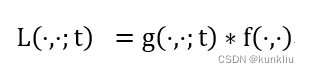什么是图像金字塔
图像金字塔是对图像的一种多尺度表达,将各个尺度的图像按照分辨率从小到大,依次从上到下排列,就会形成类似金字塔的结构,因此称为图像金字塔。
常见的图像金字塔有两类,一种是高斯金字塔(Gaussian Pyramid),另一种的拉普拉斯金字塔(Laplacian Pyramid)。
一般在图像处理中,高斯代表“模糊”,而拉普拉斯代表“差异”。
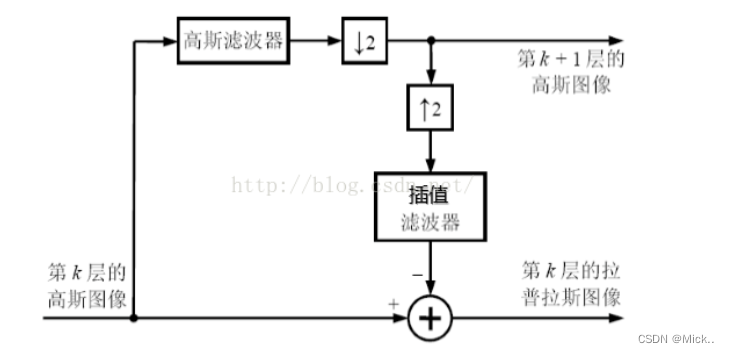
高斯金字塔通过不断对图像进行模糊且下采样而获得,下采样的因子一般是2倍。随着分辨率越来越小,图像会越来越模糊,高斯金字塔的最底层就是原始图像本身。
拉普拉斯金字塔在高斯金字塔的基础上,对所有层进行上采样(一般也是2倍上采样),然后使用原高斯金字塔结果减去通分辨率的上采样结果得到每一层差异,即为拉普拉斯金字塔。注意拉普拉斯金字塔中分辨率最小的图片等同于高斯金字塔通分辨率图片,其他层均为“求差”得到的结果。另外还需注意图像先下采样再上采样后不能复原,因为下采样会产生信息缺失,简单上采样无法弥补回这些信息缺失。
为什么要使用图像金字塔
图像金字塔有很多应用,特别是面对多尺度任务时尤为有用。比如在目标检测任务中,检测对象在图像中的大小往往非常多变,在单一图像尺度下进行滑框寻找往往不能覆盖所有目标,所以就需要在多个尺度下进行滑框,传统的目标检测和基于深度学习的目标检测均是如此。
拉普拉斯金字塔中,大部分的数值接近于0,所以一定程度上可以用于图像压缩。拉普拉斯金字塔还常用于图像融合,基于拉普拉斯金字塔的图像融合,融合边界的过渡往往会相对自然一些。
金字塔的构建
基础函数
-
模糊(卷积)
在金字塔的构建中,上下采样均需要做模糊,下采样中做模糊是为了防止锯齿现象,上采样中做模糊是因为图像金字塔分解中的上采样比较“特别”,不做模糊不行。这里一般使用一个固定的5x5卷积核做模糊,也可以1x5的卷积核,使用行列分离的卷积方法做模糊。 -
下采样
先对图像做模糊,然后直接每隔一个像素抽一个数据即可实现2倍下采样。 -
上采样
将每个像素扩展成2x2的小区域,原像素放在左上角,其他3个位置补0,然后将卷积核乘以4,再对扩展后的图像做模糊即可。
上采样还需注意一个关于数据类型的细节:拉普拉斯金字塔才需要用到上采样,生成拉普拉斯金字塔的过程中需要求差操作,并且拉普拉斯金字塔常常跟图像重建会扯上关系,而uint8在求差或者重建时会引起数据截断误差,所以有可能需要用到非uint8数据类型来作为输出。
特别注意:通过上面描述可以发现,在图像金字塔构建时,上下采样的操作非常简单粗暴,不需要用到常规resize时的图像插值。
代码如下:
文件起名resample.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npdef blur(image, kernel_scale=1.0):"""Blur image using a fixed kernel. Kernel scale can be set.Parameters----------image: image data read by opencv.kernel_scale: the scale factor of kernel."""blur_kernel = np.array([[1, 4, 6, 4, 1],[4, 16, 24, 16, 4],[6, 24, 36, 24, 6],[4, 16, 24, 16, 4],[1, 4, 6, 4, 1]]) / 256.blurred_image = cv2.filter2D(image, ddepth=-1,kernel=blur_kernel * kernel_scale,borderType=cv2.BORDER_REFLECT101)return blurred_imagedef pyramid_down(image):"""Down sample an image by 2x.Parameters----------image: image data read by opencv."""blurred_image = blur(image)image_down = blurred_image[::2, ::2]return image_downdef pyramid_up(image, dst_size=None, dtype=np.uint8):"""Up sample an image by 2x. The output size and data type can be set.Parameters----------image: image data read by opencv.dst_size: the output size. Note that the difference of dst_size and2*image_size should be <=2.dtype: the output data type."""# check dst_sizeheight, width = image.shape[:2]if dst_size is None:dst_size = (width * 2, height * 2)else:if abs(dst_size[0] - width * 2) > 2 or \abs(dst_size[1] - height * 2) > 2:raise ValueError(r'the difference of dst_size and 2*image_size 'r'should be <=2.')# create a new buffer that has the dst_sizedst_width, dst_height = dst_sizeif image.ndim == 2:image_up = np.zeros(shape=(dst_height, dst_width), dtype=dtype)else:channel = image.shape[2]image_up = np.zeros(shape=(dst_height, dst_width, channel),dtype=dtype)image_up[::2, ::2] = imageimage_up = blur(image_up, 4.0)return image_up高斯金字塔 & 拉普拉斯金字塔
高斯金字塔的实现非常简单,不断地使用pyramid_down进行下采样即可,没什么特别需要注意的。
拉普拉斯金字塔需要注意一些事项:1、在生成拉普拉斯金字塔的过程中需要求差,为了不引起数据类型的截断误差, 需要把待求差的两个变量的类型先从uint8转为float32,然后再做求差操作。2、由拉普拉斯金字塔重建图像的过程如果使用uint8也容易产生截断误差,所以在做加法时也需要转float32。
代码如下:
文件起名pyramid.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
from resample import pyramid_down
from resample import pyramid_updef image_to_gaussian_pyramid(image, level, cut_size=(3, 3)):"""Build gaussian pyramid for an image. The size of the output component isarranged in descending order.Parameters----------image: input image data read by opencv.level: level of output pyramid.cut_size: the minimal size of pyramid component, smaller than which thebuilding process will be stopped."""gaussian_pyramid = [image]if level <= 1:return gaussian_pyramidfor i in range(level - 1):# check down-sampled image size, should be >= cut_sizeheight, width = image.shape[:2]height_down = (height + 1) // 2width_down = (width + 1) // 2if width_down < cut_size[0] or height_down < cut_size[1]:break# down sampleimage = pyramid_down(image)gaussian_pyramid.append(image)return gaussian_pyramiddef gaussian_to_laplacian_pyramid(gaussian_pyramid):"""Build a laplacian pyramid from gaussian pyramid. The size of the outputcomponent is arranged in ascending order."""laplacian_pyramid = [gaussian_pyramid[-1]]level = len(gaussian_pyramid)if level == 1:return laplacian_pyramidfor i in range(level - 1, 0, -1):up_size = gaussian_pyramid[i - 1].shape[:2][::-1]image_up = pyramid_up(gaussian_pyramid[i], up_size)# compute difference, use float type to avoid exceeding uint8 limitdiff = np.float32(gaussian_pyramid[i - 1]) - np.float32(image_up)laplacian_pyramid.append(diff)return laplacian_pyramiddef image_to_laplacian_pyramid(image, level, cut_size=(3, 3)):"""Build a laplacian pyramid from an image. The size of the output componentis arranged in an ascending order.Parameters----------image: input image data read by opencv.level: level of output pyramid.cut_size: the minimal size of pyramid component, smaller than which thebuilding process will be stopped."""gaussian_pyramid = image_to_gaussian_pyramid(image, level, cut_size)laplacian_pyramid = gaussian_to_laplacian_pyramid(gaussian_pyramid)return laplacian_pyramiddef laplacian_pyramid_to_image(laplacian_pyramid):"""Reconstruct an image from laplacian pyramid."""image = laplacian_pyramid[0]level = len(laplacian_pyramid)for i in range(1, level):up_size = laplacian_pyramid[i].shape[:2][::-1]image = pyramid_up(image, up_size, np.float32)image = np.float32(image) + laplacian_pyramid[i]image = np.uint8(np.clip(np.round(image), 0, 255))return imagedef get_pyramid_index(original_index, level):"""Get the index of a certain pyramid component corresponding to an index oforiginal imageParameters----------original_index: the index of original image.level: level for pyramid component."""if level < 0:raise ValueError("level can NOT be less than 0")if level == 0:return original_indexbase = 2 ** levelmod = original_index % baseif base == 2 * mod:# decimal part is 0.5return int(round(original_index / base / 2)) * 2else:return int(round(original_index / base))以下代码是金字塔分解的demo示例。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as np
from pyramid import image_to_gaussian_pyramid
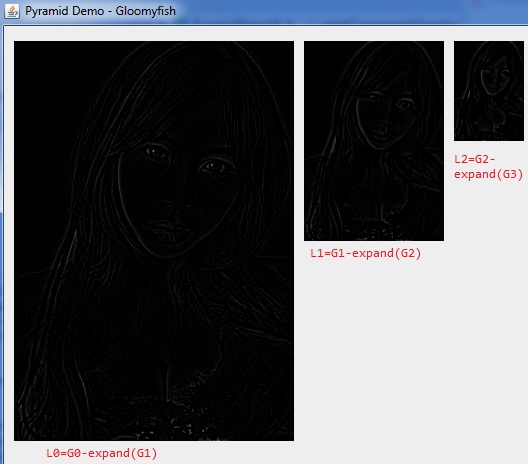
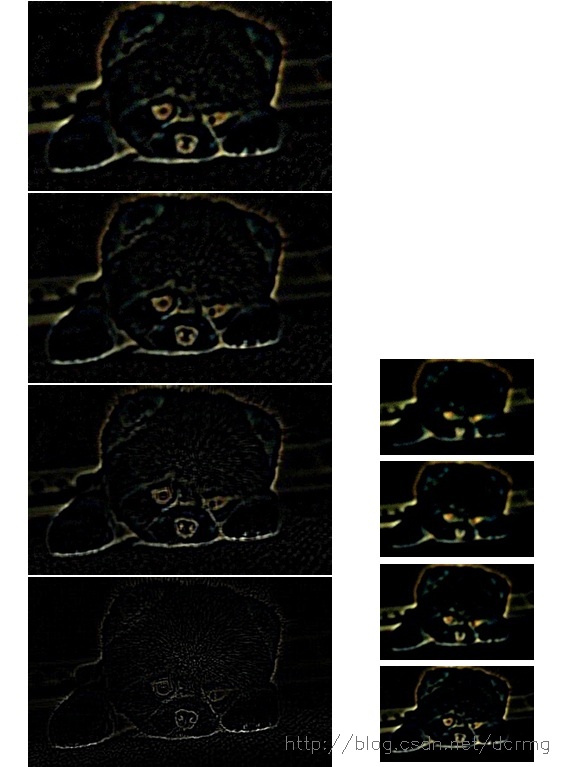
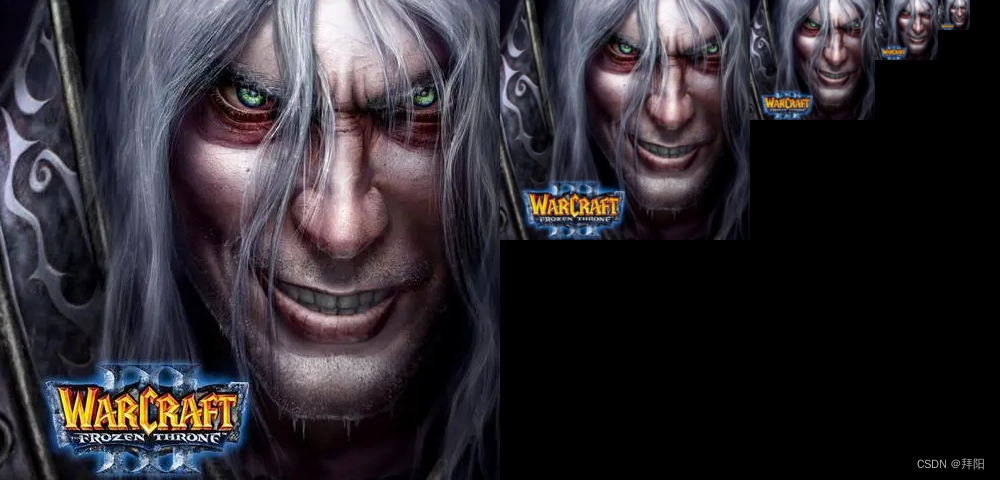
from pyramid import image_to_laplacian_pyramiddef gaussian_pyramid_test():level = 5image = cv2.imread(r'undead.png')height, width, channel = image.shapegau_pyr = image_to_gaussian_pyramid(image, level)# plotoutput = np.zeros((height, width * 2, channel), dtype=np.uint8)x = 0for i in range(level):height, width = gau_pyr[i].shape[:2]output[:height, x:x + width] = gau_pyr[i]x += widthcv2.imwrite('gaussian_pyramid_test.png', output)def laplacian_pyramid_test():level = 5image = cv2.imread(r'undead.png')height, width, channel = image.shapelap_pyr = image_to_laplacian_pyramid(image, level)# plotoutput = np.zeros((height, width * 2, channel), dtype=np.float32)x = width * 2for i in range(level - 1, -1, -1):height, width = lap_pyr[i].shape[:2]if i == 0:output[:height, x - width:x] = lap_pyr[i]else:output[:height, x - width:x] = lap_pyr[i] * 10x -= widthcv2.imwrite('laplacian_pyramid_test.png', output)if __name__ == '__main__':gaussian_pyramid_test()laplacian_pyramid_test()得到的结果如下,分别是5层的高斯金字塔和拉普拉斯金字塔,注意拉普拉斯金字塔除了最小分辨率是正常图像外,其他分量均为残差。为了能够把残差看的更清楚,乘以了一个系数。


金字塔的应用
图像融合
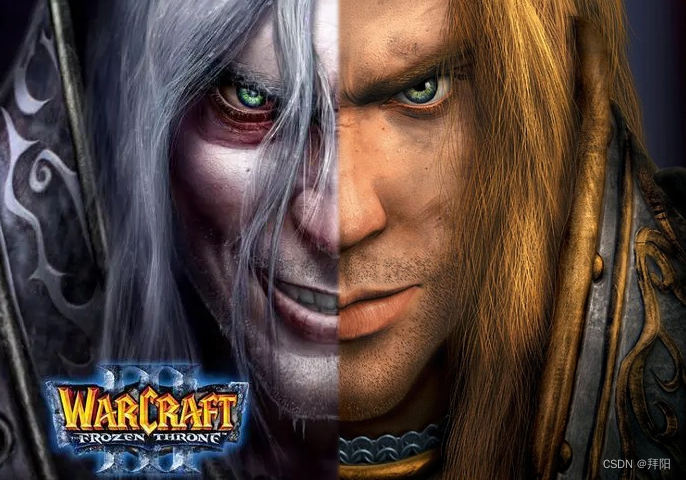
这张图打魔兽的伙计们应该都挺熟的,这是阿尔萨斯在巫妖王形态和人类王子形态的融合体。
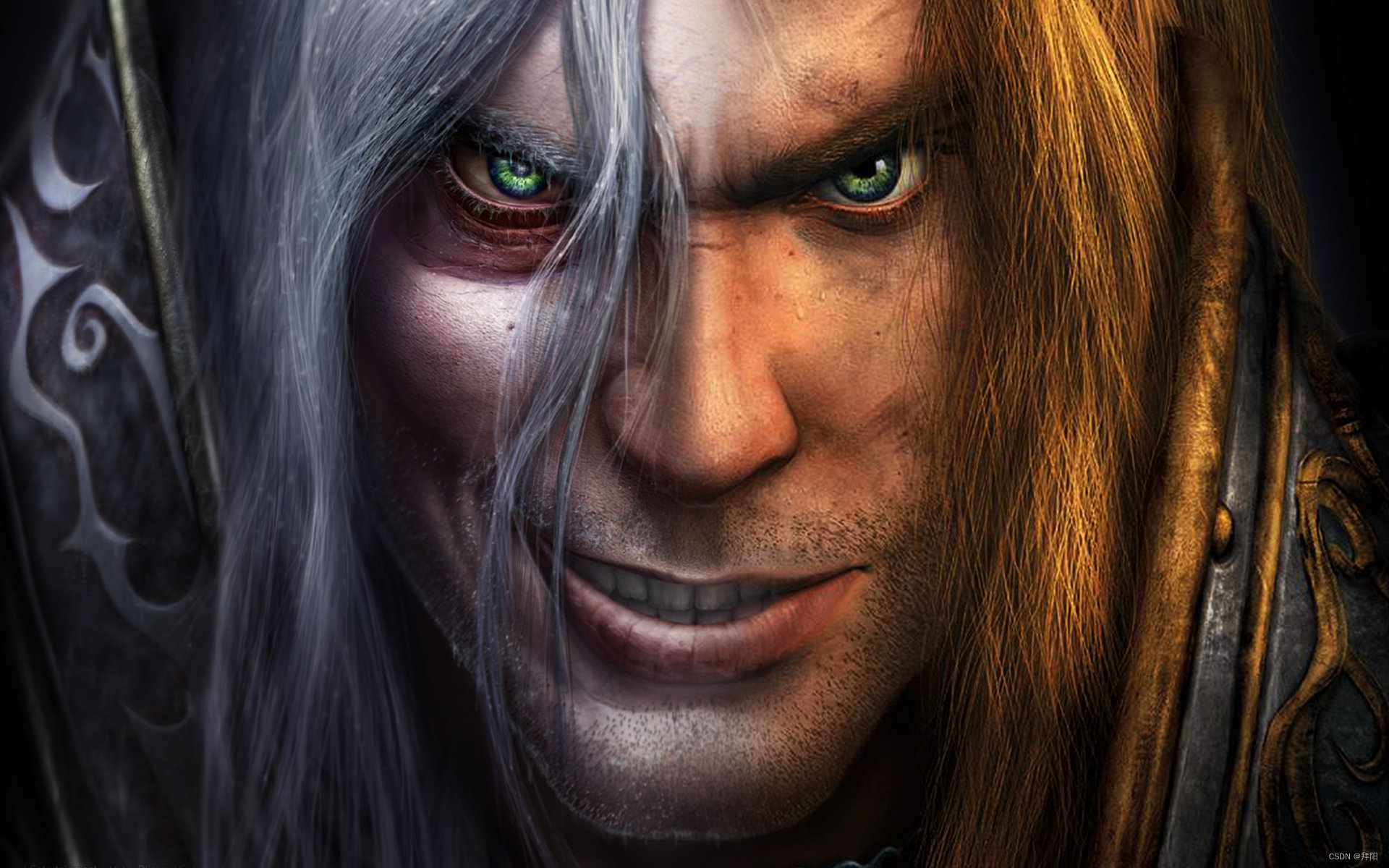

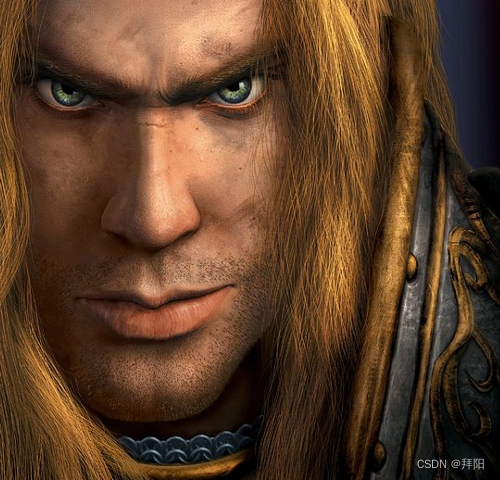
下面我分别找到了原始巫妖王形态和人类王子形态的图像,并作了一些裁减,让图像分辨率一样,并且上下位置也大概能拼在一起。


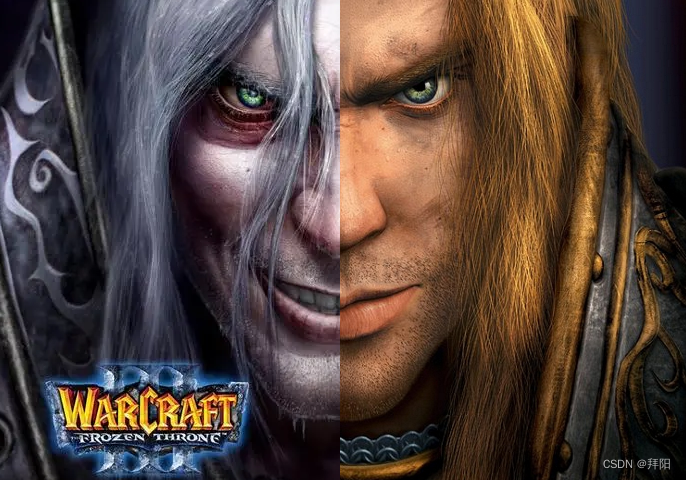
下面图像是直接对上述两个原始图像各切掉一部分,并拼接在一起的结果,可以看到整体过渡是不自然的。

下面我们将使用金字塔重建的方法进行拼接,让边缘的过渡自然一些。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as np
from pyramid import image_to_laplacian_pyramid
from pyramid import laplacian_pyramid_to_image
from pyramid import get_pyramid_indexif __name__ == '__main__':x1 = 160x2 = 154level = 5undead = cv2.imread(r'undead.png')human = cv2.imread(r'human.png')h1, w1 = undead.shape[:2]h2, w2 = human.shape[:2]laplacian_pyramid_undead = image_to_laplacian_pyramid(undead, level)laplacian_pyramid_human = image_to_laplacian_pyramid(human, level)laplacian_pyramid_blending = []for i in range(level):k = level - i - 1k1 = get_pyramid_index(w1 - x1, k)k2 = get_pyramid_index(x2, k)a = laplacian_pyramid_undead[i]b = laplacian_pyramid_human[i]splicing = np.concatenate([a[:, :k1], b[:, k2:]], axis=1)laplacian_pyramid_blending.append(splicing)blending_image = laplacian_pyramid_to_image(laplacian_pyramid_blending)cv2.imwrite('laplacian_pyramid_blending.png', blending_image)上面代码的大体流程:1、两张图分别做拉普拉斯金字塔分解;2、把金字塔的各层分量都从鼻子中间拼接在一起;3、对拼接后的金字塔进行重建,即可得到输出。
拼接后的金字塔以及拼接结果如下:

下面是5层金字塔做拼接融合的结果。除了嘴部的过渡实在搞不定以外,其他部分如鼻子,额头和下巴的过渡比直接拼接的效果顺滑很多。
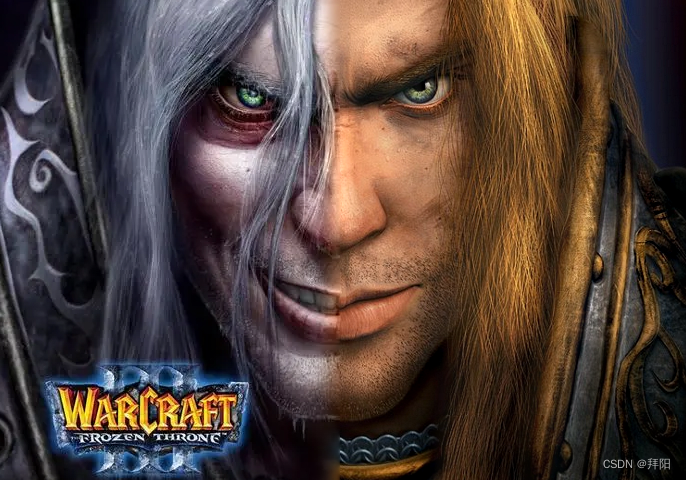

下面是3层金字塔做拼接融合的结果。过渡的顺滑性显然就不如5层金字塔。