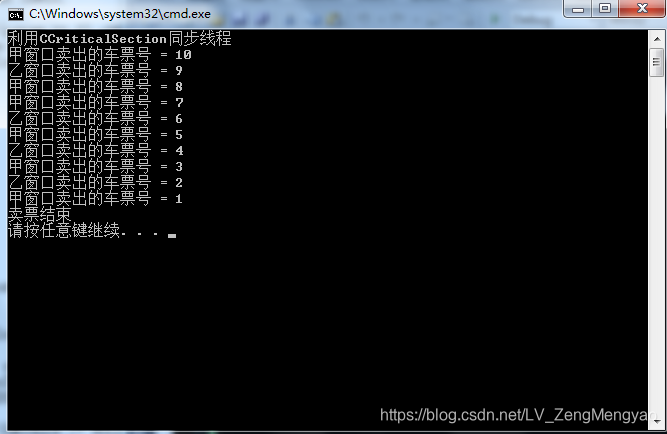
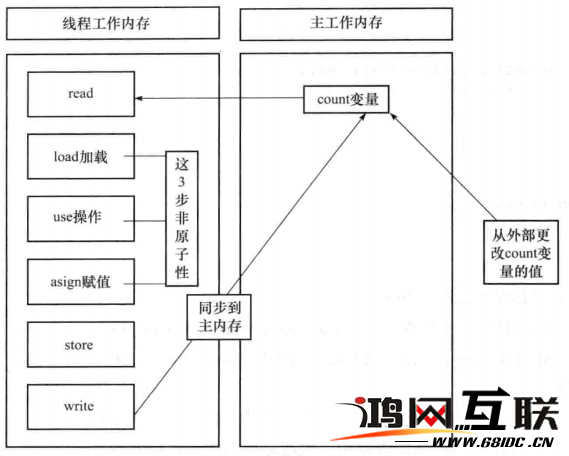
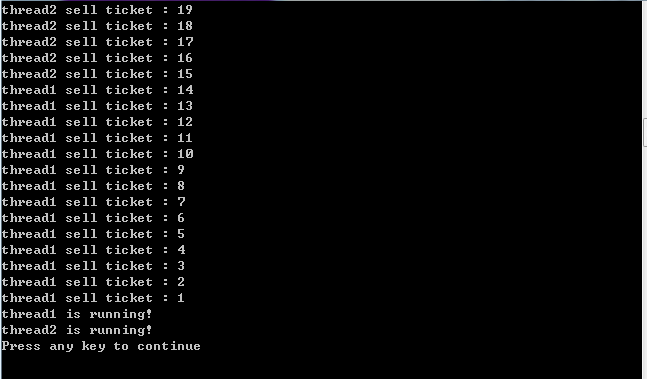
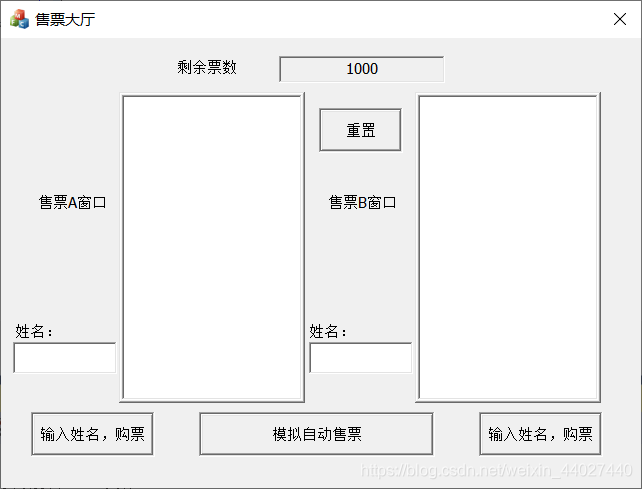
实验一 命令解释程序
实验内容
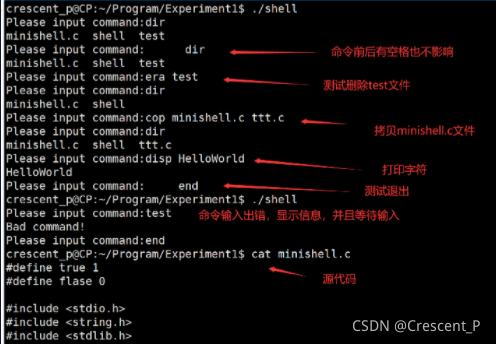
利用C语言编写一个微型命令解释程序minishell.c,该程序可接收并解释以下命令:
(1) dir 列出当前目录
(2) cop file1 file2 拷贝文件
(3) era filename 删除文件
(4) disp string 显示字符串
(5) end 结束,退出
要求:
(1)检查命令的合法性,如果有错误,显示出错信息,等待重新输入;
(2)命令前后有空格示为合法命令。
实验预备内容
- gets() 读入字符串,直到回车结束,但是不包括回车
- strcspn(str1,str2) 返回str1开头连续不包含str2的字符串
- strncpy(str1,str2,n) 将str2字符串的前n个复制到str1中
- strcmp(str1,str2) 将str1和str2进行比较
- 返回值小于0,str1 < str2
- 等于零 str1 == str2
- 大于零 str1 > str2
- system(command) 执行command
示例程序
#define true 1
#define false 0#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main(){char cmdl[80];char *scwt[] = {"exit","dir","time"};static int cmdnum = 3; // 可用命令数char cmd[80];int j,n;while(true){printf("Please input command:");gets(cmdl); // 取命令行输入n = strcspn(cmdl," ");// 取命令部分if(n > 0 || strlen(cmdl) > 0){strncpy(cmd,cmdl,n);// 构成字符串cmd[n] = '\0';for(j = 0;j < cmdnum;j++){if(strcmp(cmdl,scwt[j]) == 0) break;}if(j == 0) exit(0);if(j < cmdnum){system(cmdl);continue;}printf("Bad command!\n");}}
}
实验代码
暂时先不放出来
实验二 进程管理
实验内容
1、进程的创建
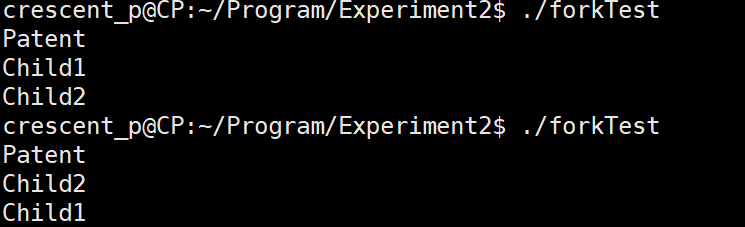
编写一段程序,使用系统调用fork()创建两个子进程。让父进程显示字符串‘Parent:’;两个子进程分别显示字符串‘Child1:’和‘Child2:’。多次运行此程序,观察屏幕显示的结果,并分析原因。
2、进程控制
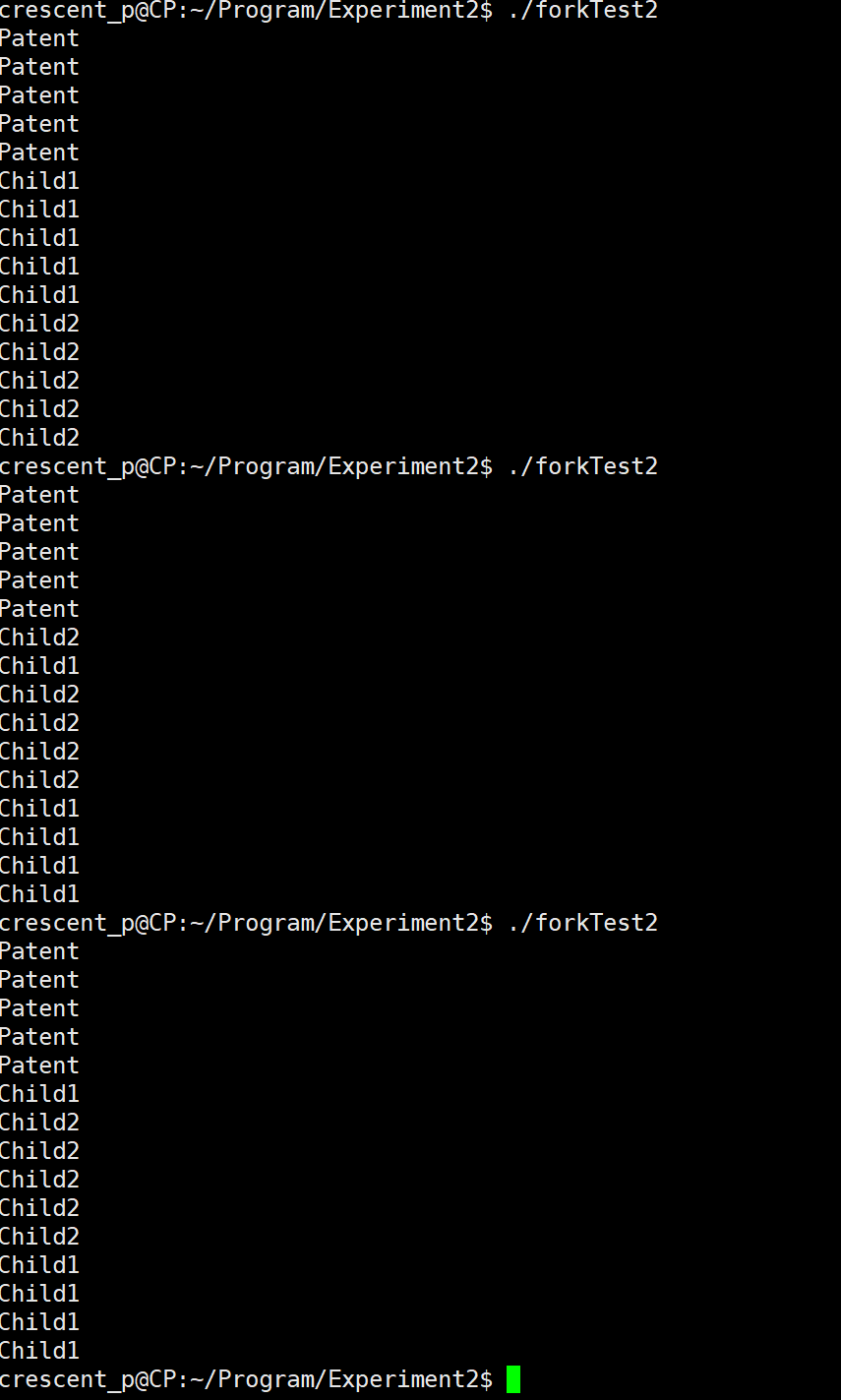
修改已编写的程序,将输出多次重复的一句话,观察程序执行时在屏幕上显示的结果,并分析原因。
若在程序中使用系统调用lockf()来给每一个进程加锁,可以实现进程之间的互斥,观察屏幕显示的结果,并分析原因。
实验预备内容和示例程序
fork 的测试
fork的功能描述:
- fork()通过复制进程来创建一个新进程。子进程类似于当前进程的副本,但是:
- 子进程有自己唯一的进程ID,而且这个进程的PID与任何进程的ID都不相同
- 子进程的父进程ID等于父进程的进程ID
- 返回值:
- 如果成功,在父进程中返回子进程的PID,在子进程中返回0
- 失败了,在父进程中返回-1,没有创建子进程
crescent_p@CP:~/Program/Experiment2$ gcc -o fork1 forkTest1.c
crescent_p@CP:~/Program/Experiment2$ ./fork1
fork test
fork test
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(){fork();printf("fork test\n");return 0;
}
分析:为什么输出了两次?
- 程序运行开始就创建了一个进程
- 当进程执行fork之后,创建了一个子进程
- 子进程的代码是父进程代码的副本
- 子进程的代码执行进度和父进程创建子进程时代码执行进度一致
测试二:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(){pid_t pid;pid = fork();// 父进程if(pid > 0){printf("I am father\n");}if(pid == 0){printf("I an son\n");}if(pid < 0){printf("fork error\n");}printf("main over\n");return 0;
}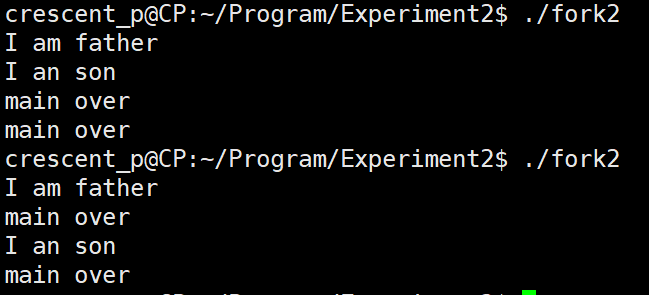
分析为什么结果不一样:
- 为什么又会出现son又会出现father?
- 在父进程中,fork()返回子进程的PID,大于0,因此会执行第一个if
- 在子进程中,fork()返回子进程的PID,等于0,因此会执行第二个if
- 为什么两次执行这个可执行文件结果不一样?
- 进程的异步性,我们设父进程为p1,子进程为p2
- 第一个执行:
- p1执行完第一个if,就轮到p2上处理机运行
- 第二个执行:
- p1执行完,才轮到p2上处理机
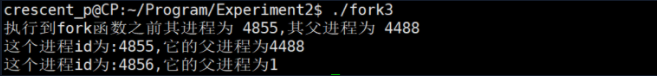
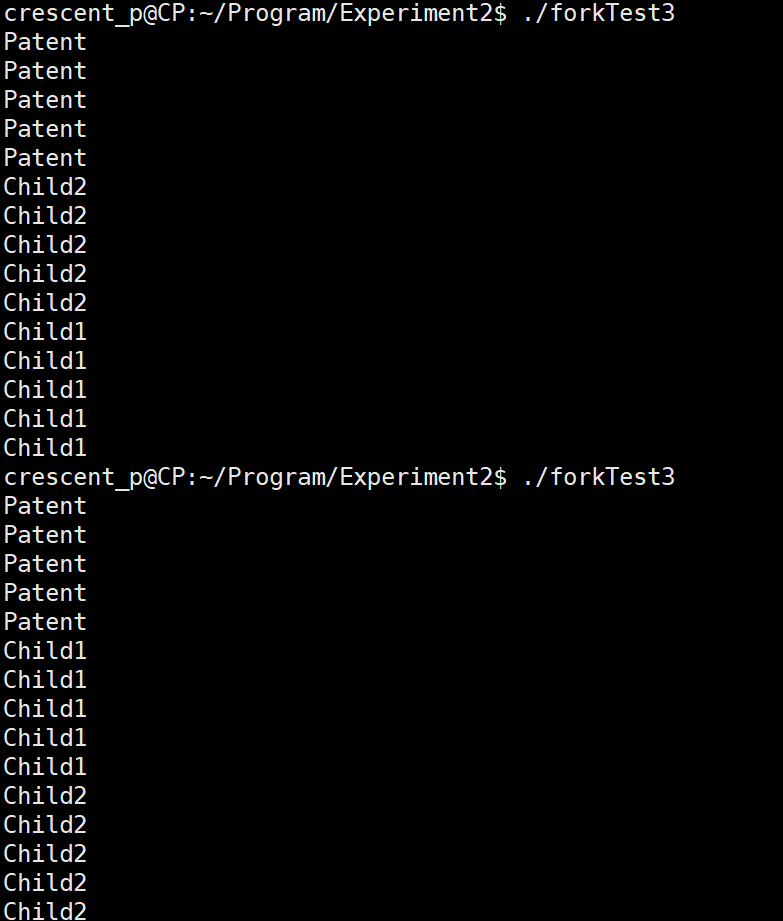
测试三:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(){printf("执行到fork函数之前其进程为 %d,其父进程为 %d\n",getpid(),getppid());sleep(1);fork();printf("这个进程id为:%d,它的父进程为%d\n",getpid(),getppid());return 0;
}
测试四:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){pid_t p1,p2;while((p1 = fork()) == -1);// 子进程if(p1 == 0) { puts("b");}else {puts("a");}return 0;
}
实验代码
暂时先不放出来
实验三进程间的通信
管道通信
实验预备内容和示例程序
测试 pipe():
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>int main(){pid_t pid;int fd[2];char buf[50],s[50];// 创建了管道,半双工pipe(fd);while((pid = fork()) == -1);// 子进程if(pid == 0){sprintf(buf,"Child is sending message!");// fd[1] 写入管道write(fd[1],buf,50);// exit 在退出前,还会把文件缓冲区中的内容写回文件// 退出进程,其实是变成了一个僵尸进程exit(0);}else{// 进程一旦调用了wait,就立即阻塞自己// 由wait自动分析是否当前进程的某个子进程已经退出// 如果让它找到了这样一个已经变成僵尸的子进程// wait就会收集这个子进程的信息,并把它彻底销毁后返回// 如果没有找到这样一个子进程,wait就会一直阻塞在这里,直到有一个出现为止。wait(0);// fd[0] 读取管道,将管道中的内容读入到s中read(fd[0],s,50);printf("%s\n",s);exit(0);}return 0;
}
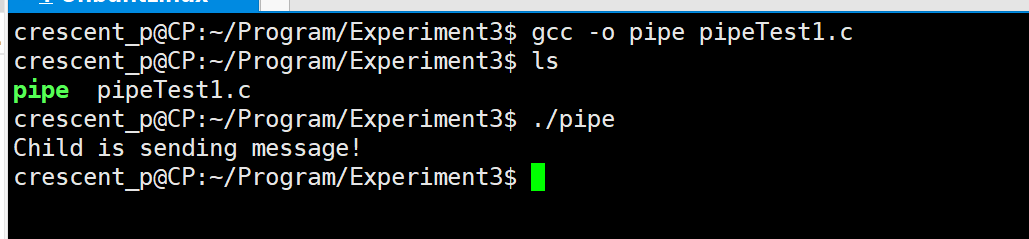
一个管道
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
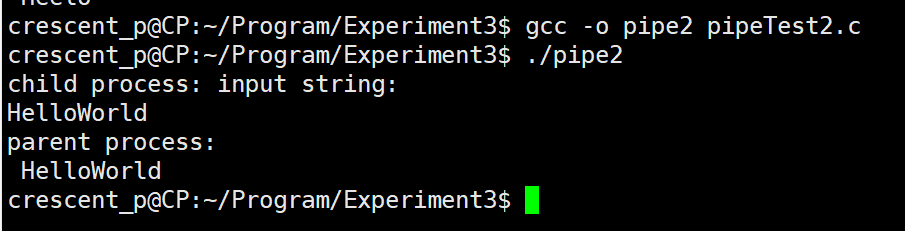
#include <string.h>int main(){// 通道数组int fd[2];pid_t pid;// 一定要先创建管道,否则fork出的子进程也会键管道pipe(fd);while((pid = fork()) == -1);// 子进程if(pid == 0){char str[100] = {0};printf("child process: input string:\n");scanf("%s",str);// 写入到管道write(fd[1],str,strlen(str));exit(0);// 父进程}else{wait(0);char buf[30] = {0};// 从管道中读入到bufread(fd[0],buf,30);printf("parent process:\n %s\n",buf);exit(0);}return 0;
}
双通道:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <string.h>int main(){// 两个管道int fd1[2],fd2[2];// 创建两个通道pipe(fd1),pipe(fd2);pid_t pid;while((pid = fork()) != -1);// 子进程if(pid == 0){char read_buf1[100] = {0};char write_buf1[100] = {0};printf("child process write:\n")scanf("%s",write_buf1);// 写入write(fd1[1],write_buf1,strlen(write_buf1));// 休眠sleep(10);// 读入read(fd2[0],read_buf1,100);printf("child process read:\n %s\n",read_buf1);exit(0);// 父进程}else{sleep(5);char read_buf2[100] = {0};char write_buf2[100] = {0};read(fd1[0],read_buf2,100);printf("parent process read:\n %s\n",read_buf2);printf("parent process write:\n")scanf("%s",write_buf2);// 写入write(fd2[1],write_buf2,strlen(write_buf2));exit(0);}return 0;
}
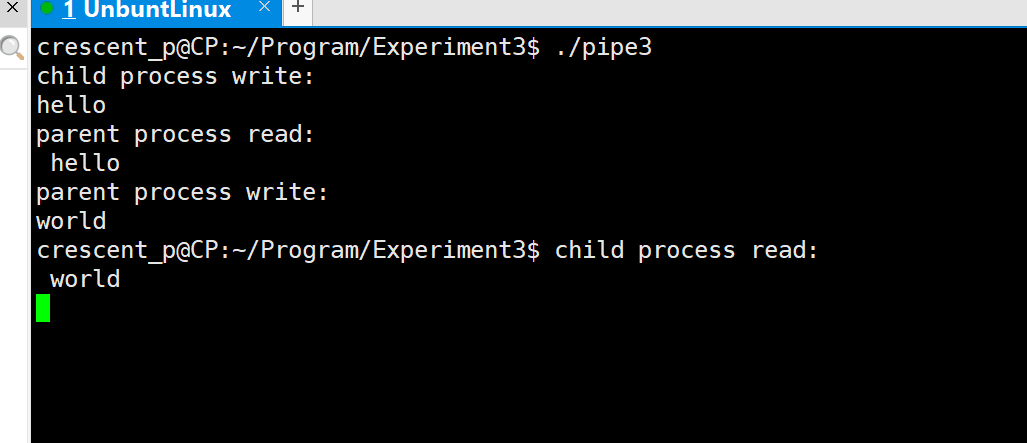
实验代码
暂时先不放出来
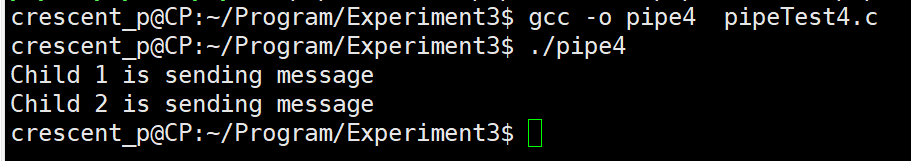
共享内存
实验预备内容和示例程序
#include<stdio.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(){// 共享内存标识符int shmid;// 创建共享内存if((shmid = shmget((key_t)0x5005,1024,0666|IPC_CREAT)) == -1){printf("shmat(0x5005) failed\n");return -1;}// 用于指向共享内存的指针char *ptext = 0;// 将共享内存连接到当前进程的地址空间,由ptext指向它ptext = (char *)shmat(shmid,0,0);// 操作本程序的ptext指针,就是操作共享内存printf("写入前:%s\n",ptext);sprintf(ptext,"本程序的进程号是:%d",getpid());printf("写入后:%s\n",ptext);// 把共享内存从当前进程中分离shmdt(shmid);// 删除共享内存if(shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,0) == -1){printf("shmctl(0x5005) failed\n");return -1;}
}
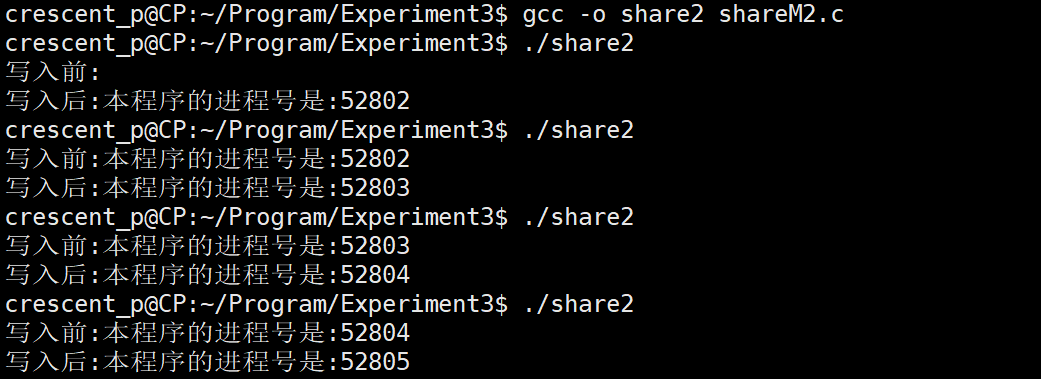
实验代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
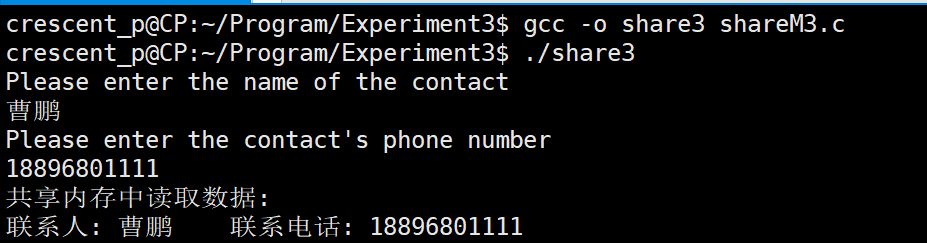
#include <unistd.h>int main(){// 共享内存标识符int shmid;// 创建共享内存if((shmid = shmget((key_t)0x5005,1024,0666|IPC_CREAT)) == -1){printf("shmat(0x5005) failed\n");return -1;}// 用于指向共享内存的指针char *ptext = 0;// 将共享内存连接到当前进程的地址空间,由ptext指向它ptext = (char *)shmat(shmid,0,0);printf("Please enter the name of the contact\n");char name[50];scanf("%s",name);printf("Please enter the contact's phone number\n");long long tel;scanf("%lld",&tel);// 操作本程序的ptext指针,就是操作共享内存// 发送消息到共享内存sprintf(ptext,"联系人: %s\t联系电话: %lld\n",name,tel);// 从共享内存读东西printf("共享内存中读取数据:\n%s\n",ptext);// 把共享内存从当前进程中分离shmdt(ptext);// 删除共享内存if(shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,0) == -1){printf("shmctl(0x5005) failed\n");return -1;}
}
消息队列
实验预备内容和示例程序
message.h
#ifndef MESSAGE_H
#define MESSAGE_H
struct mymsgbuf
{long mtype;char mtext[256];
};
#endif
msg_server.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include "message.h"int msqid = -1;// 软终端
void sig_handle(int signo){if(msqid != -1) msgctl(msqid,IPC_RMID,NULL); // 删除printf("server quit...\n");exit(0);
}int main(){struct mymsgbuf msgbuf;int left,right;char c;int length;if((msqid = msgget(999,0666)) != -1){msgctl(msqid,IPC_RMID,NULL); // 删除}if((msqid = msgget(999,IPC_CREAT|0666)) == -1 ){printf("error:getmsg\n");exit(1);}signal(SIGINT,sig_handle); // 注册软中断for(;;){if(msgrcv(msqid,&msgbuf,256,1L,0) == -1){printf("error:msgrcv\n");exit(1);}length = strlen(msgbuf.mtext);left = 0;right = length - 1;while (left < right){c = msgbuf.mtext[left];msgbuf.mtext[left] = msgbuf.mtext[right];msgbuf.mtext[right] = c;left++;right--;}msgbuf.mtext[length] = '\0';msgbuf.mtype = 2; // 类型改成2if(msgsnd(msqid,&msgbuf,256,0) == -1){printf("error:msgsnd");exit(1);}}msgctl(msqid,IPC_RMID,NULL);exit(0);
}
msg_client.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include "message.h"int main(){struct mymsgbuf msgbuf;int msqid;if((msqid = msgget(999,0666)) == -1){printf("Server is not running\n");exit(1);}printf("Input a line:");scanf("%s",msgbuf.mtext);msgbuf.mtype = 1;if(msgsnd(msqid,&msgbuf,256,0)==-1){printf("error:msgsnd\n");exit(1);}if(msgrcv(msqid,&msgbuf,256,2L,0) == -1){printf("error:msgrcv\n");exit(1);}printf("The reversed line is :%s\n",msgbuf.mtext);exit(0);
}


msgsend.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>// 消息类型,用枚举
enum MT{MI=1,MD,MS,MSTU,MEMP};
#define QUIT 0
#define MSG_MAX_LEN 1024
#define NAME_LEN 48typedef struct Msg{int msgtype; //message 的类型char msg[MSG_MAX_LEN]; // message的内容
}Msg;typedef struct Stu{int id;char name[NAME_LEN];int s[3]; // 三门成绩
}Stu;typedef struct Emp
{int id;char name[NAME_LEN];float salary;
}Emp;void menu(void){printf("***消息队列发送测试界面***\n");printf("*** %d.int类型的数据\n",MI);printf("*** %d.double类型的数据\n",MD);printf("*** %d.字符串\n",MS);printf("*** %d.学生信息\n",MSTU);printf("*** %d.员工信息\n",MEMP);printf("*** %d.退出\n",QUIT);printf(">>>");
}size_t readInt(Msg *msg){// 设置消息的类型msg->msgtype = MI;printf("input integer:");// 将消息读入到消息结构体的msg属性中scanf("%d",(int*)msg->msg);return sizeof(int);
}
size_t readDouble(Msg *msg){msg->msgtype = MD;printf("input double:");scanf("%lf",(double*)msg->msg);return sizeof(double);
}
size_t readString(Msg *msg){msg->msgtype = MS;printf("input string:");// 读取换行scanf("%*c");gets(msg->msg); // gets不安全// 加上\0return strlen(msg->msg)+1;
}
size_t readStu(Msg *msg){msg->msgtype = MSTU;// 强转Stu *pstu = (Stu*)msg->msg;printf("input stu's id:");scanf("%d",&pstu->id);printf("input stu's name:");scanf("%s",pstu->name);printf("input three score:");scanf("%d %d %d",&pstu->s[0],&pstu->s[1],&pstu->s[2]);return sizeof(Stu);
}
size_t readEmp(Msg *msg){msg->msgtype = MEMP;Emp *pe = (Emp*)msg->msg;printf("input emp's id:");scanf("%d",&pe->id);printf("input emp's name:");scanf("%s",pe->name);printf("input emp's salary:");scanf("%f",&pe->salary);return sizeof(Emp);
}int main(){key_t keyid = ftok(".",250);if(keyid == -1){perror("ftok");return -1;}// 创建消息队列int msgid = msgget(keyid,IPC_CREAT|0666);if(msgid == -1){perror("msgget");return -1;}// 创建消息Msg msg = {};bool run = true;size_t msgsz = 0;while(run){menu();int opt = 0;scanf("%d",&opt);switch (opt){case MI:msgsz = readInt(&msg);break;case MD:msgsz = readDouble(&msg);break;case MS:msgsz = readString(&msg);break;case MSTU:msgsz = readStu(&msg);break;case MEMP:msgsz = readEmp(&msg);break;case QUIT:run = false;break;default:printf("error operation!\n");}// msgsz是消息的长度,不包含消息类型的长度int ret = msgsnd(msgid,&msg,msgsz,0); //0:阻塞 IPC_NOWAIT 不阻塞的if(ret == -1){perror("msgend");run = false;}}return 0;
}
msgrecive.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>// 消息类型,用枚举
enum MT{MI=1,MD,MS,MSTU,MEMP,FIRST,ABSL};
#define QUIT 0
#define MSG_MAX_LEN 1024
#define NAME_LEN 48typedef struct Msg{int msgtype; //message 的类型char msg[MSG_MAX_LEN]; // message的内容
}Msg;typedef struct Stu{int id;char name[NAME_LEN];int s[3]; // 三门成绩
}Stu;typedef struct Emp
{int id;char name[NAME_LEN];float salary;
}Emp;void menu(void){printf("***消息队列接受测试界面***\n");printf("*** %d.int类型的数据\n",MI);printf("*** %d.double类型的数据\n",MD);printf("*** %d.字符串\n",MS);printf("*** %d.学生信息\n",MSTU);printf("*** %d.员工信息\n",MEMP);printf("*** %d.接受第一条消息 \n",FIRST);printf("*** %d.接受指定消息小于绝对值最小的消息 \n",ABSL);printf("*** %d.退出\n",QUIT);printf(">>>");
}void showMsg(Msg *msg){switch (msg->msgtype){case MI:printf("recv:%d\n",*(int*)msg->msg);break;case MD:printf("recv:%f\n",*(double*)msg->msg);break;case MS:printf("recv:%s\n",msg->msg);break;case MSTU:{Stu *ps = (Stu *)msg->msg;printf("recv:%d %s %d %d %d\n",ps->id,ps->name,ps->s[0],ps->s[1],ps->s[2]);break;}case MEMP:{Emp *pe = (Emp *)msg->msg;printf("recv:%d %s %f\n",pe->id,pe->name,pe->salary);break;}}
}int main(){key_t keyid = ftok(".",250);if(keyid == -1){perror("ftok");return -1;}// 创建消息队列int msgid = msgget(keyid,IPC_CREAT|0666);if(msgid == -1){perror("msgget");return -1;}// 创建消息Msg msg = {};bool run = true;size_t msgsz = 0;// 读到的消息类型int msgtype = 0;while(run){menu();int opt = 0;scanf("%d",&opt);if(opt >= MI && opt <=MEMP){msgtype = opt;}else if(opt == FIRST){msgtype = 0;}else if(opt == ABSL){printf("input masgtype(<0):");scanf("%d",&msgtype);if(msgtype > 0) msgtype *= -1;}else if(opt == 0){run = false;break;}int ret = msgrcv(msgid,&msg,MSG_MAX_LEN-1,msgtype,IPC_NOWAIT); if(ret == -1){if(errno == EAGAIN){printf("no this type message");}else{perror("msgend");run = false;}}else{// 显示消息内容showMsg(&msg);}}return 0;
}实验代码
暂时先不放出来