CCriticalSection
An object of class CCriticalSection represents a “critical section” — a synchronization object that allows one thread at a time to access a resource or section of code. Critical sections are useful when only one thread at a time can be allowed to modify data or some other controlled resource. For example, adding nodes to a linked list is a process that should only be allowed by one thread at a time. By using a CCriticalSection object to control the linked list, only one thread at a time can gain access to the list.
Critical sections are used instead of mutexes when speed is critical and the resource will not be used across process boundaries. For more information on using mutexes in MFC, see CMutex.
To use a CCriticalSection object, construct the CCriticalSection object when it is needed. You can then access the critical section when the constructor returns. Call Unlock when you are done accessing the critical section.
To access a resource controlled by a CCriticalSection object in this manner, first create a variable of type CSingleLock in your resource’s access member function. Then call the lock object’s Lock member function (for example, CSingleLock::Lock). At this point, your thread will either gain access to the resource, wait for the resource to be released and gain access, or wait for the resource to be released and time out, failing to gain access to the resource. In any case, your resource has been accessed in a thread-safe manner. To release the resource, use the lock object’s Unlock member function (for example, CSingleLock::Unlock), or allow the lock object to fall out of scope.
Alternatively, you can create a CCriticalSection object stand-alone, and access it explicitly before attempting to access the controlled resource. This method, while clearer to someone reading your source code, is more prone to error as you must remember to lock and unlock the critical section before and after access.
For more information on using CCriticalSection objects, see the articleMultithreading: How to Use the Synchronization Classes in Visual C++ Programmer's Guide.
#include <afxmt.h>
临界段CCriticalSection可以单独使用,也可以和CSingleLock使用,从性能上讲,临界段要优于互斥量,它是一个用于同步的对象,同一时刻只允许一个线程存取资源或代码区。临界段在控制一次只允许一个线程修改数据或其它的控制资源时非常有用,例如在链表中增加一个结点就只允许一次一个线程进行。通过使用临界段来控制链表,就可以达到这个目的。它就像是一把钥匙,哪个线程获得了它就获得了运行线程的权力,而把其他线程统统阻塞。使用是临界段要先定义在一个全局变量,比如在一个类中声明为数据成员、静态变量、或全局变量。临界段使用一个就够了,用时lock,要保护的资源放这里,不用时unlock,资源不再受保护。CCriticalSection是对CRITICAL_SECTION的封装。
临界段
CCriticalSection Class Members
Construction
| CCriticalSection | Constructs a CCriticalSection object. |
Methods
| Unlock | Releases the CCriticalSection object. virtual BOOL Unlock( ); Return Value Nonzero if the CCriticalSection object was owned by the thread and the release was successful; otherwise 0. Remarks Releases the CCriticalSection object for use by another thread. If the CCriticalSection is being used stand-alone, Unlock must be called immediately after completing use of the resource controlled by the critical section. If a CSingleLock object is being used, CCriticalSection::Unlock will be called by the lock object’s Unlock member function. |
| Lock | Use to gain access to the CCriticalSection object. BOOL Lock( ); //不带超时参数 BOOL Lock( DWORD dwTimeout ); //带超时参数 Return Value Nonzero if the function was successful; otherwise 0. Parameters dwTimeout Lock ignores this parameter value. Remarks Call this member function to gain access to the critical section object. Lock is a blocking call that will not return until the critical section object is signaled (becomes available). If timed waits are necessary, you can use a CMutex object instead of a CCriticalSection object. |
CSingleLock
CSingleLock does not have a base class.
An object of class CSingleLock represents the access-control mechanism used in controlling access to a resource in a multithreaded program. In order to use the synchronization classes CSemaphore, CMutex, CCriticalSection, and CEvent, you must create either a CSingleLock or CMultiLock object to wait on and release the synchronization object. Use CSingleLock when you only need to wait on one object at a time. Use CMultiLock when there are multiple objects that you could use at a particular time.
To use a CSingleLock object, call its constructor inside a member function in the controlled resource’s class. Then call the IsLocked member function to determine if the resource is available. If it is, continue with the remainder of the member function. If the resource is unavailable, either wait for a specified amount of time for the resource to be released, or return failure. After use of the resource is complete, either call the Unlock function if the CSingleLock object is to be used again, or allow the CSingleLock object to be destroyed.
CSingleLock objects require the presence of an object derived from CSyncObject. This is usually a data member of the controlled resource’s class. For more information on how to use CSingleLock objects, see the articleMultithreading: How to Use the Synchronization Classes in Visual C++ Programmer’s Guide.
#include <afxmt.h>
一个CSingleLock类对象代表一种访问控制机制,这种机制用于控制在一个多线程程序中对一个资源的访问。为了使用同步类CSemaphore,CMutex,CCriticalSection和CEvent,必须创建一个CSingleLock或CMultiLock对象来等待和释放这个同步对象。当每次等待一个对象时,可以使用CSingleLock,当在一个特别的时候你可以使用多个对象时,可以使用CMultiLock。
#include <iostream.h>
#include <afxmt.h>
#include <Afxwin.h>UINT Fun1Proc(LPVOID lpParameter // thread data
);UINT Fun2Proc(LPVOID lpParameter // thread data
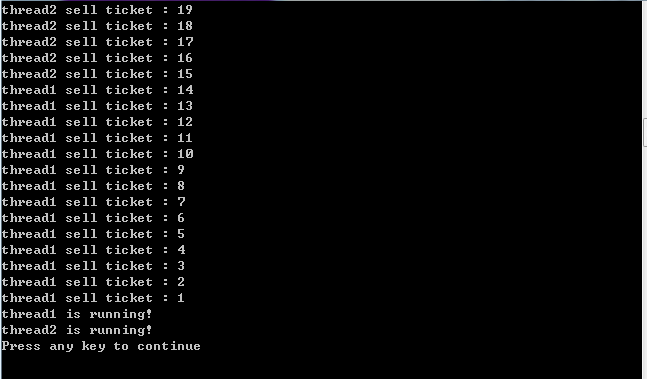
);int tickets=100;
CCriticalSection g_CriticalSection;void main()
{AfxBeginThread(Fun1Proc,NULL);AfxBeginThread(Fun2Proc,NULL);Sleep(4000);
}UINT Fun1Proc(LPVOID lpParameter // thread data
)
{while(TRUE){//g_CriticalSection.Lock();CSingleLock sLock(&g_CriticalSection);sLock.Lock();if(tickets>0){Sleep(1);cout<<"thread1 sell ticket : "<<tickets--<<endl;}elsebreak;//g_CriticalSection.Unlock();sLock.Unlock();}cout<<"thread1 is running!"<<endl;return 0;
}UINT Fun2Proc(LPVOID lpParameter // thread data
)
{while(TRUE){//g_CriticalSection.Lock();CSingleLock sLock(&g_CriticalSection);sLock.Lock();if(tickets>0){Sleep(1);cout<<"thread2 sell ticket : "<<tickets--<<endl;}elsebreak;//g_CriticalSection.Unlock();sLock.Unlock();}cout<<"thread2 is running!"<<endl;return 0;
}