一、普通 t r i e \rm trie trie 树
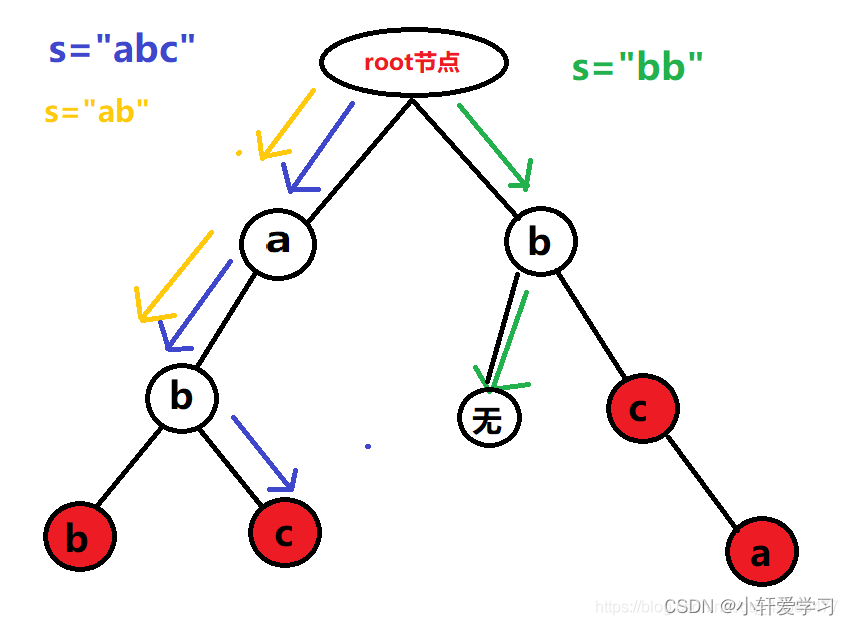
t r i e \rm trie trie 树又称字典树、前缀树,它把很多单词放到一棵树上,使用空间去换时间。
LUOGU2580 于是他错误的点名开始了
Description \text{Description} Description
给定 n n n 个互不相同且只含小写字母的字符串,以及 m m m 个问题,每个问题给出一个字符串 S S S:
-
若 S S S 在这 n n n 个字符串中出现过:
- 若 S S S 是第一次被问,输出
OK; - 若 S S S 已经被问过,输出
REPEAT。
- 若 S S S 是第一次被问,输出
-
若 S S S 在这 n n n 个字符串中未出现过,输出
WRONG。
Solution \text{Solution} Solution
我们设 t r i e p , c trie_{p,c} triep,c 来表示 t r i e trie trie 中 p p p 的儿子中第 c c c 个所对应的节点,其中 c c c 可取 1 ∼ 26 1\sim26 1∼26,分别代表 a ∼ z \text{a}\sim\text{z} a∼z。
1. 插入
当我们要插入字符串 S S S 的时候,遍历整个 S S S,同时用一个 p o s pos pos 记录当前访问到的节点, p o s pos pos 一开始指向根节点,即 p o s = 0 pos=0 pos=0,当现在遍历到第 i i i 位时,令 c = S[i] - 'a':
- 若 t r i e p o s , c = 0 trie_{pos,c}=0 triepos,c=0,说明这个位置还没有节点,那就新建一个;
- 令 p o s = t r i e p o s , c pos=trie_{pos,c} pos=triepos,c。
int tot;
int trie[MAXN][26]; //MAXN为所有字符串的总长度void insert(char *s)
{int len = strlen(s), pos = 0;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){int c = s[i] - 'a';if (!trie[pos][c]){trie[pos][c] = ++tot; //新建节点}pos = trie[pos][c];}
}
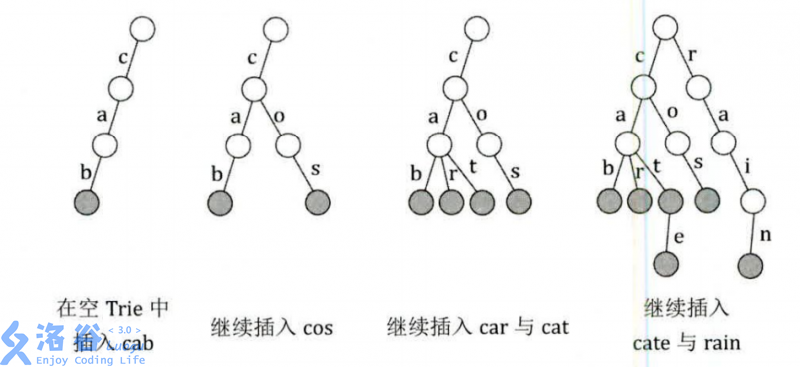
例如现在要插入单词 at,sea,see,meat \text{at,sea,see,meat} at,sea,see,meat:
首先插入 at \text{at} at,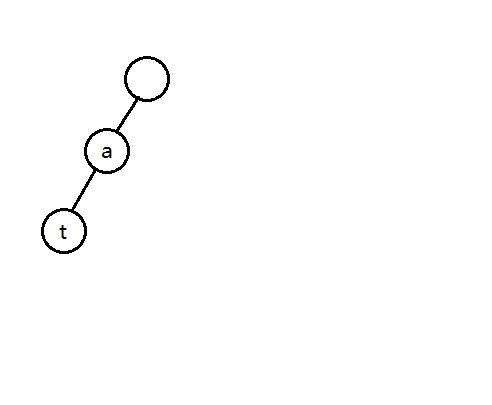
然后是 sea \text{sea} sea,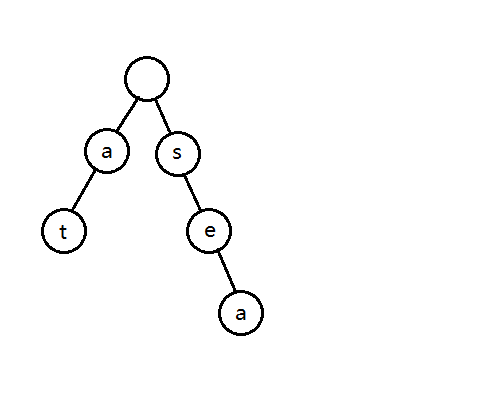
插入 see \text{see} see 时, t r i e \rm trie trie 上已有前缀 se \text{se} se,所以变成了这样: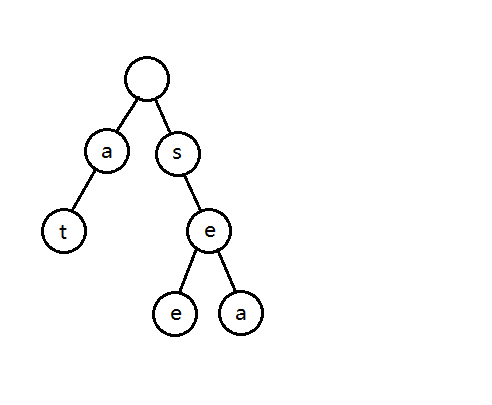
最后是 meat \text{meat} meat。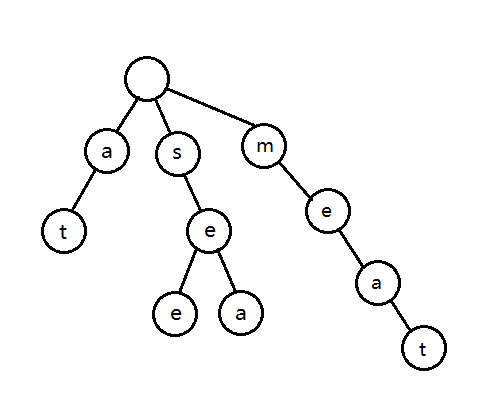
2. 查询
和插入差不多。
- 当 t r i e p o s , c = 0 trie_{pos,c}=0 triepos,c=0 时,说明 S S S 不在 t r i e \rm trie trie 中;
- 若遍历完整个字符串,说明 S S S 在 t r i e \rm trie trie 中。
对于本题,我们用一个 v i s vis vis 数组来记录 S S S 是否是第一次被询问。
int search(char *s)
{int len = strlen(s), pos = 0;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){int c = s[i] - 'a';if (!trie[pos][c]){return 0; //WRONG}pos = trie[pos][c];}if (vis[pos]){return 2; //REPEAT}vis[pos] = true;return 1; //OK
}
t r i e \rm trie trie 树的插入,查询时间复杂度均为 O ( l e n ) \mathcal{O}(len) O(len)。空间复杂度为 O ( ∑ l e n × 26 ) \mathcal{O}(\sum len\times26) O(∑len×26),这是典型的空间换时间。
Code \text{Code} Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;const int MAXN = 5e5 + 5;int tot;
int trie[MAXN][26];
bool vis[MAXN];void insert(char *s)
{int len = strlen(s), pos = 0;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){int c = s[i] - 'a';if (!trie[pos][c]){trie[pos][c] = ++tot;}pos = trie[pos][c];}
}int search(char *s)
{int len = strlen(s), pos = 0;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){int c = s[i] - 'a';if (!trie[pos][c]){return 0;}pos = trie[pos][c];}if (vis[pos]){return 2;}vis[pos] = true;return 1;
}char s[55];int main()
{int n, m;scanf("%d", &n);while (n--){scanf("%s", s);insert(s);}scanf("%d", &m);while (m--){scanf("%s", s);int res = search(s);if (!res){puts("WRONG");}else if (res == 1){puts("OK");}else{puts("REPEAT");}}return 0;
}
二、 01 \rm 01 01- t r i e \rm trie trie
01 \rm 01 01- t r i e \rm trie trie 是一种 很 大 聪 明 的 \color{White}{很大聪明的} 很大聪明的 t r i e \rm trie trie 的变形,它的树上只有 0 0 0 和 1 1 1。
LOJ#10050. 「一本通 2.3 例 2」The XOR Largest Pair
Description \text{Description} Description
给定 N N N 个整数,从中选出两个进行异或运算,问得到的结果最大是多少。
Solution \text{Solution} Solution
考虑贪心。在二进制下,一个数的第 i i i 位为 0 0 0,那我们就尽量给他找个 1 1 1,反之就找个 0 0 0,这样就能使异或后的数有尽量多的位为 1 1 1。
那么可以把所有的数转成二进制后扔到 t r i e \rm trie trie 上,这样 t r i e \rm trie trie 上就只有 0 0 0 和 1 1 1,这就是 01 \rm 01 01- t r i e \rm trie trie。
但是实际上并不需要先转成二进制,我们可以在 insert \operatorname{insert} insert 的时候顺带处理。
void insert(int val)
{int pos = 0;for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--){int c = (val >> i) & 1; //取出第i位if (!trie[pos][c]){trie[pos][c] = ++tot;}pos = trie[pos][c];}
}
然后 search \operatorname{search} search 的时候就按照上面的贪心去找,如果实在没有那就只能取相同的了。
int search(int val)
{int pos = 0, res = 0;for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--){int c = (val >> i) & 1;if (trie[pos][c ^ 1]) //如果有就取{res |= (1 << i);pos = trie[pos][c ^ 1];}else{pos = trie[pos][c];}}return res;
}
Code \text{Code} Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;const int MAXN = 1e5 + 5;int tot;
int trie[MAXN * 32][2];void insert(int val)
{int pos = 0;for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--){int c = (val >> i) & 1;if (!trie[pos][c]){trie[pos][c] = ++tot;}pos = trie[pos][c];}
}int search(int val)
{int pos = 0, res = 0;for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--){int c = (val >> i) & 1;if (trie[pos][c ^ 1]){res |= (1 << i);pos = trie[pos][c ^ 1];}else{pos = trie[pos][c];}}return res;
}int a[MAXN];int main()
{int n, ans = 0;scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){scanf("%d", a + i);ans = max(ans, search(a[i]));insert(a[i]);}printf("%d\n", ans);return 0;
}
LOJ#10056. 「一本通 2.3 练习 5」The XOR-longest Path
Descripton \text{Descripton} Descripton
给定一棵 n n n 个点的带权树,求树上最长的异或和路径。
Solution \text{Solution} Solution
预处理出 d e p dep dep 数组, d e p i dep_i depi 表示节点 i i i 到根节点的路径上所有边的边权的异或和。
比如我们要求节点 x x x 到节点 y y y 路径上所有边的边权和,设 LCA ( x , y ) = z \operatorname{LCA}(x,y)=z LCA(x,y)=z,那么 d e p x ⊕ d e p y dep_x\oplus dep_y depx⊕depy 多算了 2 2 2 个 d e p z dep_z depz,根据异或的运算律,这 2 2 2 个 d e p z dep_z depz 异或在一起会抵消,所以 d e p x ⊕ d e p y dep_x\oplus dep_y depx⊕depy 就等于 x x x 到 y y y 路径上的边的边权异或和。
所以预处理出 d e p dep dep 数组然后就变成了上面那题(((
Code \text{Code} Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;const int MAXN = 1e5 + 5;int tot;
int trie[MAXN * 100][2];void insert(int val)
{int pos = 0;for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--){int c = (val >> i) & 1;if (!trie[pos][c]){trie[pos][c] = ++tot;}pos = trie[pos][c];}
}int search(int val)
{int pos = 0, res = 0;for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--){int c = (val >> i) & 1;if (trie[pos][c ^ 1]){res |= (1 << i);pos = trie[pos][c ^ 1];}else{pos = trie[pos][c];}}return res;
}int cnt;
int head[MAXN], dep[MAXN];struct edge
{int to, dis, nxt;
}e[MAXN << 1];void add(int u, int v, int w)
{e[++cnt] = edge{v, w, head[u]};head[u] = cnt;
}void dfs(int u, int fa)
{for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt){int v = e[i].to;if (v == fa){continue;}dep[v] = dep[u] ^ e[i].dis;dfs(v, u);}
}int main()
{int n, ans;scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){int u, v, w;scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &w);add(u, v, w);add(v, u, w);}dfs(1, 0);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){insert(dep[i]);ans = max(ans, search(dep[i]));}printf("%d\n", ans);return 0;
}