replace/replaceAll
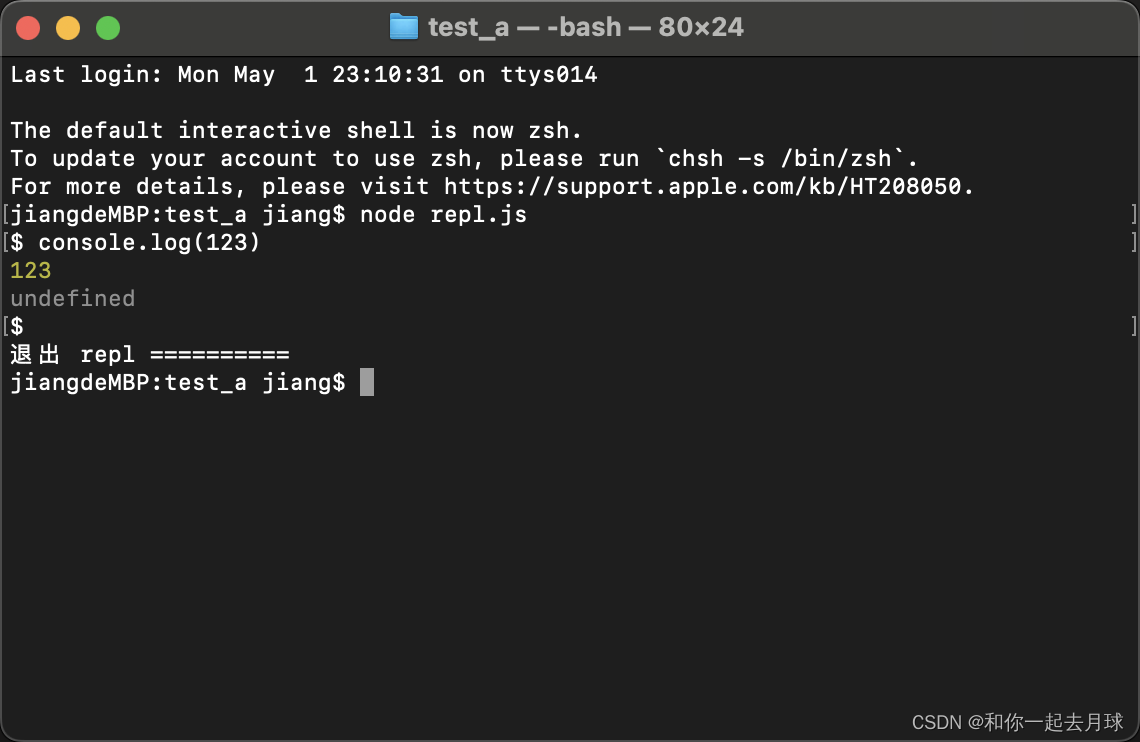
在leetcode刷到替换空格的问题,一通反复比较,发现String对象中的replace和replaceAll虽然实现效果相同,但是执行用时和内存消耗略有差异;Be Like:


难道说底层实现有哪里不一样?让我来康康源码(JDK8下);
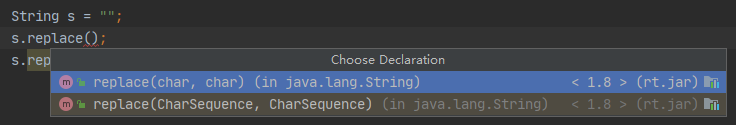
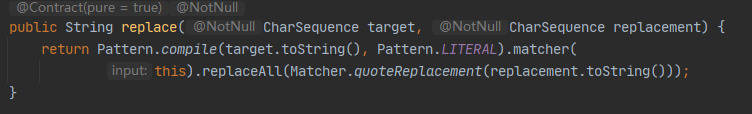
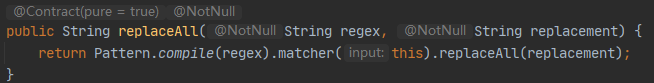
emmmm…可以看出String.replace() 和 String.replaceAll() 调用的方法是一样的,都调用了Matcher.replaceAll() 方法;那就是他们调用的方式不同啦;可以看到replaceAll() 方法没有传入参数 “Pattern.LITERAL”;
再来康康 “Pattern.LITERAL”是如何起作用?
咱就是说,既然compile()里面的不同,咱就一层一层往下翻:
图放不下了,这是compile的源码:
private void compile() {// Handle canonical equivalencesif (has(CANON_EQ) && !has(LITERAL)) {normalize();} else {normalizedPattern = pattern;}patternLength = normalizedPattern.length();// Copy pattern to int array for convenience// Use double zero to terminate patterntemp = new int[patternLength + 2];hasSupplementary = false;int c, count = 0;// Convert all chars into code pointsfor (int x = 0; x < patternLength; x += Character.charCount(c)) {c = normalizedPattern.codePointAt(x);if (isSupplementary(c)) {hasSupplementary = true;}temp[count++] = c;}patternLength = count; // patternLength now in code pointsif (! has(LITERAL))RemoveQEQuoting();// Allocate all temporary objects here.buffer = new int[32];groupNodes = new GroupHead[10];namedGroups = null;if (has(LITERAL)) {// Literal pattern handlingmatchRoot = newSlice(temp, patternLength, hasSupplementary);matchRoot.next = lastAccept;} else {// Start recursive descent parsingmatchRoot = expr(lastAccept);// Check extra pattern charactersif (patternLength != cursor) {if (peek() == ')') {throw error("Unmatched closing ')'");} else {throw error("Unexpected internal error");}}}// Peephole optimizationif (matchRoot instanceof Slice) {root = BnM.optimize(matchRoot);if (root == matchRoot) {root = hasSupplementary ? new StartS(matchRoot) : new Start(matchRoot);}} else if (matchRoot instanceof Begin || matchRoot instanceof First) {root = matchRoot;} else {root = hasSupplementary ? new StartS(matchRoot) : new Start(matchRoot);}// Release temporary storagetemp = null;buffer = null;groupNodes = null;patternLength = 0;compiled = true;}引用: 浅析Java正则中的Pattern和Matcher两个类.
在compile()方法中,创建的matchRoot和root对象很关键,是后面执行matches()方法和find()方法的基础。
而matchRoot对象是通过expr(lastAccept)方法创建的,传参lastAccept为LastNode实例。
我们可以看到源码中有一行:matchRoot = expr(lastAccept);执行此方法,就开始进行正则表达式的匹配。
源码通过if-else来判断,参数 regex 是不是一个正则表达式:
- 如果是正则,执行正则替换;
- 如果是字符串,执行字符串替换,此时和 replace() 就是一样的了。
搞明白了底层的不同,还是不明白正则替换的效率为什么会比字符替换的效率低?以及该选择哪个使用呢?
String.replace()和String.replaceAll()性能对比
在这篇博客中指出:两个API的使用场景不同。replaceAll()的功能更强大一些。同时,因为replaceAll()需要处理正则表达式,性能上应该会弱于replace()。
But!!!
jdk8环境下,java字符串使用replace()和replaceAll()方法性能对比
陷入了沉思
自己尝试这篇博客的代码
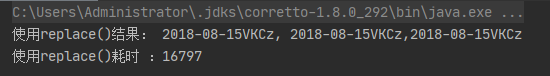
好吧,甚至差异更大;不知道是版本的问题还是有没有注意到的细节;
个人觉得简单替换可以使用replace(),更加复杂的功能实现可以使用replaceAll();