哪里有spyder呢?Where can we download it?
在"winpython"这个安装包里面,集成的有一个spyder,可以单独运行。(windows)
F6:运行配置对话框
Execute in current Python or IPython interpreter:在当前的Python控制台中运行程序。程序可以访问此控制台中的所有全局对象,控制台中已经载入的模块不需要重新载入,因此程序的启动速度较快。
Execute in a new dedicated Python interpreter:新开一个Python控制台并在其中运行程序,程序的启动速度较慢,但是由于新控制台中没有多余的全局对象,因此更接近实际的运行情况。当选择此项时,还可以选中"Interact with the Python interpreter after execution"复选框,这样当程序结束运行时,控制台进程将继续运行,因此可以通过它查看程序运行之后的所有全局对象。
在控制台中,可以按Tab按键进行自动补全
在程序编辑窗口中按住Ctrl键,并单击变量名、函数名、类名或模块名,可以快速跳转到定义位置。
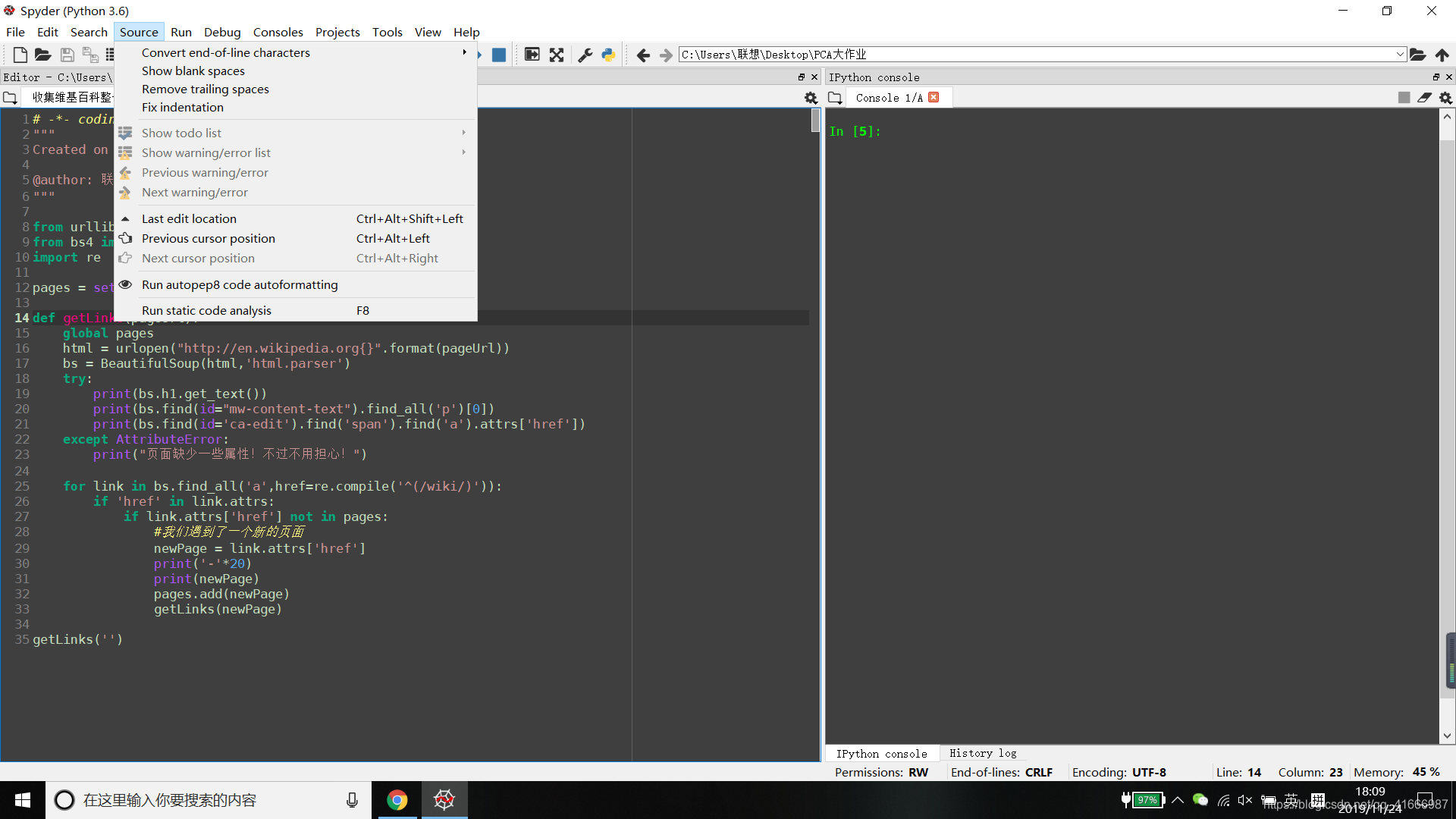
调试:
添加断点,在语句前进行双击或者选中语句后点击F12按钮。
按调试按钮后,进入调试模式,->ipdb 跟gdb的命令很像
追加:动态分配变量
p addition //程序中的变量
addition=&036 //动态分配一个变量赋值过去
p addittion
结束命令用:q
常用命令:n,s,p,c,b,l
Outline
- 1 First steps with Spyder
-
Call the hello() function from the Python prompt, i.e. type hello() in the Python Shell window (the Python prompt shows as >>>, or as In [?] if we use the IPython session where the question mark can be any positive integer number.), and press the return key.
You should find that the hello() function is executed again, i.e. Hello World is printed again. Your function call at the Python prompt together with the output should look like this:
In [ ]: hello() Hello World
-
Once an object is visible in the current name space (as is hello in this example), we can use the help function as follows to learn about it: Type help(hello) at the Python prompt, you should see output like this:
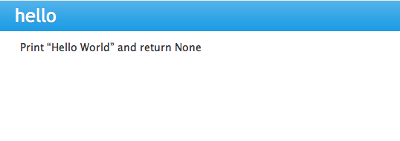
In [ ]: help(hello) Help on function hello in module __main__:hello()Print "Hello World" and return None -
The Spyder environment also provides a panel in the top right corner (by default) which is the Object inspector. If you type hello into the empty line in the Object inspector window, it will also provide the help string.
2.1 Switch to an IPython console
In the console window (lower right corner by default), you see by default a prompt with three greater than signs, i.e. >>>. This shows that we are using the console -- basically a normal Python interpreter session (with some added functionality from Spyder).
Instead, we would like to use an Interactive Python shell, short IPython from the ipython project. To do this, select Interpreters -> Open an IPython Console.
You should see in the consolse window a new shell appearing, and the IPython prompt In [1]: should be displayed.
2.2 Reset the name space
The name space can be cleared in IPython using the %reset command. Type %reset and press return, then confirm with y:
In [1]: %resetOnce deleted, variables cannot be recovered. Proceed (y/[n])? yIn [2]:3 Selected Preferences
3.1 Where are the preferences?
A lot of Spyder's behaviour can be configured through it's Preferences. Where this is located in the menu depends on your operating system:
- On Windows and Linux, go to Tools -> Preferences
- On Mac OS, go to Python -> Preferences
3.2 Change Spyder settings to always start with an IPython shell
Go to Preferences -> IPython console -> Startup and select the tickbox next to Open an IPython console at startup. Then click the OK button.
The next time Spyder starts, it will show the IPython console automatically.
3.3 Warn if PEP8 coding guidelines are violated
Go to Preferences -> Editor -> Code Introspection/Analysis and select the tickbox next to Style analysis (PEP8)
3.4 No convenience imports in Python Console
To avoid any 'magic' when the console is started, go to
Preferences -> Console -> Advanced Settings -> PYTHONSTARTUP replacement and select Default PYTHONSTARTUP script (and restart Spyder).
(This magic, amongst other things, runs the from __future__ import division command.)
The default settings may change for this in the next major release.
3.5 No convenience imports in IPython Console
To avoid import of all objects from pylab and numpy into the current name space in the IPython Console, go to Preferences -> IPython console -> Graphics and deselect the tickbox next to Automatically load Pylab and NumPy modules and also deselect Activate support.
The default settings may change for this in the next major release.
3.6 Automatic Symbolic Python
Through Preferences -> IPython console -> Advanced Settings -> Use symbolic math we can activate IPython's symbolic python mode. This will allow nicely rendered sympy output (latex style) and also imports some sympy objects automatically when the IPython console starts, and reports what it has done.
These commands were executed:
>>> from __future__ import division
>>> from sympy import *
>>> x, y, z, t = symbols('x y z t')
>>> k, m, n = symbols('k m n', integer=True)
>>> f, g, h = symbols('f g h', cls=Function)
We can then use the variables x, y, for example like this:
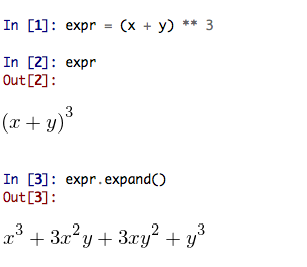
4 Shortcuts for useful functions
-
F5 executes the current buffer
-
F9 executes the currently highlighted chunk of code: this is very useful to update definitions of functions (say) in the interpreter session without having to run the whole file again
-
CTRL + <RETURN> executes the current cell (menu enty Run -> Run cell). A cell is defined as the code between two lines which start with the agreed tag #%%.
-
SHIFT + <RETURN> executes the current cell and advances the cursor to the next cell (menu entry Run -> Run cell and advance).
Cells are useful to execute a large file/code segment in smaller units. (It is a little bit like a cell in an IPython notebook, in that chunks of code can be run independently.)
-
ALT + <CURSOR UP> moves the current line up. If multiple lines are highlighted, they are moved up together. ALT+<CURSOR DOWN> works correspondingly moving line(s) down.
-
Right clicking on a function/method in the source, opens a new editor windows showing the definition of that function.
-
SHIFT+CTRL+ALT+M maximises the current window (or changes the size back to normal if pressed in a maximised window)
-
SHIFT+CTRL+F activates the search across all files.
-
On Mac OS X: CMD + + will increase the font size in the editor, CMD + - decrease. Also works in the IPython Console.
The font size for the object explorer, the Python console etc can be set individually via Preferences -> Object explorer etc.
I couldn't find a way of changing the font size in the variable explorer.
-
CTRL+SPACE autocompletes commands, function names, variable names, methods; very useful.
-
CMD+s (on Mac OS X) and CTRL+s (otherwise) in the editor window saves the file currently being edited. This also forces various warning triangles in the left column of the editor to be updated (otherwise they update every 2 to 3 seconds by default).
-
CMD+s (on Mac OS X) and CTRL+s (otherwise) in the IPython console window saves the current IPython session as an HTML file, including any figures that may be displayed inline. This is useful as a quick way of recording what has been done in a session.
(It is not possible to load this saved record back into the session - if you need functionality like this, look for the IPython Notebook.)
-
CMD+i (on Mac OS X) and CTRL+i (otherwise) when pressed while the cursor is on an object, opens documentation for that object in the object inspector.
5 Run Settings
These are the settings that define how the code in the editor is executed if we select Run -> Runor press F5.
By default, the settings box will appear the first time we try to execute a file. If we want to change the settings at any other time, they can be found under Run -> Configure or by pressing F6.
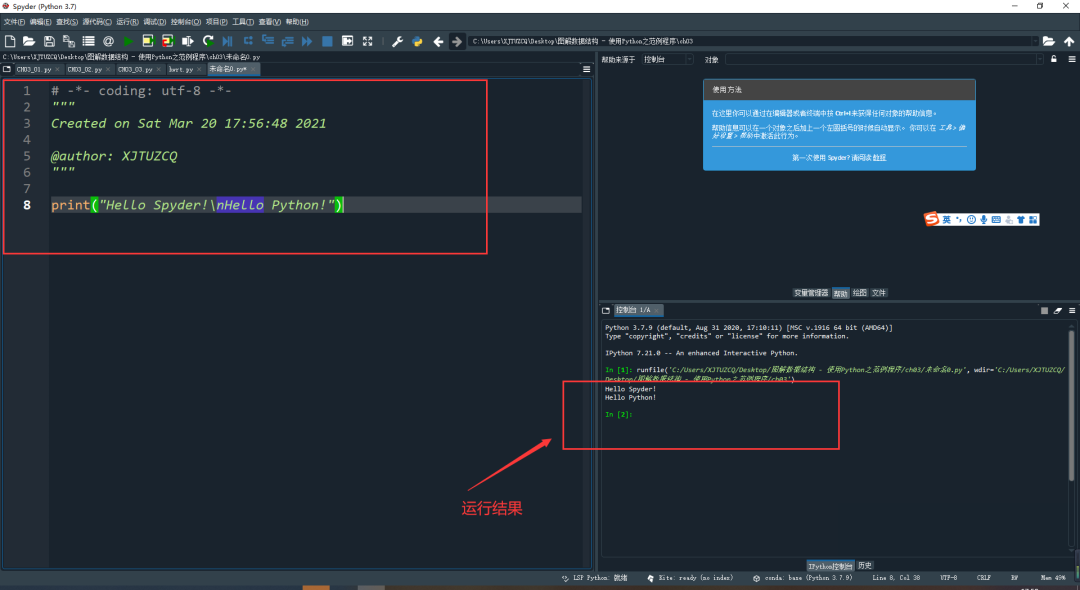
There are three choices for the interpreter to use, of which I'll discuss the first two. Let's assume we have a program hello.py in the editor which reads
def hello(name):"""Given an object 'name', print 'Hello ' and the object."""print("Hello {}".format(name))i = 42
if __name__ == "__main__":hello(i)5.2 Execute in new dedicated Python interpreter
Choosing Execute in new dedicated Python interpreter under Run -> Configure will start a new Python interpreter everytime the hello.py program is executed. The major advantage of this mode over Execute in current Python or IPython interpreter is that we can be certain that there are no global objects defined in this interpreter which originate from debugging and repeated execution of our code: every time we run the code in the editor, the python interpreter in which the code runs is restarted.
This is a safe option, but provides less flexibility and cannot use the IPyton interpreter.
5.3 How to double check your code executes correctly "on its own"
Assuming you have chosen for your code to Execute in current Python or IPython interpreter, then you two options to check that our code does work on its own (i.e. it does not depend on undefined variables, unimported modules and commands etc.)
-
Switch from Execute in current Python or IPython interpreter to Execute in new dedicated Python interpreter, and execute the code in the editor in this dedicated Python interpreter.
Alternatively, if you want to stay with the current IPython interpreter, you can
-
Use IPython's magic %reset command which will remove all objects (such as i in the example above) from the current name space, and then execute the code in the editor.
5.4 Recommendation
My recommendation for beginners would be to Execute in current Python or IPython interpreter, and to chose the IPython interpreter for this (see also Change Spyder settings to always start with an IPython shell).
Once you have completed a piece of code, double check that it executes independently using one of the options explained in How to double check your code executes correctly "on its own".
6 Other observations
6.1 Multiple windows
When multiple files are opened in the editor, the corresponding tabs at the top of the window area are arranged in alphabetical order of the filename from left to right.
On the left of the tabs, there is as icon that shows Browse tabs if the mouse hovers over it. It is useful to jump to a particular file directly, if many files are open.
6.2 Environment variables
Environment variables can be displayed from the Console window (bottom right window in default layout). Click on the Options icon (the tooltip is Options), then select Environment variables.
6.3 Reset all customisation
All customisation saved on disk can be reset by calling spyder from the command line with the switch --reset, i.e. a command like spyder --reset.
6.4 Objects in the variable explorer
Right-clicking on arrays in the variable explorer gives options to plot and analyse these further.
Double clicking on a dictionary object opens a new window that displays the dictionary nicely.
Presumably there is other 'hidden' capability for some other data types.
7 Docstring formatting
There are some conventions assumed regarding documentation strings written in restructured text. If we follow those guidelines, we can obtain beautifully formated documentation strings in Spyder.
For example, to get our average() function look like this in the Spyder Object explorer:
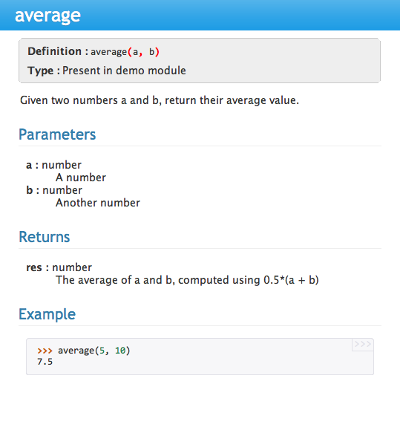
We need to format the documentation string as follows
def average(a, b):"""Given two numbers a and b, return their average value.Parameters----------a : numberA numberb : numberAnother numberReturns-------res : numberThe average of a and b, computed using 0.5*(a + b)Example------->>> average(5, 10)7.5"""return (a + b) * 0.5
What matters here, is that the word Parameters is used, and underlined. The line a : numbershows us that the type of the parameter a is number. In the next line, which is indented, we can write a more extended explanation what this variable represents, what conditions the allowed types have to fulfil etc.
The same for all Parameters, and also for the returned value.
Often it is a good idea to include an example as shown.
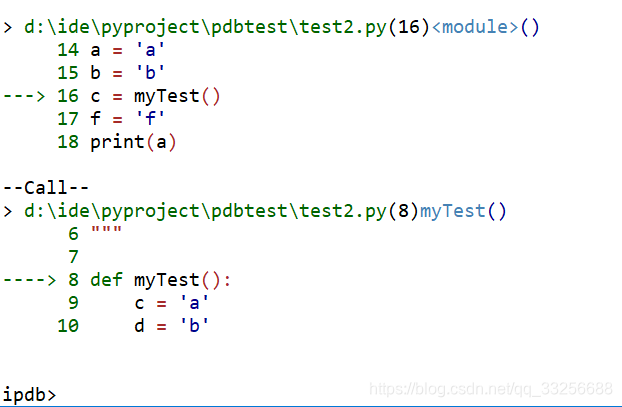
8 Debugging in the Ipython Debugger
8.1 Line by line step execution of code
Activating the debug mode (Debug -> Debug) starts the IPython debugger (ipdb) in the IPython console. This is operated as normal, but the editor display window highlights the line that is about to be executed, and the variable explorer displays variables in the current context of the point of program execution. (It only displays 'numerical' variables, i.e. not function objects etc.)
The key commands within the IPython debugger are indivdual keystrokes:
- s to Step into the current statement. If this is a function call, step into that function.
- n move to the Next statement. If the current statement is a function, do not step into that function, but execute it completely before returning control to the interactive debugger prompt.
- r complete all statements in the current function and Return from that function before returning control.
- p Print allows to display values of variables, for example p x will print the value of the variable x.
Note that at the ipdb, you can also change values of variable. For example, to modify a valiable x, you can say ipdb > x = 42 and the debugger will carry on with x being bound to 42. You can also call functions, and do many others things.
To leave the debugging mode, you can type exit or select from the menu Debug -> Debugging Control -> Exit
8.2 Debugging once an exception has occured
In the IPython console, we can call %debug straight after an exception has been raised: this will start the IPython debug mode, and allows inspection of local variables at the point where the exception occurred as described above. This is a lot more efficient than adding printstatements to the code an running it again.
If you use this, you may also want to use the commands up and down which navigate the inspection point up and down the stack. (Up the stack means to the functions that have called the current function; down is the opposite direction.)
9 Plotting
Assuming we use an IPython console with version >= 1.0.0, we can decide whether figures created with matplotlib/pylab will show
- inline, i.e. inside the IPython console, or whether they should
- appear inside a new window.
Option 1 is convenient to save a record of the interactive session (section Shortcuts for useful functions lists a shortcut to save the IPython console to an html file).
Option 2 allows to interactively zoom into the figure, manipulate it a little, and save the figure to different file formats via the menu.
The command to get the figures to appear inline in the IPython console is %matplotlib inline.
The command to get figures appear in their own window (which technically is a QT windown) is %matplotlib qt.
The Spyder preferences can be used to customise the default behaviour (in particular Preferences -> IPython Console -> Graphics -> Activate Support to switch into inline plotting).
10 Historical note
This tutorial is based on notes by Hans Fangohr, that are used at the University of Southamptonto teach Python for computational modelling to undegraduate engineers and postgraduate PhD students for the Next Generation Computational Modelling doctoral training centre
***************************************************
变成时候会import一个模块,然后spyder会提示找不到(需要手动安装)
whl包:https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#pygame
找到对应的whl文件下载:pygame-1.9.3-cp35-cp35m-win_amd64.whl //cp35 means CPython3.5, mine is Python3.5; win_amd64 means 64 bit, win_32 means 32 bit
然后win+R调出cmd.exe, cd到whl文件所在的目录运行pip install pygame-1.9.3-cp35-cp35m-win_amd64.whl
*****************************************************