文章目录
- 课程设计题目
- 1. 设计内容
- 1.1 基本命令设计
- 1.2 基本数据结构设计
- 1.3 基本命令的程序流程图
- 1) 用户注册:register
- 2) 用户登录:login
- 3) 创建文件:create(文件名)
- 4) 创建文件夹:mkdir(文件夹名)
- 5) 打开文件:open(文件名)
- 6) 关闭文件:close(文件名)
- 7) 读取文件:read(文件名)
- 8) 删除文件:del(文件名)
- 9) 删除目录:remove(文件名)
- 10) 切换目录:cd
- 11) 列文件目录:dir
- 12) 显示当前目录的文件:ls
- 13) 写入文件:write
- 14) 修改文件属性:change(文件名)
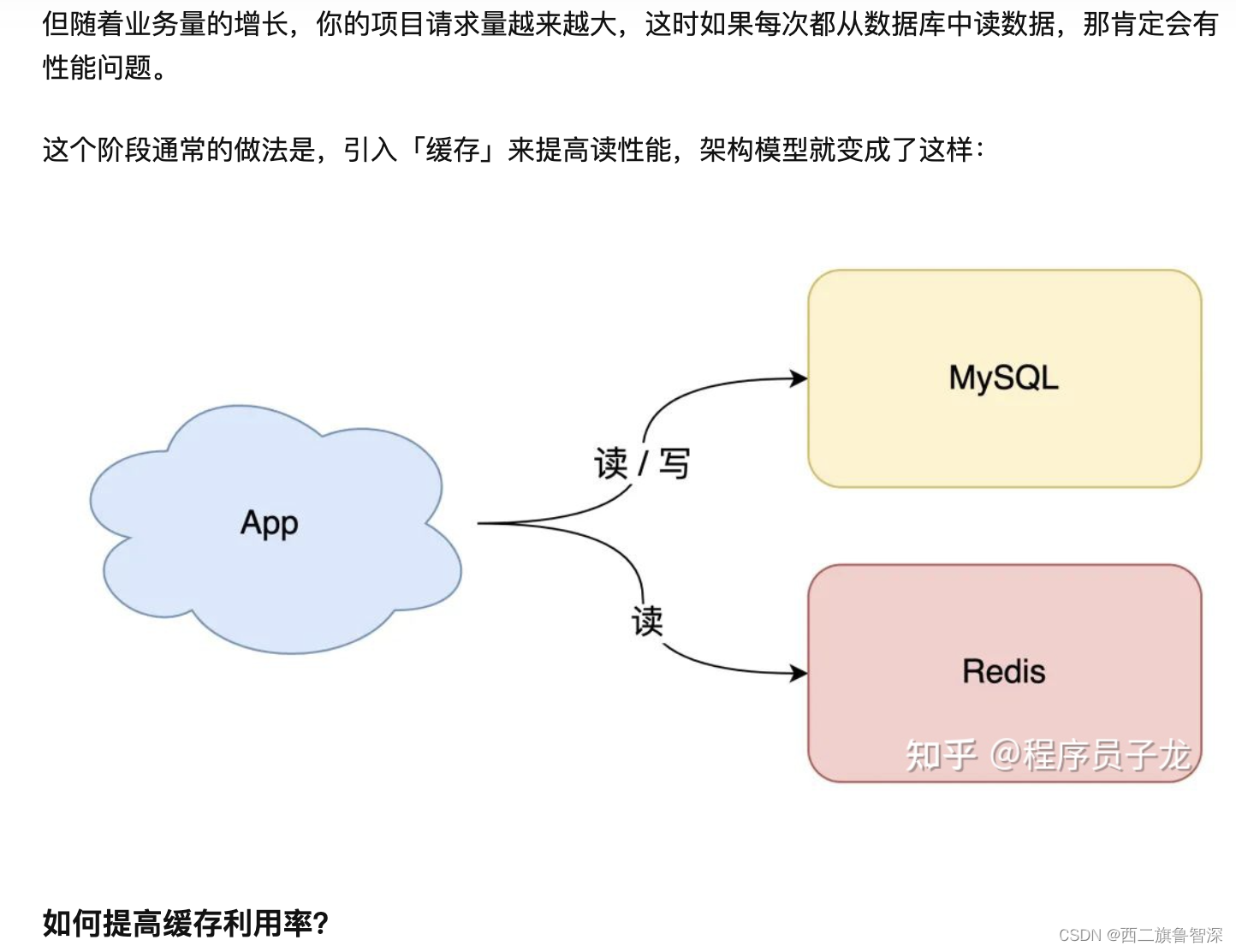
- 2. 结果 & 简要分析
- 2.1 用户注册:register
- 2.2 用户登录:login
- 2.3 创建文件:create(文件名)
- 2.4 创建文件夹:mkdir(文件夹名)
- 2.5 打开文件:open(文件名)
- 2.6 关闭文件:close(文件名)
- 2.7 读取文件:read(文件名)
- 2.8 删除文件:del(文件名)
- 2.9 删除目录:remove(文件名)
- 2.10 切换目录:cd
- 2.11 列文件目录:dir
- 2.12 显示当前目录的文件:ls
- 2.13 写入文件:write
- 2.14 修改文件属性:change(文件名)
- 2.15 清屏:clear
- 2.16 显示所有的命令:help
- 2.17 退出系统:exit
- 3. 总结分析
- 3.1 遇到的问题
- 3.2 解决方法
- 3.3 设计需要改进的内容
- 3.4 个人收获与感想
- 4. 完整代码
- 4.1 windows版本代码
- 4.2 linux版本代码
文章末尾有完整可运行代码,希望点赞支持一下。
课程设计题目
文件管理系统设计:
通过模拟文件操作命令的执行,来模拟文件管理。要求建立相应的数据结构:文件控制块、空闲盘块等,模拟盘块管理能够实现文件的建立、打开、读写、执行、属性修改、文件保护等基本功能。
1. 设计内容
1.1 基本命令设计
- 用户注册:register
- 用户登录:login
- 创建文件:create(文件名)
- 创建文件夹:mkdir(文件夹名)
- 打开文件:open(文件名)
- 关闭文件:close(文件名)
- 读取文件:read(文件名)
- 删除文件:del(文件名)
- 删除目录:remove(文件名)
- 切换目录:cd
- 列文件目录:dir
- 显示当前目录的文件:ls
- 写入文件:write(文件名,物理块要存入的数据内容,文件内数据总长度)
- 修改文件属性:change(文件名)
- 清屏:clear
- 显示所有的命令:help
- 退出系统:exit
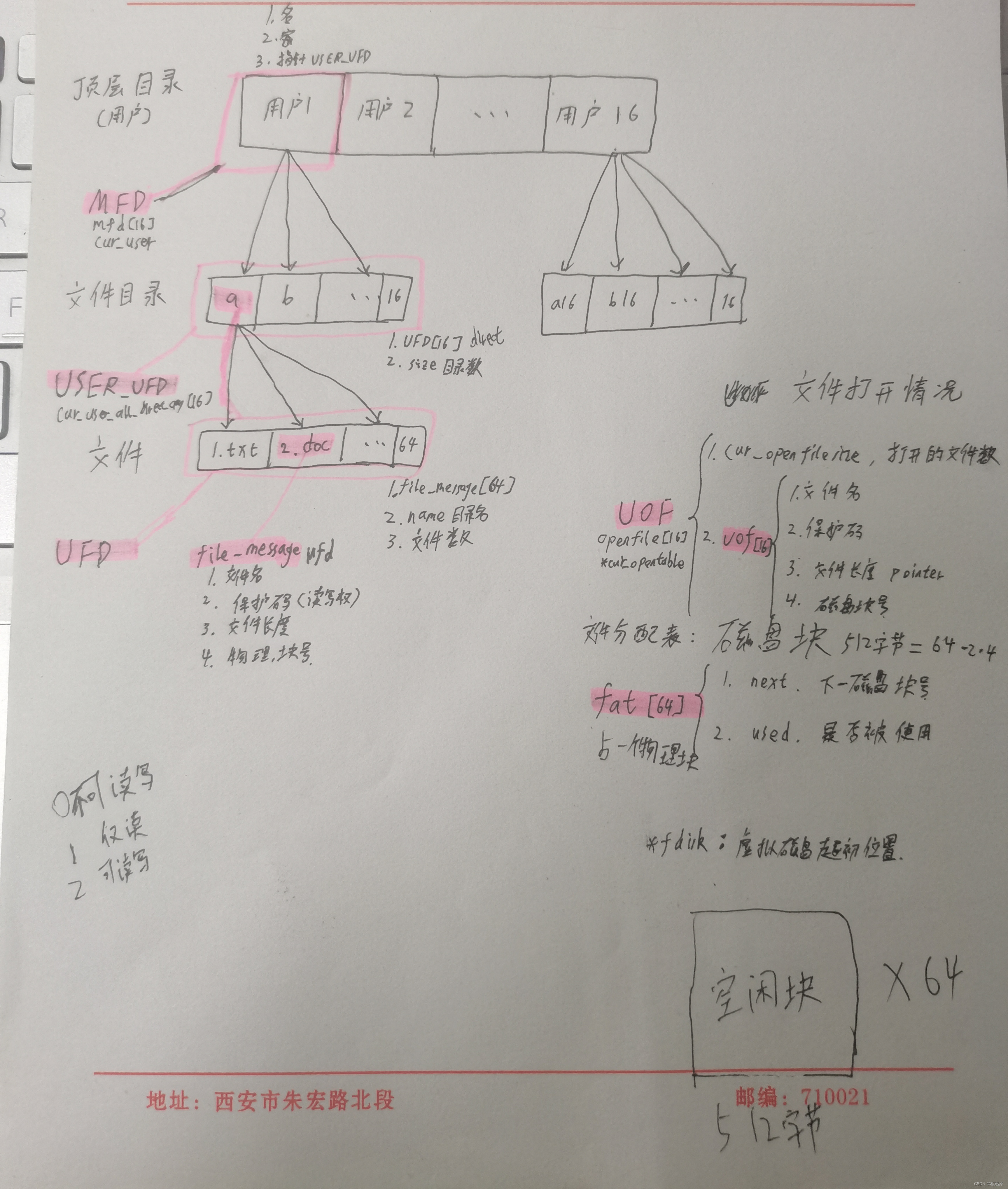
1.2 基本数据结构设计
1) (第一级)顶层目录 MFD
string username; //用户名
string password; //登录密码
struct USER_UFD *next; //指向用户目录
2) (第二级)单个用户的文件目录 USER_UFD
struct UFD direct[16]; //每个用户最多有16个目录
int cur_user_direct_size = 0; //当前用户的目录数
3) (第三层)用户的某个目录文件下的所有文件(包含一个用户的所有文件) UFD
string directname; //用户目录名(文件夹的名称)
int cur_file_size = 0; //不能在结构体内附初始值。
file_message ufd[64]; //每个文件夹下可以有64个文件
4) 第三层中的文件结构体 file_message
string filename; //文件名
int protect_code; //保护码
int length; //文件长度
int addr; //存放该文件的物理块的第一个的块号
5) 当前打开的文件控制块 UOF
int cur_openfilesize = 0; //打开的文件数uof uof[16] //最多16个文件
6) 当前打开的文件结构体 uof
string filename;//文件名
int pointer; //文件的读写指针,其实就是文件的大小
int protect_code; //2表示可读可写,1表示可读不可写, 0表示不可读不可写
int addr; //存放文件的第一个磁盘块号
7) 文件分配表 fat
int next = -1; //下一个磁盘块号
int used = 0; //1表示被使用,0表示未被使用
//注:用一块物理块存放,那么最多可以记录64块数据块的信息。记录文件占用磁盘块情况:物理块,假设一个磁盘的每个物理块大小为 512个字节 = 64*2*4字节。
整体结构的手写草稿图:
1.3 基本命令的程序流程图
注:本文中 name 均代表 文件名(或文件目录)
1) 用户注册:register
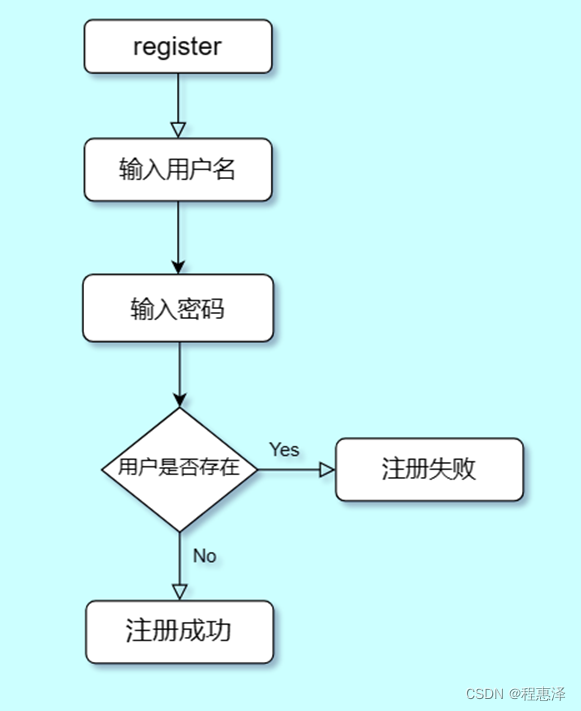
图1.1 register命令的流程图
2) 用户登录:login
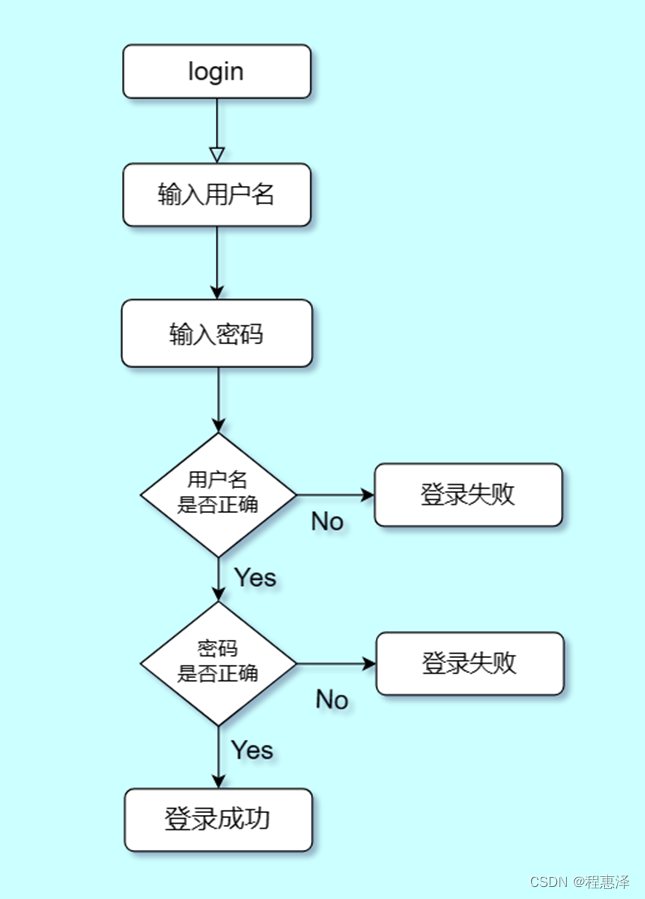
图1.2 login命令的流程图
3) 创建文件:create(文件名)
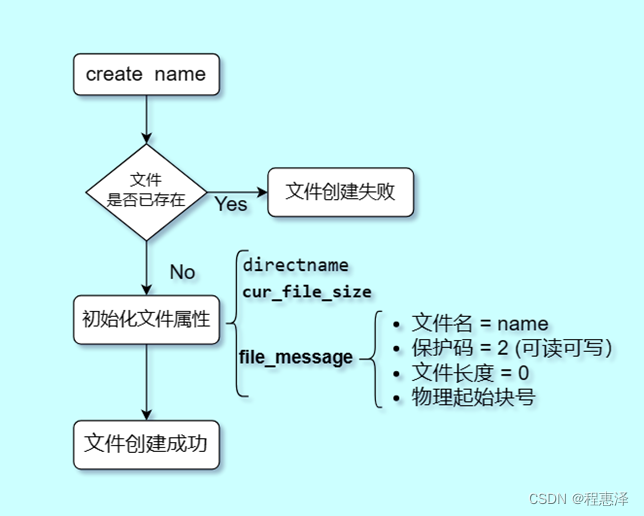
图1.3 create命令的流程图
4) 创建文件夹:mkdir(文件夹名)
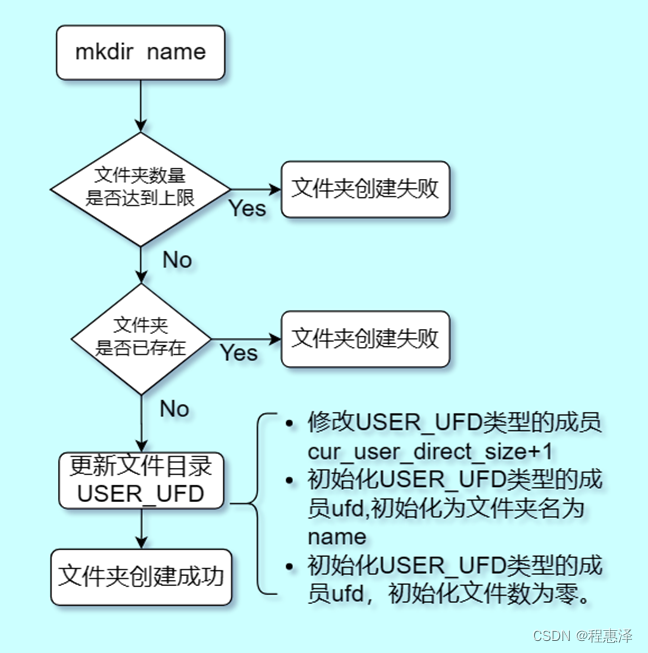
图1.4 mkdir命令的流程图
5) 打开文件:open(文件名)
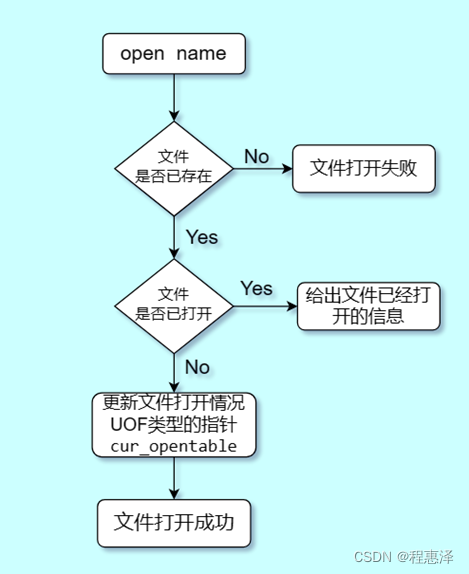
图1.5 open命令的流程图
6) 关闭文件:close(文件名)
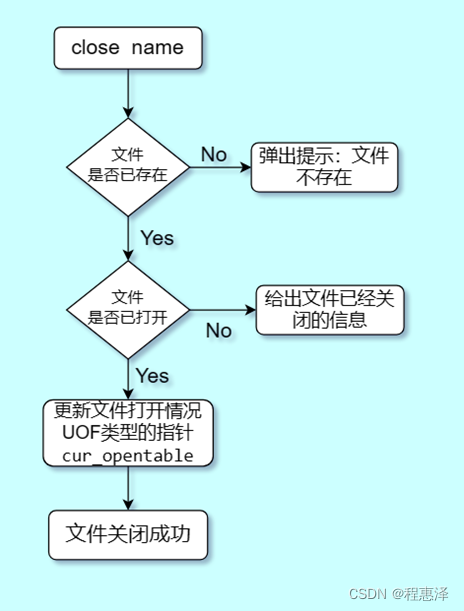
图1.6 close命令的流程图
7) 读取文件:read(文件名)
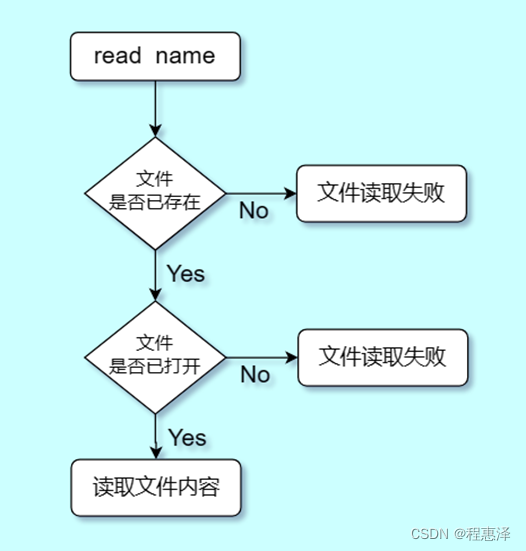 图1.7 read命令的流程图
图1.7 read命令的流程图
8) 删除文件:del(文件名)
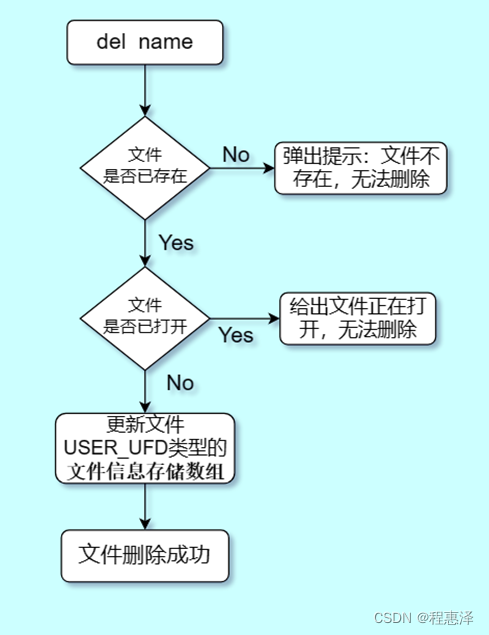
图1.8 del命令的流程图
9) 删除目录:remove(文件名)
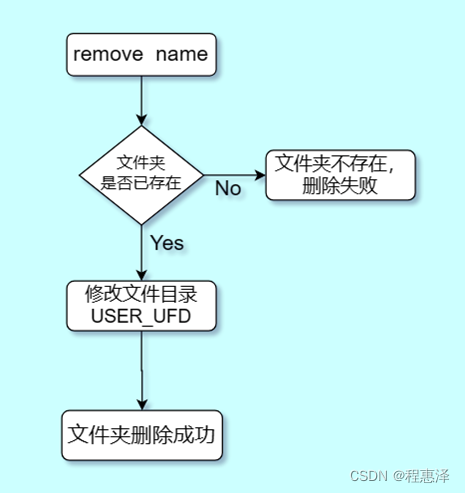
图1.9 remove命令的流程图
10) 切换目录:cd
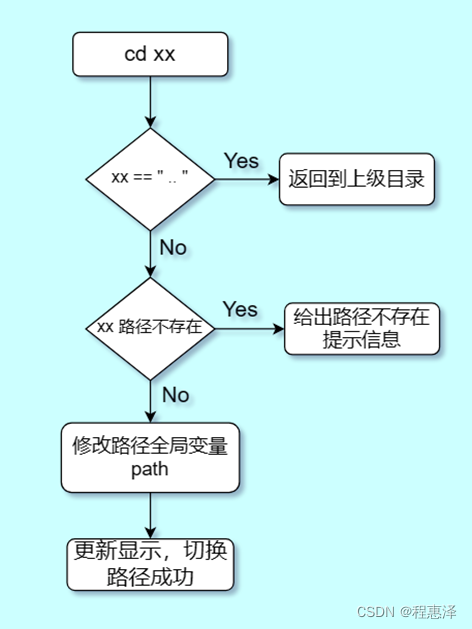
图1.10 cd命令的流程图
11) 列文件目录:dir
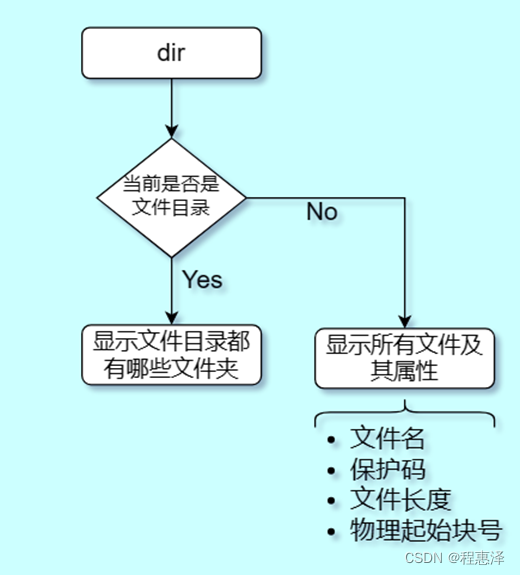
图1.11 dir命令的流程图
12) 显示当前目录的文件:ls
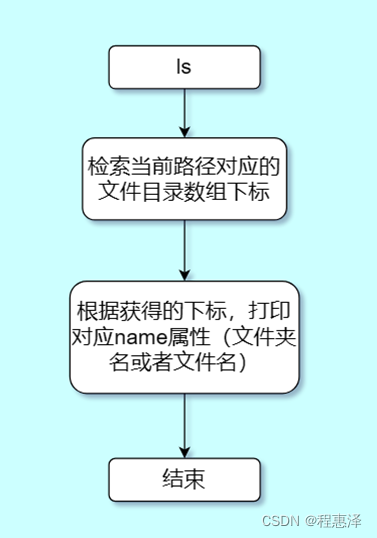
图1.12 ls命令的流程图
13) 写入文件:write
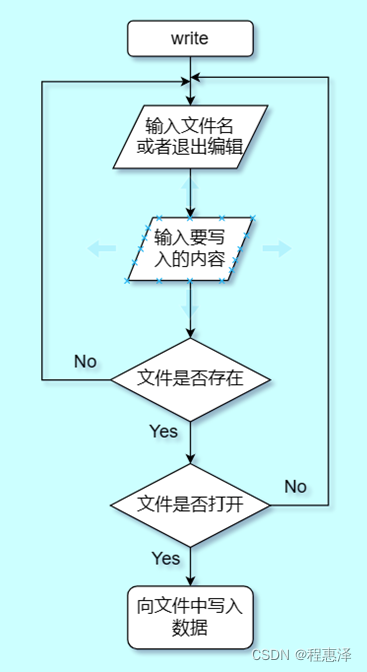
图1.13 write命令的流程图
14) 修改文件属性:change(文件名)
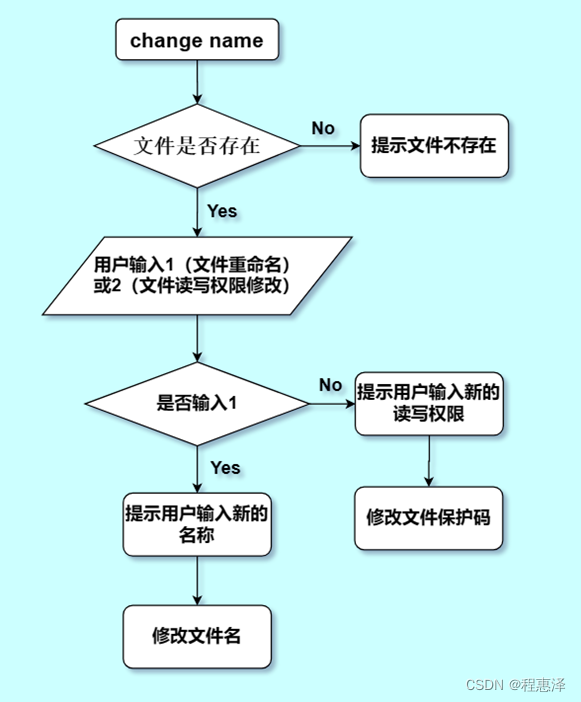
图1.14 change命令的流程图
2. 结果 & 简要分析
2.1 用户注册:register
实现结果:
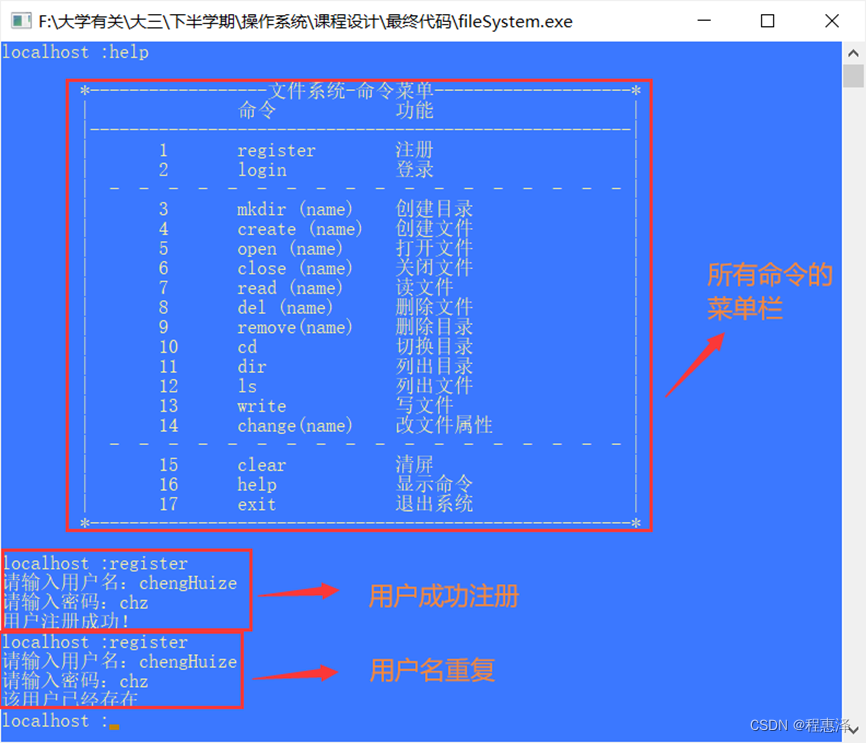
图2.1 register运行结果
设计思路:
- 首先系统提示用户输入用户名以及密码,如果用户输入的用户名没有重复,即可成功注册。
- 如果遇到用户名重复的情况,那么系统会提示“用户已经存在”。
2.2 用户登录:login
实现结果:
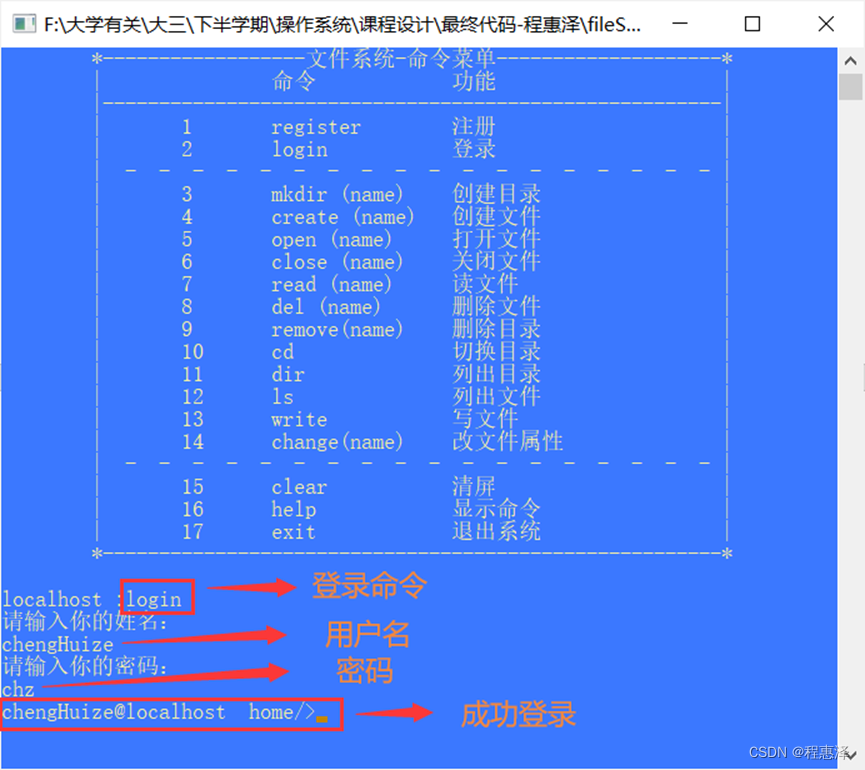
图2.2.1 login成功登陆运行结果
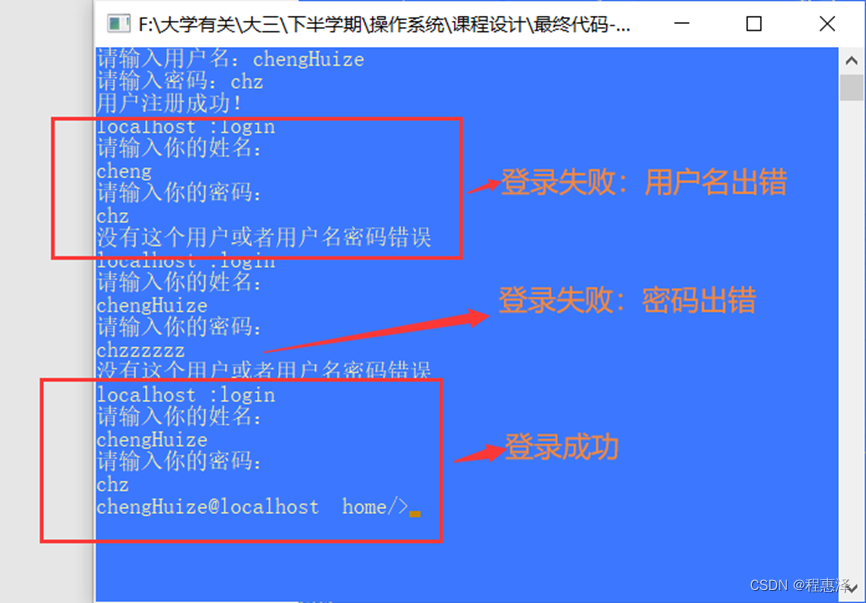 图2.2.2 login登陆信息验证
图2.2.2 login登陆信息验证
设计思路:
- 如图2.2.1所示,当用户正确输入用户名和密码时,可以成功登录进系统,但是如图2.2.2所示,当用户输入的用户名或者用户密码任意一个出现错误,那么系统会提示没有该用户或者密码错误。
2.3 创建文件:create(文件名)
实现结果:
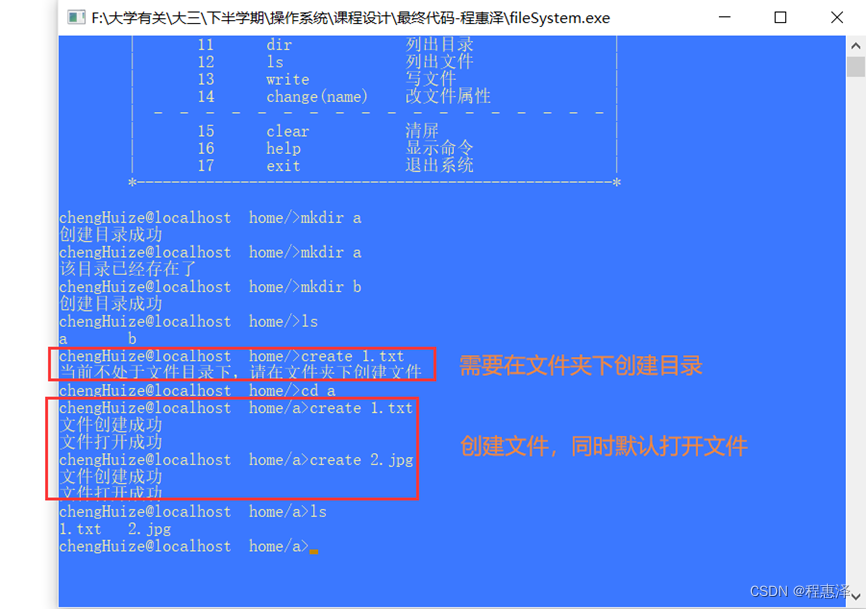
图2.3 create命令在目录下创建文件
设计思路:
- 图2.3展示了使用create命令创建文件的过程,当用户在非文件夹下创建普通文件时,将会遇到提示“当前不处于文件目录下,请在文件夹下创建文件”,当用户进入某个文件夹下(比如文件夹a),那么用户就可以创建不同后缀的文件,同时创建的文件上限是64个。
2.4 创建文件夹:mkdir(文件夹名)
实现结果:
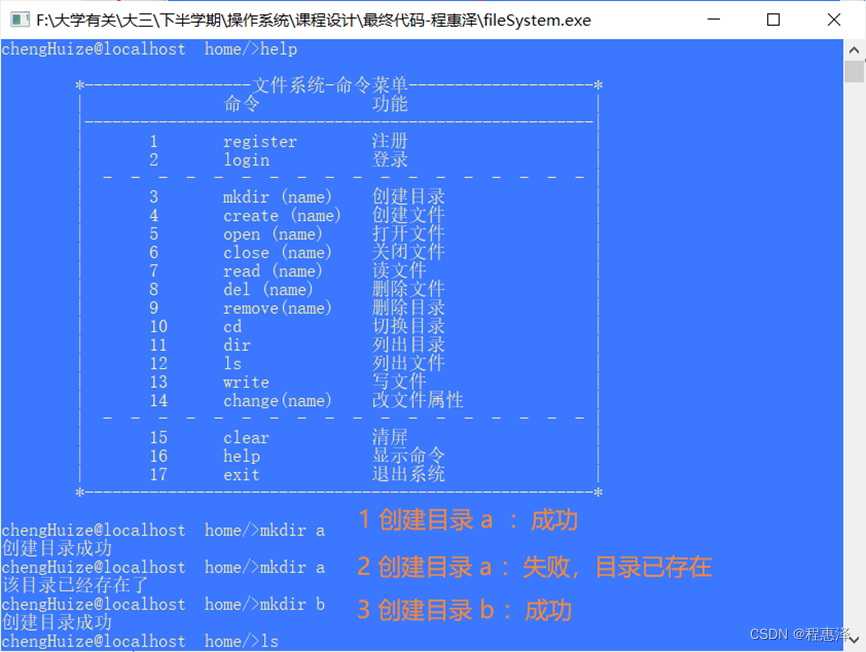 图2.4 mkdir命令创建目录结果
图2.4 mkdir命令创建目录结果
设计思路:
每当创建一个新的文件夹:
• 修改USER_UFD类型的成员cur_user_direct_size+1
• 初始化USER_UFD类型的成员ufd,初始化为文件夹名为name
• 初始化USER_UFD类型的成员ufd,初始化文件数为零。
2.5 打开文件:open(文件名)
实现结果:
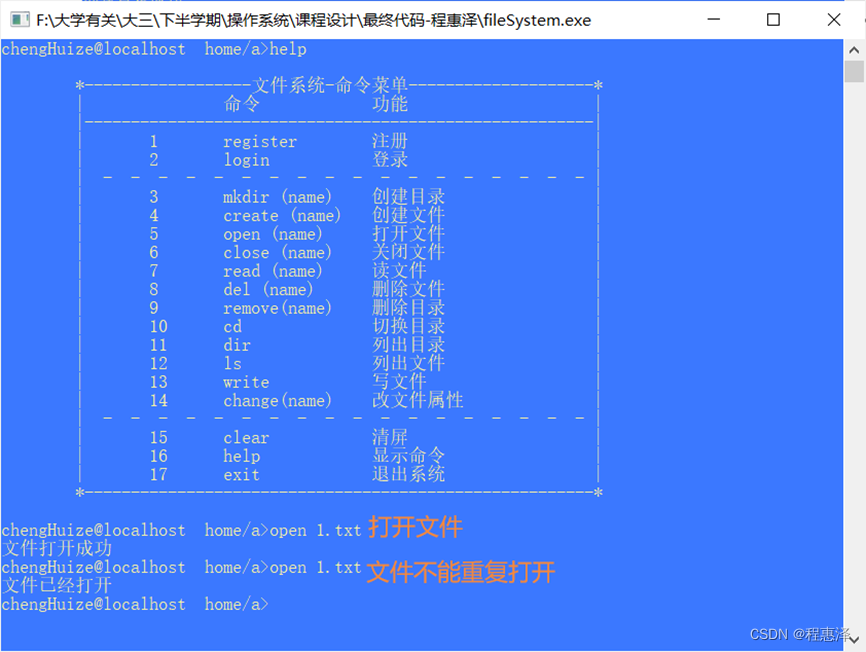
图2.5 文件打开测试结果
设计思路:
- 每次打开文件都需要判断文件是否存在,同时文件如果已经被打开,那么就提示“文件已经打开”,然后再更新文件打开表信息:
cur_openfilesize++文件打开数量加1(保存被打开文件的信息)。
只有打开的文件,才能进行相应的读写等下一步操作。
2.6 关闭文件:close(文件名)
实现结果:
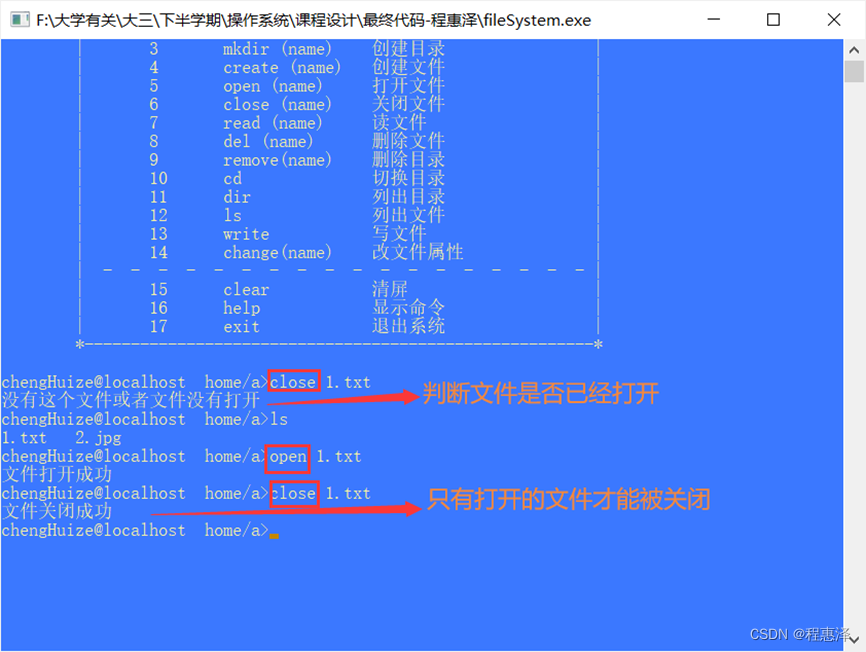 图2.6 close命令文件关闭命令测试结果
图2.6 close命令文件关闭命令测试结果
设计思路:
- 首先判断文件是否打开,以防止文件还处于操作过程中时,就被无意删除。当文件处于打开状态打开,才能被关闭。
2.7 读取文件:read(文件名)
实现结果:
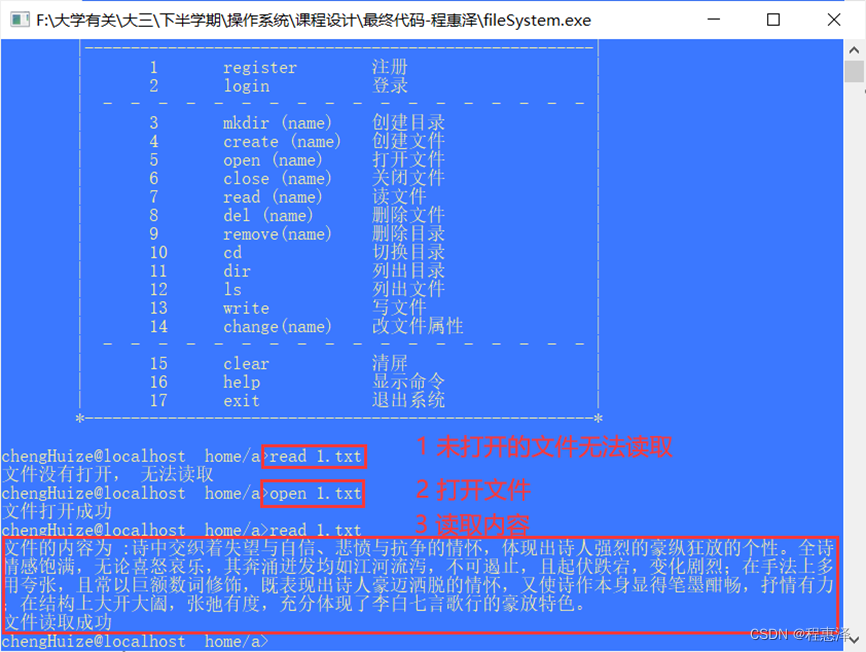 图2.7 read命令文件读取测试结果
图2.7 read命令文件读取测试结果
设计思路:
- 首先如过一个文件没有打开,那么就不能被读取;第二步展示了打开文件后,进一步才能进行读取操作。从图2.7中可以看到,文件中的内容成功被读取到了命令行中。
2.8 删除文件:del(文件名)
实现结果:
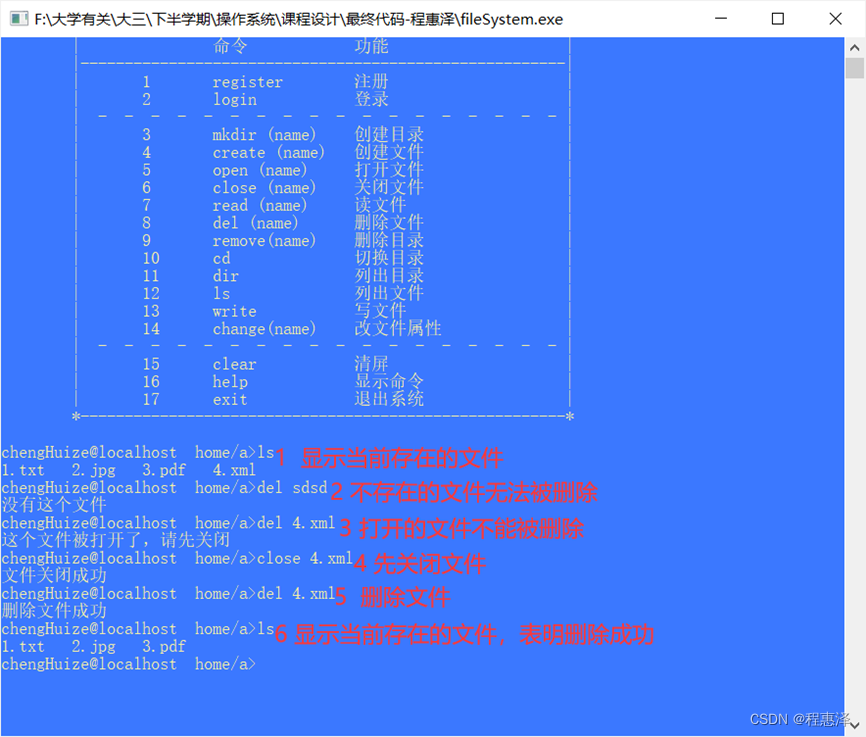
图2.8 del删除文件命令测试结果
设计思路:
- 文件删除的测试结果如图2.8所示,当用户输入命令del想要删除“不存在”的文件或者想要删除“被打开”的文件时,系统就会阻止删除操作的进一步进行。
2.9 删除目录:remove(文件名)
实现结果:
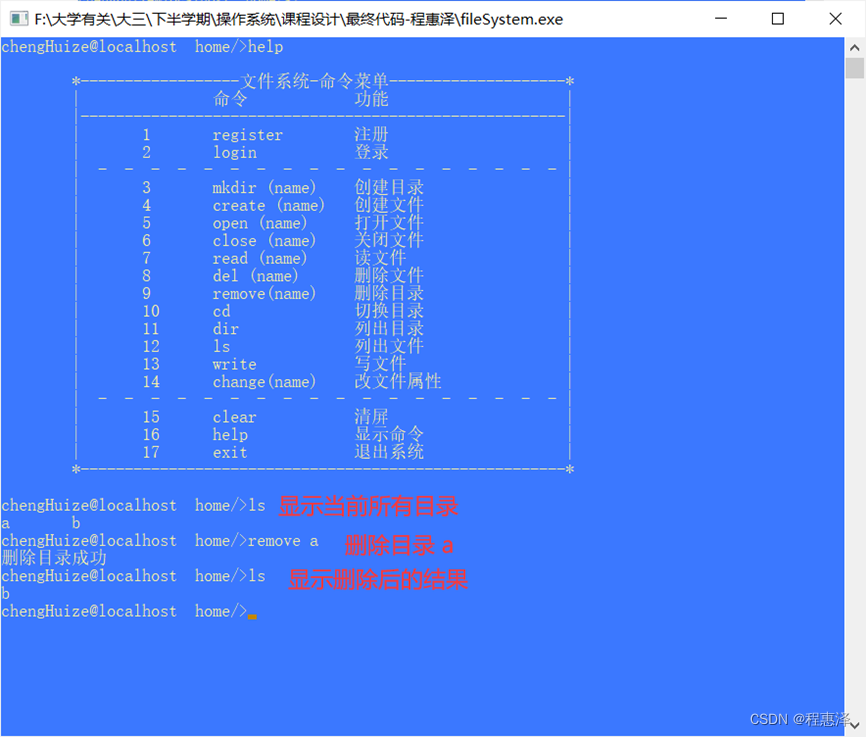 图2.9 remove命令的测试结果
图2.9 remove命令的测试结果
设计思路:
- 当用户输入命令remove,系统可以将当前文件夹及其包含的所有文件删除掉。
2.10 切换目录:cd
实现结果:
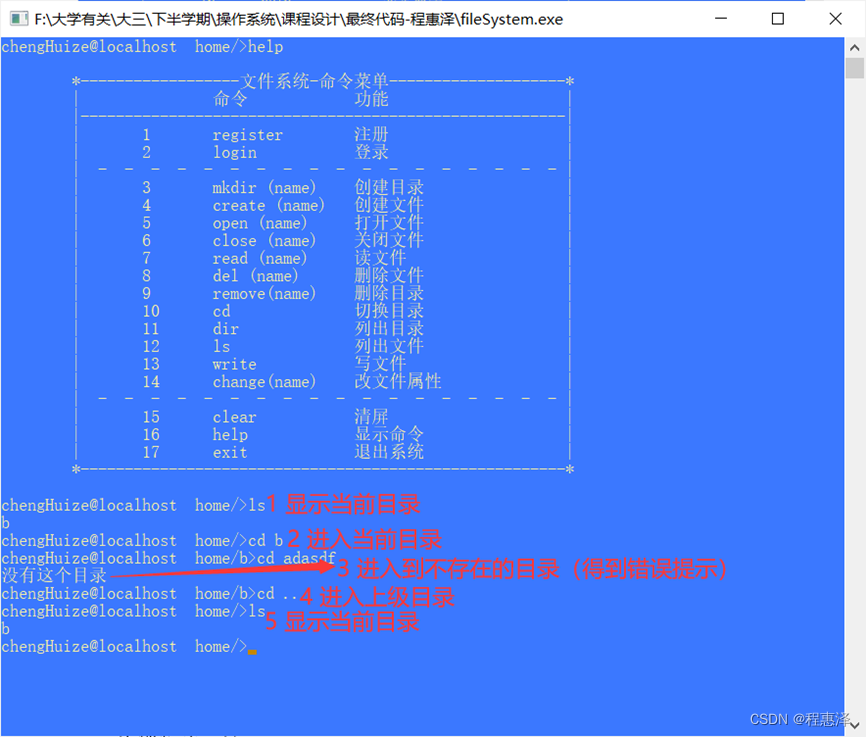 图2.10 cd命令的测试结果
图2.10 cd命令的测试结果
设计思路:
- 使用cd命令可以切换路径,包扩修改path等。从而实现了路径的切换。“…”代表返回上级目录,这里功能是通过判断语句,将path的值修改为空,直接跳转到根目录,因为目录层级只有两级,所以可以这样操作。
2.11 列文件目录:dir
实现结果:
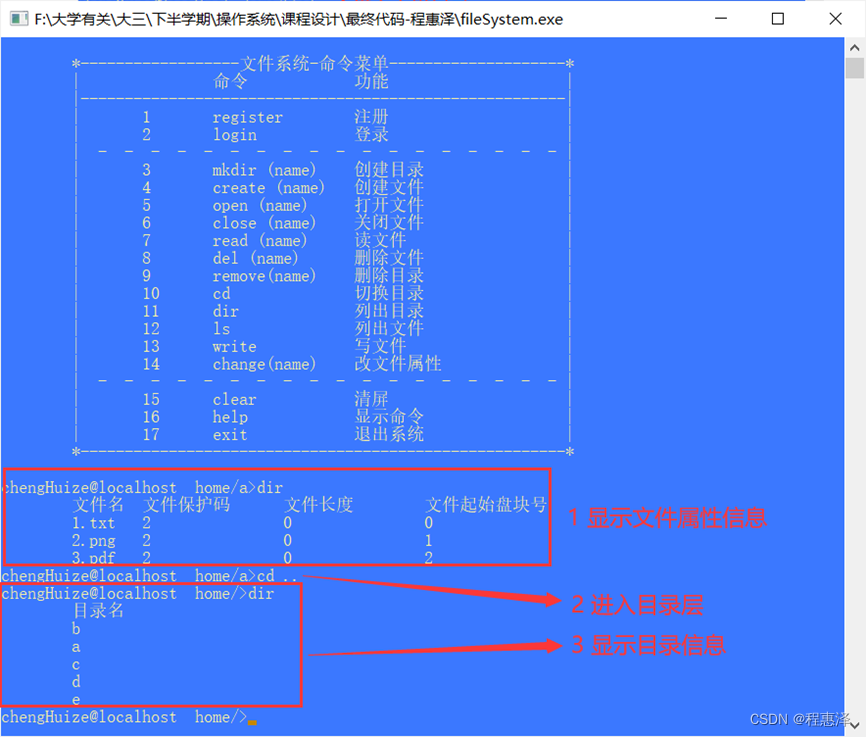
图2.11 dir命令测试结果
设计思路:
- dir命令如果是在目录层进行使用,那么就会显示所有创建好的文件夹,如果是在文件夹中使用,那么将会显示当前文件夹下所有文件的属性信息。
2.12 显示当前目录的文件:ls
实现结果:
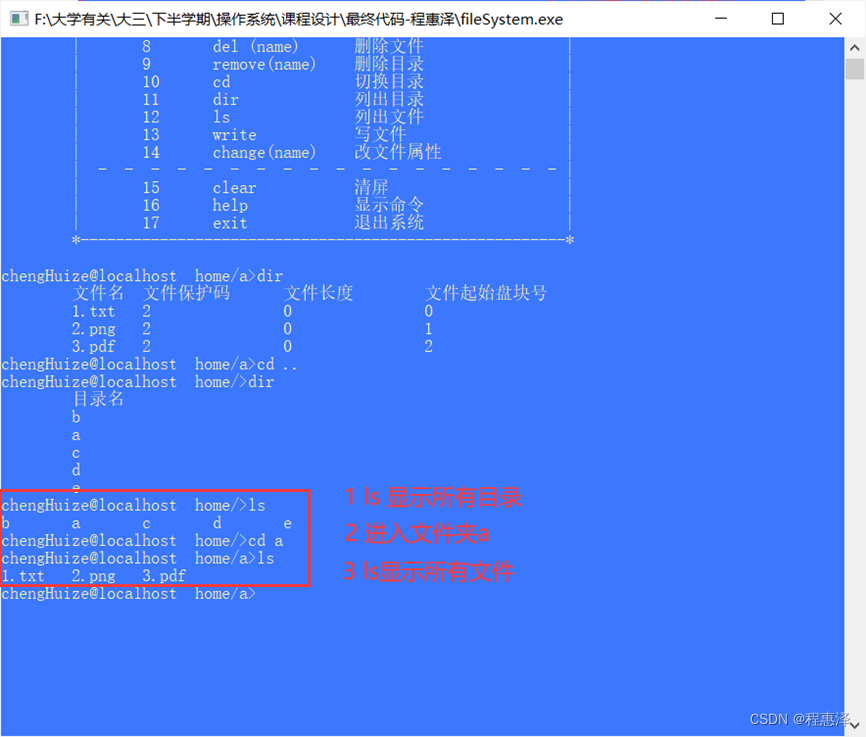
图2.12 ls命令的测试结果
设计思路:
- ls可以将当前目录或者文件列出,效果如图2.12所示。
2.13 写入文件:write
实现结果:
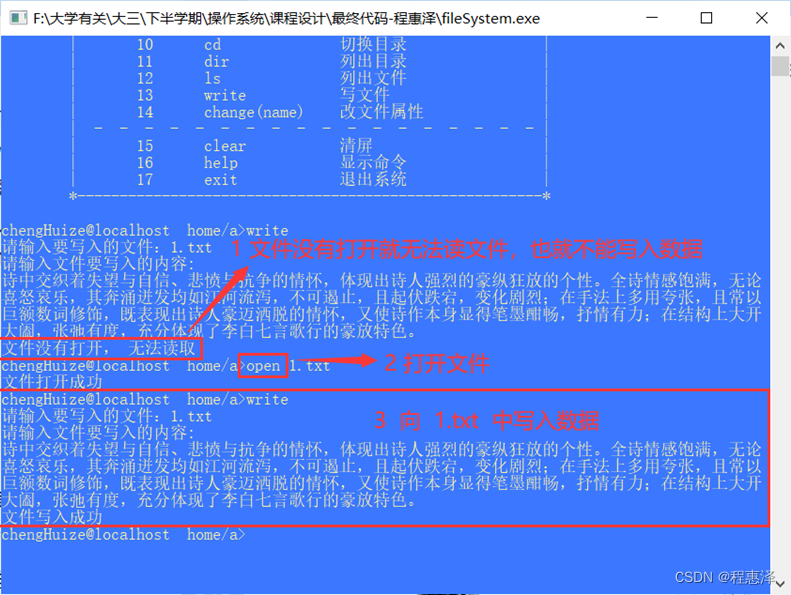
图2.13 向1.txt中写入数据测试结果
设计思路:
- 如图2.13所示,当用户使用write,系统会提示用户输入想要写入信息的文件名,文件没有打开就无法读取文件,也不能写入数据。
- 向文件中写入信息时,使用获取行得到用户输入的信息,因为回车键是确认信息写入(写信息是追加的方式)。
2.14 修改文件属性:change(文件名)
实现结果:
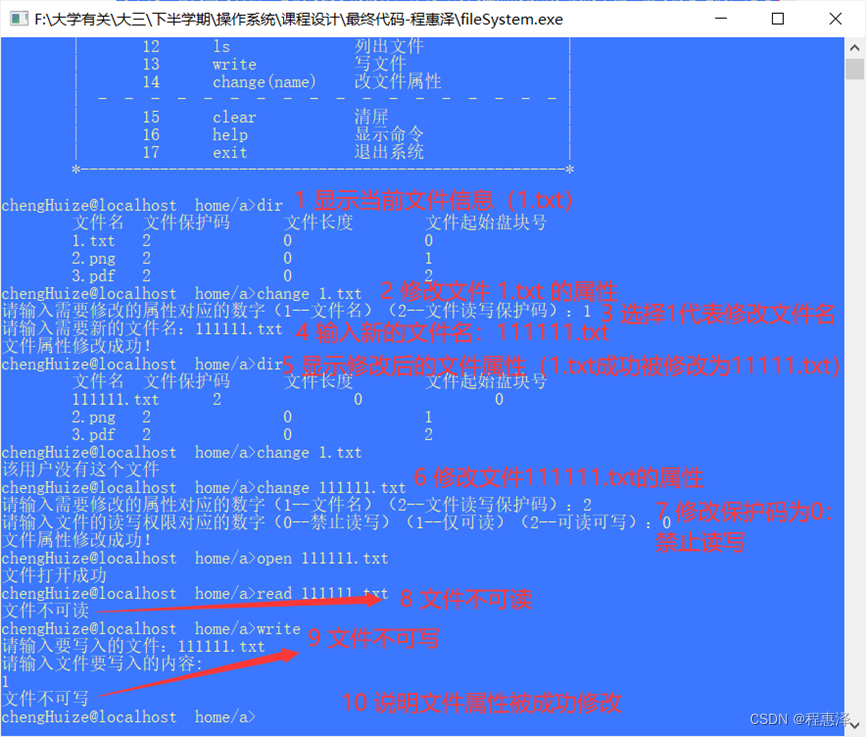
2.14 change命令的测试结果
设计思路:
- 从图2.14中可以看到,第一步显示了文件的信息,从表中可以详细的看到每个文件的名称、保护码、文件长度、文件起始物理盘块号等信息。
- 当用户使用change命令修改某个文件,需要选择对应的修改项,图中步骤4和步骤5展示了修改文件属性名后的结果,同时文件的属性修改还支持文件保护码的修改。
2.15 清屏:clear
实现结果:
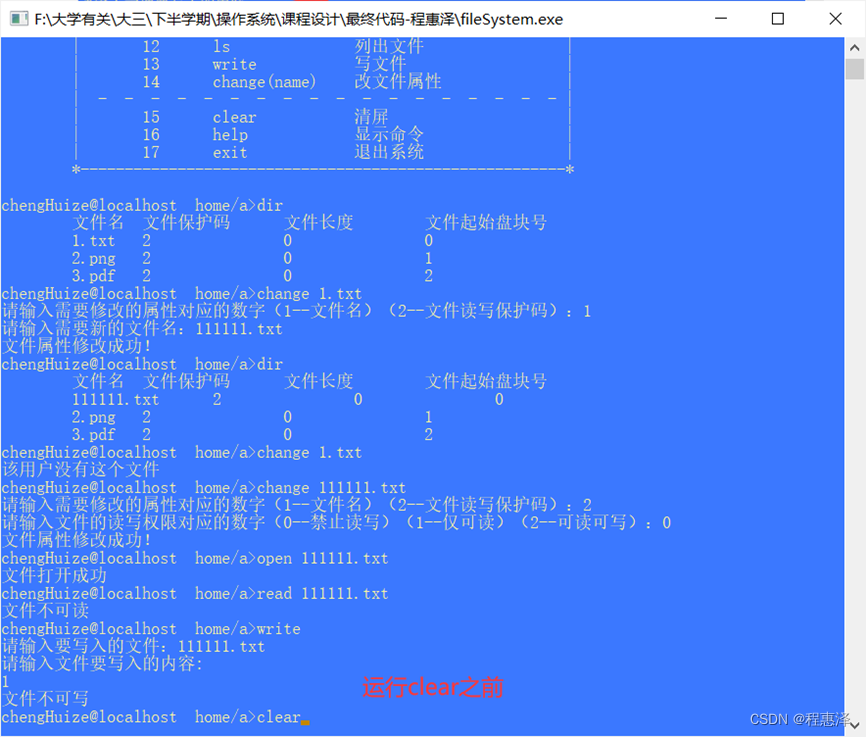
图2.15.1 运行clear之前
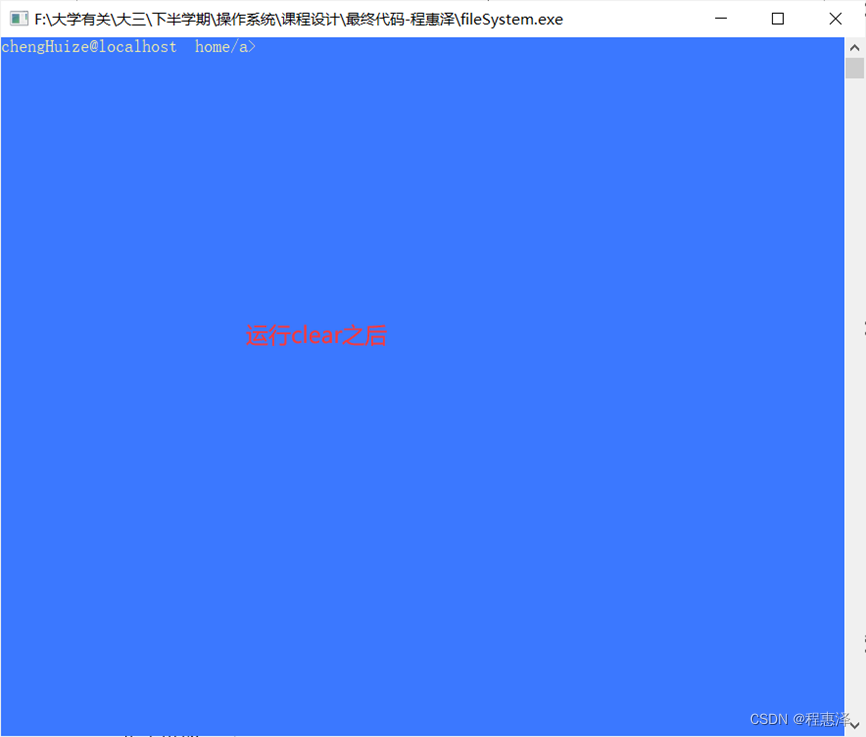
图2.15.2 运行clear之后
设计思路:
- 根据图2.15.1和图2.15.2对比,可以看出程序运行完,命令行被清空,这同时会导致所有的文件被自动关闭,所以再次进行文件相关操作时,需要重新打开文件。
2.16 显示所有的命令:help
实现结果:
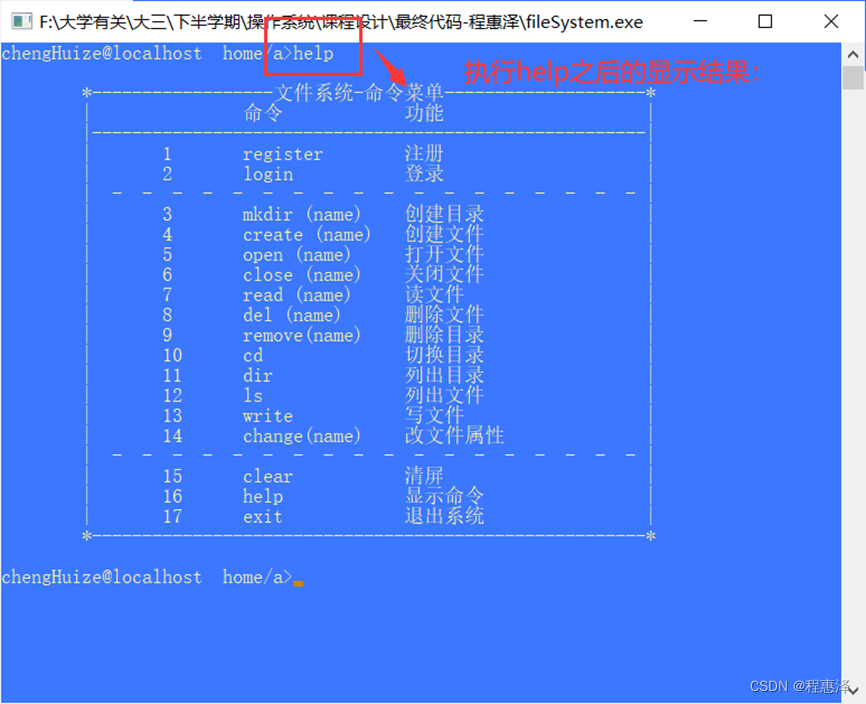
图2.16 help命令的测试结果
设计思路:
- 当用户输入命令help时,如图2.16所示,系统将会打印命令菜单。
2.17 退出系统:exit
实现结果: 文件系统释放内存,程序关闭
设计思路:
- 当用户输入命令exit,系统将会退出,同时清空占用的缓存,释放系统资源。
3. 总结分析
3.1 遇到的问题
- 实现文件控制块、空闲盘块等数据结构相对较为复杂。
- 文件的打开、关闭、读写、修改属性等操作实现起来比较繁琐。
- 在设计过程中需要考虑多用户、多目录、多文件的情况,容易出现数据混乱。
3.2 解决方法
- 第一个问题,可以通过前置课程的学习和查阅资料等方式深入了解和掌握数据结构的知识点,并根据实际需求灵活应用。
- 第二个问题,可以通过封装函数来简化操作,同时加强代码的可读性和可维护性。
- 第三个问题,可以采用各种数据结构来提高程序的鲁棒性,例如采用链表等数据结构。
3.3 设计需要改进的内容
- 在文件控制块、UFD、UOF等数据结构的设计中,应该加入更多的属性和方法,使得系统功能更加完善。
- 在用户交互方面,可以引入图形界面等方式,提高用户操作的便利性和用户体验。
3.4 个人收获与感想
- 通过这次课程设计,我对于数据结构和文件操作有了更深入的理解。同时,也提高了自己的编程能力和解决问题的能力。
- 最重要的是,这次经历让我更深刻地认识到了操作系统的魅力和挑战,同时也让我愈发热爱这个领域。
4. 完整代码
包含详细注释的代码如下,可运行。
两个版本的代码基本没有区别,不同之处在于清屏操作。
除了clear和exit命令有系统调用,其他功能均没有系统函数调用。
4.1 windows版本代码
fileSystem.cpp
//--------------------------------【文件管理】--------------------------------//
//文件管理系统设计:通过模拟文件操作命令的执行,来模拟文件管理。 //
//要求建立相应的数据结构:文件控制块、空闲盘块等。 //
//模拟盘块管理能够实现文件的建立、打开、读写、执行、属性修改、文件保护等基本功能。 //
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------////#include <conio.h> // 定义了一些控制台操作函数,例如getch、clrscr和gotoxy等。这些函数只在Windows平台上可用,在Linux或macOS上不可用。
#include <iostream> // 标准输入输出头文件,包含cout,cin等
#include <string> // 定义了字符串类string
#include <stdio.h> // 定义了输入输出函数,例如printf
#include <stdlib.h> // 定义了一些常用的函数和变量类型,例如malloc、exit、size_t和NULL等
#include <time.h> // 获取当前系统时间,用于记录文件创建时间等信息。
using namespace std; //命名空间std//函数声明
void register_user(); //1.用户注册
int login(); //2.登录,返回用户在用户目录数组中的下标
int create(string); //3.文件创建(文件名)
void mkdir(string); //4.创建文件夹(文件夹名)
int open(string name); //5.打开文件(文件名)
int close(string); //6.关闭文件(文件名)
int read(string); //7.读取文件(文件名)
int del(string); //8.删除文件(文件名)
void remove(string name);//9.删除目录(文件名)
void cd(); //10.切换目录
void dir(); //11.列文件目录
void ls(); //12.显示当前目录的文件
int write(string, char *, int); //13.写入文件(文件名,物理块要存入的数据内容,文件内数据总长度)
void change(string name);//14.修改文件属性(文件名)
void input_operation(); //用户交互
void display(); //列出所有命令以及用法
bool login_or_not(); //检测是否有用户登录 //-------第一级:顶层目录(所有的用户)
struct MFD // 16个用户-----------------------2的幂次方
{string username; //用户名string password; //登录密码struct USER_UFD *next; //指向用户目录
};//-------第三层:用户的某个目录文件下的所有文件(包含一个用户的所有文件)
struct UFD //一个用户可以用16个文件夹
{struct file_message //每个文件夹下可以有64个文件{string filename; //文件名int protect_code; //保护码int length; //文件长度int addr; //存放该文件的物理块的第一个的块号}ufd[64];string directname; //用户目录名(文件夹的名称)int cur_file_size = 0; //不能在结构体内附初始值。
};//-------第二级:单个用户的文件目录
struct USER_UFD
{struct UFD direct[16]; //每个用户最多有16个目录int cur_user_direct_size = 0; //当前用户的目录数
};// user open file:当前打开的文件控制块
struct UOF //假设一个用户最多同时打开16个文件
{struct uof{string filename;//文件名int pointer; //文件的读写指针,其实就是文件的大小int protect_code; //2表示可读可写,1表示可读不可写, 0表示不可读不可写int addr; //存放文件的第一个磁盘块号}uof[16];int cur_openfilesize = 0; //打开的文件数
};//-------记录文件占用磁盘块情况:物理块,假设一个磁盘的每个物理块大小为 512个字节 = 64*2*4字节
struct fat //文件分配表 用一块物理块存放,那么最多可以记录64块数据块的信息。
{int next = -1; //下一个磁盘块号 int used = 0; //1表示被使用,0表示未被使用
}fat[64];int max_usersize = 16; //最大用户数量
int max_userfilesize = 64; //每个用户最大文件夹数量
int max_openfilesize = 16; //用户可以同时打开的文件数量MFD mfd[16]; //-------用户信息:16个用户(身份登录信息)
USER_UFD cur_all_direct[16]; //-------第一级:16个用户的所有目录的对象(文件目录信息)
MFD cur_user; //-------第二级:当前用户,可检索到当前用户下所有的目录(同时只能有一个用户处于登录状态)
UOF openfile[16]; //当前用户的文件打开表对象,为全局变量
UOF *cur_opentable; //指向当前文件打开表char *fdisk; //虚拟磁盘的起始位置
int cur_user_size = 0; //记录当前用户的人数(上限16)
string path; //记录当前用户的路径
bool login_or = false; //记录当前是否有用户登录 //文件创建
int create(string name)
{// 0 判断当前路径if(path == ""){cout << "当前不处于文件目录下,请在文件夹下创建文件" << endl;return -1;} // 1 获取文件夹下标 int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++) //遍历当前用户所有的文件夹{if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname) //判断{break;}}// 2 文件重名判断 int i;for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //遍历当前目录,查看是否有文件重名{if (name == cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename)break;}if (i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size) //判断文件名是否重复{cout << "文件名重复" << endl;return -1;}// 3 文件数目判断 if (cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size == 64) //判断当前目录的文件到达64个{cout << "用户文件已经达到64个" << endl;return -1;}// 4 文件是否可分配到新的空闲块 //寻找空闲块int j;for (j = 0; j < 64; j++) //判断是否有空的空闲块。{if (fat[j].used == 0)break;}if (j >= 64){cout << "磁盘没有空闲块了" << endl;return -1;}// 5 创建文件:修改ufd信息 cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].filename = name;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].addr = j; //文件起始盘块号cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].length = 0; //文件初始没有数据cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].protect_code = 2; //表示可读可写cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size++;//用户文件数量加1fat[j].used = 1; //被使用fat[j].next = -1; //只是个空文件,所有没有后序的块//写入文件打开表中,就是调用open()cout << "文件创建成功" << endl;int fd = open(name);return fd;
}//打开文件
int open(string name)
{// 1 遍历该用户所有的文件夹,获取当前文件夹的文件目录下标int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个//cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size 代表 目录数for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname) //找指定名称的目录{break;}}// 2 遍历该文件夹下的文件,获取文件下标//cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size 代表 文件数int i;for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //当前目录有没有这个文件,没有就自然不能打开{if (name == cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename)break;}// 3 判断文件是否存在//-------这里的判断应当是大于等于,而不是大于 if (i >= cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size){cout << "该用户没有这个文件" << endl;return -1;}// 4 判断文件是否可以被打开(是否达到打开上限)//cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize 代表 UOF指针->打开的文件数if (cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize == max_openfilesize) //如果打开文件的数量达到最大值,那么就无法打开{cout << "文件打开数量已经达到最大值" << endl;return -1;}// 5 判断文件是否已经被打开for (int j = 0; j < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; j++) //如果文件已经打开,就无需打开{if (cur_opentable->uof[j].filename == name){cout << "文件已经打开" << endl;return -1;}}// 6 更新文件打开表信息//cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size 代表 当前文件数int k;for (k = 0; k < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; k++) //找到要打开的文件在文件数组中的第几个{if (cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].filename == name)break;}//打开文件:更新打开表(保存被打开文件的信息),cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].filename = name;cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].protect_code = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].protect_code;cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].pointer = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].length;cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].addr = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].addr;cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize++; //文件打开数量加1cout << "文件打开成功" << endl;return k; //返回文件在文件打开表中的第几项}//修改文件属性
void change(string name)
{// 1 遍历该用户所有的文件夹int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个//cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size 代表 目录数for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname) //找指定名称的目录{break;}}// 2 遍历该文件夹下的文件//cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size 代表 文件数int i;for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //当前目录有没有这个文件,没有就自然不能打开{if (name == cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename)break;}// 3 判断文件是否存在//-------这里的判断应当是大于等于,而不是大于 if (i >= cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size){cout << "该用户没有这个文件" << endl;return ;}// 4 修改文件属性:修改ufd信息 cout << "请输入需要修改的属性对应的数字(1--文件名)(2--文件读写保护码):";int which;cin >> which; //选项if(which == 1){cout << "请输入需要新的文件名:";string name;cin >> name; //文件名cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename = name;}if(which == 2){cout << "请输入文件的读写权限对应的数字(0--禁止读写)(1--仅可读)(2--可读可写):";int code;cin >> code; //读写权限if(code == 0 || code == 1 || code == 2 )cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].protect_code = code; elsecout << "输入有误,请重新change" << endl;}cout << "文件属性修改成功!" << endl;
}//关闭文件
int close(string name)
{// 1 获取当前文件在文件打开表的对应下标int fd;for (int i = 0; i < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; i++) //找到要关闭的文件在表中的第几项{if (cur_opentable->uof[i].filename == name) //根据文件名查找{fd = i;break;}}if (fd >= cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize){cout << "没有这个文件或者文件没有打开" << endl;return -1;}// 2 将要删除的项目与最后一个项目交换,因为是数组存放。(这样,仅仅需要将cur_openfilesize--,就等价于删除)cur_opentable->uof[fd].filename = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].filename;cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].pointer;cur_opentable->uof[fd].protect_code = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].protect_code;cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].addr;cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize--;cout << "文件关闭成功" << endl;return 0;}//删除文件
int del(string name) //删除文件打开表的文件数量不用减一,因为文件打开就不能删除文件
{// 1 找到当前目录int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname){break;}}// 2 遍历当前目录下的文件int i;for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //判断当前目录下有没有这个文件{if (cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename == name)break;}if (i >= cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size){cout << "没有这个文件" << endl;return -1;}// 3 遍历打开的文件int j;for (j = 0; j < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; j++) //判断该文件是否被打开{if (cur_opentable->uof[j].filename == name)break;}if (j < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize) //说明文件被打开了{cout << "这个文件被打开了,请先关闭" << endl;return -1;}// 4 更新当前用户目录下文件数组信息,就是将最后一个文件的信息替换到要删除的文件的位置fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].used = 0; //没有使用cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].filename;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].addr;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].length = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].length;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].protect_code = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].protect_code;cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size--; //用户文件数量减1// 5 回收磁盘:更新文件分配表fat//cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr 即 起始地址的块号(下标表示,所以从0开始)//temp 记录文件分配表下标int temp = fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].next;while (temp != -1){fat[temp].used = 0;temp = fat[temp].next;}cout << "删除文件成功" << endl;return 0;
}//读取文件
int read(string name)
{// 1 文件目录下标int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname){break;}}// 2 文件下标int a; //遍历文件for (a = 0; a < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; a++) //判断文件是否存在{if (cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[a].filename == name)break;}if (a >= cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size){cout << "没有这个文件" << endl;return -1;}int i;// 3 判读文件是否打开(通过在文件打开情况结构体的实例中寻找待读取文件的文件名)for (i = 0; i < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; i++){if (cur_opentable->uof[i].filename == name)break;}if (i >= cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize){cout << "文件没有打开, 无法读取" << endl;return -1;}// 4 如果文件已经打开,那么此时的 i 就是打开的文件数组uof的下标int fd = i; //获取文件描述字//判断读文件的合法性if (cur_opentable->uof[fd].protect_code == 0) //创建的文件都是默认可读可写的{cout << "文件不可读" << endl;return -1;}else{int len = cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer; //文件的长度int block_size = len / 512; //磁盘的个数int offset = len % 512; //偏移量if (offset != 0)block_size++; //包含偏移量的磁盘//如果用一个文件表示磁盘的引导块,用另一个文件表示磁盘的数据块,那么我们计算文件的起始位置就不用加上磁盘的引导块了//关于文件的存放文件,我们char *fdisk表示一整个磁盘,然后不同文件的内容存放在这个指针所指向的不同字符段char * first = fdisk + cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr * 512; //文件的起始地址char * buf = (char *)malloc(512 * sizeof(char)); //缓冲区(大小等于一个空闲块大小)cout << "文件的内容为 :";for (int k = 0; k < block_size; k++) //遍历文件包含的块,k代表相对起址的块号{if (k == block_size - 1) //如果是最后一个磁盘块,就不是将全部512字节输出,而是输出偏移量大小的数据{for (int j = 0; j < len - k * 512; j++) //赋值文件剩余的字符------偏移量{buf[j + k * 512] = first[j]; //缓冲区存放待输出的字符}for (int u = 0; u < len - k * 512; u++){cout << buf[u + k * 512]; //输出剩余长度,之所以这样输出,printf(),将整个buf的内容全部输出,如果没有读满就会出现乱码}}else //不在最后一个磁盘块,也就是在其他已经读满的磁盘块{for (int j = 0; j < len - i * 512; j++)buf[j + k * 512] = first[j]; //缓冲区读满就输出内容printf("%s\n", buf); //输出文件的内容int next_block = fat[cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr].next; //读完一个磁盘块后,在接着读下一个磁盘块first = fdisk + next_block * 512;}}cout << endl;cout << "文件读取成功" << endl;free(buf); //释放缓冲区return 0;}}//类似于文件拷贝,每次赋值缓冲区到虚拟磁盘中
//待完成问题:更新表的文件长度
int write(string name, char * buf, int len)
{// 1 获取文件目录数组下标(当前是哪个文件夹)int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname){break;}}// 2 从已打开文件寻找文件下标 i (之后重命名为 fd )int i;//判读文件是否打开for (i = 0; i < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; i++){if (cur_opentable->uof[i].filename == name)break;}if (i >= cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize){cout << "文件没有打开, 无法读取" << endl;return -1;}// 3 文件共享和保护int fd = i; //获取文件描述字//判断读文件的合法性if (cur_opentable->uof[fd].protect_code != 2){cout << "文件不可写" << endl;return -1;}else //文件可写入{int temp; //保存当前所写的文件在用户文件目录表的第几项,为了后面修改文件的大小int first_block = cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr; //用户文件存放的第一个磁盘块// 4 遍历当前目录下所有文件,获取文件下标temp(打开表下标是fd ; 文件下标是temp)for (int k = 0; k < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; k++){if (cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[k].addr == first_block){temp = k;break;}}//追加写// 5 找到该文件存放的最后一个磁盘块while (fat[first_block].next != -1){first_block = fat[first_block].next;}//计算该文件存放的最后一个地址char * first;first = fdisk + first_block * 512 + cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512;// 6 如果最后一个文件剩下的空间大于要写入的长度(不需要继续分配新的空闲块)if (len <= 512 - cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512){//strcpy(first, buf); 这句代码出现问题,可能是由于buf没有读满,后面的值被访问了,非法!for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){first[i] = buf[i];//将缓冲区的内容写入虚拟磁盘中}cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer = cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer + len; //更新文件打开表cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length = cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length + len; //更新用户目录文件表}else // 7 如果之前的半块磁盘剩下的空间不足写入{// 7.1 写入一部分的内容到最后一个磁盘块的剩余空间for (i = 0; i < 512 - cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512; i++){ first[i] = buf[i];}// 7.2 计算分配完最后一个磁盘的剩余空间后,还剩下多少字节没有存储,计算还需要分配多少空闲块int last_size = len - (512 - cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512); //剩余待写入的大小int need_block_size = last_size / 512; //待分配的空闲块数int need_offset_size = last_size % 512; //偏移量if (need_offset_size > 0)need_block_size++; //总共需要这么磁盘块// 7.3 判断磁盘剩余空间是否足够int unused_block_size = 0; //记录没有使用过的磁盘块的个数for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++){if (fat[i].used == 0){unused_block_size++;}}if (unused_block_size < need_block_size){cout << "磁盘没有空间存放了" << endl;return -1;}// 7.4 磁盘还有足够的空间:分配空闲块,else{int item = cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr;for (int p = 0; p < need_block_size; p++) //执行多次寻找空闲磁盘的操作,{for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++){if (fat[i].used == 0) //没有被使用{first = fdisk + i * 512; //当前要写入的磁盘块的起始地址fat[i].used = 1; //标记被使用fat[item].next = i; //标记下一个磁盘item = i;break;}}if (p == need_block_size - 1){for (int k = 0; k < need_offset_size; k++) //将文件的偏移量写入最后一个文件中first[k] = buf[k];//更新最后一个磁盘块的next值fat[i].next = -1;}else //如果不是最后一个空闲块{ //待解决问题,就是如果更新fat的next值for (int k = 0; k < 512; k++)first[k] = buf[k];}}//更新文件打开表cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer = cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer + last_size; //更新用户目录文件表cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length = cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length + last_size; }}cout << "文件写入成功" << endl;return 0;}
}// 列文件目录
void dir()
{int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname){break;}}if (path == "") //表示此时路径在用户的目录表,显示文件目录{cout << "\t" << "目录名" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++){cout << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[i].directname << endl;}}else //显示目录下的文件{cout << "\t" << "文件名" << "\t" << "文件保护码" << "\t" << "文件长度" << "\t" <<"文件起始盘块号" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; i++) //输出文件的信息{cout << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].filename << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].protect_code << "\t" << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].length <<"\t" << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].addr << endl;}}
}//登录
int login()
{//用户名string name;//密码string password;cout << "请输入你的姓名:" << endl; //用户输入cin >> name;cout << "请输入你的密码:" << endl;cin >> password;int i; // 用户目录循环变量for ( i = 0; i < cur_user_size; i++) //遍历用户目录mfd{if (mfd[i].username == name && mfd[i].password == password){break;}}//如果遍历一遍之后,没有任何一项匹配成功,给出提示信息并返回if (i >= cur_user_size) {cout << "没有这个用户或者用户名密码错误" << endl;return -1;}//信息验证成功,分配内存mfd[i].next = & (cur_all_direct[i]); //用户指向自己的所有目录的结构//初始化当前用户的信息cur_user = mfd[i];cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size = mfd[i].next->cur_user_direct_size; //当前用户的文件夹数量cur_user_size++; //用户人数++?cur_opentable = &openfile[cur_user_size]; //指针指向文件打开表对象cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize = 0; //设初始值(初始打开的文件数为0)path = ""; //指定当前路径为用户的全部目录处login_or = true; //当前有用户登录 return 1;
}void cd()
{string temp_path;cin >> temp_path;if (temp_path == "..") //两级目录,等价于返回到根目录{path = "";return;}int i; //遍历文件目录for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++) //判断path是否存在{if (temp_path == cur_user.next->direct[i].directname) //根据文件夹名称 与 路径名称 判断是否存在break;}if (i >= cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size){cout << "没有这个目录" << endl;return;}path = temp_path;return;}// 创建文件夹
void mkdir(string name)
{//判断当前用户的文件目录的数目是否达到最大值if (cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size == 16){cout << "用户目录已经达到最大值,不能在创建目录了" << endl;return;}//遍历目录int i;for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++) //判断创建的目录是否存在{if (cur_user.next->direct[i].directname == name)break;}if (i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size) //找到同名后代表已经存在{cout << "该目录已经存在了" << endl;return;}//如果文件夹可以创建,最后一个下标位置下,创建新的目录cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size].directname = name; //目录名cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size].cur_file_size = 0; //新创建的目录里面的文件个数为0cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size++; //用户的目录数加1cout << "创建目录成功" << endl;return;}// 检测登录状态
bool login_or_not()
{if(!login_or){cout<<"当前没有登录,请使用login进行登录,或者使用register进行注册"<<endl;return 0; }else return 1; } // 显示用户创建的文件
void ls()
{if(path == "") //如果是根目录{for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++) //遍历创建的目录{cout << cur_user.next->direct[i].directname << "\t" ;}}int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个-----找当前文件夹对应的下标 for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname){break;}}for (int a = 0; a < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; a++) //遍历文件 {cout << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[a].filename << "\t" ;}cout << endl;
} void input_operation() //用户输入命令
{if (cur_user.username == "")cout << "localhost :";elsecout << cur_user.username << "@localhost home/" <<path << ">";string operation;cin >> operation;if (operation == "login"){login();}else if (operation == "dir" && login_or_not())dir();else if (operation == "create" && login_or_not()){string filename;cin >> filename;create(filename);}else if (operation == "del" && login_or_not()){string filename;cin >> filename;del(filename);}else if (operation == "open" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;open(name);}else if (operation == "close" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;close(name);}else if (operation == "read" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;read(name);}else if (operation == "write" && login_or_not()){string content;string name;cout << "请输入要写入的文件:";cin >> name;cin.ignore(); //清空缓冲区的内容,不然getline读到上一个回车直接结束。。。cout << "请输入文件要写入的内容: " << endl;;getline(cin, content); //读入一整行内容char buf[512];int times = content.length() / 512;int offset = content.length() % 512;if (offset != 0)times++;for (int i = 0; i < times; i++){if (i == times - 1) //注意这里不能写成times--{for (int j = 0; j < offset; j++)buf[j] = content[j];}else{for (int j = 0; j < 512; j++)buf[j] = content[j];}write(name, buf, content.length());}}else if (operation == "ls" && login_or_not()){ls();}else if (operation == "exit"){exit(0);}else if (operation == "cd" && login_or_not()){cd();}else if (operation == "mkdir" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;mkdir(name);}else if (operation == "register"){register_user();}else if (operation == "remove" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;remove(name);}else if (operation == "change" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;change(name);}else if (operation == "help"){display(); }else if (operation == "clear"){system("cls");//windows下//system("clear");//linux下}else{cout << "你的命令错误,重新输入" << endl;}}void register_user() //用户注册
{cout << "请输入用户名:";string username; //用户名cin >> username;cout << "请输入密码:";string password; //密码cin >> password;int i;for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) //判断用户名是否存在{if (mfd[i].username == username) //如果已经存在{cout << "该用户已经存在" << endl;return;}}mfd[cur_user_size].username = username; //保存在mfd中(第一级目录)mfd[cur_user_size].password = password;cur_user_size++; //用户人数加1cout << "用户注册成功!" << endl;}void remove(string name) //删除目录
{int index;for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++){if (name == cur_user.next->direct[i].directname){index = i;break;}}for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //删除目录里面的文件{//直接释这些文件所占的磁盘块fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].used = 0; //没有使用int temp = fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].next;while (temp != -1){fat[temp].used = 0;temp = fat[temp].next;}}//删除目录项,就是将两个目录项的内容进行交换cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].cur_file_size; //注意这里需要减一,由于本身结构的限制cur_user.next->direct[index].directname = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].directname;for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].cur_file_size; i++) //注意这里的减一{cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].ufd[i].addr;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].ufd[i].filename;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].length = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].ufd[i].length;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].protect_code = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].ufd[i].protect_code;}cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size--; //目录数量减1cout << "删除目录成功" << endl;return;
}void display() //展示命令{cout << endl << "\t" << "*------------------文件系统-命令菜单--------------------*" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << "\t" << "命令" << "\t" << "\t" << "功能" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|-------------------------------------------------------|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 1 << "\t" << "register" << "\t" << "注册" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 2 << "\t" << "login" << "\t" << "\t" << "登录" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "| - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - |" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 3 << "\t" << "mkdir (name)" << "\t" << "创建目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 4 << "\t" << "create (name)" << "\t" << "创建文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 5 << "\t" << "open (name)" << "\t" << "打开文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 6 << "\t" << "close (name)" << "\t" << "关闭文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 7 << "\t" << "read (name)" << "\t" << "读文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 8 << "\t" << "del (name)" << "\t" << "删除文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 9 << "\t" << "remove(name)" << "\t" << "删除目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 10 << "\t" << "cd" << "\t" << "\t" << "切换目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 11 << "\t" << "dir" << "\t" << "\t" << "列出目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 12 << "\t" << "ls" << "\t" << "\t" << "列出文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 13 << "\t" << "write" << "\t" << "\t" << "写文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 14 << "\t" << "change(name)" << "\t" << "改文件属性" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "| - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - |" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 15 << "\t" << "clear" << "\t" << "\t" << "清屏" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 16 << "\t" << "help" << "\t" << "\t" << "显示命令" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 17 << "\t" << "exit" << "\t" << "\t" << "退出系统" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "*-------------------------------------------------------*" << endl<< endl;}int main()
{system("color 9E"); //系统背景色 cur_user.username = ""; //初始化当前用户的用户名为空path = ""; //文件路径fdisk = (char *)malloc(1024 * 1024 * sizeof(char)); //用内存模拟外存,申请内存空间,初始化display(); while (true)input_operation();free(fdisk); //程序结束,释放资源 return 0;
}4.2 linux版本代码
fileSystem-linux.cpp
//--------------------------------【文件管理】--------------------------------
//文件管理系统设计:通过模拟文件操作命令的执行,来模拟文件管理。
//要求建立相应的数据结构:文件控制块、空闲盘块等。
//模拟盘块管理能够实现文件的建立、打开、读写、执行、属性修改、文件保护等基本功能。
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------#include <iostream> // 标准输入输出头文件,包含cout,cin等
#include <string> // 定义了字符串类string
#include <stdio.h> // 定义了输入输出函数,例如printf
#include <stdlib.h> // 定义了一些常用的函数和变量类型,例如malloc、exit、size_t和NULL等
//#include <conio.h> // 定义了一些控制台操作函数,例如getch、clrscr和gotoxy等。这些函数只在Windows平台上可用,在Linux或macOS上不可用。
#include <time.h> // 获取当前系统时间,用于记录文件创建时间等信息。
using namespace std; //命名空间std//函数声明
void register_user(); //1.用户注册
int login(); //2.登录,返回用户在用户目录数组中的下标
int create(string); //3.文件创建(文件名)
void mkdir(string); //4.创建文件夹(文件夹名)
int open(string name); //5.打开文件(文件名)
int close(string); //6.关闭文件(文件名)
int read(string); //7.读取文件(文件名)
int del(string); //8.删除文件(文件名)
void remove(string name);//9.删除目录(文件名)
void cd(); //10.切换目录
void dir(); //11.列文件目录
void ls(); //12.显示当前目录的文件
int write(string, char *, int); //13.写入文件(文件名,物理块要存入的数据内容,文件内数据总长度)
void change(string name);//14.修改文件属性(文件名)
void input_operation(); //用户交互
void display(); //列出所有命令以及用法
bool login_or_not(); //检测是否有用户登录 //-------第一级:顶层目录(所有的用户)
struct MFD // 16个用户-----------------------2的幂次方
{string username; //用户名string password; //登录密码struct USER_UFD *next; //指向用户目录
};//-------第三层:用户的某个目录文件下的所有文件(包含一个用户的所有文件)
struct UFD //一个用户可以用16个文件夹
{struct file_message //每个文件夹下可以有64个文件{string filename; //文件名int protect_code; //保护码int length; //文件长度int addr; //存放该文件的物理块的第一个的块号}ufd[64];string directname; //用户目录名(文件夹的名称)int cur_file_size = 0; //不能在结构体内附初始值。
};//-------第二级:单个用户的文件目录
struct USER_UFD
{struct UFD direct[16]; //每个用户最多有16个目录int cur_user_direct_size = 0; //当前用户的目录数
};// user open file:当前打开的文件控制块
struct UOF //假设一个用户最多同时打开16个文件
{struct uof{string filename;//文件名int pointer; //文件的读写指针,其实就是文件的大小int protect_code; //2表示可读可写,1表示可读不可写, 0表示不可读不可写int addr; //存放文件的第一个磁盘块号}uof[16];int cur_openfilesize = 0; //打开的文件数
};//-------记录文件占用磁盘块情况:物理块,假设一个磁盘的每个物理块大小为 512个字节 = 64*2*4字节
struct fat //文件分配表 用一块物理块存放,那么最多可以记录64块数据块的信息。
{int next = -1; //下一个磁盘块号 int used = 0; //1表示被使用,0表示未被使用
}fat[64];int max_usersize = 16; //最大用户数量
int max_userfilesize = 64; //每个用户最大文件夹数量
int max_openfilesize = 16; //用户可以同时打开的文件数量MFD mfd[16]; //-------用户信息:16个用户(身份登录信息)
USER_UFD cur_user_all_direct_array[16]; //-------第一级:16个用户的所有目录的对象(文件目录信息)
MFD cur_user; //-------第二级:当前用户,可检索到当前用户下所有的目录(同时只能有一个用户处于登录状态)
UOF openfile[16]; //当前用户的文件打开表对象,为全局变量
UOF *cur_opentable; //指向当前文件打开表char *fdisk; //虚拟磁盘的起始位置
int cur_user_size = 0; //记录当前用户的人数(上限16)
string path; //记录当前用户的路径
bool login_or = false; //记录当前是否有用户登录 //文件创建
int create(string name)
{// 0 判断当前路径if(path == ""){cout << "当前不处于文件目录下,请在文件夹下创建文件" << endl;return -1;} // 1 获取文件夹下标 int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++) //遍历当前用户所有的文件夹{if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname) //判断{break;}}// 2 文件重名判断 int i;for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //遍历当前目录,查看是否有文件重名{if (name == cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename)break;}if (i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size) //判断文件名是否重复{cout << "文件名重复" << endl;return -1;}// 3 文件数目判断 if (cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size == 64) //判断当前目录的文件到达64个{cout << "用户文件已经达到64个" << endl;return -1;}// 4 文件是否可分配到新的空闲块 //寻找空闲块int j;for (j = 0; j < 64; j++) //判断是否有空的空闲块。{if (fat[j].used == 0)break;}if (j >= 64){cout << "磁盘没有空闲块了" << endl;return -1;}// 5 创建文件:修改ufd信息 cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].filename = name;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].addr = j; //文件起始盘块号cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].length = 0; //文件初始没有数据cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].protect_code = 2; //表示可读可写cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size++;//用户文件数量加1fat[j].used = 1; //被使用fat[j].next = -1; //只是个空文件,所有没有后序的块//写入文件打开表中,就是调用open()cout << "文件创建成功" << endl;int fd = open(name);return fd;
}//打开文件
int open(string name)
{//遍历该用户所有的文件夹int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个//cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size 代表 目录数for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname) //找指定名称的目录{break;}}//遍历该文件夹下的文件//cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size 代表 文件数int i;for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //当前目录有没有这个文件,没有就自然不能打开{if (name == cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename)break;}//判断文件是否存在//-------这里的判断应当是大于等于,而不是大于 if (i >= cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size){cout << "该用户没有这个文件" << endl;return -1;}//判断文件是否可以被打开(是否达到打开上限)//cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize 代表 UOF指针->打开的文件数if (cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize == max_openfilesize) //如果打开文件的数量达到最大值,那么就无法打开{cout << "文件打开数量已经达到最大值" << endl;return -1;}//判断文件是否已经被打开for (int j = 0; j < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; j++) //如果文件已经打开,就无需打开{if (cur_opentable->uof[j].filename == name){cout << "文件已经打开" << endl;return -1;}}//cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size 代表 当前文件数int k;for (k = 0; k < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; k++) //找到要打开的文件在文件数组中的第几个{if (cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].filename == name)break;}//打开文件:更新打开表(保存被打开文件的信息),cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].filename = name;cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].protect_code = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].protect_code;cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].pointer = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].length;cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].addr = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].addr;cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize++; //文件打开数量加1cout << "文件打开成功" << endl;return k; //返回文件在文件打开表中的第几项}//修改文件属性
void change(string name)
{// 1 遍历该用户所有的文件夹int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个//cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size 代表 目录数for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname) //找指定名称的目录{break;}}// 2 遍历该文件夹下的文件//cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size 代表 文件数int i;for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //当前目录有没有这个文件,没有就自然不能打开{if (name == cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename)break;}// 3 判断文件是否存在//-------这里的判断应当是大于等于,而不是大于 if (i >= cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size){cout << "该用户没有这个文件" << endl;return ;}// 4 修改文件属性:修改ufd信息 cout << "请输入需要修改的属性对应的数字(1--文件名)(2--文件读写保护码):";int which;cin >> which; //选项if(which == 1){cout << "请输入需要新的文件名:";string name;cin >> name; //文件名cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename = name;}if(which == 2){cout << "请输入文件的读写权限对应的数字(0--禁止读写)(1--仅可读)(2--可读可写):";int code;cin >> code; //读写权限if(code == 0 || code == 1 || code == 2 )cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].protect_code = code; elsecout << "输入有误,请重新change" << endl;}cout << "文件属性修改成功!" << endl;
}//关闭文件
int close(string name)
{int fd;for (int i = 0; i < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; i++) //找到要关闭的文件在表中的第几项{if (cur_opentable->uof[i].filename == name) //根据文件名查找{fd = i;break;}}if (fd >= cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize){cout << "没有这个文件或者文件没有打开" << endl;return -1;}//将要删除的项目与最后一个项目交换,因为是数组存放。(这样,仅仅需要将cur_openfilesize--,就等价于删除)cur_opentable->uof[fd].filename = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].filename;cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].pointer;cur_opentable->uof[fd].protect_code = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].protect_code;cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].addr;cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize--;cout << "文件关闭成功" << endl;return 0;}//删除文件
int del(string name) //删除文件打开表的文件数量不用减一,因为文件打开就不能删除文件
{// 1 找到当前目录int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname){break;}}// 2 遍历当前目录下的文件int i;for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //判断当前目录下有没有这个文件{if (cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename == name)break;}if (i >= cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size){cout << "没有这个文件" << endl;return -1;}// 3 遍历打开的文件int j;for (j = 0; j < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; j++) //判断该文件是否被打开{if (cur_opentable->uof[j].filename == name)break;}if (j < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize) //说明文件被打开了{cout << "这个文件被打开了,请先关闭" << endl;return -1;}// 4 更新当前用户目录下文件数组信息,就是将最后一个文件的信息替换到要删除的文件的位置fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].used = 0; //没有使用cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].filename;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].addr;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].length = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].length;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].protect_code = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].protect_code;cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size--; //用户文件数量减1// 5 回收磁盘:更新文件分配表fat//cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr 即 起始地址的块号(下标表示,所以从0开始)//temp 记录文件分配表下标int temp = fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].next;while (temp != -1){fat[temp].used = 0;temp = fat[temp].next;}cout << "删除文件成功" << endl;return 0;
}//读取文件
int read(string name)
{// 1 文件目录下标int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname){break;}}// 2 文件下标int a; //遍历文件for (a = 0; a < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; a++) //判断文件是否存在{if (cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[a].filename == name)break;}if (a >= cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size){cout << "没有这个文件" << endl;return -1;}int i;//判读文件是否打开(通过在文件打开情况结构体的实例中寻找待读取文件的文件名)for (i = 0; i < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; i++){if (cur_opentable->uof[i].filename == name)break;}if (i >= cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize){cout << "文件没有打开, 无法读取" << endl;return -1;}//如果文件已经打开,那么此时的 i 就是打开的文件数组uof的下标int fd = i; //获取文件描述字//判断读文件的合法性if (cur_opentable->uof[fd].protect_code == 0) //创建的文件都是默认可读可写的{cout << "文件不可读" << endl;return -1;}else{int len = cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer; //文件的长度int block_size = len / 512; //磁盘的个数int offset = len % 512; //偏移量if (offset != 0)block_size++; //包含偏移量的磁盘//如果用一个文件表示磁盘的引导块,用另一个文件表示磁盘的数据块,那么我们计算文件的起始位置就不用加上磁盘的引导块了//关于文件的存放文件,我们char *fdisk表示一整个磁盘,然后不同文件的内容存放在这个指针所指向的不同字符段char * first = fdisk + cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr * 512; //文件的起始地址char * buf = (char *)malloc(512 * sizeof(char)); //缓冲区(大小等于一个空闲块大小)cout << "文件的内容为 :";for (int k = 0; k < block_size; k++) //遍历文件包含的块,k代表相对起址的块号{if (k == block_size - 1) //如果是最后一个磁盘块,就不是将全部512字节输出,而是输出偏移量大小的数据{for (int j = 0; j < len - k * 512; j++) //赋值文件剩余的字符------偏移量{buf[j + k * 512] = first[j]; //缓冲区存放待输出的字符}for (int u = 0; u < len - k * 512; u++){cout << buf[u + k * 512]; //输出剩余长度,之所以这样输出,printf(),将整个buf的内容全部输出,如果没有读满就会出现乱码}}else //不在最后一个磁盘块,也就是在其他已经读满的磁盘块{for (int j = 0; j < len - i * 512; j++)buf[j + k * 512] = first[j]; //缓冲区读满就输出内容printf("%s\n", buf); //输出文件的内容int next_block = fat[cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr].next; //读完一个磁盘块后,在接着读下一个磁盘块first = fdisk + next_block * 512;}}cout << endl;cout << "文件读取成功" << endl;free(buf); //释放缓冲区return 0;}}//类似于文件拷贝,每次赋值缓冲区到虚拟磁盘中
//待完成问题:更新表的文件长度
int write(string name, char * buf, int len)
{// 1 获取文件目录数组下标(当前是哪个文件夹)int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname){break;}}// 2 从已打开文件寻找文件下标 i (之后重命名为 fd )int i;//判读文件是否打开for (i = 0; i < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; i++){if (cur_opentable->uof[i].filename == name)break;}if (i >= cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize){cout << "文件没有打开, 无法读取" << endl;return -1;}// 3 文件共享和保护int fd = i; //获取文件描述字//判断读文件的合法性if (cur_opentable->uof[fd].protect_code != 2){cout << "文件不可写" << endl;return -1;}else //文件可写入{int temp; //保存当前所写的文件在用户文件目录表的第几项,为了后面修改文件的大小int first_block = cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr; //用户文件存放的第一个磁盘块// 4 遍历当前目录下所有文件,获取文件下标temp(打开表下标是fd ; 文件下标是temp)for (int k = 0; k < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; k++){if (cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[k].addr == first_block){temp = k;break;}}//追加写// 5 找到该文件存放的最后一个磁盘块while (fat[first_block].next != -1){first_block = fat[first_block].next;}//计算该文件存放的最后一个地址char * first;first = fdisk + first_block * 512 + cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512;// 6 如果最后一个文件剩下的空间大于要写入的长度(不需要继续分配新的空闲块)if (len <= 512 - cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512){//strcpy(first, buf); 这句代码出现问题,可能是由于buf没有读满,后面的值被访问了,非法!for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){first[i] = buf[i];//将缓冲区的内容写入虚拟磁盘中}cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer = cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer + len; //更新文件打开表cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length = cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length + len; //更新用户目录文件表}else // 7 如果之前的半块磁盘剩下的空间不足写入{// 7.1 写入一部分的内容到最后一个磁盘块的剩余空间for (i = 0; i < 512 - cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512; i++){ first[i] = buf[i];}// 7.2 计算分配完最后一个磁盘的剩余空间后,还剩下多少字节没有存储,计算还需要分配多少空闲块int last_size = len - (512 - cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512); //剩余待写入的大小int need_block_size = last_size / 512; //待分配的空闲块数int need_offset_size = last_size % 512; //偏移量if (need_offset_size > 0)need_block_size++; //总共需要这么磁盘块// 7.3 判断磁盘剩余空间是否足够int unused_block_size = 0; //记录没有使用过的磁盘块的个数for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++){if (fat[i].used == 0){unused_block_size++;}}if (unused_block_size < need_block_size){cout << "磁盘没有空间存放了" << endl;return -1;}// 7.4 磁盘还有足够的空间:分配空闲块,else{int item = cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr;for (int p = 0; p < need_block_size; p++) //执行多次寻找空闲磁盘的操作,{for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++){if (fat[i].used == 0) //没有被使用{first = fdisk + i * 512; //当前要写入的磁盘块的起始地址fat[i].used = 1; //标记被使用fat[item].next = i; //标记下一个磁盘item = i;break;}}if (p == need_block_size - 1){for (int k = 0; k < need_offset_size; k++) //将文件的偏移量写入最后一个文件中first[k] = buf[k];//更新最后一个磁盘块的next值fat[i].next = -1;}else //如果不是最后一个空闲块{ //待解决问题,就是如果更新fat的next值for (int k = 0; k < 512; k++)first[k] = buf[k];}}//更新文件打开表cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer = cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer + last_size; //更新用户目录文件表cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length = cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length + last_size; }}cout << "文件写入成功" << endl;return 0;}
}// 列文件目录
void dir()
{int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname){break;}}if (path == "") //表示此时路径在用户的目录表,显示文件目录{cout << "\t" << "目录名" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++){cout << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[i].directname << endl;}}else //显示目录下的文件{cout << "\t" << "文件名" << "\t" << "文件保护码" << "\t" << "文件长度" << "\t" <<"文件起始盘块号" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; i++) //输出文件的信息{cout << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].filename << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].protect_code << "\t" << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].length <<"\t" << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].addr << endl;}}
}//登录
int login()
{//用户名string name;//密码string password;cout << "请输入你的姓名:" << endl; //用户输入cin >> name;cout << "请输入你的密码:" << endl;cin >> password;int i; // 用户目录循环变量for ( i = 0; i < cur_user_size; i++) //遍历用户目录mfd{if (mfd[i].username == name && mfd[i].password == password){break;}}//如果遍历一遍之后,没有任何一项匹配成功,给出提示信息并返回if (i >= cur_user_size) {cout << "没有这个用户或者用户名密码错误" << endl;return -1;}//信息验证成功,分配内存mfd[i].next = & (cur_user_all_direct_array[i]); //用户指向自己的所有目录的结构//初始化当前用户的信息cur_user = mfd[i];cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size = mfd[i].next->cur_user_direct_size; //当前用户的文件夹数量cur_user_size++; //用户人数++?cur_opentable = &openfile[cur_user_size]; //指针指向文件打开表对象cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize = 0; //设初始值(初始打开的文件数为0)path = ""; //指定当前路径为用户的全部目录处login_or = true; //当前有用户登录 return 1;
}void cd()
{string temp_path;cin >> temp_path;if (temp_path == "..") //两级目录,等价于返回到根目录{path = "";return;}int i; //遍历文件目录for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++) //判断path是否存在{if (temp_path == cur_user.next->direct[i].directname) //根据文件夹名称 与 路径名称 判断是否存在break;}if (i >= cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size){cout << "没有这个目录" << endl;return;}path = temp_path;return;}// 创建文件夹
void mkdir(string name)
{//判断当前用户的文件目录的数目是否达到最大值if (cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size == 16){cout << "用户目录已经达到最大值,不能在创建目录了" << endl;return;}//遍历目录int i;for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++) //判断创建的目录是否存在{if (cur_user.next->direct[i].directname == name)break;}if (i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size) //找到同名后代表已经存在{cout << "该目录已经存在了" << endl;return;}//如果文件夹可以创建,最后一个下标位置下,创建新的目录cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size].directname = name; //目录名cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size].cur_file_size = 0; //新创建的目录里面的文件个数为0cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size++; //用户的目录数加1cout << "创建目录成功" << endl;return;}// 检测登录状态
bool login_or_not()
{if(!login_or){cout<<"当前没有登录,请使用login进行登录,或者使用register进行注册"<<endl;return 0; }else return 1; } // 显示用户创建的文件
void ls()
{if(path == "") //如果是根目录{for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++) //遍历创建的目录{cout << cur_user.next->direct[i].directname << "\t" ;}}int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个-----找当前文件夹对应的下标 for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++){if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname){break;}}for (int a = 0; a < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; a++) //遍历文件 {cout << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[a].filename << "\t" ;}cout << endl;
} void input_operation() //用户输入命令
{if (cur_user.username == "")cout << "localhost :";elsecout << cur_user.username << "@localhost home/" <<path << ">";string operation;cin >> operation;if (operation == "login"){login();}else if (operation == "dir" && login_or_not())dir();else if (operation == "create" && login_or_not()){string filename;cin >> filename;create(filename);}else if (operation == "del" && login_or_not()){string filename;cin >> filename;del(filename);}else if (operation == "open" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;open(name);}else if (operation == "close" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;close(name);}else if (operation == "read" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;read(name);}else if (operation == "write" && login_or_not()){string content;string name;cout << "请输入要写入的文件:";cin >> name;cin.ignore(); //清空缓冲区的内容,不然getline读到上一个回车直接结束。。。cout << "请输入文件要写入的内容: " << endl;;getline(cin, content); //读入一整行内容char buf[512];int times = content.length() / 512;int offset = content.length() % 512;if (offset != 0)times++;for (int i = 0; i < times; i++){if (i == times - 1) //注意这里不能写成times--{for (int j = 0; j < offset; j++)buf[j] = content[j];}else{for (int j = 0; j < 512; j++)buf[j] = content[j];}write(name, buf, content.length());}}else if (operation == "ls" && login_or_not()){ls();}else if (operation == "exit"){exit(0);}else if (operation == "cd" && login_or_not()){cd();}else if (operation == "mkdir" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;mkdir(name);}else if (operation == "register"){register_user();}else if (operation == "remove" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;remove(name);}else if (operation == "change" && login_or_not()){string name;cin >> name;change(name);}else if (operation == "help"){display(); }else if (operation == "clear"){//system("cls");//windows下system("clear");//linux下}else{cout << "你的命令错误,重新输入" << endl;}}void register_user() //用户注册
{cout << "请输入用户名:";string username; //用户名cin >> username;cout << "请输入密码:";string password; //密码cin >> password;int i;for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) //判断用户名是否存在{if (mfd[i].username == username) //如果已经存在{cout << "该用户已经存在" << endl;return;}}mfd[cur_user_size].username = username; //保存在mfd中(第一级目录)mfd[cur_user_size].password = password;cur_user_size++; //用户人数加1cout << "用户注册成功!" << endl;}void remove(string name) //删除目录
{int index;for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++){if (name == cur_user.next->direct[i].directname){index = i;break;}}for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //删除目录里面的文件{//直接释这些文件所占的磁盘块fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].used = 0; //没有使用int temp = fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].next;while (temp != -1){fat[temp].used = 0;temp = fat[temp].next;}}//删除目录项,就是将两个目录项的内容进行交换cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].cur_file_size; //注意这里需要减一,由于本身结构的限制cur_user.next->direct[index].directname = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].directname;for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].cur_file_size; i++) //注意这里的减一{cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].ufd[i].addr;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].ufd[i].filename;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].length = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].ufd[i].length;cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].protect_code = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size-1].ufd[i].protect_code;}cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size--; //目录数量减1cout << "删除目录成功" << endl;return;
}void display() //展示命令{cout << endl << "\t" << "*------------------文件系统-命令菜单--------------------*" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << "\t" << "命令" << "\t" << "\t" << "功能" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|-------------------------------------------------------|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 1 << "\t" << "register" << "\t" << "注册" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 2 << "\t" << "login" << "\t" << "\t" << "登录" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "| - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - |" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 3 << "\t" << "mkdir (name)" << "\t" << "创建目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 4 << "\t" << "create (name)" << "\t" << "创建文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 5 << "\t" << "open (name)" << "\t" << "打开文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 6 << "\t" << "close (name)" << "\t" << "关闭文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 7 << "\t" << "read (name)" << "\t" << "读文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 8 << "\t" << "del (name)" << "\t" << "删除文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 9 << "\t" << "remove(name)" << "\t" << "删除目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 10 << "\t" << "cd" << "\t" << "\t" << "切换目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 11 << "\t" << "dir" << "\t" << "\t" << "列出目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 12 << "\t" << "ls" << "\t" << "\t" << "列出文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 13 << "\t" << "write" << "\t" << "\t" << "写文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 14 << "\t" << "change(name)" << "\t" << "改文件属性" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "| - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - |" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 15 << "\t" << "clear" << "\t" << "\t" << "清屏" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 16 << "\t" << "help" << "\t" << "\t" << "显示命令" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 17 << "\t" << "exit" << "\t" << "\t" << "退出系统" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;cout << "\t" << "*-------------------------------------------------------*" << endl<< endl;}int main()
{//system("color 9E"); //windows系统背景色 cur_user.username = ""; //初始化当前用户的用户名为空path = ""; //文件路径fdisk = (char *)malloc(1024 * 1024 * sizeof(char)); //用内存模拟外存,申请内存空间,初始化display(); while (true)input_operation();free(fdisk); //程序结束,释放资源 return 0;
}


![[计算机通信网络]以太网的帧格式详解](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/86a9d734b264400684b64db2bd485400.png)