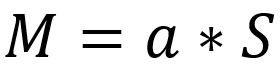r语言 支持向量机实现
Support Vector Machine, popularly abbreviated as SVM is a supervised learning algorithm used for both regression and classification but more commonly used for classification. SVMs have been shown to outperform well in a variety of setting and are often considered as one of the best “out of box” classifiers.
支持向量机(Support Vector Machine),通常缩写为SVM,是一种用于回归和分类的监督学习算法,但更常用于分类。 SVM在各种设置下均表现出色,通常被认为是最好的“开箱即用”分类器。
In this article we will discuss SVMs for a 2-class classification setting. The approach used in Support Vector Machines is based on finding a separting hyperplane.
在本文中,我们将讨论用于2类分类设置的SVM。 支持向量机中使用的方法是基于找到分离的超平面 。
Let us start by defining a hyperplane.
让我们首先定义一个超平面。
什么是超平面? (What is a hyperplane?)
In a p dimensional space, a hyperplane(H) is a flat affine subspace of dimension p-1. In other words, if V is a p-dimensional vector space than H is a (p-1) dimensional subspace. Examples of hyperplanes in 2 dimensions are any straight line through the origin. In 3 dimensions, any plane containing the origin.
在ap维空间中,超平面(H)是维p-1的平仿射子空间。 换句话说,如果V是p维向量空间,则H是(p-1)维子空间。 二维超平面的示例是通过原点的任何直线。 在3维中,包含原点的任何平面。
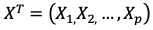
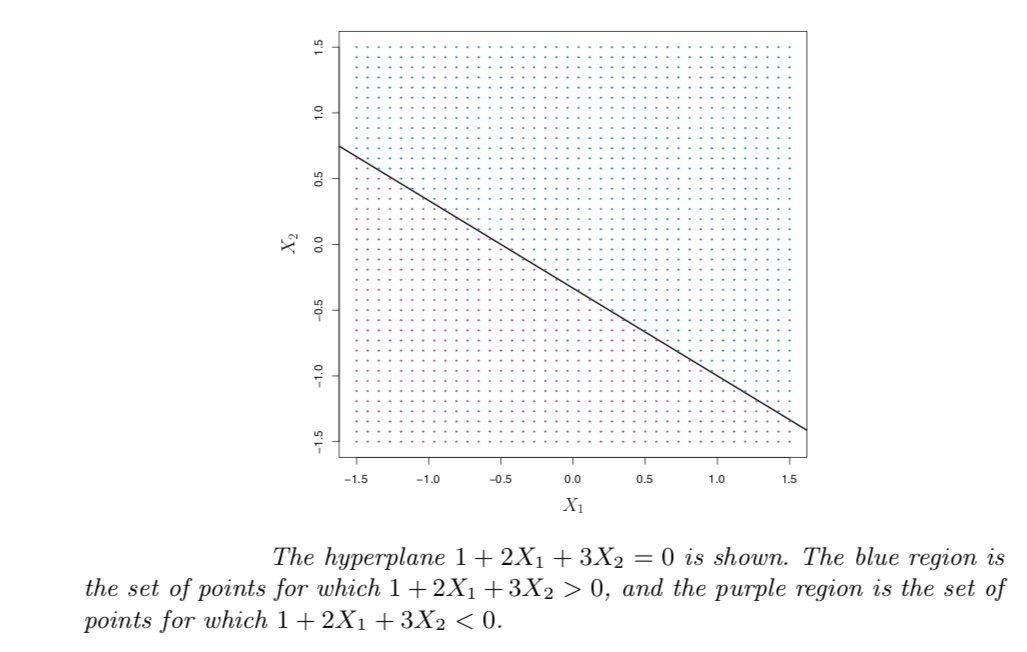
The hyperplane mentioned above divides the p-dimensional space into two halves. Depending on whether the equation is >0 or <0 , the point X lies on either sides of the hyperplane.
上述超平面将p维空间分为两半。 根据等式是> 0还是<0,点X位于超平面的两侧。
使用分离的超平面进行分类 (Classification Using a Separating Hyperplane)
Now that we have understood what a hyperplane is, let us take another step forward towards building a classifier based on a separating hyperplane. If such a hyperplane exists which can separate our training observations into two classes namely y_i=1 and y_i=-1 then the hyperplane has the following properties;
既然我们已经了解了什么是超平面,那么让我们朝着基于分离的超平面构建分类器又迈出一步。 如果存在这样的超平面,可以将我们的训练观察结果分为两类,即y_i = 1和y_i = -1,则该超平面具有以下属性;
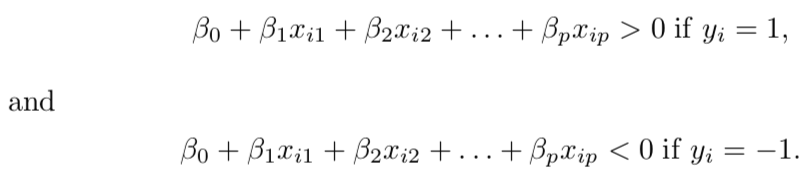
De facto, this can be written in one single equation as;
实际上,这可以写成一个方程:
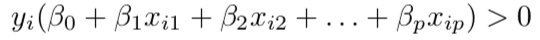
There could be infinite number of such hyperplanes. The figure below shows three such hyperplanes;
这样的超平面可能是无限的。 下图显示了三个这样的超平面;
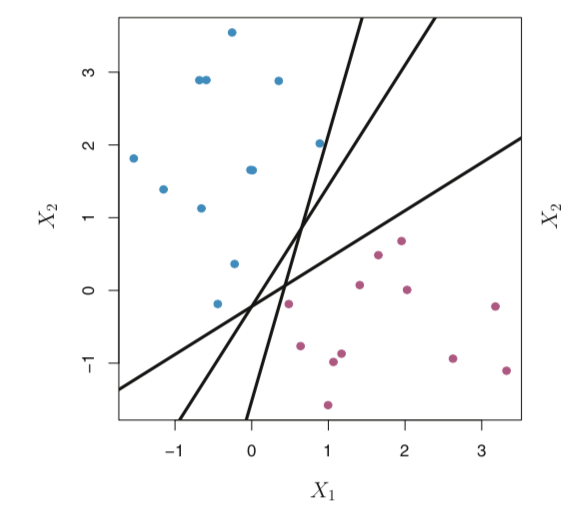
If a separating hyperplane exists, we can use it to construct a very trivial classifier : a test observation(x) is assigned a class depending on which side of the hyperplane it is located(by looking at the sign of the above equation) . We can also make use of the magnitude of the equation of the hyperplane. If it is large, x lies far away from the hyperplane so we can be more confident about our class assignment for x.
如果存在分离的超平面,我们可以使用它构造一个非常简单的分类器:根据测试观测值(x)所在的超平面的哪一侧为其分配一个类(通过查看上述方程式的符号)。 我们还可以利用超平面方程的大小。 如果它很