以太坊EVM源码分析之执行流程
业务流程概述
EVM是用来执行智能合约的。输入一笔交易,内部会将之转换成一个Message对象,传入 EVM 执行。在合约中,msg 全局变量记录了附带当前合约的交易的信息,可能是为了一致,这里也将transaction转换成Message传给 EVM 对象。

如果是普通转账交易,执行时完全不需要EVM的操作(EVM进行的是空操作),直接修改 StateDB 中对应的账户余额即可。
如果是智能合约的创建或者调用,则通过 EVM 中的解释器加载和执行字节码,执行过程中可能会查询或者修改StateDB。[6]

接下来我们按照这个顺序分析源码。
Create EVM
core/state_processor.go
// ApplyTransaction attempts to apply a transaction to the given state database
// and uses the input parameters for its environment. It returns the receipt
// for the transaction, gas used and an error if the transaction failed,
// indicating the block was invalid.
// ApplyTransaction尝试将事务应用于给定的状态数据库,并为其环境使用输入参数。
// 它返回事务的receipt、使用的gas,如果事务失败,返回一个错误指示块无效。
// 将交易的信息记录到以太坊状态数据库(state.StateDB)中,这其中包括转账信息和执行合约信息(如果交易中有合约的话)。
func ApplyTransaction(config *params.ChainConfig, bc ChainContext, author *common.Address, gp *GasPool, statedb *state.StateDB, header *types.Header, tx *types.Transaction, usedGas *uint64, cfg vm.Config) (*types.Receipt, error) {// 将交易转化为message,在合约中,msg 全局变量记录了附带当前合约的交易信息, 可能是为了一致,这里也将`transaction`转换成`Message`传给 EVM 对象。msg, err := tx.AsMessage(types.MakeSigner(config, header.Number))if err != nil {return nil, err}// Create a new context to be used in the EVM environment// 创建一个要在EVM环境中使用的上下文context := NewEVMContext(msg, header, bc, author)// Create a new environment which holds all relevant information// about the transaction and calling mechanisms.// 创建一个新环境,其中包含关于事务和调用机制的所有相关信息。vmenv := vm.NewEVM(context, statedb, config, cfg)// Apply the transaction to the current state (included in the env)// 将事务应用于当前状态_, gas, failed, err := ApplyMessage(vmenv, msg, gp)if err != nil {return nil, err}// Update the state with pending changes// 使用挂起的更改更新状态var root []byte// 根据版本采用不同的状态更新方法if config.IsByzantium(header.Number) {statedb.Finalise(true)} else {root = statedb.IntermediateRoot(config.IsEIP158(header.Number)).Bytes()}*usedGas += gas// Create a new receipt for the transaction, storing the intermediate root and gas used by the tx// based on the eip phase, we're passing whether the root accounts.// 为交易创建一个新的receipt,存储中间根和基于eip阶段交易使用的gas,我们正在传递是否根touch-delete帐户。receipt := types.NewReceipt(root, failed, *usedGas)receipt.TxHash = tx.Hash()receipt.GasUsed = gas// if the transaction created a contract, store the creation address in the receipt.// 如果事务创建了一个合约,则将创建地址存储在receipt中。if msg.To() == nil {receipt.ContractAddress = crypto.CreateAddress(vmenv.Context.Origin, tx.Nonce())}// Set the receipt logs and create a bloom for filtering// 设置receipt日志并创建用于过滤的bloomreceipt.Logs = statedb.GetLogs(tx.Hash())receipt.Bloom = types.CreateBloom(types.Receipts{receipt})receipt.BlockHash = statedb.BlockHash()receipt.BlockNumber = header.Numberreceipt.TransactionIndex = uint(statedb.TxIndex())return receipt, err
}
这个函数首先将transaction转换成了Message,然后创建了一个Context,接下来调用vm.NewEVM创建了新的EVM,通过ApplyMessage执行相关功能。也就是说每处理一笔交易,就要创建一个 EVM 来执行交易中的数据。执行完成后,该函数更新状态、创建receipt以及进行日志记录。ApplyMessage只有一行代码,调用了StateTransition.TransitionDb函数。
状态转换模型
core/state_tansaction.go
/*
The State Transitioning Model 状态转换模型A state transition is a change made when a transaction is applied to the current world state
The state transitioning model does all the necessary work to work out a valid new state root.
状态转换是将事务应用到当前世界状态(world state)时所做的更改。状态转换模型执行所有必要的工作,以计算出一个有效的新状态根。1) Nonce handling 处理Nonce
2) Pre pay gas 提前支付gas
3) Create a new state object if the recipient is \0*32 如果接收方是\0*32,则创建一个新的stateObject
4) Value transfer 价值转移
== If contract creation 如果是合约创建 ==4a) Attempt to run transaction data 尝试运行事务数据4b) If valid, use result as code for the new state object 如果有效,则使用result作为新stateObject的代码
== end ==
5) Run Script section 运行脚本部分
6) Derive new state root 导出新状态根
*/
// 记录了在处理一笔交易过程中的状态数据,比如 gas 的花费等
type StateTransition struct {gp *GasPoolmsg Messagegas uint64 // 此交易过程当前剩余的gasgasPrice *big.IntinitialGas uint64 // 此交易初始的gas,即消息发送者指定用于此交易的gas量value *big.Intdata []bytestate vm.StateDBevm *vm.EVM
}// TransitionDb will transition the state by applying the current message and
// returning the result including the used gas. It returns an error if failed.
// An error indicates a consensus issue.
// TransitionDb将通过应用当前消息来转换状态并返回结果(包括使用的gas)。如果失败,它将返回一个错误。错误表示存在共识问题。
func (st *StateTransition) TransitionDb() (ret []byte, usedGas uint64, failed bool, err error) {if err = st.preCheck(); err != nil {return}msg := st.msgsender := vm.AccountRef(msg.From())homestead := st.evm.ChainConfig().IsHomestead(st.evm.BlockNumber)istanbul := st.evm.ChainConfig().IsIstanbul(st.evm.BlockNumber)// 判断是否是创建新合约contractCreation := msg.To() == nil// Pay intrinsic gas// 支付固定gasgas, err := IntrinsicGas(st.data, contractCreation, homestead, istanbul)if err != nil {return nil, 0, false, err}if err = st.useGas(gas); err != nil {return nil, 0, false, err}var (evm = st.evm// vm errors do not effect consensus and are therefor// not assigned to err, except for insufficient balance// error.// vm错误不会影响共识,因此不会被分配为err,除非余额不足。vmerr error)if contractCreation {// 调用evm.Create创建合约ret, _, st.gas, vmerr = evm.Create(sender, st.data, st.gas, st.value)} else {// Increment the nonce for the next transaction// 为下一个事务增加noncest.state.SetNonce(msg.From(), st.state.GetNonce(sender.Address())+1)// 不是创建合约,则调用 evm.Call调用合约ret, st.gas, vmerr = evm.Call(sender, st.to(), st.data, st.gas, st.value)}if vmerr != nil {log.Debug("VM returned with error", "err", vmerr)// The only possible consensus-error would be if there wasn't// sufficient balance to make the transfer happen. The first// balance transfer may never fail.// 唯一可能的共识错误是,如果没有足够的余额进行交易。if vmerr == vm.ErrInsufficientBalance {return nil, 0, false, vmerr}}// 返还gas,并将已消耗的 gas 计入矿工账户中st.refundGas()st.state.AddBalance(st.evm.Coinbase, new(big.Int).Mul(new(big.Int).SetUint64(st.gasUsed()), st.gasPrice))return ret, st.gasUsed(), vmerr != nil, err
}
StateTransition.TransitionDb()方法首先调用 StateTransaction.preCheck 验证交易的 Nonce 值,并从交易的发送者账户余额扣除gasLimit*gasPrice,用来「购买」交易执行需要的 gas。具体可参考gas的详细介绍。
然后先将交易的固有成本扣除。发送一笔交易的gas包含两部分:固有成本和执行成本。
执行成本根据该交易需要使用多少EVM的资源来运算而定,执行一笔交易所需的操作越多,则它的执行成本就越高。
固有成本(intrinsic gas)由交易的基础成本(base fee)和负载(payload)决定,每个零字节4 gas,非零字节68 gas。交易负载分为以下三种负载:
- 若是创建智能合约,则负载就是创建智能合约的 EVM 代码
- 若是调用智能合约的函数,则负载就是执行消息的输入数据
- 若只是单纯在两个账户间转账,则负载为空
接下来判断当前的交易是否是创建合约,根据交易的接收者是否为空来判断。如果需要创建合约,则调用EVM.Create进行创建;如果不是,则调用EVM.Call执行合约代码。(如果是转账交易,接收者肯定不为空,那么就会调用 EVM.Call 实现转账功能)[5]。
EVM 对象执行完相关功能后,调用 StateTransaction.refundGas 将未用完的 gas 还给交易的发送者。然后将消耗的 gas 计入矿工账户中。
创建合约
/core/vm/evm.go
// create creates a new contract using code as deployment code.
// create使用code作为部署代码创建一个新合约
func (evm *EVM) create(caller ContractRef, codeAndHash *codeAndHash, gas uint64, value *big.Int, address common.Address) ([]byte, common.Address, uint64, error) {// Depth check execution. Fail if we're trying to execute above the// limit.// 检查合约创建的递归调用次数。若超过深度限制(1024)执行代码,则失败。if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {return nil, common.Address{}, gas, ErrDepth}// 检查余额if !evm.CanTransfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), value) {return nil, common.Address{}, gas, ErrInsufficientBalance}// 增加合约创建者的 Nonce 值 确保合约地址不冲突 nonce: Number used once或Number once的缩写nonce := evm.StateDB.GetNonce(caller.Address())evm.StateDB.SetNonce(caller.Address(), nonce+1)// Ensure there's no existing contract already at the designated address// 确保特定的地址没有合约存在contractHash := evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(address)if evm.StateDB.GetNonce(address) != 0 || (contractHash != (common.Hash{}) && contractHash != emptyCodeHash) {return nil, common.Address{}, 0, ErrContractAddressCollision}// Create a new account on the state// 在现有状态上创建一个新合约snapshot := evm.StateDB.Snapshot() // 创建一个StateDB的快照,以便回滚evm.StateDB.CreateAccount(address) // 创建账户if evm.chainRules.IsEIP158 {evm.StateDB.SetNonce(address, 1) // 设置nonce,从1开始}// 执行交易evm.Transfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), address, value)// Initialise a new contract and set the code that is to be used by the EVM.// The contract is a scoped environment for this execution context only.contract := NewContract(caller, AccountRef(address), value, gas)contract.SetCodeOptionalHash(&address, codeAndHash)// NoRecursion禁用call, callcode, delegate call 和 create。// 以太坊虚拟机被配置成不可递归创建合约,而当前创建合约的过程正是在递归过程中if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {return nil, address, gas, nil}// Debug模式,捕获跟踪程序启动事件if evm.vmConfig.Debug && evm.depth == 0 {evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureStart(caller.Address(), address, true, codeAndHash.code, gas, value)}start := time.Now() // 当前时间// ret所存的就是新合约的代码ret, err := run(evm, contract, nil, false)// check whether the max code size has been exceeded// 判断返回的合约代码是否超过大小限制maxCodeSizeExceeded := evm.chainRules.IsEIP158 && len(ret) > params.MaxCodeSize// if the contract creation ran successfully and no errors were returned// calculate the gas required to store the code. If the code could not// be stored due to not enough gas set an error and let it be handled// by the error checking condition below.// 如果合约创建操作执行成功并且没有返回错误。计算存储代码所需gas。// 如果因为gas不足而不能存储代码,设置一个错误,然后让下面的错误检查条件来处理它。if err == nil && !maxCodeSizeExceeded {// 合约创建成功,将合约保存到 StateDB 之前,先 useGascreateDataGas := uint64(len(ret)) * params.CreateDataGas // 计算gasif contract.UseGas(createDataGas) { // gas充足,evm.StateDB.SetCode(address, ret) // 往StateDB中存代码} else {err = ErrCodeStoreOutOfGas // 否则设置错误}}// When an error was returned by the EVM or when setting the creation code// above we revert to the snapshot and consume any gas remaining. Additionally// when we're in homestead this also counts for code storage gas errors.// 代码大小超过限制 或者 有错误并且IsHomestead或者错误不是合约创建代码存储gas不足if maxCodeSizeExceeded || (err != nil && (evm.chainRules.IsHomestead || err != ErrCodeStoreOutOfGas)) {evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)if err != errExecutionReverted {contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)}}// Assign err if contract code size exceeds the max while the err is still empty.// 如果合约代码大小超过限制并且err仍未空,设置err = errMaxCodeSizeExceededif maxCodeSizeExceeded && err == nil {err = errMaxCodeSizeExceeded}// Debug模式,捕获跟踪程序结束事件if evm.vmConfig.Debug && evm.depth == 0 {evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureEnd(ret, gas-contract.Gas, time.Since(start), err)}// 返回结果return ret, address, contract.Gas, err}// Create creates a new contract using code as deployment code.
func (evm *EVM) Create(caller ContractRef, code []byte, gas uint64, value *big.Int) (ret []byte, contractAddr common.Address, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {// CreateAddress根据给定的地址和nonce生成一个以太坊地址contractAddr = crypto.CreateAddress(caller.Address(), evm.StateDB.GetNonce(caller.Address()))return evm.create(caller, &codeAndHash{code: code}, gas, value, contractAddr)
}// Create2 creates a new contract using code as deployment code.
//
// The different between Create2 with Create is Create2 uses sha3(0xff ++ msg.sender ++ salt ++ sha3(init_code))[12:]
// instead of the usual sender-and-nonce-hash as the address where the contract is initialized at.
// Create2和Create的区别就是,Create2使用sha3(0xff ++ msg.sender ++ salt ++ sha3(init_code))[12:]作为新合约的地址,
// 而不是通常的msg.sender + nonce的hash
func (evm *EVM) Create2(caller ContractRef, code []byte, gas uint64, endowment *big.Int, salt *big.Int) (ret []byte, contractAddr common.Address, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {codeAndHash := &codeAndHash{code: code}// CreateAddress2根据给定的sender地址、初始代码的hash、salt生成一个以太坊地址contractAddr = crypto.CreateAddress2(caller.Address(), common.BigToHash(salt), codeAndHash.Hash().Bytes())return evm.create(caller, codeAndHash, gas, endowment, contractAddr)
}
如果交易的接收者为空,则代表此条交易的目的是要创建一条合约。此方法中存储的合约代码是合约运行后的返回码,而不是原来交易中的数据(即 Transaction.data.Payload,或者说EVM.Create 方法的 code 参数)。这是因为合约源代码在编译成二进制数据时,除了合约原有的代码外,编译器还另外插入了一些代码,以便执行有关功能。对于创建来说,编译器插入了执行合约构造函数(即合约的constructor 方法)的代码。在将编译器编译后的二进制字节码提交到以太坊节点创建合约时,EVM 执行这段二进制代码,实际上主要执行了合约的 constructor方法,然后将合约的其它代码返回,所以才会有这里的ret变量作为合约的真正代码存储到状态数据库(StateDB)中。[5]
调用合约
/core/vm/evm.go
// 无论转账或者是执行合约代码都会调用到Call方法,同时合约里面的call指令也会执行到这里。// Call executes the contract associated with the addr with the given input as
// parameters. It also handles any necessary value transfer required and takes
// the necessary steps to create accounts and reverses the state in case of an
// execution error or failed value transfer.
// Call 执行与addr相关联的合约,以给定的input作为参数。
// 它还处理所需的任何必要的转账操作,并采取必要的步骤来创建帐户
// 并在任意错误的情况下回滚所做的操作。
func (evm *EVM) Call(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64, value *big.Int) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {// NoRecursion禁用call, callcode, delegate call 和 create。 depth > 0 ??if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {return nil, gas, nil}// Fail if we're trying to execute above the call depth limit// 如果我们试图超过调用深度限制执行代码,则会失败// 调用深度最大1024if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {return nil, gas, ErrDepth}// Fail if we're trying to transfer more than the available balance// 如果我们试图交易比可用余额多的钱,失败// 查看余额是否充足if !evm.Context.CanTransfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), value) {return nil, gas, ErrInsufficientBalance}var (// 接收方to = AccountRef(addr)// 系统当前状态快照snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot())// Exist报告给定帐户是否存在。值得注意的是,对于自杀账户也应该返回true。if !evm.StateDB.Exist(addr) { //地址不存在// 检查是否是预编译的合约precompiles := PrecompiledContractsHomesteadif evm.chainRules.IsByzantium {precompiles = PrecompiledContractsByzantium}if evm.chainRules.IsIstanbul {precompiles = PrecompiledContractsIstanbul}// 不是预编译合约,IsEIP158,并且value的值为0if precompiles[addr] == nil && evm.chainRules.IsEIP158 && value.Sign() == 0 {// Calling a non existing account, don't do anything, but ping the tracer// 调用不存在的账户,什么都不做,但触发跟踪程序。不消耗Gas// Debug模式if evm.vmConfig.Debug && evm.depth == 0 {evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureStart(caller.Address(), addr, false, input, gas, value)evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureEnd(ret, 0, 0, nil)}return nil, gas, nil}// 在本地状态中创建指定地址addr的状态evm.StateDB.CreateAccount(addr)}// 执行交易evm.Transfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), to.Address(), value)// Initialise a new contract and set the code that is to be used by the EVM.// The contract is a scoped environment for this execution context only.// 初始化一个新的合约,并设置EVM要使用的代码。// 这个合约只是此执行上下文作用域内的环境。contract := NewContract(caller, to, value, gas)contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))// Even if the account has no code, we need to continue because it might be a precompile// 即使该账户没有代码,也需要继续执行,因为它可能是预编译的start := time.Now() //开始时间// Capture the tracer start/end events in debug mode// 在调试模式下捕获跟踪程序 启动/结束 事件if evm.vmConfig.Debug && evm.depth == 0 {evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureStart(caller.Address(), addr, false, input, gas, value)defer func() { // Lazy evaluation of the parameters 参数的延迟计算evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureEnd(ret, gas-contract.Gas, time.Since(start), err)}()}// 运行该合约ret, err = run(evm, contract, input, false)// When an error was returned by the EVM or when setting the creation code// above we revert to the snapshot and consume any gas remaining. Additionally// when we're in homestead this also counts for code storage gas errors.// 当EVM返回一个错误时,或者在设置上面的创建代码时,我们将恢复系统状态到快照并用完剩余的gas// 此外,当我们在homestead版本时,代码存储gas错误也会触发上述操作。if err != nil {evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot) // 回滚状态到快照if err != errExecutionReverted {// 如果是由revert指令触发的错误,因为ICO一般设置了人数限制或者资金限制// 在大家抢购的时候很可能会触发这些限制条件,导致被抽走不少钱。这个时候// 又不能设置比较低的GasPrice和GasLimit。因为要速度快。// 那么不会使用剩下的全部Gas,而是只会使用代码执行的Gas// 不然会被抽走 GasLimit * GasPrice的钱,那可不少。contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)}}return ret, contract.Gas, err
}
该函数首先判断递归层次和合约调用者是否有足够的余额。需要注意的是input参数,这是调用合约的public方法的参数。判断合约地址是否存在,使用当前的信息生成一个合约对象,从状态数据库中获取合约的代码,填充到合约对象中。
一般情况下,被调用的合约地址应该存在于以太坊状态数据库中,也就是合约已经创建。否则就返回失败。但有一种例外,就是被调用的合约地址是预编译的情况,此时即使地址不在状态数据库中,也要立即创建一个。
最后主要是对 run 函数的调用,然后处理其返回值并返回。
Call与Create异同
Call方法和create方法的逻辑大体相同,通过执行不同的合约指令,达到创建或调用的目的。这里分析下他们的不同之处:
-
call调用的是一个已经存在合约账户的合约,create是新建一个合约账户。这个区别在于:合约编译器在编译时,会插入一些代码。在合约创建时,编译器插入的是创建合约的代码,解释器执行这些代码,就可以将合约的真正代码返回;在调用合约时,编译器会插入一些调用合约的代码,只要使用正确的参数执行这些代码,就可以「调用」到我们想调用的合约的 public方法。[5]
-
call里
evm.Transfer发生在合约的发送方和接收方之间evm.Transfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), to.Address(), value)create里则是创建合约的账户和该合约之间
contractAddr = crypto.CreateAddress(caller.Address(), evm.StateDB.GetNonce(caller.Address())) evm.Transfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), contractAddr, value)
四种调用合约的方式异同
除了最基本的call函数可以调用合约之外,还有其他三种形式。CallCode 和 DelegateCall 的存在是为了实现合约的库的特性。它们修改了被调用合约的上下文环境,可以让被调用的合约代码就像自己写的代码一样,从而达到库合约的目的。
StaticCall不允许执行会修改storage的指令。如果执行过程中遇到这样的指令,就会失败。目前 Solidity 中并没有一个 low level API 可以直接调用它,仅仅是计划将来在编译器层面把调用 view 和 pure 类型的函数编译成 StaticCall 指令。view 类型的函数表明其不能修改状态变量,pure 类型的函数连读取状态变量都不允许。目前是在编译阶段来检查这一点的,如果不符合规定则会出现编译错误。如果将来换成 StaticCall 指令,就可以完全在运行阶段来保证这一点了。
这三个特殊的消息调用只能由指令触发,不像Call可以由外部调用。
CallCode与Call方法的不同在于,它在调用者的上下文中执行给定地址的代码。具体来说,Call修改的是被调用者的storage,而CallCode修改的是调用者的storage。// CallCode executes the contract associated with the addr with the given input // as parameters. It also handles any necessary value transfer required and takes // the necessary steps to create accounts and reverses the state in case of an // execution error or failed value transfer. // 同Call方法 // // CallCode differs from Call in the sense that it executes the given address' // code with the caller as context. // CallCode与Call方法的不同在于,它在调用者的上下文中执行给定地址的代码 // 具体来说,CALL 修改的是被调用者的 storage,而 CALLCODE 修改的是调用者的 storage。 func (evm *EVM) CallCode(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64, value *big.Int) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {// 同Callif evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {return nil, gas, nil}// Fail if we're trying to execute above the call depth limitif evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {return nil, gas, ErrDepth}// Fail if we're trying to transfer more than the available balanceif !evm.CanTransfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), value) {return nil, gas, ErrInsufficientBalance}var (snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot()// 此处接收方是调用者,与Call不同to = AccountRef(caller.Address()))// Initialise a new contract and set the code that is to be used by the EVM.// The contract is a scoped environment for this execution context only.contract := NewContract(caller, to, value, gas)contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))// 运行合约ret, err = run(evm, contract, input, false)if err != nil {evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)if err != errExecutionReverted {contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)}}return ret, contract.Gas, err}

2. DelegateCall与CallCode的不同在于,它的调用者被设置为调用者的调用者。具体来说,CallCode 和 DelegateCall 的区别在于:msg.sender 不同.DelegateCall 会一直使用原始调用者的地址,而 CallCode 不会。可以认为 DelegateCall 是 CallCode 的一个 bugfix 版本,官方已经不建议使用 CallCode 了。
// DelegateCall executes the contract associated with the addr with the given input
// as parameters. It reverses the state in case of an execution error.
// DelegateCall执行与addr相关联的合约,以给定的input作为参数。
// 它在执行错误的情况下回滚状态。
//
// DelegateCall differs from CallCode in the sense that it executes the given address'
// code with the caller as context and the caller is set to the caller of the caller.
// DelegateCall与CallCode的不同在于,它在调用者的上下文中执行给定地址的代码并且调用者被设置为调用者的调用者。
// 具体来说,CALLCODE 和 DELEGATECALL 的区别在于:msg.sender 不同。
// DELEGATECALL 会一直使用原始调用者的地址,而 CALLCODE 不会。
// 可以认为 DELEGATECALL 是 CALLCODE 的一个 bugfix 版本,官方已经不建议使用 CALLCODE 了。
func (evm *EVM) DelegateCall(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {return nil, gas, nil}// Fail if we're trying to execute above the call depth limitif evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {return nil, gas, ErrDepth}var (snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot()to = AccountRef(caller.Address()))// Initialise a new contract and make initialise the delegate values// 初始化一个新合约并将合约设置为委托调用contract := NewContract(caller, to, nil, gas).AsDelegate()contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))ret, err = run(evm, contract, input, false)if err != nil {evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)if err != errExecutionReverted {contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)}}return ret, contract.Gas, err}

- staticCall在调用期间不允许执行任何修改状态的操作,试图修改状态的指令会引发异常。
// StaticCall executes the contract associated with the addr with the given input// as parameters while disallowing any modifications to the state during the call.// Opcodes that attempt to perform such modifications will result in exceptions// instead of performing the modifications.// StaticCall执行与addr相关联的合约,以给定的input作为参数并且在调用期间不允许执行任何修改状态的操作。// 试图修改状态的指令会引发异常,而不是执行修改操作。func (evm *EVM) StaticCall(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {return nil, gas, nil}// Fail if we're trying to execute above the call depth limitif evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {return nil, gas, ErrDepth}var (to = AccountRef(addr)snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot())// Initialise a new contract and set the code that is to be used by the EVM.// The contract is a scoped environment for this execution context only.contract := NewContract(caller, to, new(big.Int), gas)contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))// We do an AddBalance of zero here, just in order to trigger a touch.// This doesn't matter on Mainnet, where all empties are gone at the time of Byzantium,// but is the correct thing to do and matters on other networks, in tests, and potential// future scenarios// 我们在这里做一个参数为0的AddBalance操作,只是为了触发一个touch操作。// 这对于主网来说并不重要,Byzantium版本中所有的空值都不见了。// 但这对于其他网络,测试中的或者潜在的应用场景来说,是一件正确而且重要的操作。evm.StateDB.AddBalance(addr, bigZero)// When an error was returned by the EVM or when setting the creation code// above we revert to the snapshot and consume any gas remaining. Additionally// when we're in Homestead this also counts for code storage gas errors.ret, err = run(evm, contract, input, true) // readOnly=true,只读,不允许任何更新状态的操作if err != nil {evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)if err != errExecutionReverted {contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)}}return ret, contract.Gas, err}
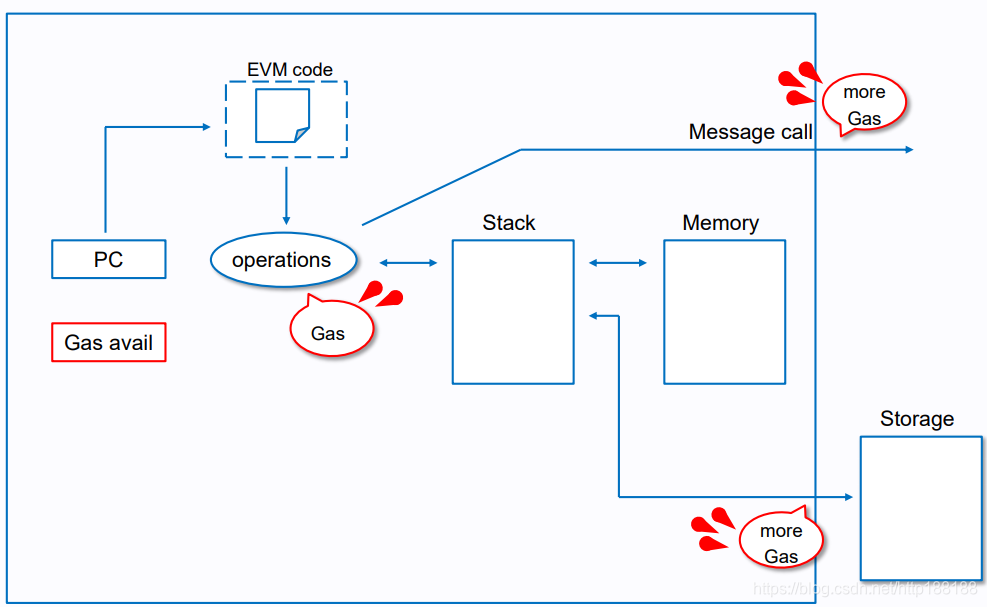
evm 运行环境
/core/vm/evm.go
// run runs the given contract and takes care of running precompiles with a fallback to the byte code interpreter.
// run运行给定的合约并通过回退到字节码解释器来运行预编译合约
// evm 运行环境 contract 要运行的合约 input 输入 readOnly 只读标志,若为true, 不允许进行写入和修改操作
func run(evm *EVM, contract *Contract, input []byte, readOnly bool) ([]byte, error) {if contract.CodeAddr != nil { //如果合约代码地址不为空precompiles := PrecompiledContractsHomestead // HomeStead预编译合约集// 根据当前采用的链规则采用不同版本的预编译合约集if evm.chainRules.IsByzantium {precompiles = PrecompiledContractsByzantium}if evm.chainRules.IsIstanbul {precompiles = PrecompiledContractsIstanbul}// 如果合约代码地址对应的是预编译合约,则调用RunPrecompiledContractif p := precompiles[*contract.CodeAddr]; p != nil {return RunPrecompiledContract(p, input, contract)}}for _, interpreter := range evm.interpreters {// CanRun告诉当前解释器是否可以运行当前合约,合约作为参数传递。if interpreter.CanRun(contract.Code) {if evm.interpreter != interpreter { // 如果evm的解释器不是当前解释器// Ensure that the interpreter pointer is set back// to its current value upon return.// 确保解释器指针在返回时被设置回当前值。defer func(i Interpreter) {evm.interpreter = i}(evm.interpreter)evm.interpreter = interpreter // 那就设置为当前解释器}// 解释器运行并返回结果return interpreter.Run(contract, input, readOnly)}}//运行到此处说明没有兼容的解释器,返回错误return nil, ErrNoCompatibleInterpreter
}
函数前半部分判断合约的地址是否是一些特殊地址,如果是则执行其对应的对象的 Run 方法。这些特殊的地址都是一些预编译合约。以下是一个预编译合约集:
core/vm/contracts.go
// PrecompiledContract is the basic interface for native Go contracts. The implementation
// requires a deterministic gas count based on the input size of the Run method of the
// contract.
// PrecompiledContract是本地Go合约的基本接口。
// 该接口的实现需要基于合约的运行方法的输入大小来确定gas。
type PrecompiledContract interface {// RequiredGas 负责计算合约的gas使用量RequiredGas(input []byte) uint64 // RequiredPrice calculates the contract gas use// Run负责运行预编译好的合约Run(input []byte) ([]byte, error) // Run runs the precompiled contract
}// homestead byzantium Istanbul三种预编译的合约集// PrecompiledContractsIstanbul contains the default set of pre-compiled Ethereum
// contracts used in the Istanbul release.
// Istanbul版本的预编译合约集
var PrecompiledContractsIstanbul = map[common.Address]PrecompiledContract{common.BytesToAddress([]byte{1}): &ecrecover{},common.BytesToAddress([]byte{2}): &sha256hash{},common.BytesToAddress([]byte{3}): &ripemd160hash{},common.BytesToAddress([]byte{4}): &dataCopy{},common.BytesToAddress([]byte{5}): &bigModExp{},common.BytesToAddress([]byte{6}): &bn256AddIstanbul{},common.BytesToAddress([]byte{7}): &bn256ScalarMulIstanbul{},common.BytesToAddress([]byte{8}): &bn256PairingIstanbul{},common.BytesToAddress([]byte{9}): &blake2F{},
}
run 函数的后半部分代码是一个 for 循环,从当前 EVM 对象中选择一个可以运行的解释器,运行当前的合约并返回。当前源代码中只有一个版本的解释器,就是 EVMInterpreter。下一代解释器好像叫做EWASMInterperter。
解释器执行
core/vm/interpreter.go
// Run loops and evaluates the contract's code with the given input data and returns
// the return byte-slice and an error if one occurred.
// 用给定的入参循环执行合约的代码,并返回返回结果的字节切片,如果出现错误的话返回错误。
//
// It's important to note that any errors returned by the interpreter should be
// considered a revert-and-consume-all-gas operation except for
// errExecutionReverted which means revert-and-keep-gas-left.
// 应该注意的是,除了errExecutionReverted错误表示回滚状态但保留gas以外,解释器返回的任何错误应该会导致状态回滚并消耗掉所有gas。
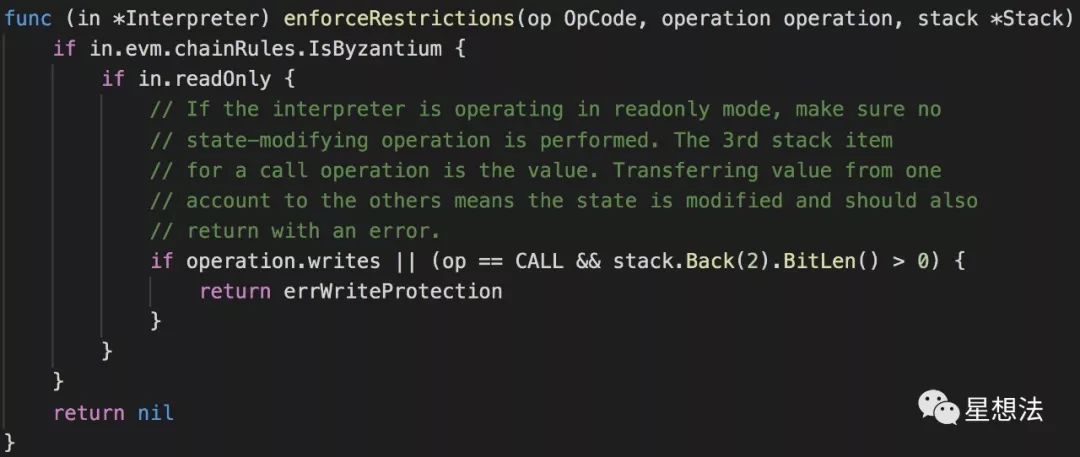
func (in *EVMInterpreter) Run(contract *Contract, input []byte, readOnly bool) (ret []byte, err error) {if in.intPool == nil { // 初始化intPoolin.intPool = poolOfIntPools.get()defer func() { // 用完再放回去poolOfIntPools.put(in.intPool)in.intPool = nil}()}// Increment the call depth which is restricted to 1024// 调用深度自增,最大调用深度为1024.in.evm.depth++defer func() { in.evm.depth-- }() // 合约执行完,调用深度减一。// Make sure the readOnly is only set if we aren't in readOnly yet.// This makes also sure that the readOnly flag isn't removed for child calls.// 确保只有在还没有设置readOnly时才设置readOnly。// 这也确保了readOnly标志不会被子调用移除。if readOnly && !in.readOnly {in.readOnly = truedefer func() { in.readOnly = false }()}// Reset the previous call's return data. It's unimportant to preserve the old buffer// as every returning call will return new data anyway.// 重置前一个调用的返回数据。保留旧的缓冲区并不重要,因为每次返回调用都会返回新的数据。in.returnData = nil// Don't bother with the execution if there's no code.// 如果没有代码,就不用执行。直接返回if len(contract.Code) == 0 {return nil, nil}var (op OpCode // current opcode 当前指令mem = NewMemory() // bound memory 绑定内存stack = newstack() // local stack 本地堆栈// For optimisation reason we're using uint64 as the program counter.// It's theoretically possible to go above 2^64. The YP defines the PC// to be uint256. Practically much less so feasible.// 出于优化的原因,我们使用uint64作为程序计数器。理论上有可能超过2^64。// YP将PC定义为uint256。实际上不太可行。pc = uint64(0) // program counter 程序计算器cost uint64// copies used by tracer// 跟踪程序使用的拷贝pcCopy uint64 // needed for the deferred Tracer 延迟的跟踪程序需要此字段gasCopy uint64 // for Tracer to log gas remaining before execution 用于跟踪程序记录执行前剩余的gaslogged bool // deferred Tracer should ignore already logged steps 延迟跟踪程序应忽略已记录的步骤res []byte // result of the opcode execution function 指令执行函数的结果)contract.Input = input// Reclaim the stack as an int pool when the execution stops// 当执行停止时,将堆栈作为int池回收defer func() { in.intPool.put(stack.data...) }()// 若处于调试模式,执行结束记录状态if in.cfg.Debug {defer func() {if err != nil {if !logged {in.cfg.Tracer.CaptureState(in.evm, pcCopy, op, gasCopy, cost, mem, stack, contract, in.evm.depth, err)} else {in.cfg.Tracer.CaptureFault(in.evm, pcCopy, op, gasCopy, cost, mem, stack, contract, in.evm.depth, err)}}}()}// The Interpreter main run loop (contextual). This loop runs until either an// explicit STOP, RETURN or SELFDESTRUCT is executed, an error occurred during// the execution of one of the operations or until the done flag is set by the// parent context.// 解释器的主循环。解释器的主要循环, 直到遇到STOP,RETURN,SELFDESTRUCT指令被执行,// 或者是遇到任意错误,或者父上下文设置了done标志。for atomic.LoadInt32(&in.evm.abort) == 0 { // 程序没被终止if in.cfg.Debug {// Capture pre-execution values for tracing.// 记录执行前的值以进行跟踪。logged, pcCopy, gasCopy = false, pc, contract.Gas}// Get the operation from the jump table and validate the stack to ensure there are// enough stack items available to perform the operation.// 从指令表拿到对应的operation,并验证堆栈,以确保有足够的堆栈项可用于执行操作。op = contract.GetOp(pc)operation := in.cfg.JumpTable[op]if !operation.valid {return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid opcode 0x%x", int(op))}// Validate stack// 验证堆栈if sLen := stack.len(); sLen < operation.minStack {return nil, fmt.Errorf("stack underflow (%d <=> %d)", sLen, operation.minStack)} else if sLen > operation.maxStack {return nil, fmt.Errorf("stack limit reached %d (%d)", sLen, operation.maxStack)}// If the operation is valid, enforce and write restrictions// 如果operation有效,检查是否有写入限制if in.readOnly && in.evm.chainRules.IsByzantium {// If the interpreter is operating in readonly mode, make sure no// state-modifying operation is performed. The 3rd stack item// for a call operation is the value. Transferring value from one// account to the others means the state is modified and should also// return with an error.// 如果解释器在只读模式下运行,请确保不执行任何状态修改操作。// 第三个堆栈项是call指令携带的值。将值从一个帐户转移到其他帐户意味着状态被修改,应该返回一个错误。if operation.writes || (op == CALL && stack.Back(2).Sign() != 0) {return nil, errWriteProtection}}// Static portion of gas// gas静态部分cost = operation.constantGas // For tracing 用于跟踪程序if !contract.UseGas(operation.constantGas) { // 先扣掉固定gasreturn nil, ErrOutOfGas}// 如果将要执行的指令需要用到内存存储空间,则计算所需要的空间大小var memorySize uint64// calculate the new memory size and expand the memory to fit// the operation// Memory check needs to be done prior to evaluating the dynamic gas portion,// to detect calculation overflows// 计算新的内存大小并扩展内存以适应该指令。在评估动态气体部分之前,需要进行内存检查,以检测计算溢位。// 计算内存使用量if operation.memorySize != nil {memSize, overflow := operation.memorySize(stack)if overflow {return nil, errGasUintOverflow}// memory is expanded in words of 32 bytes. Gas// is also calculated in words.// 内存扩展为32字节的字。Gas也以字为单位进行计算。if memorySize, overflow = math.SafeMul(toWordSize(memSize), 32); overflow {return nil, errGasUintOverflow}}// Dynamic portion of gas// consume the gas and return an error if not enough gas is available.// cost is explicitly set so that the capture state defer method can get the proper cost// gas的动态部分// 用掉gas,如果gas不足返回一个错误。// cost是显式设置的,这样随后捕获状态的方法可以获得正确的cost。if operation.dynamicGas != nil {var dynamicCost uint64// 调用指令对应的gas计算函数dynamicCost, err = operation.dynamicGas(in.evm, contract, stack, mem, memorySize)// gas 花费cost += dynamicCost // total cost, for debug tracingif err != nil || !contract.UseGas(dynamicCost) { // 用掉gasreturn nil, ErrOutOfGas}}if memorySize > 0 {mem.Resize(memorySize) // 扩展内存}// 记录状态if in.cfg.Debug {in.cfg.Tracer.CaptureState(in.evm, pc, op, gasCopy, cost, mem, stack, contract, in.evm.depth, err)logged = true}// execute the operation// 执行指令,调用指令对应的执行函数res, err = operation.execute(&pc, in, contract, mem, stack)// verifyPool is a build flag. Pool verification makes sure the integrity// of the integer pool by comparing values to a default value.// verifyPool是一个生成标志。池的验证函数通过将值与默认值进行比较来确保整数池的完整性。if verifyPool {verifyIntegerPool(in.intPool)}// if the operation clears the return data (e.g. it has returning data)// set the last return to the result of the operation.// 如果有返回值,那么就设置返回值。 只有最后一个返回有效。if operation.returns {in.returnData = res}switch {case err != nil:return nil, errcase operation.reverts:return res, errExecutionRevertedcase operation.halts:return res, nilcase !operation.jumps: // 若不跳转,程序计数器向前移动一个指令。pc++}}return nil, nil
}
解释器会为新合约的执行创建新的 Stack 和 Memory,从而不会破环原合约的执行环境。新合约执行完成后,通过 RETURN 指令把执行结果写入之前指定的内存地址,然后原合约继续向后执行。总的来说该方法主循环就是从给定的代码的第 0 个字节开始执行,直到退出。

首先 PC 会从合约字节码中读取一个OpCode,然后从一个 JumpTable 中检索出对应的 operation,也就是与其相关联的函数集合。接下来会计算该操作需要消耗的gas,如果gas用光则执行失败,返回 ErrOutOfGas 错误。如果油费充足,则调用相应的execute函数执行该指令,根据指令类型的不同,会分别对Stack、Memory 或者 StateDB进行读写操作。
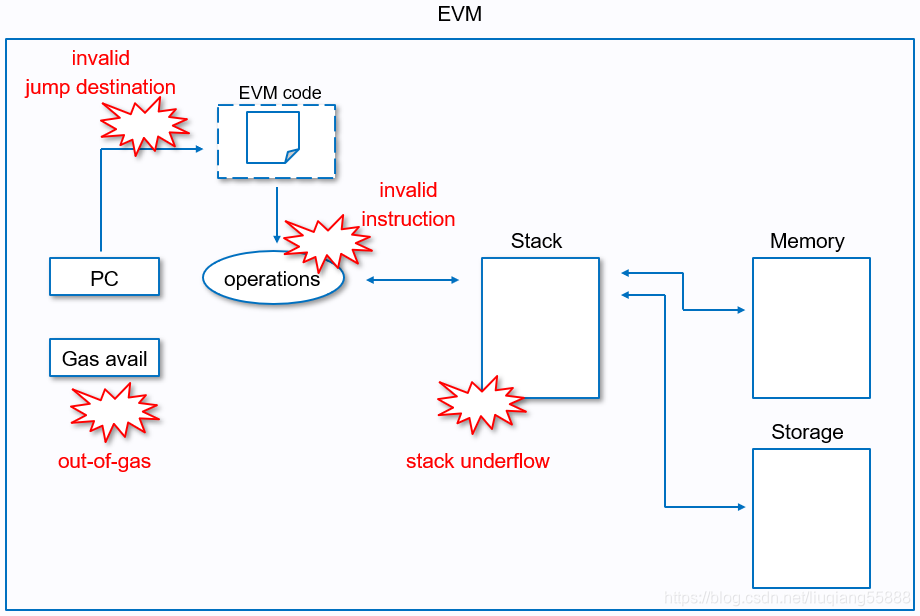
可能出现的错误(errors)
在core/vm/errors.go中列举了执行时错误:
// List execution errors
// 列出执行时错误
var (// gas不足ErrOutOfGas = errors.New("out of gas")// 合约创建代码存储gas不足ErrCodeStoreOutOfGas = errors.New("contract creation code storage out of gas")// 超过了最大调用深度ErrDepth = errors.New("max call depth exceeded")// 日志的数量达到了指定的限制ErrTraceLimitReached = errors.New("the number of logs reached the specified limit")// 交易余额不足ErrInsufficientBalance = errors.New("insufficient balance for transfer")// 合约地址冲突ErrContractAddressCollision = errors.New("contract address collision")// 没有兼容的解释器ErrNoCompatibleInterpreter = errors.New("no compatible interpreter")
)
下图也描述了一些异常发生的场景:
参考文献
- Ethereum Yellow Paper
ETHEREUM: A SECURE DECENTRALISED GENERALISED TRANSACTION LEDGER
https://ethereum.github.io/yellowpaper/paper.pdf - Ethereum White Paper
A Next-Generation Smart Contract and Decentralized Application Platform
https://github.com/ethereum/wiki/wiki/White-Paper - Ethereum EVM Illustrated
https://github.com/takenobu-hs/ethereum-evm-illustrated - Go Ethereum Code Analysis
https://github.com/ZtesoftCS/go-ethereum-code-analysis - 以太坊源码解析:evm
https://yangzhe.me/2019/08/12/ethereum-evm/ - 以太坊 - 深入浅出虚拟机
https://learnblockchain.cn/2019/04/09/easy-evm/