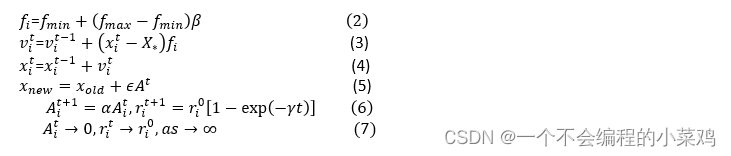蚁群算法
什么是蚁群算法
蚁群算法(ant colony optimization, ACO),又称蚂蚁算法,是仿照蚂蚁寻找食物的最短路径行为来设计的仿生算法,是一种概率型算法,适用于优化组合问题。

特点
- 对图的对称性和目标函数无特殊要求
- 可以解决各种对称不对称,线性和非线性的问题
- 鲁棒性、扩展性强、全局性
应用领域
TSP(商旅问题)
路径优化问题
调度问题
着色问题
聚类分析
网络路由
数据挖掘
工业PCB 板
其它组合优化
原理
1、蚂蚁在路径上释放信息素。
2、碰到还没走过的路口,就随机挑选一条路走。同 时,释放与路径长度有关的信息素。
3、信息素浓度与路径长度成反比。后来的蚂蚁再次碰 到该路口时,就选择信息素浓度较高路径。
4、最优路径上的信息素浓度越来越大。
5、最终蚁群找到最优寻食路径。

如上图所示,t0时刻有两只蚂蚁从蚁穴出发,分别向不同方向往前走,(三角形ABC是等边三角形),蚂蚁在沿途会留下信息素。
t1时刻,蚂蚁2到达B处,蚂蚁1到达C处;蚂蚁2准备回到A处面临两个选择,一个往A方向走,一个往B方向走,而路径AB间信息素浓度大于BC间的所以选择了AB 路径。
同理,t2时刻时蚂蚁1也做出了同样的选择。因此随着时间的推移AB间的信息素堆积就会越来越多,而BC,AC间就会随着时间推移信息素挥发后就越来越少。最终得出最短的路径AB
数学模型
访问某个节点的概率:


信息素更新方程


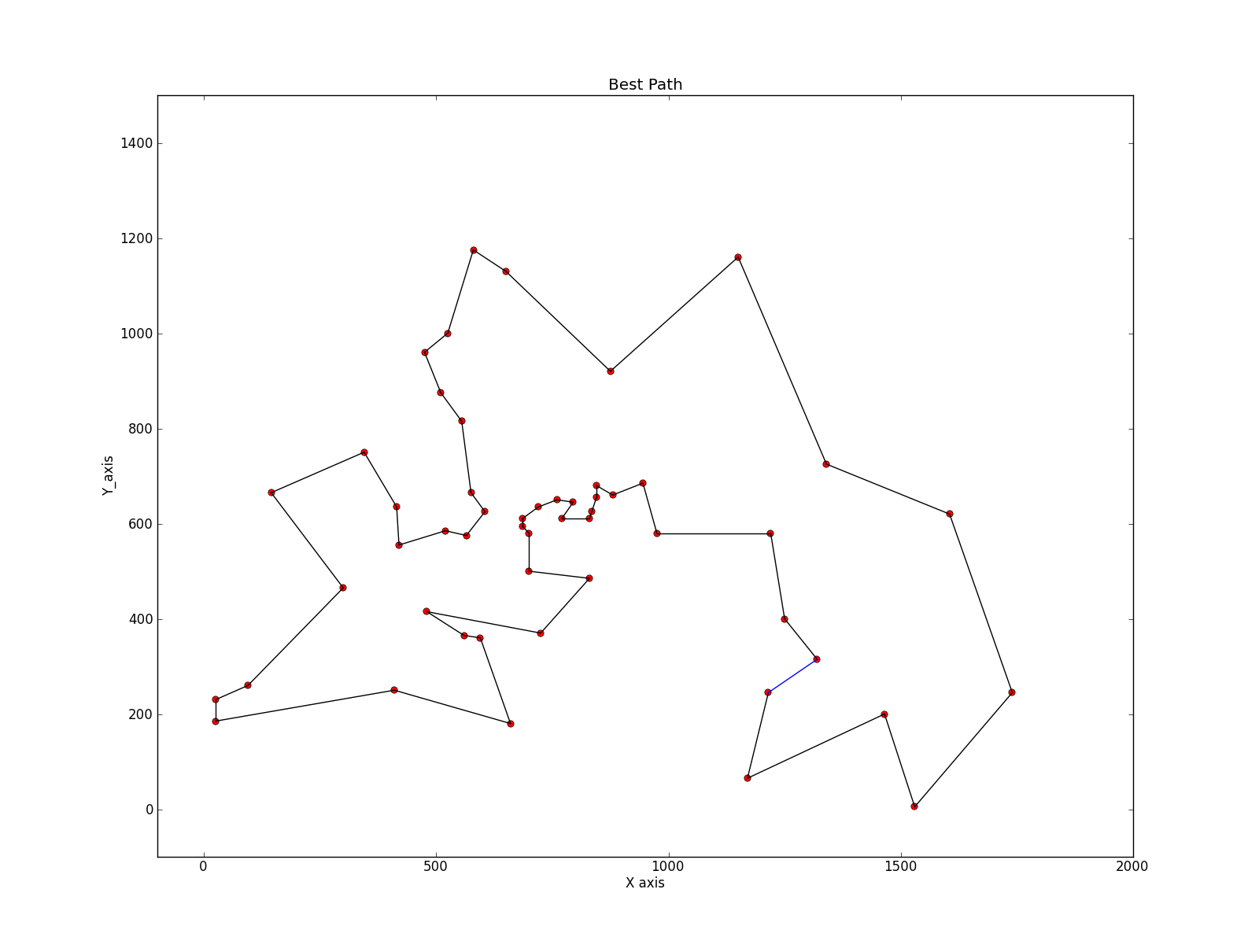
TSP应用例子
问题简单描述就是:假设一个旅行商人,他要遍历n个城市,但是每个城市只能遍历一次,最终还要回到最初所在的城市,要求制定一个遍历方案,使经过的总路程最短。

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import random
import copy
import time
import sys
import math
import tkinter # //GUI模块
import threading
from functools import reduce# 参数
'''
ALPHA:信息启发因子,值越大,则蚂蚁选择之前走过的路径可能性就越大,值越小,则蚁群搜索范围就会减少,容易陷入局部最优
BETA:Beta值越大,蚁群越就容易选择局部较短路径,这时算法收敛速度会加快,但是随机性不高,容易得到局部的相对最优
'''
(ALPHA, BETA, RHO, Q) = (1.0, 2.0, 0.5, 100.0)
# 城市数,蚁群
(city_num, ant_num) = (50, 50)
distance_x = [178, 272, 176, 171, 650, 499, 267, 703, 408, 437, 491, 74, 532,416, 626, 42, 271, 359, 163, 508, 229, 576, 147, 560, 35, 714,757, 517, 64, 314, 675, 690, 391, 628, 87, 240, 705, 699, 258,428, 614, 36, 360, 482, 666, 597, 209, 201, 492, 294]
distance_y = [170, 395, 198, 151, 242, 556, 57, 401, 305, 421, 267, 105, 525,381, 244, 330, 395, 169, 141, 380, 153, 442, 528, 329, 232, 48,498, 265, 343, 120, 165, 50, 433, 63, 491, 275, 348, 222, 288,490, 213, 524, 244, 114, 104, 552, 70, 425, 227, 331]
# 城市距离和信息素
distance_graph = [[0.0 for col in range(city_num)] for raw in range(city_num)]
pheromone_graph = [[1.0 for col in range(city_num)] for raw in range(city_num)]# ----------- 蚂蚁 -----------
class Ant(object):# 初始化def __init__(self, ID):self.ID = ID # IDself.__clean_data() # 随机初始化出生点# 初始数据def __clean_data(self):self.path = [] # 当前蚂蚁的路径self.total_distance = 0.0 # 当前路径的总距离self.move_count = 0 # 移动次数self.current_city = -1 # 当前停留的城市self.open_table_city = [True for i in range(city_num)] # 探索城市的状态city_index = random.randint(0, city_num - 1) # 随机初始出生点self.current_city = city_indexself.path.append(city_index)self.open_table_city[city_index] = Falseself.move_count = 1# 选择下一个城市def __choice_next_city(self):next_city = -1select_citys_prob = [0.0 for i in range(city_num)] # 存储去下个城市的概率total_prob = 0.0# 获取去下一个城市的概率for i in range(city_num):if self.open_table_city[i]:try:# 计算概率:与信息素浓度成正比,与距离成反比select_citys_prob[i] = pow(pheromone_graph[self.current_city][i], ALPHA) * pow((1.0 / distance_graph[self.current_city][i]), BETA)total_prob += select_citys_prob[i]except ZeroDivisionError as e:print('Ant ID: {ID}, current city: {current}, target city: {target}'.format(ID=self.ID,current=self.current_city,target=i))sys.exit(1)# 轮盘选择城市if total_prob > 0.0:# 产生一个随机概率,0.0-total_probtemp_prob = random.uniform(0.0, total_prob)for i in range(city_num):if self.open_table_city[i]:# 轮次相减temp_prob -= select_citys_prob[i]if temp_prob < 0.0:next_city = ibreak# 未从概率产生,顺序选择一个未访问城市# if next_city == -1:# for i in range(city_num):# if self.open_table_city[i]:# next_city = i# breakif (next_city == -1):next_city = random.randint(0, city_num - 1)while ((self.open_table_city[next_city]) == False): # if==False,说明已经遍历过了next_city = random.randint(0, city_num - 1)# 返回下一个城市序号return next_city# 计算路径总距离def __cal_total_distance(self):temp_distance = 0.0for i in range(1, city_num):start, end = self.path[i], self.path[i - 1]temp_distance += distance_graph[start][end]# 回路end = self.path[0]temp_distance += distance_graph[start][end]self.total_distance = temp_distance# 移动操作def __move(self, next_city):self.path.append(next_city)self.open_table_city[next_city] = Falseself.total_distance += distance_graph[self.current_city][next_city]self.current_city = next_cityself.move_count += 1# 搜索路径def search_path(self):# 初始化数据self.__clean_data()# 搜素路径,遍历完所有城市为止while self.move_count < city_num:# 移动到下一个城市next_city = self.__choice_next_city()self.__move(next_city)# 计算路径总长度self.__cal_total_distance()# ----------- TSP问题 -----------class TSP(object):def __init__(self, root, width=800, height=600, n=city_num):# 创建画布self.root = rootself.width = widthself.height = height# 城市数目初始化为city_numself.n = n# tkinter.Canvasself.canvas = tkinter.Canvas(root,width=self.width,height=self.height,bg="#EBEBEB", # 背景白色xscrollincrement=1,yscrollincrement=1)self.canvas.pack(expand=tkinter.YES, fill=tkinter.BOTH)self.title("TSP蚁群算法(n:初始化 e:开始搜索 s:停止搜索 q:退出程序)")self.__r = 5self.__lock = threading.RLock() # 线程锁self.__bindEvents()self.new()# 计算城市之间的距离for i in range(city_num):for j in range(city_num):temp_distance = pow((distance_x[i] - distance_x[j]), 2) + pow((distance_y[i] - distance_y[j]), 2)temp_distance = pow(temp_distance, 0.5)distance_graph[i][j] = float(int(temp_distance + 0.5))# 按键响应程序def __bindEvents(self):self.root.bind("q", self.quite) # 退出程序self.root.bind("n", self.new) # 初始化self.root.bind("e", self.search_path) # 开始搜索self.root.bind("s", self.stop) # 停止搜索# 更改标题def title(self, s):self.root.title(s)# 初始化def new(self, evt=None):# 停止线程self.__lock.acquire()self.__running = Falseself.__lock.release()self.clear() # 清除信息self.nodes = [] # 节点坐标self.nodes2 = [] # 节点对象# 初始化城市节点for i in range(len(distance_x)):# 在画布上随机初始坐标x = distance_x[i]y = distance_y[i]self.nodes.append((x, y))# 生成节点椭圆,半径为self.__rnode = self.canvas.create_oval(x - self.__r,y - self.__r, x + self.__r, y + self.__r,fill="#ff0000", # 填充红色outline="#000000", # 轮廓白色tags="node",)self.nodes2.append(node)# 显示坐标self.canvas.create_text(x, y - 10, # 使用create_text方法在坐标(302,77)处绘制文字text='(' + str(x) + ',' + str(y) + ')', # 所绘制文字的内容fill='black' # 所绘制文字的颜色为灰色)# 顺序连接城市# self.line(range(city_num))# 初始城市之间的距离和信息素for i in range(city_num):for j in range(city_num):pheromone_graph[i][j] = 1.0self.ants = [Ant(ID) for ID in range(ant_num)] # 初始蚁群self.best_ant = Ant(-1) # 初始最优解self.best_ant.total_distance = 1 << 31 # 初始最大距离self.iter = 1 # 初始化迭代次数# 将节点按order顺序连线def line(self, order):# 删除原线self.canvas.delete("line")def line2(i1, i2):p1, p2 = self.nodes[i1], self.nodes[i2]self.canvas.create_line(p1, p2, fill="#000000", tags="line")return i2# order[-1]为初始值reduce(line2, order, order[-1])# 清除画布def clear(self):for item in self.canvas.find_all():self.canvas.delete(item)# 退出程序def quite(self, evt):self.__lock.acquire()self.__running = Falseself.__lock.release()self.root.destroy()print(u"\n程序已退出...")sys.exit()# 停止搜索def stop(self, evt):self.__lock.acquire()self.__running = Falseself.__lock.release()# 开始搜索def search_path(self, evt=None):# 开启线程self.__lock.acquire()self.__running = Trueself.__lock.release()while self.__running:# 遍历每一只蚂蚁for ant in self.ants:# 搜索一条路径ant.search_path()# 与当前最优蚂蚁比较if ant.total_distance < self.best_ant.total_distance:# 更新最优解self.best_ant = copy.deepcopy(ant)# 更新信息素self.__update_pheromone_gragh()print(u"迭代次数:", self.iter, u"最佳路径总距离:", int(self.best_ant.total_distance))# 连线self.line(self.best_ant.path)# 设置标题self.title("TSP蚁群算法(n:随机初始 e:开始搜索 s:停止搜索 q:退出程序) 迭代次数: %d" % self.iter)# 更新画布self.canvas.update()self.iter += 1# 更新信息素def __update_pheromone_gragh(self):# 获取每只蚂蚁在其路径上留下的信息素temp_pheromone = [[0.0 for col in range(city_num)] for raw in range(city_num)]for ant in self.ants:for i in range(1, city_num):start, end = ant.path[i - 1], ant.path[i]# 在路径上的每两个相邻城市间留下信息素,与路径总距离反比temp_pheromone[start][end] += Q / ant.total_distancetemp_pheromone[end][start] = temp_pheromone[start][end]# 更新所有城市之间的信息素,旧信息素衰减加上新迭代信息素for i in range(city_num):for j in range(city_num):pheromone_graph[i][j] = pheromone_graph[i][j] * RHO + temp_pheromone[i][j]# 主循环def mainloop(self):self.root.mainloop()# ----------- 程序的入口处 -----------if __name__ == '__main__':TSP(tkinter.Tk()).mainloop()结果