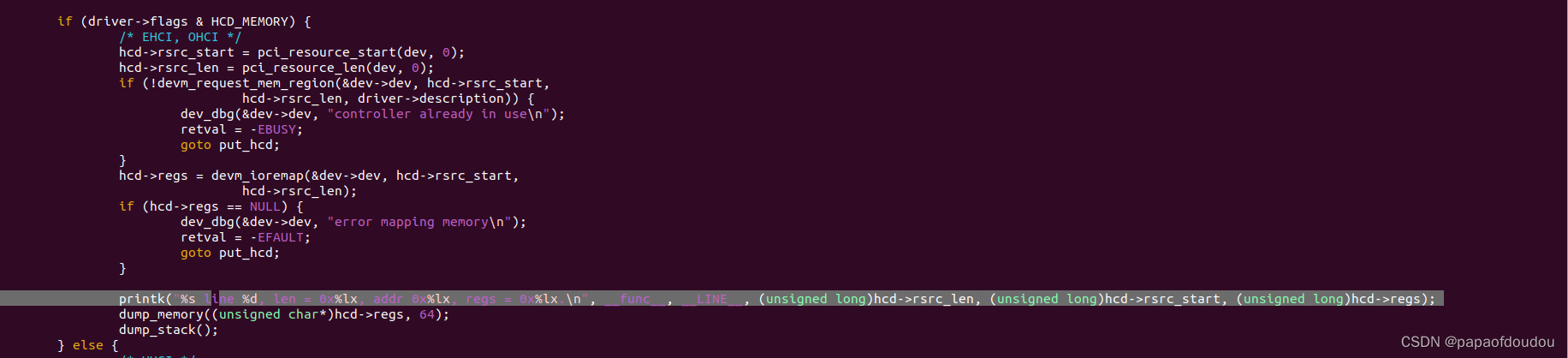
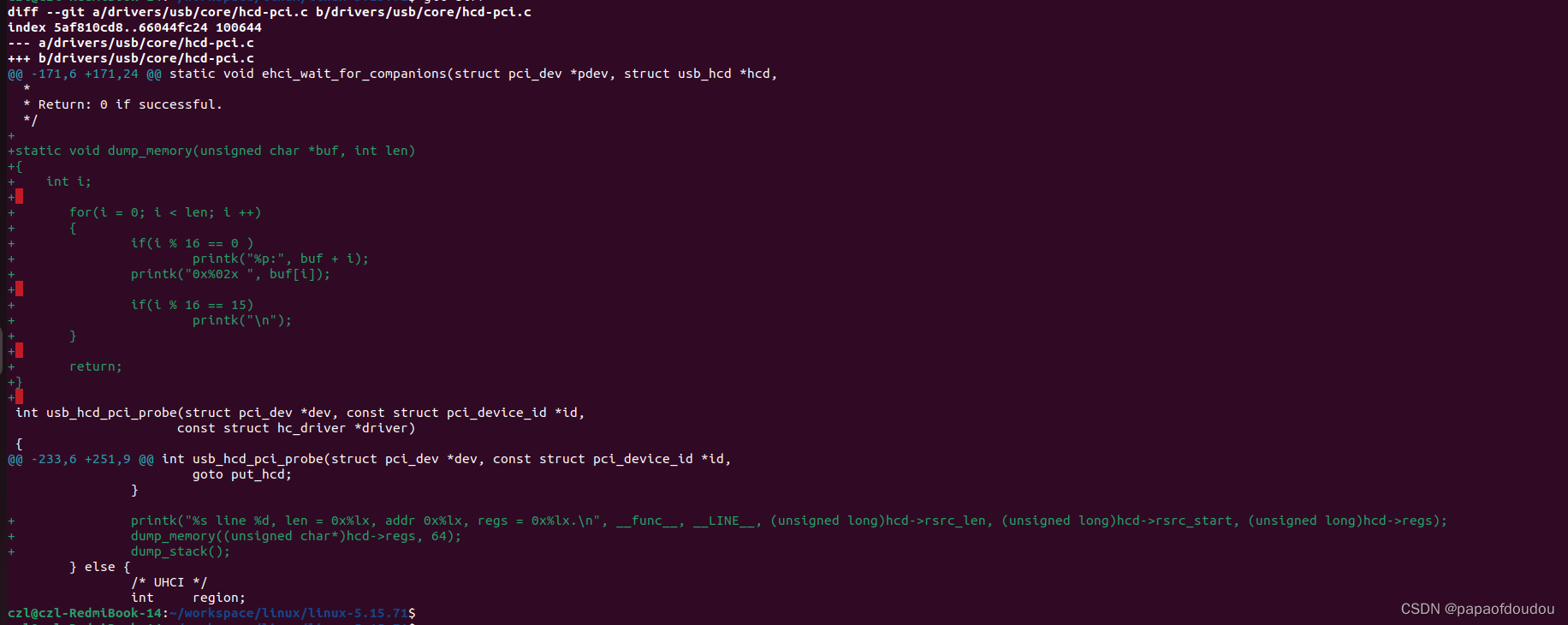
the iomapped address and its content is:
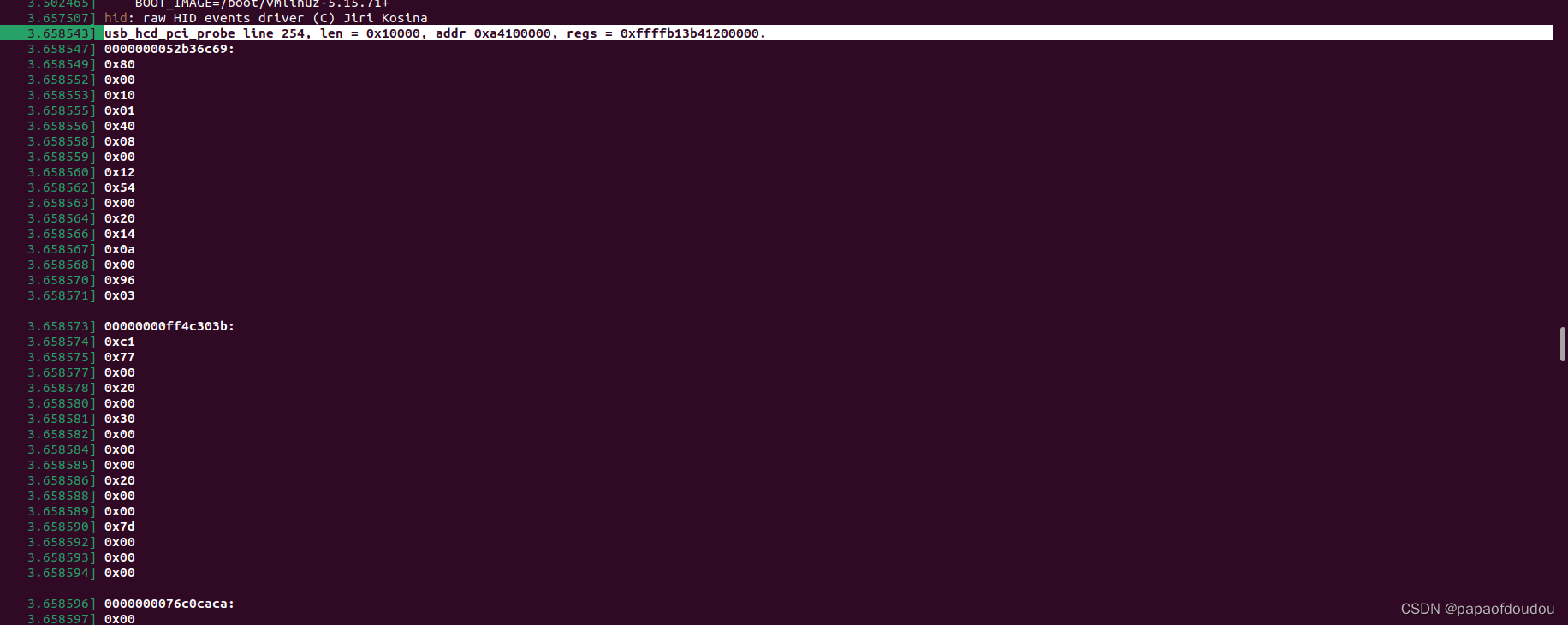
use the user space mmap bar0 to display the content
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <errno.h>// bdf:bus, device, function,bus number take 8bits, device number take 5bits, function number
// take 3bits,so, pcie RC support max 256 child buses,support 32 devices each buses, 8 functions each
// device. BUS0 is RC(root complex).void dump_memory(unsigned char *buf, int len)
{int i;for(i = 0; i < len; i ++){if(i % 16 == 0 )printf("%p:", buf + i);printf("0x%02x ", buf[i]);if(i % 16 == 15)printf("\n");}return;
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{char *filename;struct stat statbuf;int bar=0;// bdf address, domain:bus:slot.funcfilename = "/sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:00:14.0/resource0";printf("open file %s.\n", filename);int fd = open(filename, O_RDWR | O_SYNC);if(fd < 0){printf("%s line %d, fatal error, open file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);return -1;}int status = fstat(fd, &statbuf);if(status < 0){printf("%s line %d, status file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);return -1;}printf("%s line %d, bar zone size %ld bytes, %ld Kbytes, %ld Mbytes, %ld Gbytes.\n", \__func__, __LINE__, statbuf.st_size, statbuf.st_size/1024, statbuf.st_size/1024/1024, statbuf.st_size/1024/1024/1024);unsigned char* maddr = (unsigned char *)mmap(NULL,(size_t)(statbuf.st_size),PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,MAP_SHARED,fd,0);if(maddr == (unsigned char *)MAP_FAILED){printf("%s line %d, failure for mmap bar err %s.\n", __func__, __LINE__, strerror(errno));close(fd);return -1;}printf("%s line %d, fw 0x%p.\n", __func__, __LINE__, maddr);filename = "/sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:00:14.0/config";int fdcfg = open(filename, O_RDWR | O_SYNC);if(fdcfg < 0){printf("%s line %d, fatal error, open file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);return -1;}status = lseek(fdcfg, 0x10 + 4*bar, SEEK_SET);if(status < 0){printf("%s line %d, status file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);close(fdcfg);return -1;}unsigned int phys;status = read(fdcfg, &phys, 4);if(status < 0){printf("%s line %d, status file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);close(fdcfg);return -1;}printf("%s line %d phys 0x%x.\n", __func__, __LINE__, phys);int offset = ((phys & 0xFFFFFFF0) % 0x1000);unsigned char* addr = maddr + offset;printf("%s line %d, addr = %p.\n", __func__, __LINE__, addr);dump_memory(addr, 256);close(fd);close(fdcfg);return 0;
}以上代码依据的是PCIE的配置空间分布
the mmap fd is as belows:
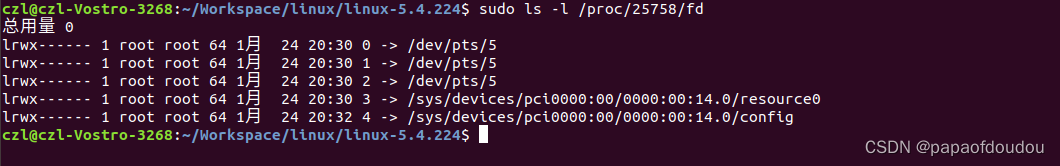
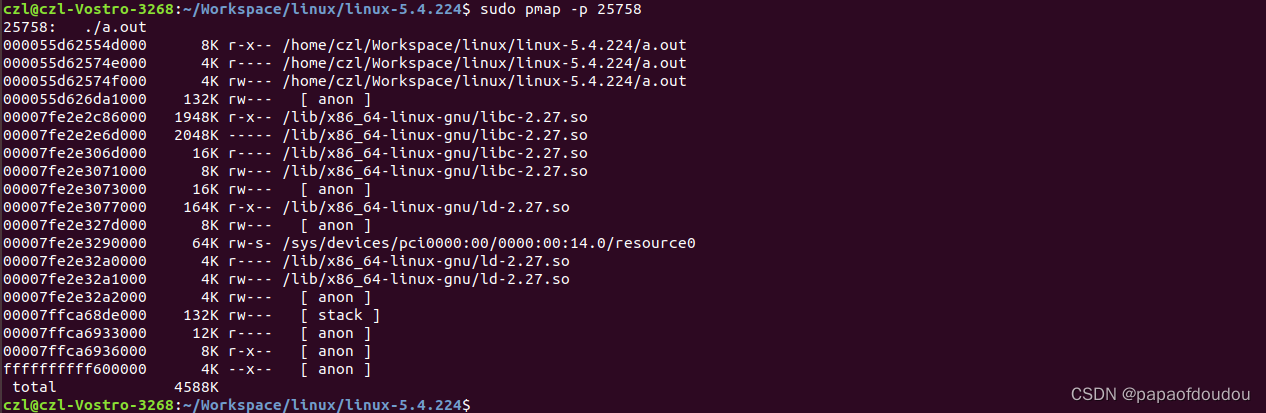
the maximum BAR number cant exceed 6, you can find the definition of BAR in linux kernel are match above map.
user space print, you can find it is very same with the upper kernel printk output.
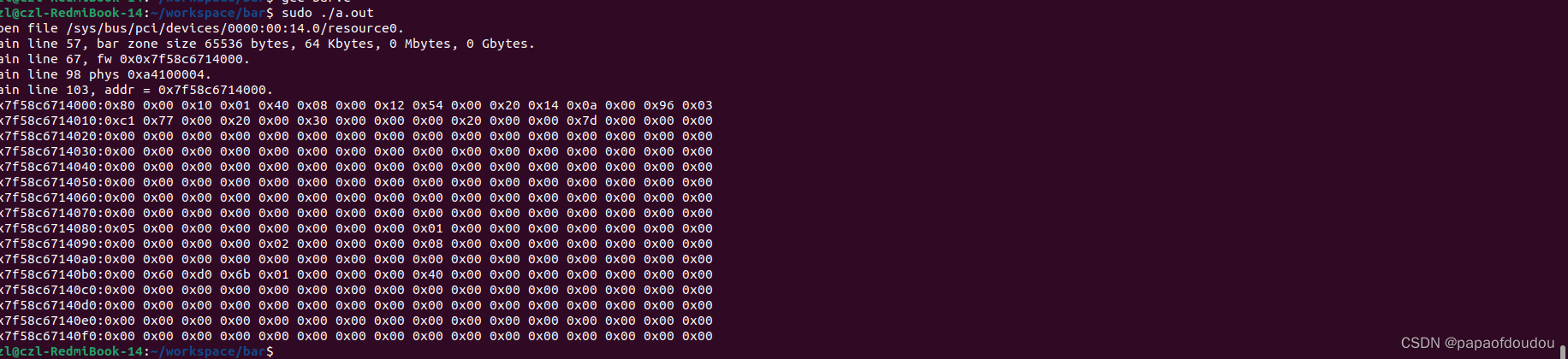
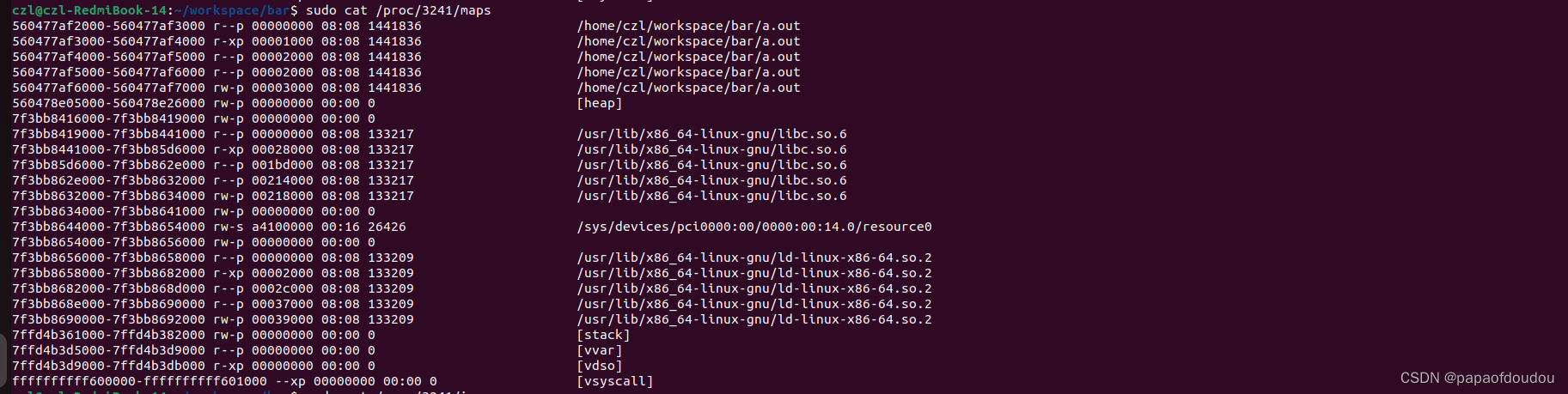
compare allwinner sunxi usb ECHI controller register, you can sure that we above really get the acdtual EHCI Base address from bar space.
the hcd->regs value origin from usb_vbase.
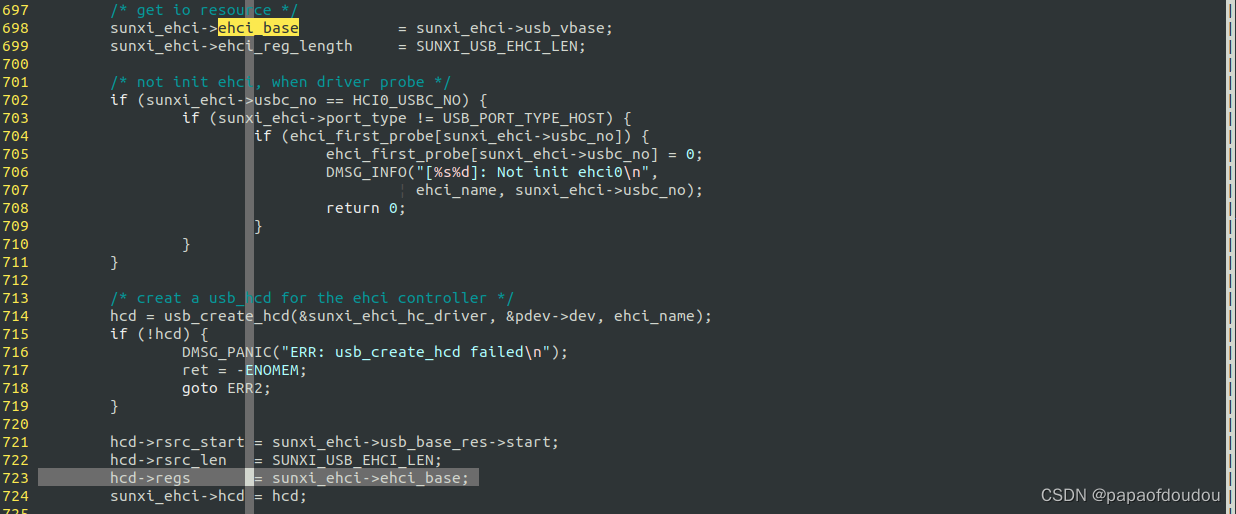
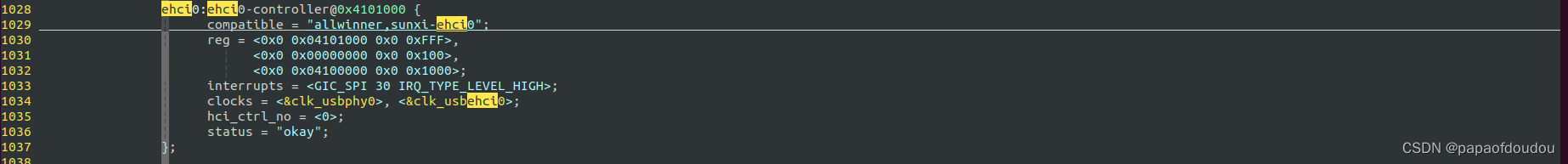
the usb_vbase are initialize from the DEVICE TREE.
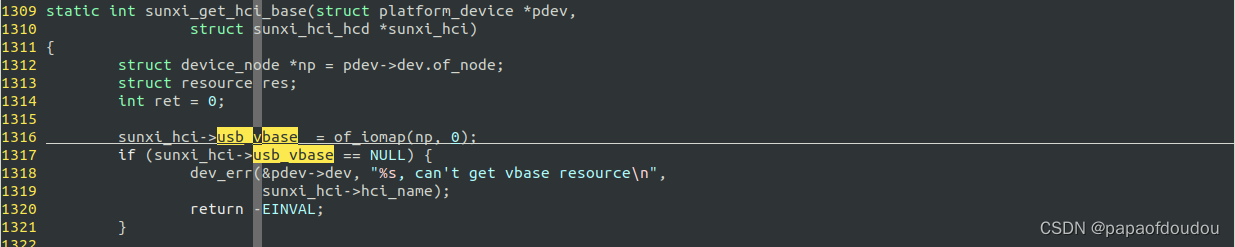
which define the EHCI Base
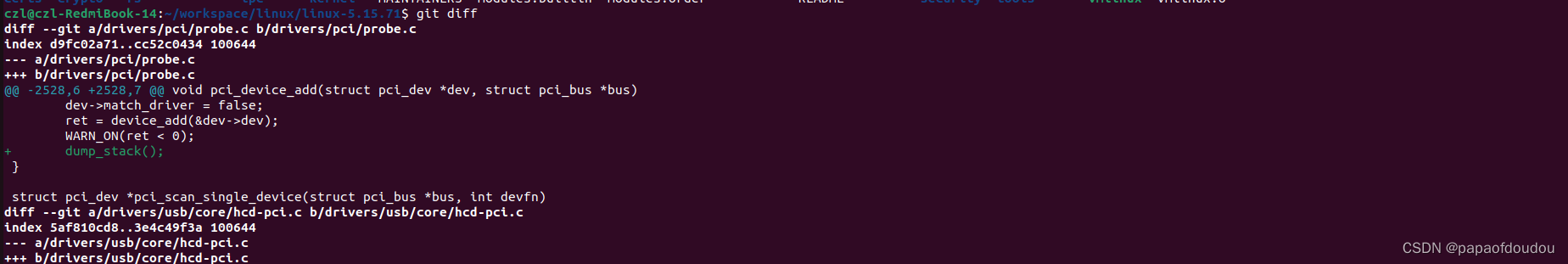
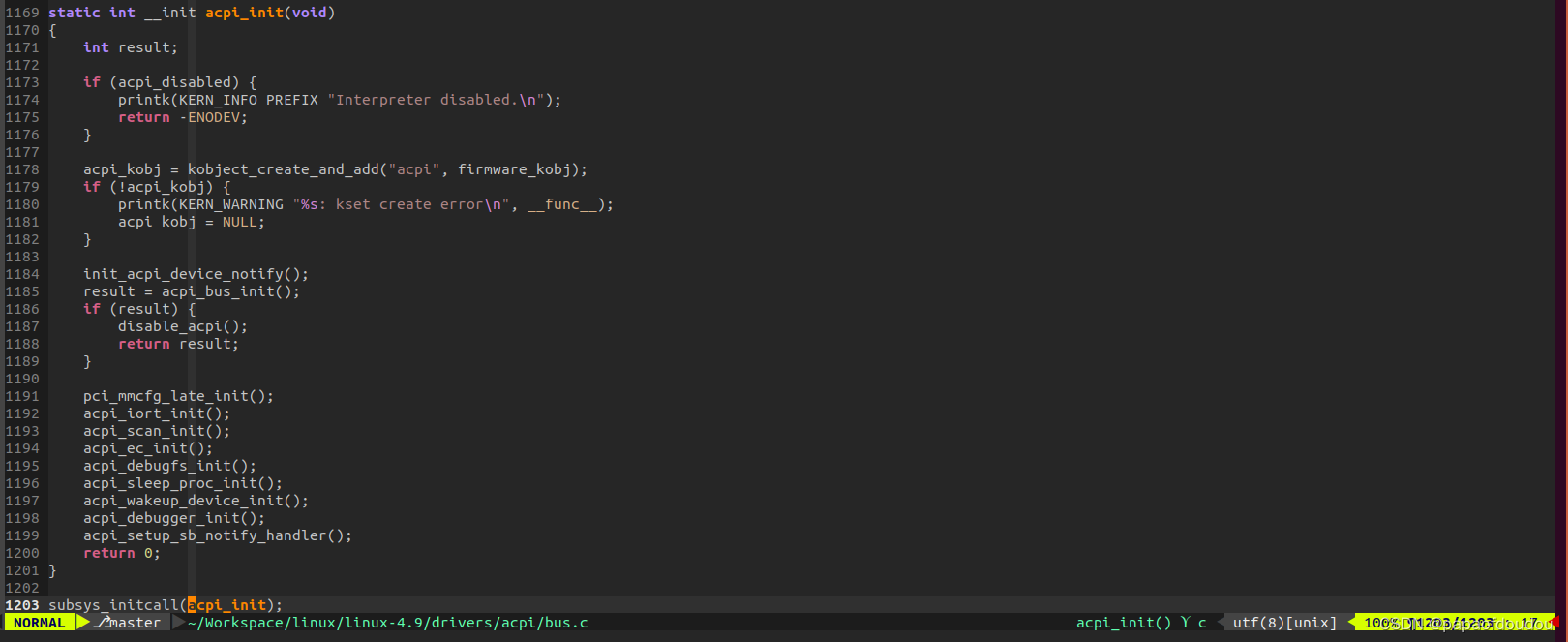
up is the pci driver register flow,but we know device and driver are couples in linux driver, so where is the device register?
in pci driver, the devie register function is pci_device_add.
the device register flow is;
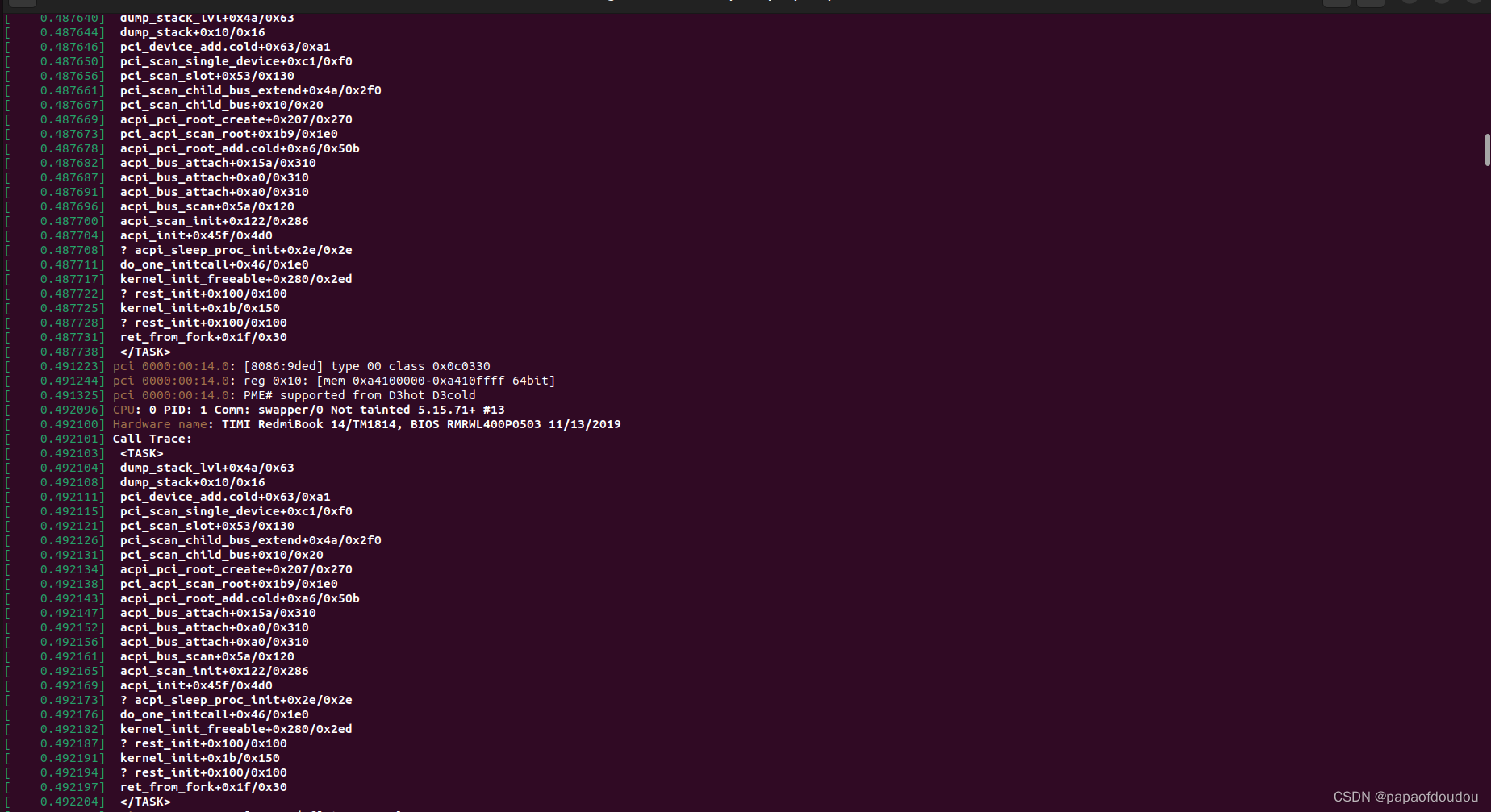
pci_device_add
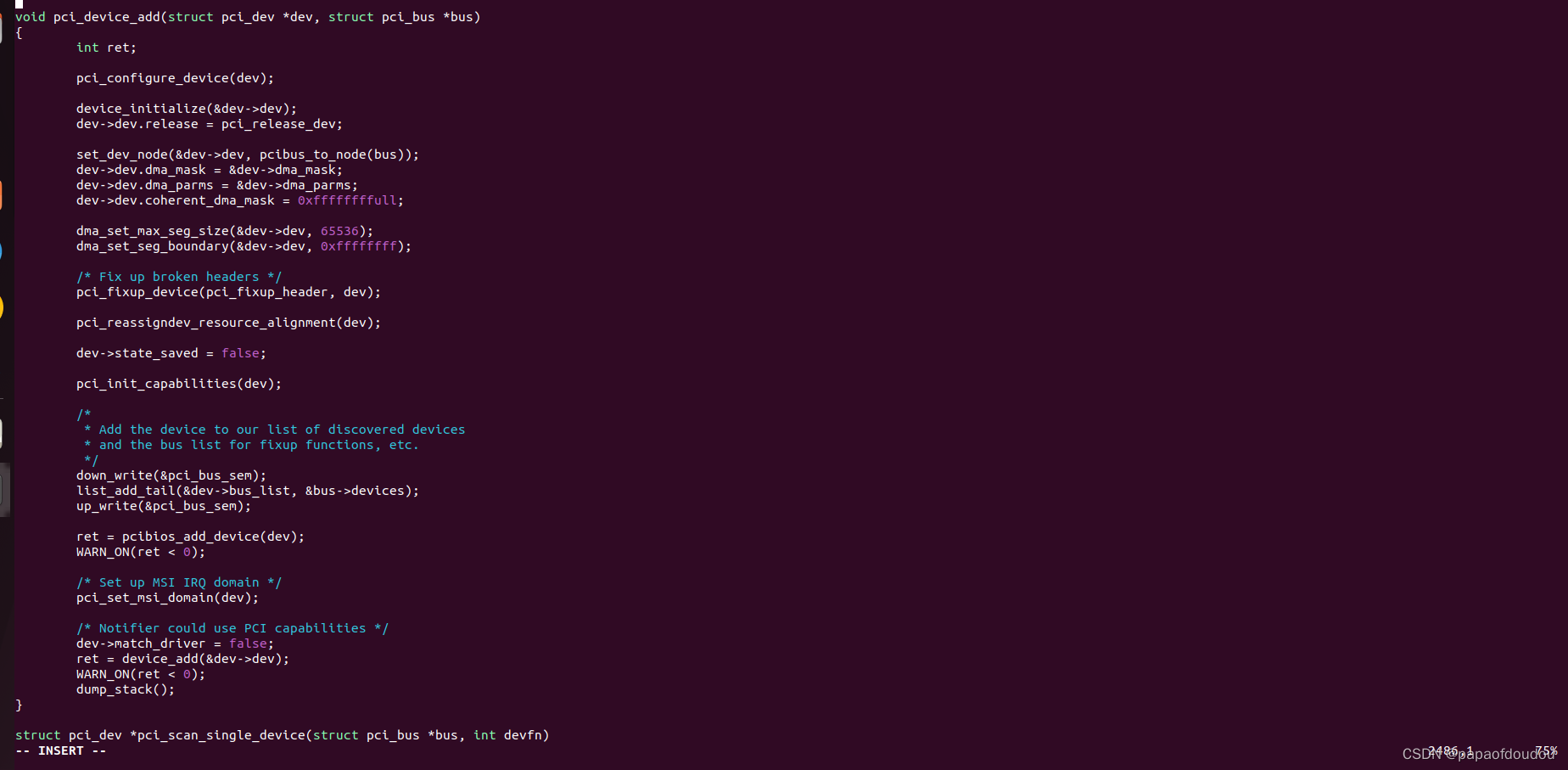
acpi_init
写代码MAP BAR空间:
下面代码将网卡设备的BAR4空间映射到系统,并且打印部分数据.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <errno.h>// bdf:bus, device, function,bus number take 8bits, device number take 5bits, function number
// take 3bits,so, pcie RC support max 256 child buses,support 32 devices each buses, 8 functions each
// device. BUS0 is RC(root complex).void dump_memory(unsigned char *buf, int len)
{int i;for(i = 0; i < len; i ++){if(i % 16 == 0 )printf("%p:", buf + i);printf("0x%02x ", buf[i]);if(i % 16 == 15)printf("\n");}return;
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{char filename[256];struct stat statbuf;int domain = 0;if(argc != 5){printf("%s line %d, the command use like this: ./program bus slot function bar.\n", __func__, __LINE__);return -1;}int bus = atoi(argv[1]);int slot = atoi(argv[2]);int func = atoi(argv[3]);int bar = atoi(argv[4]);memset(filename, 0x00, 256);// bdf address, domain:bus:slot.funcsnprintf(filename, 99, "/sys/bus/pci/devices/%04x:%02x:%02x.%1x/resource%d", domain, bus, slot, func, bar);printf("open file %s.\n", filename);int fd = open(filename, O_RDWR | O_SYNC);if(fd < 0){printf("%s line %d, fatal error, open file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);return -1;}int status = fstat(fd, &statbuf);if(status < 0){printf("%s line %d, status file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);return -1;}printf("%s line %d, bar zone size %ld bytes, %ld Kbytes, %ld Mbytes, %ld Gbytes.\n", \__func__, __LINE__, statbuf.st_size, statbuf.st_size/1024, statbuf.st_size/1024/1024, statbuf.st_size/1024/1024/1024);unsigned char* maddr = (unsigned char *)mmap(NULL,(size_t)(statbuf.st_size),PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,MAP_SHARED,fd,0);if(maddr == (unsigned char *)MAP_FAILED){printf("%s line %d, failure for mmap bar err %s.\n", __func__, __LINE__, strerror(errno));close(fd);return -1;}printf("%s line %d, fw 0x%p.\n", __func__, __LINE__, maddr);memset(filename, 0x00, 256);snprintf(filename, 99, "/sys/bus/pci/devices/%04x:%02x:%02x.%1x/config", domain, bus, slot, func);int fdcfg = open(filename, O_RDWR | O_SYNC);if(fdcfg < 0){printf("%s line %d, fatal error, open file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);return -1;}status = lseek(fdcfg, 0x10 + 4*bar, SEEK_SET);if(status < 0){printf("%s line %d, status file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);close(fdcfg);return -1;}unsigned int phys;status = read(fdcfg, &phys, 4);if(status < 0){printf("%s line %d, status file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);close(fdcfg);return -1;}printf("%s line %d phys 0x%x.\n", __func__, __LINE__, phys);int offset = ((phys & 0xFFFFFFF0) % 0x1000);unsigned char* addr = maddr + offset;printf("%s line %d, addr = %p.\n", __func__, __LINE__, addr);dump_memory(addr, 256);close(fd);close(fdcfg);return 0;
}
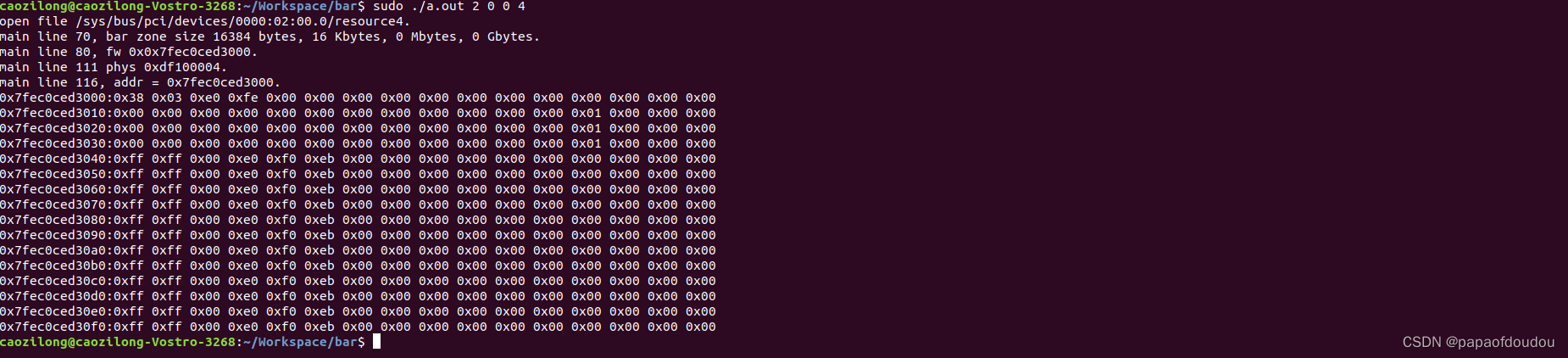
执行结果,可以看到正确的读出了BAR4空间的内存。
关于BAR空间映射:
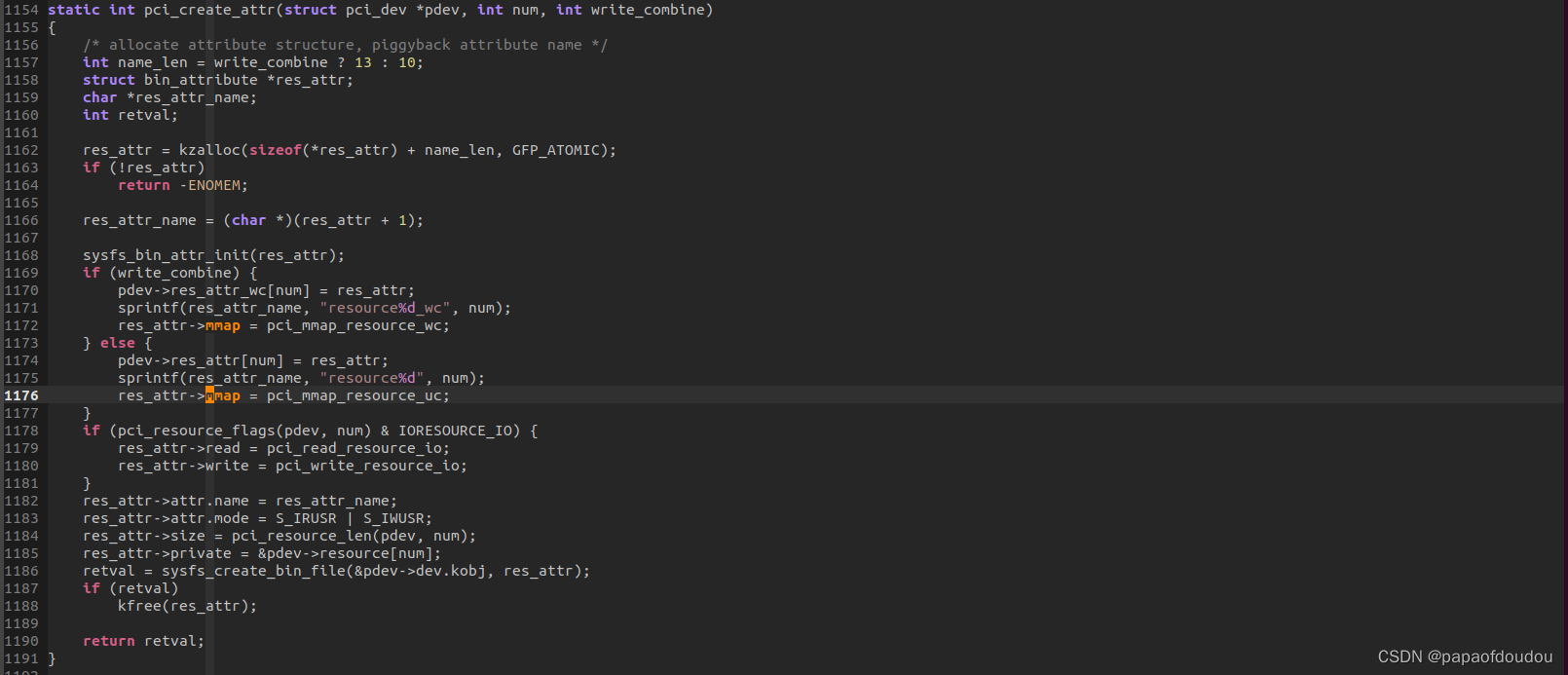
代码中对BAR的映射基于resource节点
/sys/bus/pci/devices/%04x:%02x:%02x.%1x/resource%resource节点在内核代码中的创建是在如下位置pci_create_attr:
发起调用的地方在sysfs_kf_bin_mmap:

map调用路径为pci_mmap_resource:
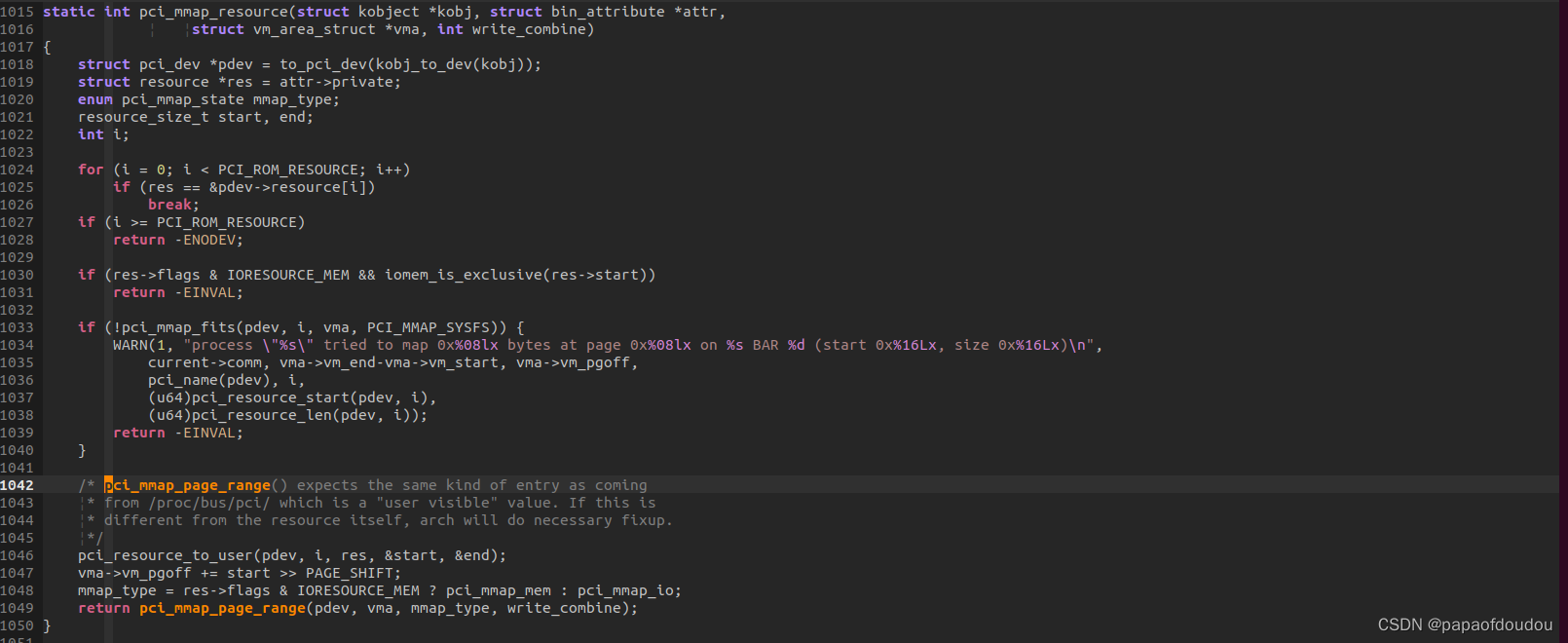
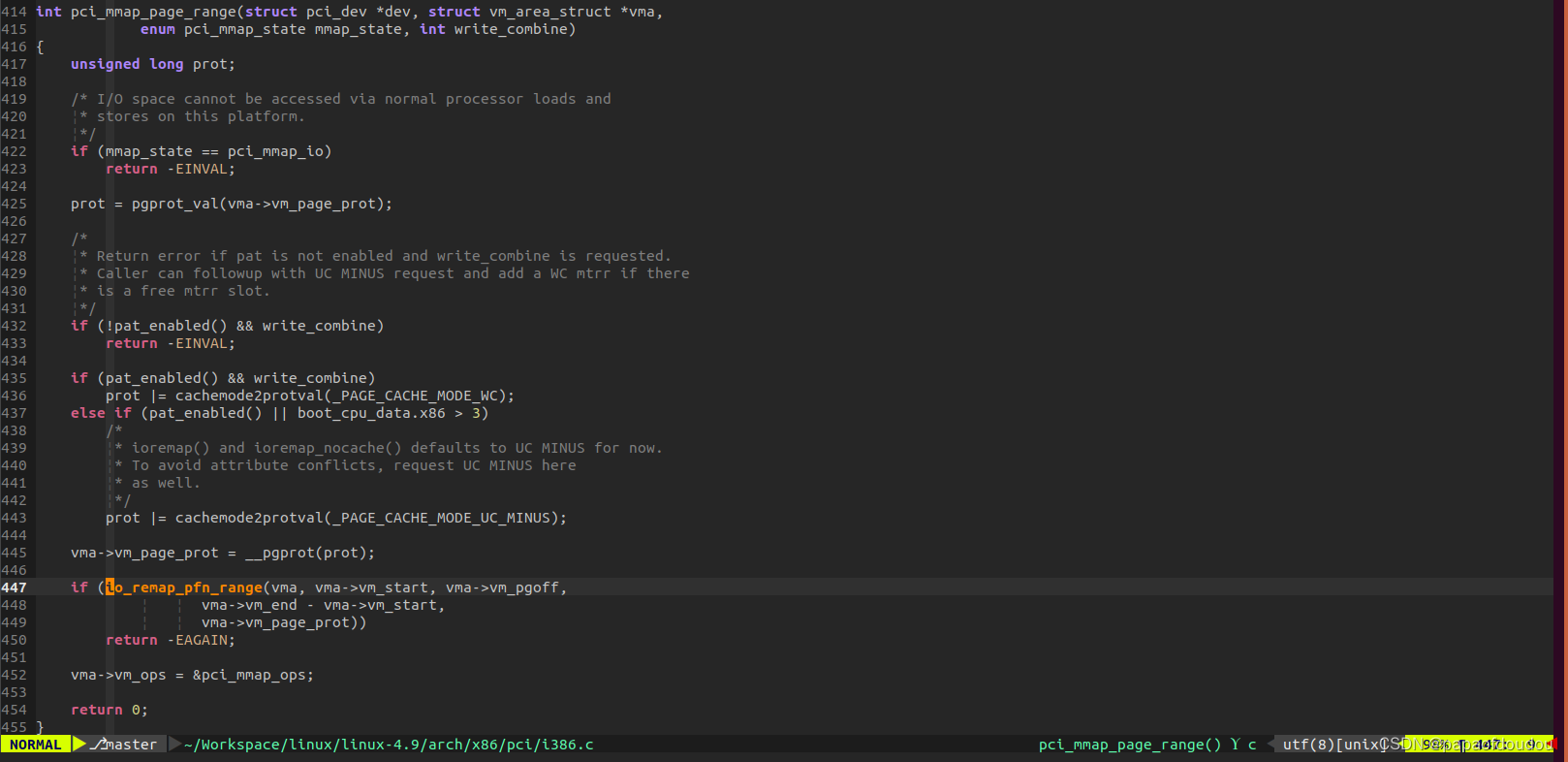

可以看到,对BAR空间的映射也是基于通用的iomap函数。并且其映物理地址来源于resource中记录的对应的BAR空间地址。所以用户空间的MAP本质上是把内核BAR空间的地址当作物理地址映射给用户态,内核也是按照页去分。

Read VRAM of NVIDIA GPU CARD
./a.out 2 0 0 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
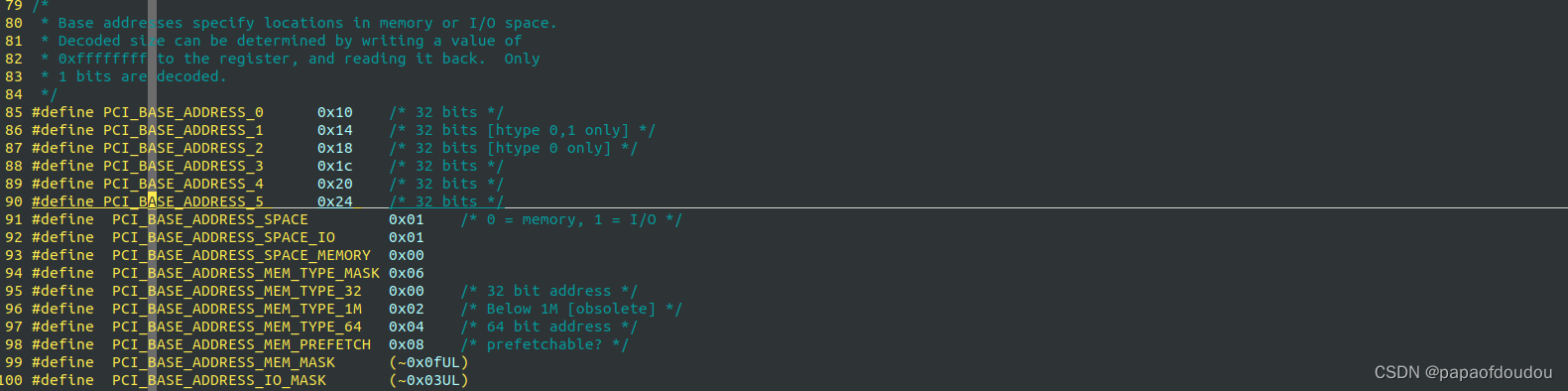
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <errno.h>// bdf:bus, device, function,bus number take 8bits, device number take 5bits, function number
// take 3bits,so, pcie RC support max 256 child buses,support 32 devices each buses, 8 functions each
// device. BUS0 is RC(root complex).void dump_memory(unsigned char *buf, int len)
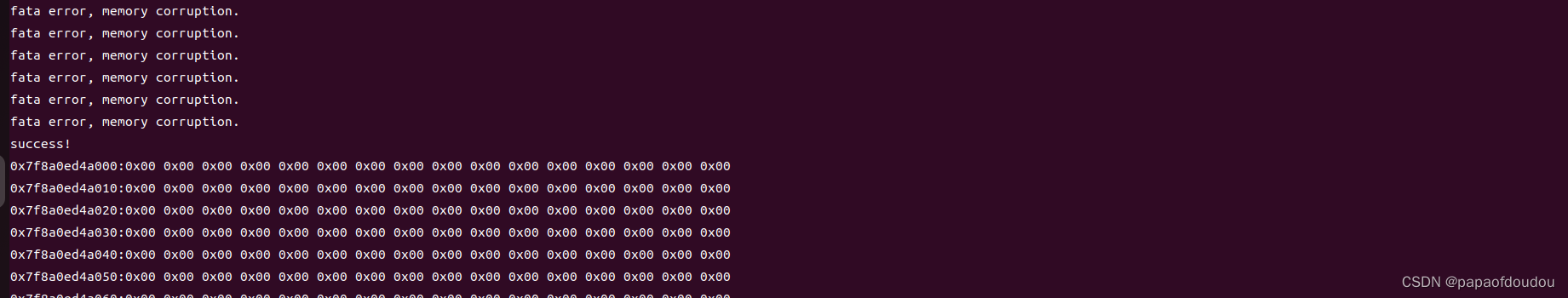
{int i;for(i = 0; i < len; i ++){buf[i] = i;}for(i = 0; i < len; i ++){if(buf[i] != i){printf("fata error, memory corruption.\n");}}printf("success!\n");for(i = 0; i < len; i ++){if(i % 16 == 0 )printf("%p:", buf + i);printf("0x%02x ", buf[i]);if(i % 16 == 15)printf("\n");}return;
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{char filename[256];struct stat statbuf;int domain = 0;if(argc != 5){printf("%s line %d, the command use like this: ./program bus slot function bar.\n", __func__, __LINE__);return -1;}int bus = atoi(argv[1]);int slot = atoi(argv[2]);int func = atoi(argv[3]);int bar = atoi(argv[4]);memset(filename, 0x00, 256);// bdf address, domain:bus:slot.funcsnprintf(filename, 99, "/sys/bus/pci/devices/%04x:%02x:%02x.%1x/resource%d", domain, bus, slot, func, bar);printf("open file %s.\n", filename);int fd = open(filename, O_RDWR | O_SYNC);if(fd < 0){printf("%s line %d, fatal error, open file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);return -1;}int status = fstat(fd, &statbuf);if(status < 0){printf("%s line %d, status file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);return -1;}printf("%s line %d, bar zone size %ld bytes, %ld Kbytes, %ld Mbytes, %ld Gbytes.\n", \__func__, __LINE__, statbuf.st_size, statbuf.st_size/1024, statbuf.st_size/1024/1024, statbuf.st_size/1024/1024/1024);unsigned char* maddr = (unsigned char *)mmap(NULL,(size_t)(statbuf.st_size - 0x600000),PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,MAP_SHARED,fd,0);if(maddr == (unsigned char *)MAP_FAILED){printf("%s line %d, failure for mmap bar err %s.\n", __func__, __LINE__, strerror(errno));close(fd);return -1;}printf("%s line %d, fw 0x%p.\n", __func__, __LINE__, maddr);memset(filename, 0x00, 256);snprintf(filename, 99, "/sys/bus/pci/devices/%04x:%02x:%02x.%1x/config", domain, bus, slot, func);int fdcfg = open(filename, O_RDWR | O_SYNC);if(fdcfg < 0){printf("%s line %d, fatal error, open file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);return -1;}status = lseek(fdcfg, 0x10 + 4*bar, SEEK_SET);if(status < 0){printf("%s line %d, status file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);close(fdcfg);return -1;}unsigned int phys;status = read(fdcfg, &phys, 4);if(status < 0){printf("%s line %d, status file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);close(fd);close(fdcfg);return -1;}printf("%s line %d phys 0x%x.\n", __func__, __LINE__, phys);int offset = ((phys & 0xFFFFFFF0) % 0x1000);unsigned char* addr = maddr + offset;printf("%s line %d, addr = %p.\n", __func__, __LINE__, addr);dump_memory(addr, 256);close(fd);close(fdcfg);return 0;
}
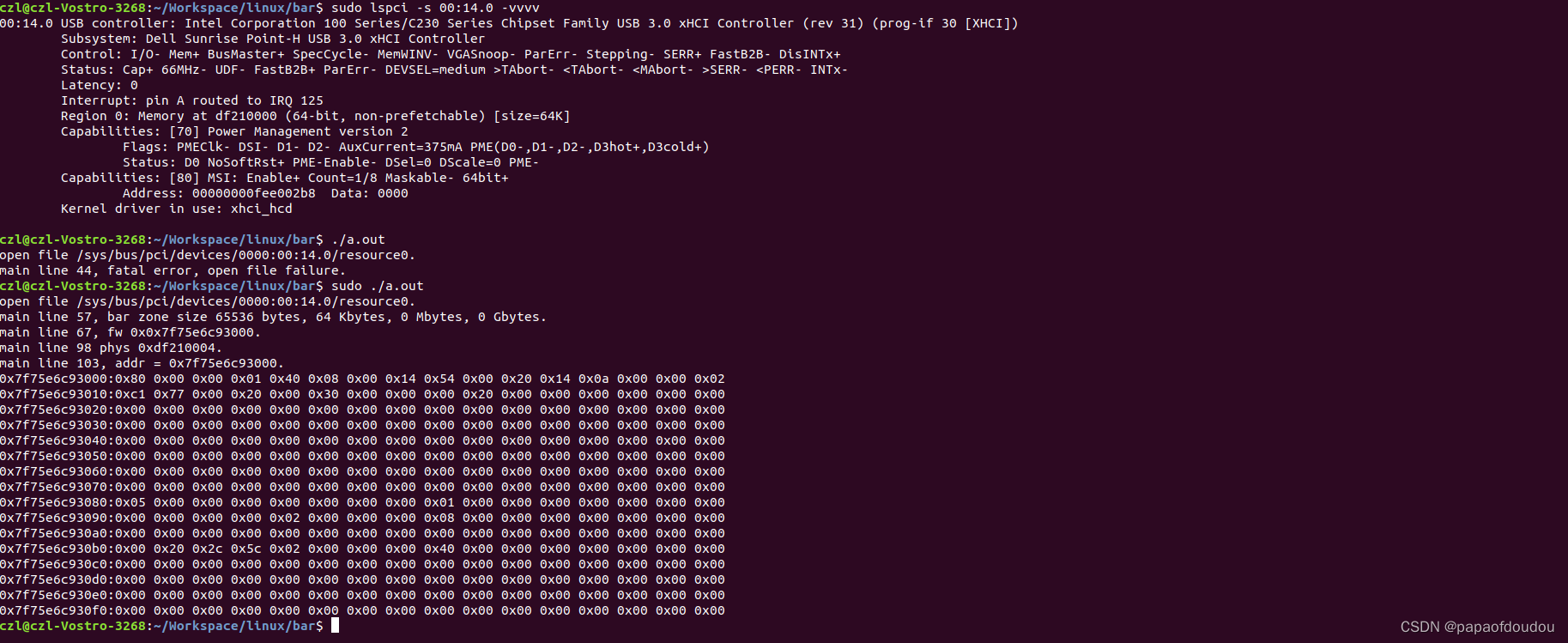
Read bar address from config file
the bar address read from config are identical with which read from the lspci output,you can find this principle from below picture.
configuration
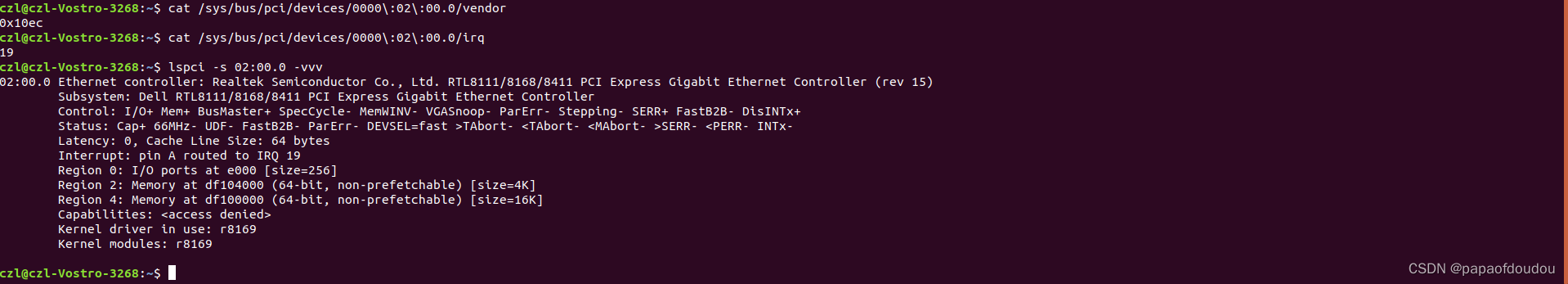
in pci device system directory including many different files:

config is a binary files, you can read the orignal configuration from this file. vendor, device, subsystem_device, subsystem_vendor, and class are all represents the specify value of pci device.
you also can get he IRQ NO from the the irq file.
Install PCIE工具
sudo apt install pciutils-devPCIE的复位等级
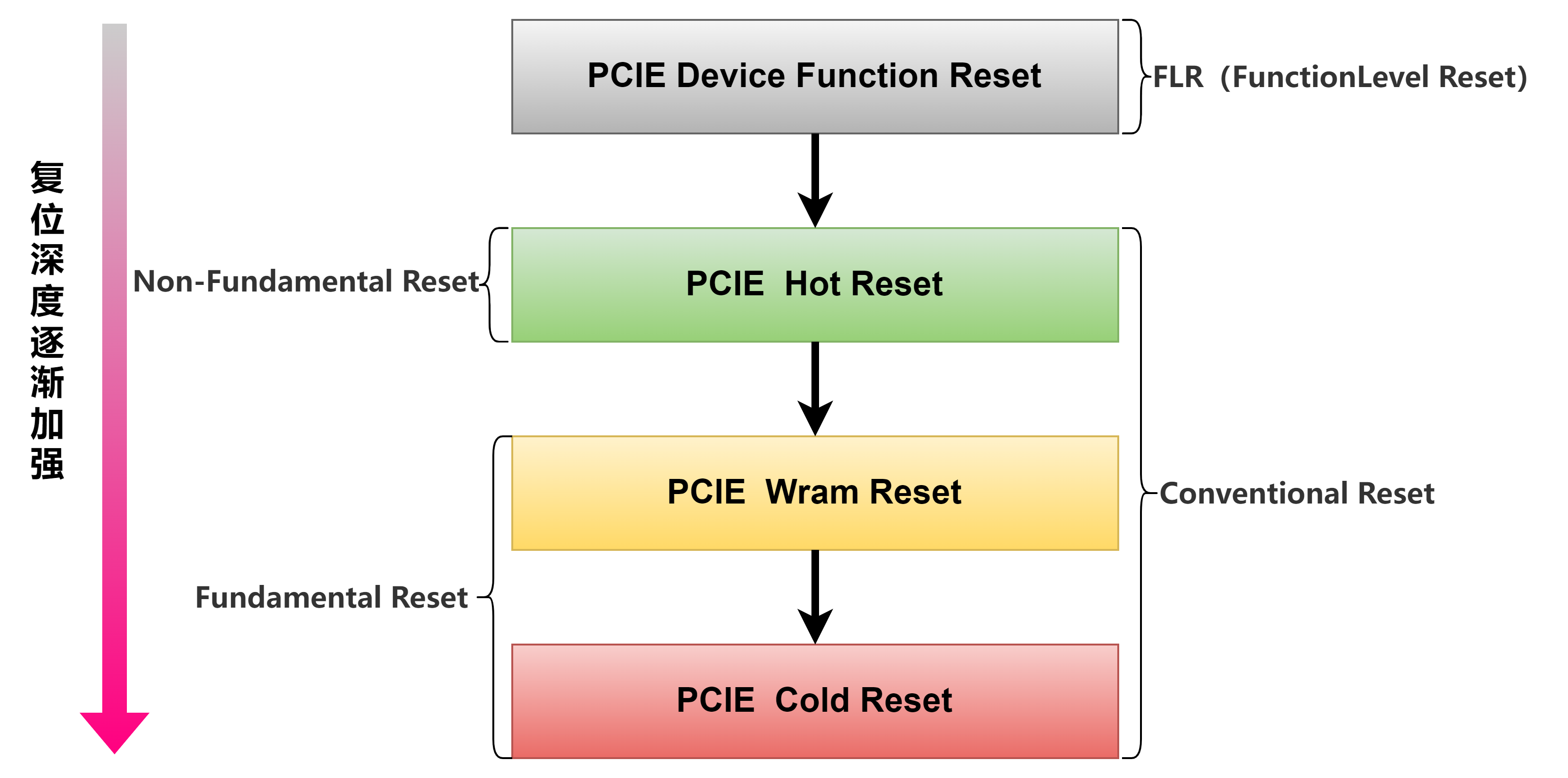
PCIE Based NPU Driver Init flow
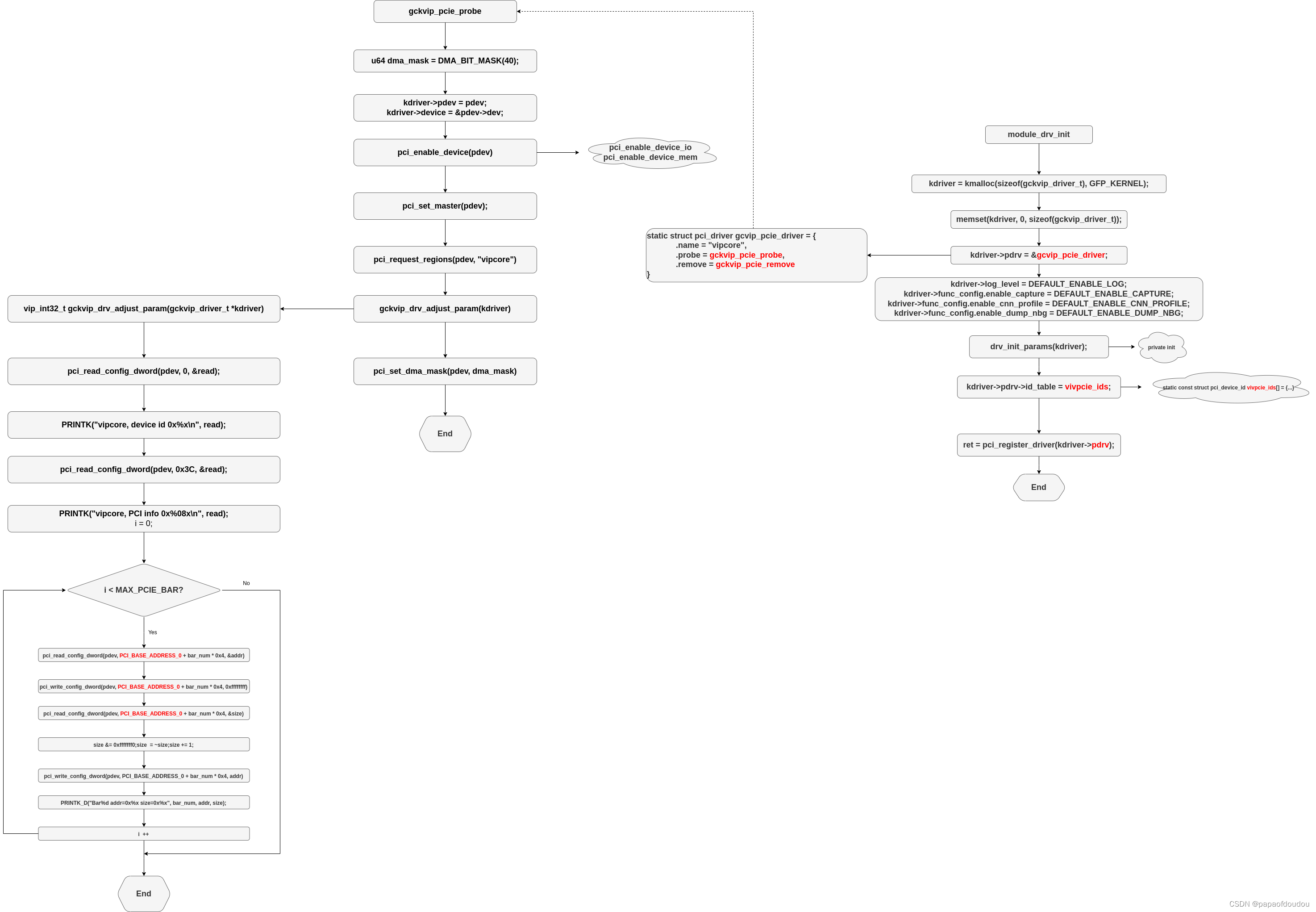
An example map of PCI System
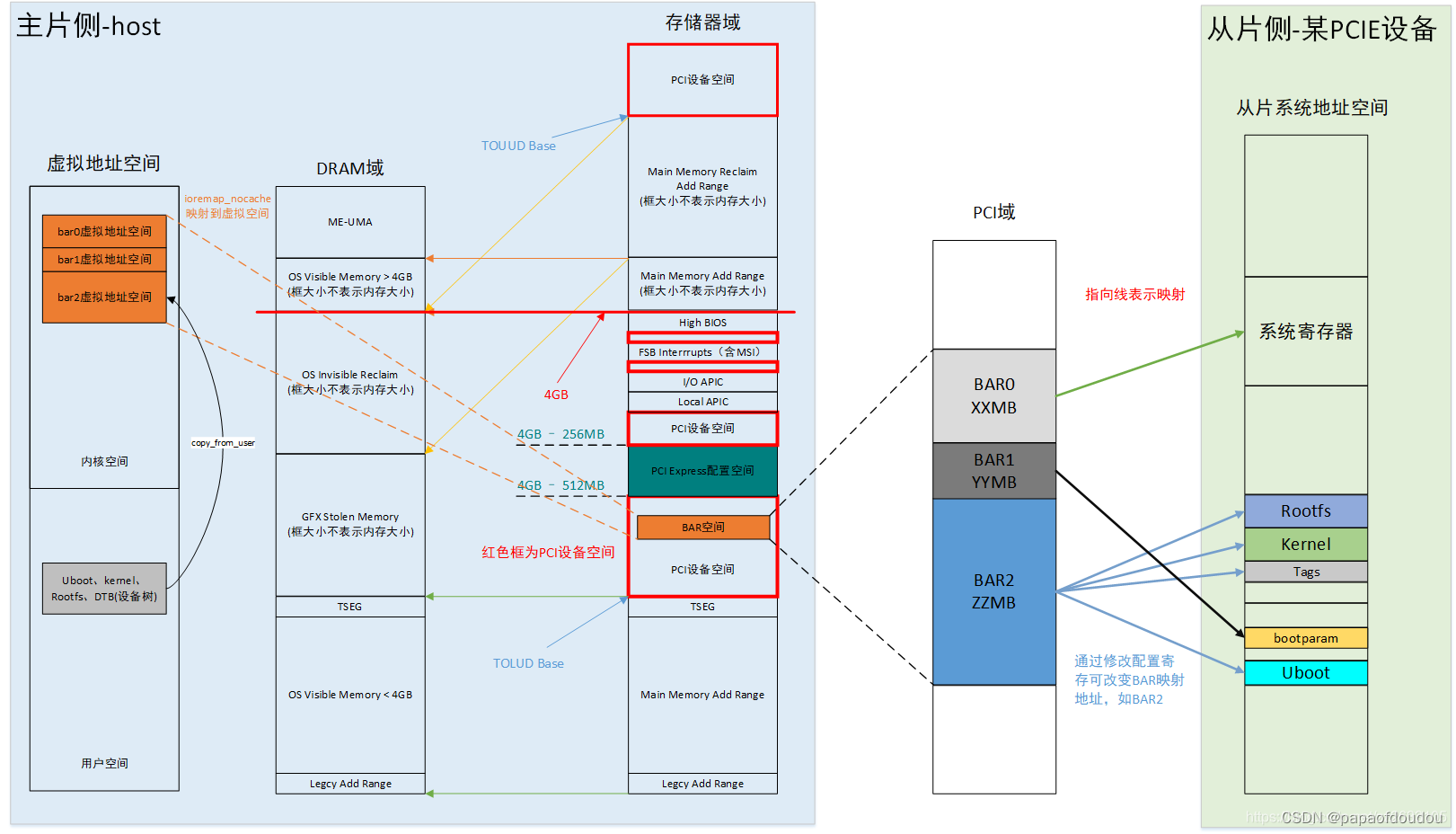
how to iter the PCI bus system and read all the availble device config data?
通过PCI的IOPORT 0xcf8-0xcff 口可以对PCI设备的配置信息进行读取,/proc/ioports文件对此IO口有记录:

#include <sys/io.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>//define pcie device info limit
#define MAX_BUS 256
#define MAX_DEVICE 32
#define MAX_FUNCTION 8//define CONFIG_ADDRESS and CONFIG_DATA
#define CONFIG_ADDRESS 0xCF8
#define CONFIG_DATA 0xCFC
#define BASE_ADDR 0x80000000
typedef unsigned int WORD;//4byteint main()
{WORD bus,device,func,reg;WORD data,address;//read info from CONFIG_DATA,address set to CONFIG_ADDRESSint ret=0;//unsigned char tmpc; ret = iopl(3);if(ret<0){perror("iopl set to high level error\n");return -1;}//printf("bus\tdev\func\n");for(bus=0;bus<MAX_BUS;bus++) {for(device=0;device<MAX_DEVICE;device++) {for(func=0;func<MAX_FUNCTION;func++) {address = BASE_ADDR|(bus<<16)|(device<<11)|(func<<8);// put addr to config_addressoutl(address,CONFIG_ADDRESS);// read data from config data;data = inl(CONFIG_DATA);// valid feedback of this bdf slot.if((data!=0xffffffff) && (data!=0)) {printf("\n%02x:%02x.%x\n",bus,device,func);for(reg=0;reg<16;reg++) {if(reg%4==0) {printf("%02x:",reg*4);}address = BASE_ADDR|(bus<<16)|(device<<11)|(func<<8)|(reg<<2); outl(address,CONFIG_ADDRESS);//put addr to config_addressdata = inl(CONFIG_DATA);//read data from config data;printf("%02x ",(data>>0)&0xff);printf("%02x ",(data>>8)&0xff);printf("%02x ",(data>>16)&0xff);printf("%02x ",(data>>24)&0xff);if(reg%4==3) printf("\n");}}}}}iopl(0);if(ret<0){perror("iopl set to low level error\n");return -1;}return 0;
}result compare with the lspci -nn output
czl@czl-Vostro-3268:~/Workspace/linux/bar$ sudo ./a.out 00:00.0
00:86 80 1f 59 06 01 90 20 05 00 00 06 00 00 00 00
10:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
20:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 28 10 62 07
30:00 00 00 00 e0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00:01.0
00:86 80 01 19 07 05 10 00 05 00 04 06 00 00 81 00
10:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 01 01 00 f0 00 00 00
20:f0 ff 00 00 f1 ff 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
30:00 00 00 00 88 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 01 12 00 00:02.0
00:86 80 12 59 07 04 10 00 04 00 00 03 00 00 00 00
10:04 00 00 de 00 00 00 00 0c 00 00 c0 00 00 00 00
20:01 f0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 28 10 62 07
30:00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 01 00 00 00:14.0
00:86 80 2f a1 06 05 90 02 31 30 03 0c 00 00 80 00
10:04 00 21 df 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
20:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 28 10 62 07
30:00 00 00 00 70 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 01 00 00 00:14.2
00:86 80 31 a1 02 01 10 00 31 00 80 11 00 00 00 00
10:04 e0 22 df 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
20:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 28 10 62 07
30:00 00 00 00 50 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 03 00 00 00:16.0
00:86 80 3a a1 06 04 10 00 31 00 80 07 00 00 80 00
10:04 d0 22 df 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
20:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 28 10 62 07
30:00 00 00 00 50 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 01 00 00 00:17.0
00:86 80 02 a1 07 05 b0 02 31 01 06 01 00 00 00 00
10:00 80 22 df 00 c0 22 df 91 f0 00 00 81 f0 00 00
20:61 f0 00 00 00 b0 22 df 00 00 00 00 28 10 62 07
30:00 00 00 00 80 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 03 00 00 00:1c.0
00:86 80 14 a1 07 05 10 00 f1 00 04 06 00 00 81 00
10:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 02 02 00 e0 e0 00 20
20:10 df 10 df f1 ff 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
30:00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 01 12 00 00:1c.6
00:86 80 16 a1 07 05 10 00 f1 00 04 06 00 00 81 00
10:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 03 03 00 f0 00 00 20
20:00 df 00 df f1 ff 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
30:00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 03 12 00 00:1f.0
00:86 80 43 a1 07 01 00 02 31 00 01 06 00 00 80 00
10:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
20:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 28 10 62 07
30:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00:1f.2
00:86 80 21 a1 00 00 00 00 31 00 80 05 00 00 80 00
10:00 40 22 df 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
20:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 28 10 62 07
30:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00:1f.3
00:86 80 70 a1 06 05 10 00 31 00 03 04 00 20 00 00
10:04 00 22 df 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
20:04 00 20 df 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 28 10 62 07
30:00 00 00 00 50 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 01 00 00 00:1f.4
00:86 80 23 a1 03 01 80 02 31 00 05 0c 00 00 00 00
10:04 a0 22 df 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
20:41 f0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 28 10 62 07
30:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 01 00 00 02:00.0
00:ec 10 68 81 07 05 10 00 15 00 00 02 10 00 00 00
10:01 e0 00 00 00 00 00 00 04 40 10 df 00 00 00 00
20:04 00 10 df 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 28 10 62 07
30:00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 01 00 00 03:00.0
00:8c 16 36 00 06 01 10 00 01 00 80 02 10 00 00 00
10:04 00 00 df 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
20:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 28 10 0e 02
30:00 00 08 df 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 01 00 00 03:00.1
00:8c 16 ce ab 00 00 10 00 01 10 03 0c 00 00 80 00
10:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
20:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
30:00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff 02 00 00
czl@czl-Vostro-3268:~/Workspace/linux/bar$
czl@czl-Vostro-3268:~/Workspace/linux/bar$ lspci -nn
00:00.0 Host bridge [0600]: Intel Corporation Xeon E3-1200 v6/7th Gen Core Processor Host Bridge/DRAM Registers [8086:591f] (rev 05)
00:01.0 PCI bridge [0604]: Intel Corporation Xeon E3-1200 v5/E3-1500 v5/6th Gen Core Processor PCIe Controller (x16) [8086:1901] (rev 05)
00:02.0 VGA compatible controller [0300]: Intel Corporation HD Graphics 630 [8086:5912] (rev 04)
00:14.0 USB controller [0c03]: Intel Corporation 100 Series/C230 Series Chipset Family USB 3.0 xHCI Controller [8086:a12f] (rev 31)
00:14.2 Signal processing controller [1180]: Intel Corporation 100 Series/C230 Series Chipset Family Thermal Subsystem [8086:a131] (rev 31)
00:16.0 Communication controller [0780]: Intel Corporation 100 Series/C230 Series Chipset Family MEI Controller #1 [8086:a13a] (rev 31)
00:17.0 SATA controller [0106]: Intel Corporation Q170/Q150/B150/H170/H110/Z170/CM236 Chipset SATA Controller [AHCI Mode] [8086:a102] (rev 31)
00:1c.0 PCI bridge [0604]: Intel Corporation 100 Series/C230 Series Chipset Family PCI Express Root Port #5 [8086:a114] (rev f1)
00:1c.6 PCI bridge [0604]: Intel Corporation 100 Series/C230 Series Chipset Family PCI Express Root Port #7 [8086:a116] (rev f1)
00:1f.0 ISA bridge [0601]: Intel Corporation H110 Chipset LPC/eSPI Controller [8086:a143] (rev 31)
00:1f.2 Memory controller [0580]: Intel Corporation 100 Series/C230 Series Chipset Family Power Management Controller [8086:a121] (rev 31)
00:1f.3 Audio device [0403]: Intel Corporation 100 Series/C230 Series Chipset Family HD Audio Controller [8086:a170] (rev 31)
00:1f.4 SMBus [0c05]: Intel Corporation 100 Series/C230 Series Chipset Family SMBus [8086:a123] (rev 31)
02:00.0 Ethernet controller [0200]: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller [10ec:8168] (rev 15)
03:00.0 Network controller [0280]: Qualcomm Atheros QCA9565 / AR9565 Wireless Network Adapter [168c:0036] (rev 01)

LINUX内核中对此口的使用:


![python自动翻译视频字幕_音视频自动字幕生成(翻译)—[autosub]](https://www.wmdxcn.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/logo_onwhite-1-300x72.png)








![[转]魔兽世界私服Trinity,从源码开始](https://img-blog.csdn.net/20160914114928805?watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nkbi5uZXQv/font/5a6L5L2T/fontsize/400/fill/I0JBQkFCMA==/dissolve/70/gravity/Center)